Application of Gas Welding in Telecommunications Infrastructure
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Gas Welding Evolution in Telecom Infrastructure
Gas welding has played a significant role in the evolution of telecommunications infrastructure, adapting to the changing needs of the industry over time. In the early days of telecom, gas welding was primarily used for joining copper cables and constructing support structures for antennas and towers. The technique provided a reliable and cost-effective method for creating strong, durable connections in the field.
As telecommunications networks expanded rapidly in the mid-20th century, gas welding became increasingly important for the installation and maintenance of large-scale infrastructure. It was particularly useful for constructing microwave towers and satellite ground stations, where precision welding of steel components was crucial. The portability of gas welding equipment made it ideal for on-site work in remote locations, contributing to the rapid deployment of telecom networks across diverse geographical areas.
The advent of fiber optic technology in the 1970s and 1980s brought new challenges and opportunities for gas welding in telecom infrastructure. While fiber optics themselves did not require welding, the supporting structures and housings for fiber optic cables still relied heavily on welded components. Gas welding techniques were adapted to create specialized enclosures and junction boxes that could protect delicate fiber optic connections from environmental factors.
In the mobile telecommunications era, gas welding continued to evolve to meet the demands of cell tower construction and maintenance. The technique was refined to create stronger, lighter structures capable of supporting multiple antennas and withstanding extreme weather conditions. Specialized alloys and welding procedures were developed to enhance the corrosion resistance and longevity of telecom infrastructure in diverse environments.
Recent advancements in gas welding technology have focused on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Modern gas welding equipment used in telecom infrastructure projects now incorporates features such as precise flame control, automated welding processes, and eco-friendly fuel mixtures. These innovations have not only improved the quality and consistency of welds but also reduced emissions and energy consumption associated with the welding process.
The ongoing rollout of 5G networks has presented new opportunities for gas welding in telecom infrastructure. The dense network of small cells required for 5G coverage has led to an increased demand for precision welding of compact, weatherproof enclosures. Gas welding techniques have been adapted to work with the advanced materials used in these new components, ensuring reliable connections and long-term durability in urban and rural environments alike.
As telecommunications networks expanded rapidly in the mid-20th century, gas welding became increasingly important for the installation and maintenance of large-scale infrastructure. It was particularly useful for constructing microwave towers and satellite ground stations, where precision welding of steel components was crucial. The portability of gas welding equipment made it ideal for on-site work in remote locations, contributing to the rapid deployment of telecom networks across diverse geographical areas.
The advent of fiber optic technology in the 1970s and 1980s brought new challenges and opportunities for gas welding in telecom infrastructure. While fiber optics themselves did not require welding, the supporting structures and housings for fiber optic cables still relied heavily on welded components. Gas welding techniques were adapted to create specialized enclosures and junction boxes that could protect delicate fiber optic connections from environmental factors.
In the mobile telecommunications era, gas welding continued to evolve to meet the demands of cell tower construction and maintenance. The technique was refined to create stronger, lighter structures capable of supporting multiple antennas and withstanding extreme weather conditions. Specialized alloys and welding procedures were developed to enhance the corrosion resistance and longevity of telecom infrastructure in diverse environments.
Recent advancements in gas welding technology have focused on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Modern gas welding equipment used in telecom infrastructure projects now incorporates features such as precise flame control, automated welding processes, and eco-friendly fuel mixtures. These innovations have not only improved the quality and consistency of welds but also reduced emissions and energy consumption associated with the welding process.
The ongoing rollout of 5G networks has presented new opportunities for gas welding in telecom infrastructure. The dense network of small cells required for 5G coverage has led to an increased demand for precision welding of compact, weatherproof enclosures. Gas welding techniques have been adapted to work with the advanced materials used in these new components, ensuring reliable connections and long-term durability in urban and rural environments alike.
Market Demand Analysis for Telecom Welding Solutions
The telecommunications industry has witnessed a significant surge in demand for reliable and efficient welding solutions, particularly in the realm of gas welding for infrastructure development. As the global telecom market continues to expand, driven by the increasing need for high-speed connectivity and the rollout of 5G networks, the demand for specialized welding techniques in telecom infrastructure construction has grown exponentially.
Market analysis reveals that the telecommunications sector is experiencing robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is primarily fueled by the rapid adoption of advanced technologies such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. As a result, there is a pressing need for the expansion and upgrading of existing telecom infrastructure, creating a substantial market for gas welding solutions.
The deployment of 5G networks, in particular, has emerged as a key driver for the increased demand in telecom welding solutions. The intricate nature of 5G infrastructure, which requires a dense network of small cells and advanced antenna systems, necessitates precise and reliable welding techniques. Gas welding, known for its versatility and ability to join various materials, has become a preferred choice for many telecom companies engaged in infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the growing trend of network densification to support higher data capacities has led to a surge in the installation of new cell towers and the modification of existing ones. This has created a significant market opportunity for gas welding solutions, as these techniques are essential for the fabrication and installation of tower components, antenna mounts, and other critical infrastructure elements.
The market demand for telecom welding solutions is not limited to new installations alone. With the increasing focus on network reliability and uptime, there is a growing need for maintenance and repair services. Gas welding techniques play a crucial role in the quick and efficient repair of damaged infrastructure, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous network operation.
Geographically, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Africa are showing the highest growth potential for telecom welding solutions. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization and digital transformation, driving the need for extensive telecom infrastructure development. Developed markets in North America and Europe, while more mature, are also seeing steady demand due to the ongoing transition to 5G and the need for infrastructure upgrades.
In conclusion, the market demand for gas welding solutions in the telecommunications sector is robust and poised for continued growth. The convergence of technological advancements, infrastructure expansion, and the critical need for reliable connectivity is creating a favorable environment for companies specializing in telecom welding solutions. As the industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and efficient welding techniques is expected to remain strong, presenting significant opportunities for market players in this space.
Market analysis reveals that the telecommunications sector is experiencing robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is primarily fueled by the rapid adoption of advanced technologies such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. As a result, there is a pressing need for the expansion and upgrading of existing telecom infrastructure, creating a substantial market for gas welding solutions.
The deployment of 5G networks, in particular, has emerged as a key driver for the increased demand in telecom welding solutions. The intricate nature of 5G infrastructure, which requires a dense network of small cells and advanced antenna systems, necessitates precise and reliable welding techniques. Gas welding, known for its versatility and ability to join various materials, has become a preferred choice for many telecom companies engaged in infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the growing trend of network densification to support higher data capacities has led to a surge in the installation of new cell towers and the modification of existing ones. This has created a significant market opportunity for gas welding solutions, as these techniques are essential for the fabrication and installation of tower components, antenna mounts, and other critical infrastructure elements.
The market demand for telecom welding solutions is not limited to new installations alone. With the increasing focus on network reliability and uptime, there is a growing need for maintenance and repair services. Gas welding techniques play a crucial role in the quick and efficient repair of damaged infrastructure, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous network operation.
Geographically, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Africa are showing the highest growth potential for telecom welding solutions. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization and digital transformation, driving the need for extensive telecom infrastructure development. Developed markets in North America and Europe, while more mature, are also seeing steady demand due to the ongoing transition to 5G and the need for infrastructure upgrades.
In conclusion, the market demand for gas welding solutions in the telecommunications sector is robust and poised for continued growth. The convergence of technological advancements, infrastructure expansion, and the critical need for reliable connectivity is creating a favorable environment for companies specializing in telecom welding solutions. As the industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and efficient welding techniques is expected to remain strong, presenting significant opportunities for market players in this space.
Current Gas Welding Challenges in Telecom
Gas welding has been a cornerstone in telecommunications infrastructure construction for decades. However, as the industry evolves and demands for faster, more reliable networks increase, several challenges have emerged in the application of gas welding techniques.
One of the primary challenges is the precision required for modern fiber optic connections. Gas welding, while effective for larger metal components, often lacks the fine control needed for delicate fiber optic splicing. The heat generated during the welding process can potentially damage the sensitive optical fibers, leading to signal degradation or complete failure of the connection.
Safety concerns also pose significant challenges in the telecom sector. Gas welding involves the use of flammable gases and high temperatures, which can be hazardous in confined spaces often encountered in telecommunications installations. This risk is particularly pronounced in underground cable vaults or crowded urban environments where space is limited and ventilation may be inadequate.
The mobility of gas welding equipment presents another hurdle. As telecom infrastructure expands into remote and challenging terrains, transporting bulky gas cylinders and welding apparatus becomes increasingly difficult. This limitation can slow down deployment in areas where rapid network expansion is crucial.
Environmental considerations have also come to the forefront. The emissions produced by gas welding, while not substantial on an individual basis, can contribute to air quality issues when considering the scale of telecom infrastructure projects. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more environmentally friendly joining methods.
Consistency and quality control in gas welding processes are additional challenges. The variability inherent in manual gas welding techniques can lead to inconsistencies in joint quality, potentially compromising the integrity of critical telecom structures. This is particularly problematic in applications where long-term reliability is paramount, such as in backbone network infrastructure.
The skill gap in the workforce presents yet another obstacle. As experienced welders retire, there is a growing shortage of skilled professionals capable of performing high-quality gas welding in telecom applications. This shortage is exacerbated by the increasing complexity of telecom systems, which require welders to have a broader understanding of the technology they are supporting.
Lastly, the speed of installation is a critical factor in today's fast-paced telecom industry. Gas welding, while reliable, is often slower compared to newer joining technologies. This can lead to bottlenecks in project timelines, particularly in large-scale network rollouts where time-to-market is a crucial competitive advantage.
One of the primary challenges is the precision required for modern fiber optic connections. Gas welding, while effective for larger metal components, often lacks the fine control needed for delicate fiber optic splicing. The heat generated during the welding process can potentially damage the sensitive optical fibers, leading to signal degradation or complete failure of the connection.
Safety concerns also pose significant challenges in the telecom sector. Gas welding involves the use of flammable gases and high temperatures, which can be hazardous in confined spaces often encountered in telecommunications installations. This risk is particularly pronounced in underground cable vaults or crowded urban environments where space is limited and ventilation may be inadequate.
The mobility of gas welding equipment presents another hurdle. As telecom infrastructure expands into remote and challenging terrains, transporting bulky gas cylinders and welding apparatus becomes increasingly difficult. This limitation can slow down deployment in areas where rapid network expansion is crucial.
Environmental considerations have also come to the forefront. The emissions produced by gas welding, while not substantial on an individual basis, can contribute to air quality issues when considering the scale of telecom infrastructure projects. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more environmentally friendly joining methods.
Consistency and quality control in gas welding processes are additional challenges. The variability inherent in manual gas welding techniques can lead to inconsistencies in joint quality, potentially compromising the integrity of critical telecom structures. This is particularly problematic in applications where long-term reliability is paramount, such as in backbone network infrastructure.
The skill gap in the workforce presents yet another obstacle. As experienced welders retire, there is a growing shortage of skilled professionals capable of performing high-quality gas welding in telecom applications. This shortage is exacerbated by the increasing complexity of telecom systems, which require welders to have a broader understanding of the technology they are supporting.
Lastly, the speed of installation is a critical factor in today's fast-paced telecom industry. Gas welding, while reliable, is often slower compared to newer joining technologies. This can lead to bottlenecks in project timelines, particularly in large-scale network rollouts where time-to-market is a crucial competitive advantage.
Existing Gas Welding Solutions for Telecom
01 Welding equipment and techniques
Gas welding involves specialized equipment and techniques for joining metals using heat generated by combustible gases. This includes the use of torches, regulators, and various gas mixtures to achieve optimal welding results. Advancements in equipment design and gas composition have improved welding efficiency and quality.- Gas welding equipment and techniques: This category covers various aspects of gas welding equipment and techniques, including torch designs, gas mixing systems, and welding process improvements. Innovations in this area focus on enhancing welding efficiency, precision, and safety for operators.
- Welding gas composition and control: This point addresses the development of specialized gas mixtures and control systems for gas welding applications. It includes innovations in gas composition, flow regulation, and pressure control to optimize welding performance and quality across different materials and conditions.
- Automated and robotic gas welding systems: This category focuses on the integration of automation and robotics in gas welding processes. It covers advancements in computer-controlled welding systems, robotic welding arms, and intelligent welding parameter adjustment for improved consistency and productivity.
- Safety features and protective equipment: This point encompasses innovations in safety measures and protective equipment for gas welding operations. It includes developments in flame arrestors, gas leak detection systems, personal protective equipment, and workplace safety protocols to minimize risks associated with gas welding.
- Specialized gas welding applications: This category covers gas welding techniques and equipment designed for specific applications or materials. It includes innovations in underwater gas welding, high-temperature alloy welding, and micro-scale gas welding for precision manufacturing processes.
02 Safety measures in gas welding
Safety is paramount in gas welding operations. This includes the development of protective gear, ventilation systems, and safety protocols to prevent accidents and protect welders from harmful fumes and radiation. Innovations in this area focus on improving personal protective equipment and implementing fail-safe mechanisms in welding equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automation and robotics in gas welding
The integration of automation and robotics in gas welding processes has led to increased precision, consistency, and productivity. Robotic welding systems can perform complex welding tasks with high accuracy, reducing human error and improving overall weld quality. These systems often incorporate advanced sensors and control algorithms for real-time adjustments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Gas mixture optimization
Research into optimal gas mixtures for different welding applications has led to improved weld quality and efficiency. This includes the development of specialized gas blends for specific materials and welding conditions, as well as systems for precise gas flow control and mixing during the welding process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy efficiency and environmental considerations
Efforts to improve the energy efficiency of gas welding processes and reduce their environmental impact have resulted in new technologies and methodologies. This includes the development of more efficient burners, waste heat recovery systems, and the use of alternative, more environmentally friendly gases for welding applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Telecom Gas Welding Industry
The application of gas welding in telecommunications infrastructure is in a mature stage, with a well-established market and proven technologies. The global market size for welding equipment and consumables is substantial, estimated to be over $20 billion annually. Key players in this sector include industry giants like Illinois Tool Works Inc., Kobe Steel, Ltd., and Siemens AG, alongside specialized welding equipment manufacturers such as Leister Technologies AG and Lorch Schweißtechnik GmbH. These companies offer a range of advanced welding solutions, from traditional gas welding to more modern techniques, catering to the specific needs of telecommunications infrastructure development. The technology's maturity is evident in the continuous innovations and improvements in welding efficiency, precision, and safety features offered by these industry leaders.
Illinois Tool Works Inc.
Technical Solution: Illinois Tool Works (ITW) has developed advanced gas welding solutions specifically tailored for telecommunications infrastructure. Their approach integrates precision gas flow control systems with specialized alloys designed to withstand the unique environmental challenges faced in telecom installations. ITW's gas welding equipment utilizes a proprietary mixture of gases that optimizes heat distribution, resulting in stronger, more durable welds for telecom components such as antenna mounts, tower structures, and equipment enclosures[1]. The company has also introduced automated gas welding systems that can be remotely operated, allowing for efficient maintenance and installation of telecom infrastructure in hard-to-reach locations[3].
Strengths: Specialized alloys and gas mixtures for telecom applications, automated systems for remote operations. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial equipment costs, requires specialized training for operators.
Hobart Brothers LLC
Technical Solution: Hobart Brothers has developed a range of gas welding solutions specifically for telecommunications infrastructure. Their approach focuses on portable gas welding systems that can be easily transported to remote telecom sites. These systems feature lightweight, high-pressure cylinders containing a proprietary gas mixture optimized for welding thin-walled telecom components[2]. Hobart's gas welding equipment incorporates advanced temperature control mechanisms that prevent overheating of sensitive electronic components often present in telecom installations. The company has also introduced a line of filler metals designed to create corrosion-resistant welds, crucial for outdoor telecom infrastructure exposed to various weather conditions[4].
Strengths: Highly portable systems, specialized filler metals for corrosion resistance. Weaknesses: Limited to smaller-scale applications, may not be suitable for large structural welds in telecom towers.
Innovative Gas Welding Techniques for Telecom
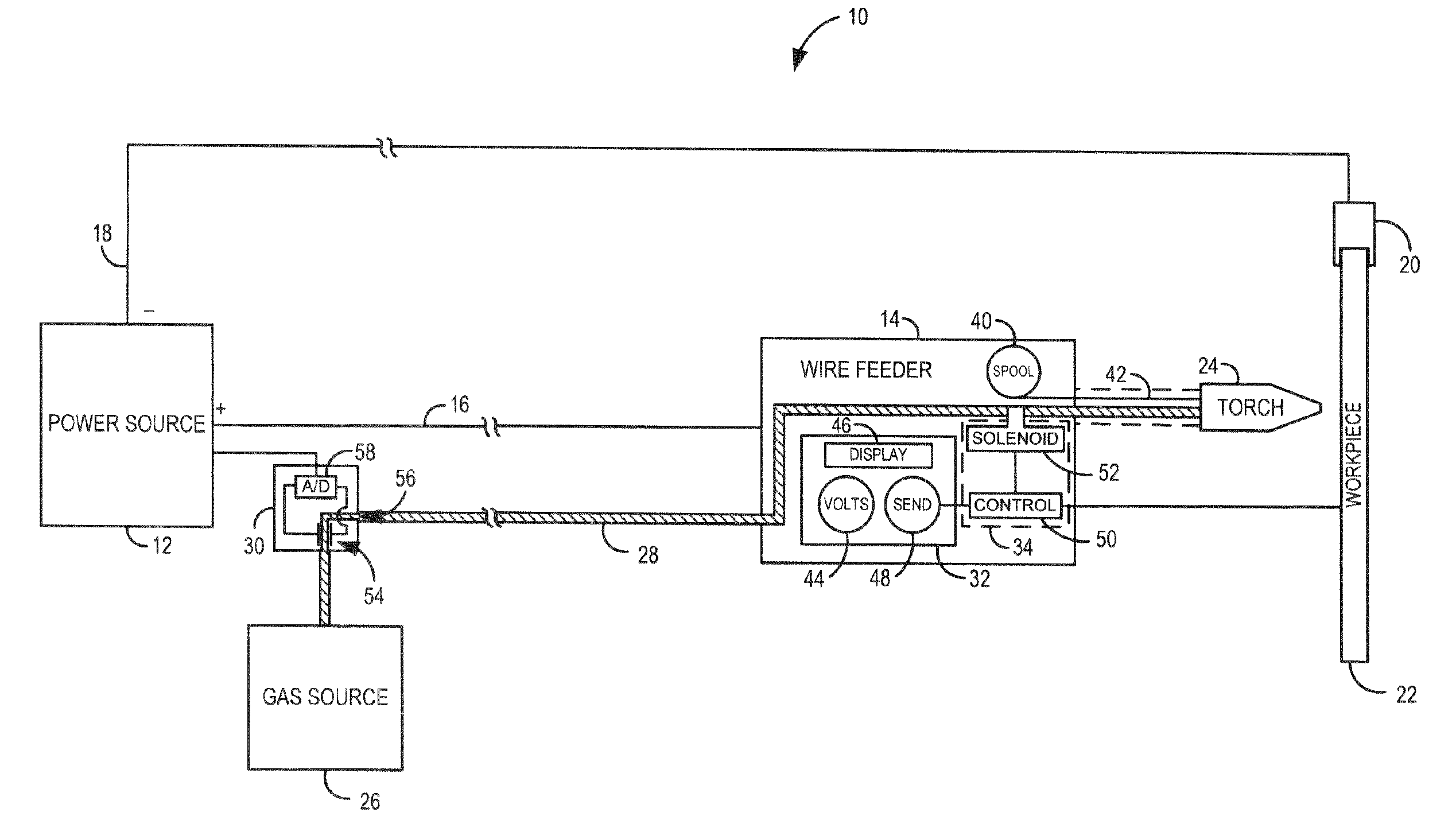
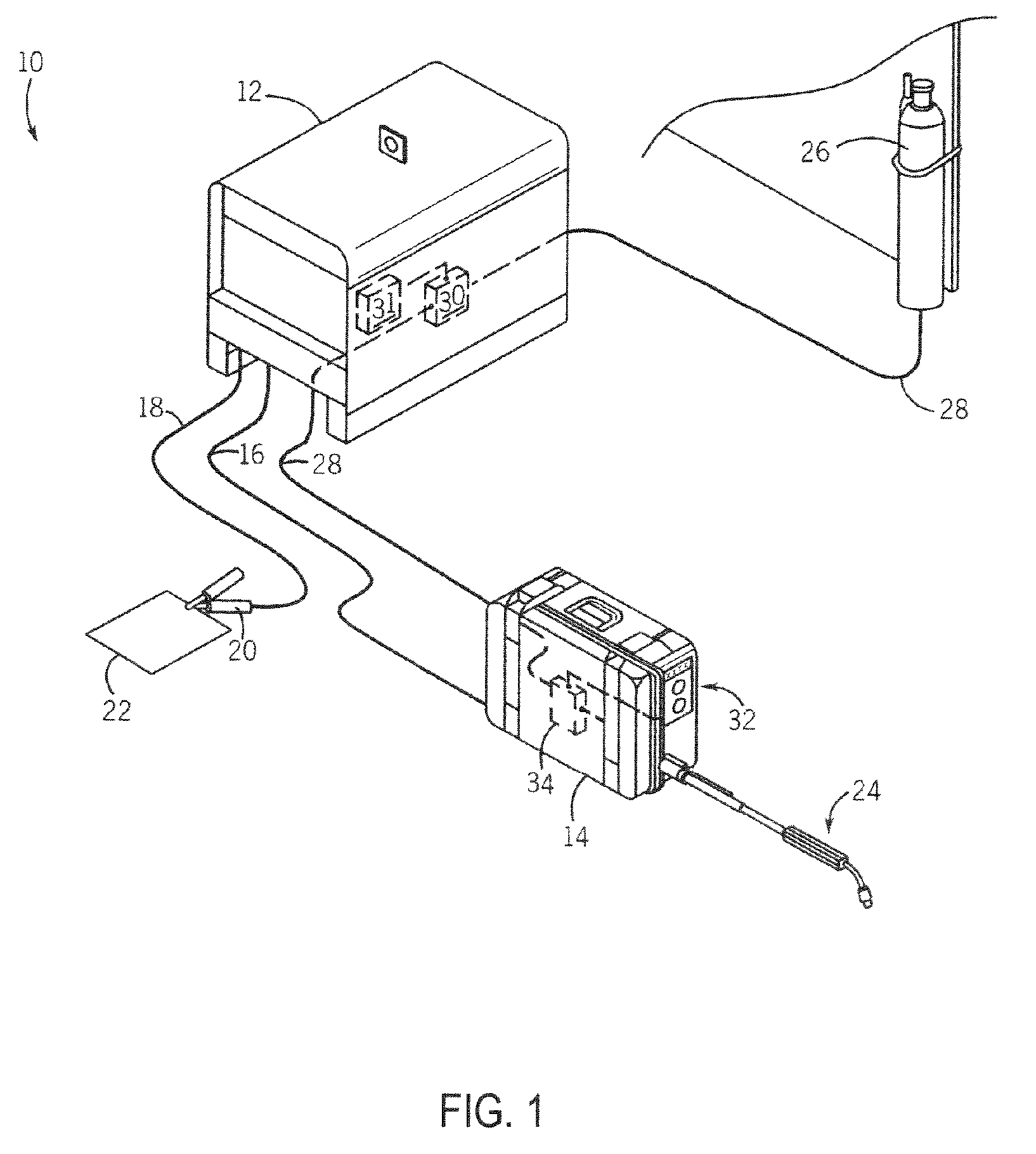
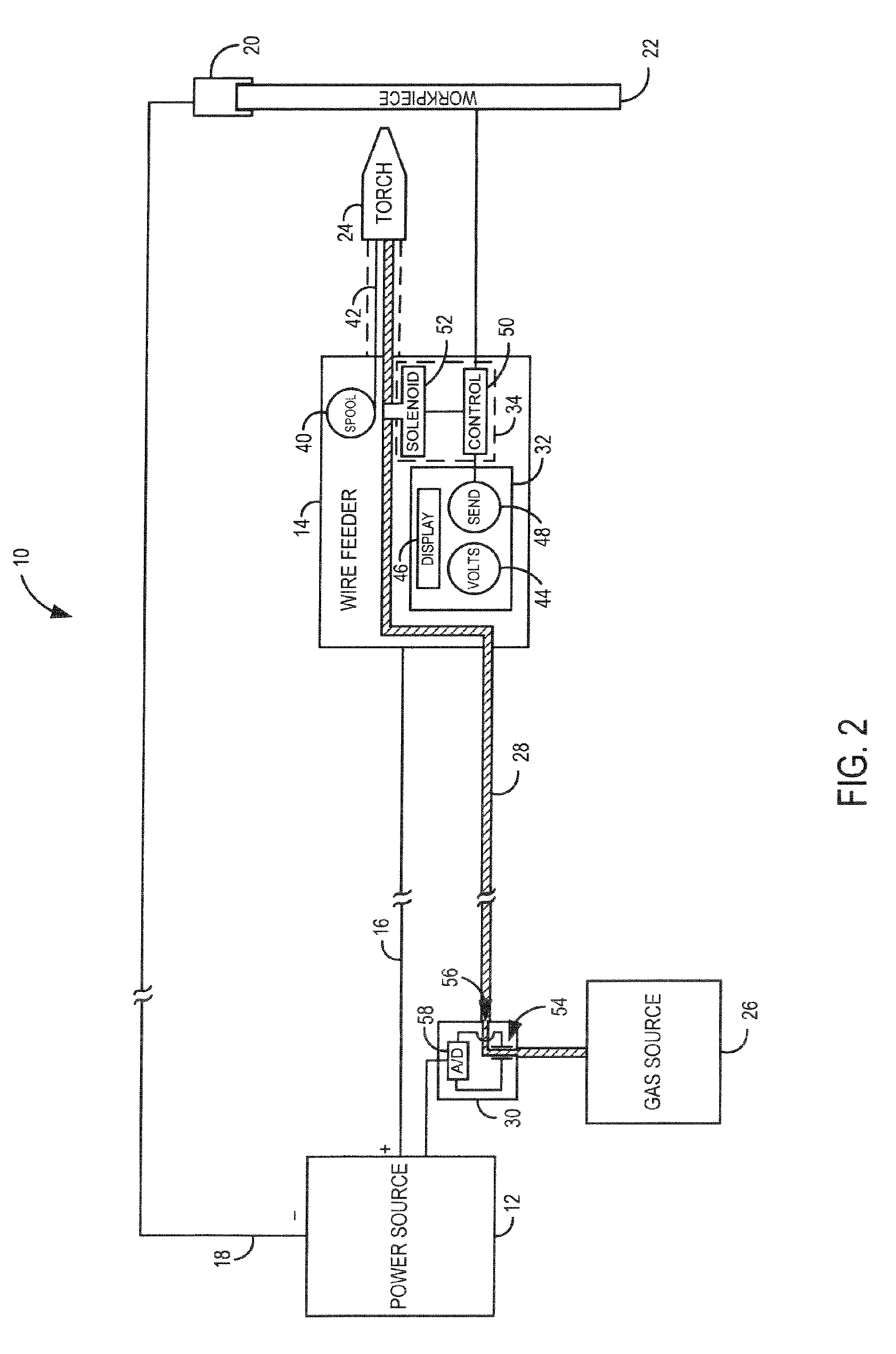
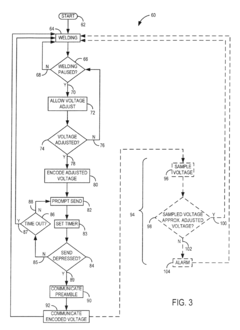
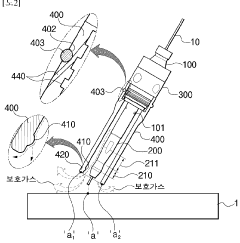
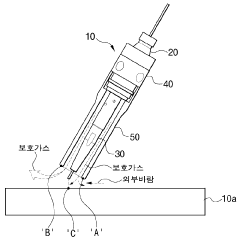
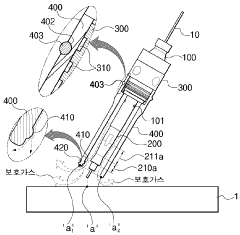
System and method for data communications over a gas hose in a welding-type application
PatentInactiveUS7247814B2
Innovation
- A communications system that uses the shielding gas line to transmit operational parameters by modifying the gas flow state, allowing a transmitter to encode and send data as a bit stream through the gas supply line, which is interpreted by a receiver to adjust the welding power source, eliminating the need for additional cables and reducing interference.
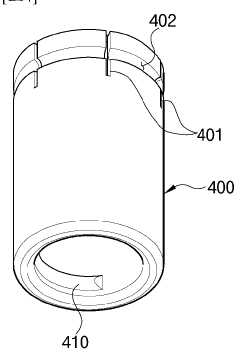
Torch head for gas welding
PatentWO2023128175A1
Innovation
- The torch head incorporates a gas spreading guide on the welding tip and a protective gas concentration guide on the nozzle, directing shielding gas flow towards the welding area and increasing its velocity vector, even when the nozzle is inclined, to effectively block external air and reduce gas consumption.
Safety Standards in Telecom Gas Welding
Safety standards in telecom gas welding are crucial for ensuring the protection of workers and the integrity of telecommunications infrastructure. These standards encompass a wide range of regulations and best practices designed to mitigate risks associated with gas welding operations in the telecom industry.
One of the primary safety considerations is the proper handling and storage of welding gases. Strict guidelines are in place for the transportation, storage, and usage of flammable gases such as acetylene and oxygen. Telecom companies must adhere to specific requirements for gas cylinder storage, including proper ventilation, secure fastening, and clear labeling of contents and hazards.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is another critical aspect of safety standards in telecom gas welding. Workers are required to wear appropriate protective gear, including flame-resistant clothing, welding helmets with proper eye protection, and heat-resistant gloves. Additionally, respiratory protection may be necessary when working in confined spaces or areas with poor ventilation.
Fire prevention measures are paramount in telecom gas welding operations. Safety standards mandate the presence of fire extinguishers and other fire suppression equipment in welding areas. Welding operations must be conducted at a safe distance from flammable materials, and fire watches may be required in high-risk environments.
Proper training and certification of welding personnel is a key component of safety standards. Telecom companies must ensure that all workers involved in gas welding operations are adequately trained in equipment operation, safety procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher courses and safety audits are typically required to maintain compliance with industry standards.
Electrical safety is also a significant concern in telecom gas welding. Standards address the proper grounding of welding equipment, protection against electric shock, and the use of appropriate insulation materials. Special precautions are necessary when welding near live electrical components or in areas with potential electromagnetic interference.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in telecom gas welding safety standards. Regulations often cover the management of welding fumes and gases, proper disposal of welding waste, and measures to minimize the environmental impact of welding operations.
Emergency response planning is a critical element of safety standards. Telecom companies must have well-defined procedures for handling accidents, gas leaks, fires, or other emergencies related to gas welding activities. This includes evacuation plans, communication protocols, and coordination with local emergency services.
Regular equipment maintenance and inspection are mandated by safety standards to ensure the reliability and safety of welding apparatus. This includes periodic testing of gas cylinders, hoses, regulators, and welding torches to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents.
One of the primary safety considerations is the proper handling and storage of welding gases. Strict guidelines are in place for the transportation, storage, and usage of flammable gases such as acetylene and oxygen. Telecom companies must adhere to specific requirements for gas cylinder storage, including proper ventilation, secure fastening, and clear labeling of contents and hazards.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is another critical aspect of safety standards in telecom gas welding. Workers are required to wear appropriate protective gear, including flame-resistant clothing, welding helmets with proper eye protection, and heat-resistant gloves. Additionally, respiratory protection may be necessary when working in confined spaces or areas with poor ventilation.
Fire prevention measures are paramount in telecom gas welding operations. Safety standards mandate the presence of fire extinguishers and other fire suppression equipment in welding areas. Welding operations must be conducted at a safe distance from flammable materials, and fire watches may be required in high-risk environments.
Proper training and certification of welding personnel is a key component of safety standards. Telecom companies must ensure that all workers involved in gas welding operations are adequately trained in equipment operation, safety procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher courses and safety audits are typically required to maintain compliance with industry standards.
Electrical safety is also a significant concern in telecom gas welding. Standards address the proper grounding of welding equipment, protection against electric shock, and the use of appropriate insulation materials. Special precautions are necessary when welding near live electrical components or in areas with potential electromagnetic interference.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in telecom gas welding safety standards. Regulations often cover the management of welding fumes and gases, proper disposal of welding waste, and measures to minimize the environmental impact of welding operations.
Emergency response planning is a critical element of safety standards. Telecom companies must have well-defined procedures for handling accidents, gas leaks, fires, or other emergencies related to gas welding activities. This includes evacuation plans, communication protocols, and coordination with local emergency services.
Regular equipment maintenance and inspection are mandated by safety standards to ensure the reliability and safety of welding apparatus. This includes periodic testing of gas cylinders, hoses, regulators, and welding torches to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents.
Environmental Impact of Gas Welding in Telecom
Gas welding, while an effective technique in telecommunications infrastructure construction, poses significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. The process releases various pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on local air quality, potentially impacting both human health and surrounding ecosystems.
The high temperatures involved in gas welding also lead to the generation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and metal fumes. These substances can be particularly harmful when released in enclosed spaces or areas with poor ventilation, which is often the case in telecommunications infrastructure projects. Long-term exposure to these pollutants may result in respiratory issues and other health problems for workers and nearby residents.
Furthermore, the use of gas welding in telecom infrastructure projects often requires the transportation and storage of flammable gases, such as acetylene and oxygen. This presents potential risks of accidental releases or leaks, which can contribute to localized environmental contamination and pose safety hazards.
The energy-intensive nature of gas welding also raises concerns about its carbon footprint. The combustion of fossil fuels to generate the necessary heat for welding contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change impacts. As the telecommunications industry expands and upgrades its infrastructure, the cumulative environmental impact of gas welding operations becomes increasingly significant.
Noise pollution is another environmental consideration associated with gas welding in telecom projects. The process generates high-decibel sounds that can disturb local wildlife and disrupt nearby communities, particularly in residential areas or sensitive ecosystems where telecommunications infrastructure is being installed or maintained.
Additionally, the disposal of welding consumables and waste materials presents environmental challenges. Spent welding rods, slag, and other byproducts may contain hazardous substances that require proper handling and disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the telecommunications industry is increasingly exploring alternative welding technologies and implementing best practices. These include the use of more environmentally friendly welding gases, improved ventilation systems, and the adoption of electric arc welding techniques where feasible. Some companies are also investing in training programs to enhance welders' skills in minimizing emissions and optimizing welding efficiency, thereby reducing overall environmental impact.
The high temperatures involved in gas welding also lead to the generation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and metal fumes. These substances can be particularly harmful when released in enclosed spaces or areas with poor ventilation, which is often the case in telecommunications infrastructure projects. Long-term exposure to these pollutants may result in respiratory issues and other health problems for workers and nearby residents.
Furthermore, the use of gas welding in telecom infrastructure projects often requires the transportation and storage of flammable gases, such as acetylene and oxygen. This presents potential risks of accidental releases or leaks, which can contribute to localized environmental contamination and pose safety hazards.
The energy-intensive nature of gas welding also raises concerns about its carbon footprint. The combustion of fossil fuels to generate the necessary heat for welding contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change impacts. As the telecommunications industry expands and upgrades its infrastructure, the cumulative environmental impact of gas welding operations becomes increasingly significant.
Noise pollution is another environmental consideration associated with gas welding in telecom projects. The process generates high-decibel sounds that can disturb local wildlife and disrupt nearby communities, particularly in residential areas or sensitive ecosystems where telecommunications infrastructure is being installed or maintained.
Additionally, the disposal of welding consumables and waste materials presents environmental challenges. Spent welding rods, slag, and other byproducts may contain hazardous substances that require proper handling and disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the telecommunications industry is increasingly exploring alternative welding technologies and implementing best practices. These include the use of more environmentally friendly welding gases, improved ventilation systems, and the adoption of electric arc welding techniques where feasible. Some companies are also investing in training programs to enhance welders' skills in minimizing emissions and optimizing welding efficiency, thereby reducing overall environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!