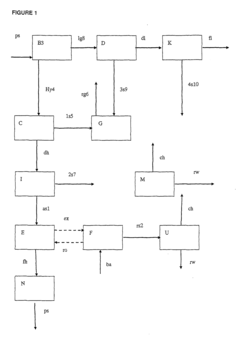
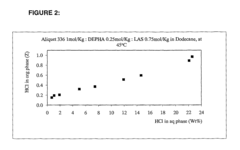
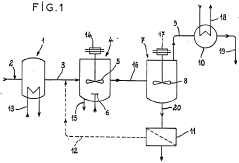
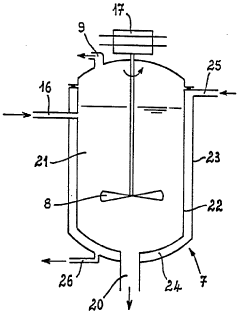
Emerging Technologies for Hydrochloric Acid Recovery
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Recovery Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) recovery has become a critical focus in various industries due to its widespread use and environmental implications. The evolution of HCl recovery technologies spans several decades, with significant advancements in recent years driven by the need for more efficient and sustainable processes. This technological progression has been shaped by increasing environmental regulations, economic pressures, and the pursuit of circular economy principles.
The primary objective of emerging HCl recovery technologies is to maximize the reclamation of acid from waste streams while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact. These technologies aim to address the limitations of traditional recovery methods, such as distillation and membrane separation, which often suffer from high energy requirements or limited efficiency. By developing more advanced recovery systems, industries seek to reduce raw material costs, decrease waste disposal expenses, and improve overall process sustainability.
One of the key drivers behind the development of new HCl recovery technologies is the growing demand for hydrochloric acid in various sectors, including chemical manufacturing, steel pickling, and oil and gas production. As global industrial activities expand, the need for efficient acid recovery becomes increasingly crucial to ensure a stable supply chain and reduce dependence on virgin acid production. This demand has spurred research into novel recovery techniques that can handle diverse waste streams and achieve higher purity levels in recovered acid.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in shaping the objectives of HCl recovery technologies. Stringent regulations on industrial effluents and waste disposal have necessitated the development of cleaner recovery processes that minimize harmful emissions and reduce the overall environmental footprint of acid-using industries. Emerging technologies are thus focused on not only recovering HCl but also addressing associated challenges such as the removal of contaminants and the treatment of residual waste streams.
The technological landscape of HCl recovery is characterized by a convergence of chemical engineering principles, materials science, and process optimization. Recent advancements have explored the integration of membrane technologies, electrochemical processes, and advanced separation techniques to enhance recovery efficiency and selectivity. These emerging approaches aim to overcome the limitations of conventional methods by offering improved energy efficiency, higher recovery rates, and the ability to handle complex waste streams.
As the field progresses, the objectives of HCl recovery technologies are expanding beyond mere acid reclamation. There is a growing emphasis on developing versatile systems that can adapt to varying feed compositions and process conditions, enabling their application across different industries. Additionally, the integration of smart monitoring and control systems is becoming increasingly important to optimize recovery processes in real-time and ensure consistent product quality.
The primary objective of emerging HCl recovery technologies is to maximize the reclamation of acid from waste streams while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact. These technologies aim to address the limitations of traditional recovery methods, such as distillation and membrane separation, which often suffer from high energy requirements or limited efficiency. By developing more advanced recovery systems, industries seek to reduce raw material costs, decrease waste disposal expenses, and improve overall process sustainability.
One of the key drivers behind the development of new HCl recovery technologies is the growing demand for hydrochloric acid in various sectors, including chemical manufacturing, steel pickling, and oil and gas production. As global industrial activities expand, the need for efficient acid recovery becomes increasingly crucial to ensure a stable supply chain and reduce dependence on virgin acid production. This demand has spurred research into novel recovery techniques that can handle diverse waste streams and achieve higher purity levels in recovered acid.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in shaping the objectives of HCl recovery technologies. Stringent regulations on industrial effluents and waste disposal have necessitated the development of cleaner recovery processes that minimize harmful emissions and reduce the overall environmental footprint of acid-using industries. Emerging technologies are thus focused on not only recovering HCl but also addressing associated challenges such as the removal of contaminants and the treatment of residual waste streams.
The technological landscape of HCl recovery is characterized by a convergence of chemical engineering principles, materials science, and process optimization. Recent advancements have explored the integration of membrane technologies, electrochemical processes, and advanced separation techniques to enhance recovery efficiency and selectivity. These emerging approaches aim to overcome the limitations of conventional methods by offering improved energy efficiency, higher recovery rates, and the ability to handle complex waste streams.
As the field progresses, the objectives of HCl recovery technologies are expanding beyond mere acid reclamation. There is a growing emphasis on developing versatile systems that can adapt to varying feed compositions and process conditions, enabling their application across different industries. Additionally, the integration of smart monitoring and control systems is becoming increasingly important to optimize recovery processes in real-time and ensure consistent product quality.
Market Analysis for HCl Recovery Solutions
The global market for hydrochloric acid (HCl) recovery solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the rising demand for sustainable industrial practices. The market is primarily segmented into industries such as chemical manufacturing, steel pickling, oil and gas, and semiconductor production, where large volumes of HCl are utilized and subsequently require recovery.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, the demand for HCl recovery solutions is particularly strong due to the widespread use of HCl in various processes. The steel pickling industry, which uses HCl for surface treatment of steel, is another major contributor to the market growth. The oil and gas sector, where HCl is used in well acidizing and other processes, is also showing increased interest in recovery technologies.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market, with China and India being the largest consumers of HCl recovery solutions. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization and stringent environmental regulations in these countries. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by mature industries and advanced environmental policies.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Key market players are focusing on developing more efficient and cost-effective recovery technologies. There is a growing trend towards the adoption of membrane-based recovery systems and advanced distillation techniques, which offer higher recovery rates and lower energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
Economic factors play a crucial role in market dynamics. The cost of raw materials for HCl production, energy prices, and the overall economic health of key industries influence the demand for recovery solutions. Additionally, the increasing focus on circular economy principles is pushing industries to invest in recovery technologies, viewing waste streams as potential resources.
Technological advancements are shaping the market landscape. Emerging technologies such as electrochemical recovery methods and novel adsorption materials are gaining traction. These innovations promise higher efficiency and lower environmental impact, potentially disrupting the current market structure.
The regulatory environment is a significant driver for market growth. Stringent regulations on industrial waste disposal and emissions are compelling companies to invest in recovery solutions. This is particularly evident in developed economies, where environmental compliance is strictly enforced.
Looking ahead, the market for HCl recovery solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing industrial activities in emerging economies, growing awareness of environmental issues, and ongoing technological innovations are likely to fuel this growth. The market is also seeing a shift towards integrated solutions that combine recovery with other waste management processes, offering comprehensive environmental management systems to industries.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, the demand for HCl recovery solutions is particularly strong due to the widespread use of HCl in various processes. The steel pickling industry, which uses HCl for surface treatment of steel, is another major contributor to the market growth. The oil and gas sector, where HCl is used in well acidizing and other processes, is also showing increased interest in recovery technologies.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market, with China and India being the largest consumers of HCl recovery solutions. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization and stringent environmental regulations in these countries. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by mature industries and advanced environmental policies.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Key market players are focusing on developing more efficient and cost-effective recovery technologies. There is a growing trend towards the adoption of membrane-based recovery systems and advanced distillation techniques, which offer higher recovery rates and lower energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
Economic factors play a crucial role in market dynamics. The cost of raw materials for HCl production, energy prices, and the overall economic health of key industries influence the demand for recovery solutions. Additionally, the increasing focus on circular economy principles is pushing industries to invest in recovery technologies, viewing waste streams as potential resources.
Technological advancements are shaping the market landscape. Emerging technologies such as electrochemical recovery methods and novel adsorption materials are gaining traction. These innovations promise higher efficiency and lower environmental impact, potentially disrupting the current market structure.
The regulatory environment is a significant driver for market growth. Stringent regulations on industrial waste disposal and emissions are compelling companies to invest in recovery solutions. This is particularly evident in developed economies, where environmental compliance is strictly enforced.
Looking ahead, the market for HCl recovery solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing industrial activities in emerging economies, growing awareness of environmental issues, and ongoing technological innovations are likely to fuel this growth. The market is also seeing a shift towards integrated solutions that combine recovery with other waste management processes, offering comprehensive environmental management systems to industries.
Current Challenges in HCl Recovery
The recovery of hydrochloric acid (HCl) faces several significant challenges in current industrial processes. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption associated with traditional recovery methods. Conventional techniques often require substantial thermal energy for distillation or evaporation, leading to increased operational costs and environmental concerns.
Another major challenge is the corrosive nature of HCl, which necessitates the use of specialized materials for equipment and infrastructure. This requirement not only increases capital expenditure but also poses maintenance and safety challenges. The corrosion resistance of materials used in HCl recovery systems is critical to ensure long-term operational efficiency and prevent potential hazards.
The presence of impurities in HCl-containing waste streams presents a significant obstacle to efficient recovery. These impurities can interfere with the recovery process, reduce the quality of the recovered acid, and potentially damage equipment. Developing effective separation and purification techniques that can handle diverse waste compositions remains a key challenge in the field.
Environmental regulations pose another hurdle for HCl recovery processes. Stringent emission standards and waste disposal regulations require industries to implement more sophisticated recovery systems. Balancing regulatory compliance with cost-effectiveness is an ongoing challenge for many operators.
The scale-up of laboratory-proven technologies to industrial-scale operations presents its own set of challenges. Many promising recovery methods that show potential in controlled environments face difficulties when implemented at larger scales, often due to issues related to process stability, equipment design, and operational complexities.
Furthermore, the variability in HCl concentrations across different industrial processes complicates the development of universally applicable recovery solutions. Industries ranging from chemical manufacturing to metal processing generate HCl waste streams with varying concentrations and impurity profiles, necessitating tailored recovery approaches.
Lastly, the economic viability of HCl recovery remains a significant challenge, particularly for smaller operations. The capital investment required for advanced recovery systems can be prohibitive, and the fluctuating market value of recovered HCl may not always justify the recovery costs. Developing cost-effective technologies that can be implemented across various scales of operation is crucial for widespread adoption of HCl recovery practices.
Another major challenge is the corrosive nature of HCl, which necessitates the use of specialized materials for equipment and infrastructure. This requirement not only increases capital expenditure but also poses maintenance and safety challenges. The corrosion resistance of materials used in HCl recovery systems is critical to ensure long-term operational efficiency and prevent potential hazards.
The presence of impurities in HCl-containing waste streams presents a significant obstacle to efficient recovery. These impurities can interfere with the recovery process, reduce the quality of the recovered acid, and potentially damage equipment. Developing effective separation and purification techniques that can handle diverse waste compositions remains a key challenge in the field.
Environmental regulations pose another hurdle for HCl recovery processes. Stringent emission standards and waste disposal regulations require industries to implement more sophisticated recovery systems. Balancing regulatory compliance with cost-effectiveness is an ongoing challenge for many operators.
The scale-up of laboratory-proven technologies to industrial-scale operations presents its own set of challenges. Many promising recovery methods that show potential in controlled environments face difficulties when implemented at larger scales, often due to issues related to process stability, equipment design, and operational complexities.
Furthermore, the variability in HCl concentrations across different industrial processes complicates the development of universally applicable recovery solutions. Industries ranging from chemical manufacturing to metal processing generate HCl waste streams with varying concentrations and impurity profiles, necessitating tailored recovery approaches.
Lastly, the economic viability of HCl recovery remains a significant challenge, particularly for smaller operations. The capital investment required for advanced recovery systems can be prohibitive, and the fluctuating market value of recovered HCl may not always justify the recovery costs. Developing cost-effective technologies that can be implemented across various scales of operation is crucial for widespread adoption of HCl recovery practices.
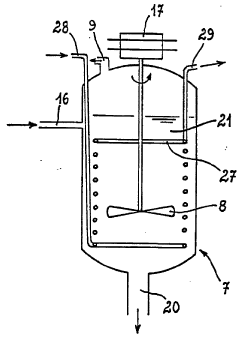
Existing HCl Recovery Methods
01 Distillation and condensation techniques
Hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency can be improved through advanced distillation and condensation techniques. These methods involve separating the acid from other components in the mixture by vaporization and subsequent condensation. Optimizing the distillation column design and operating parameters can significantly enhance the recovery rate of hydrochloric acid.- Absorption and desorption techniques: Hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency can be improved through advanced absorption and desorption processes. These techniques involve using specialized materials or equipment to capture HCl from gas streams and then release it in a concentrated form. This method can significantly increase the recovery rate and purity of the recovered acid.
- Membrane separation technology: Membrane separation technology is an effective method for recovering hydrochloric acid. This process uses selective membranes to separate HCl from other components in the waste stream. The technology can achieve high recovery efficiency and produce high-purity hydrochloric acid while reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Distillation and rectification processes: Distillation and rectification processes can be optimized to improve hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency. These methods involve separating HCl from other components based on differences in boiling points. Advanced column designs and operating conditions can enhance the separation efficiency and increase the recovery rate of high-quality hydrochloric acid.
- Integrated recovery systems: Integrated recovery systems combine multiple technologies to maximize hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency. These systems may incorporate absorption, desorption, membrane separation, and distillation processes in a single, optimized setup. By leveraging the strengths of each technology, integrated systems can achieve higher recovery rates and better quality of recovered acid.
- Process optimization and control: Improving hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency can be achieved through process optimization and advanced control strategies. This includes implementing real-time monitoring systems, adjusting operating parameters based on feed composition, and using predictive models to optimize recovery conditions. These approaches can lead to significant improvements in recovery rates and overall process efficiency.
02 Absorption and desorption processes
Utilizing absorption and desorption processes can increase hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency. This involves using specialized absorbents to capture HCl from gas streams, followed by a desorption step to release and concentrate the acid. Selecting appropriate absorbents and optimizing process conditions can lead to higher recovery rates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Membrane separation technology
Membrane separation technology offers an efficient method for hydrochloric acid recovery. By using selective membranes, it's possible to separate HCl from other components in the mixture. This technique can be particularly effective for recovering acid from dilute solutions or waste streams, improving overall recovery efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrodialysis and electrochemical methods
Electrodialysis and other electrochemical methods can be employed to recover hydrochloric acid with high efficiency. These techniques use electrical potential differences to separate ionic species, allowing for the concentration and purification of HCl. Optimizing electrode materials and operating conditions can enhance the recovery efficiency of these processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated recycling systems
Developing integrated recycling systems that combine multiple recovery techniques can significantly improve overall hydrochloric acid recovery efficiency. These systems may incorporate a combination of distillation, absorption, membrane separation, and electrochemical methods tailored to specific process requirements. By optimizing the integration of these techniques, higher recovery rates and purity levels can be achieved.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HCl Recovery Industry
The emerging technologies for hydrochloric acid recovery market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the need for sustainable industrial processes. The market size is expanding, with a growing demand across various industries such as chemical, petrochemical, and metallurgical sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like LG Chem, Halliburton, and Andritz AG leading innovation. These firms are developing sophisticated recovery systems, membrane technologies, and process optimization solutions. Smaller players like Nantong Xingqiu Graphite and Jiangsu Sunpower Technology are also contributing to technological advancements, particularly in graphite-based recovery systems and energy-efficient solutions. Academic institutions such as the Institute of Process Engineering, CAS, and Nanjing Tech University are further driving research and development in this area.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has developed an innovative membrane-based technology for hydrochloric acid recovery. Their process utilizes advanced ion exchange membranes to selectively separate and concentrate HCl from waste streams. The system employs a multi-stage electrodialysis setup, allowing for efficient acid recovery with minimal energy consumption. LG Chem's technology can achieve recovery rates of up to 95% for HCl concentrations ranging from 5% to 20%[1]. The recovered acid can be reused in various industrial processes, promoting circular economy principles and reducing waste disposal costs[2].
Strengths: High recovery rate, energy-efficient, applicable to a wide range of HCl concentrations. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment, potential membrane fouling issues in certain applications.
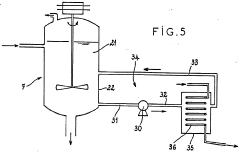
Andritz AG
Technical Solution: Andritz AG has developed a cutting-edge pyrohydrolysis process for hydrochloric acid recovery, particularly focused on the metallurgical industry. Their technology involves high-temperature treatment of metal chlorides in the presence of steam, effectively converting them into metal oxides while liberating HCl gas. The process operates at temperatures between 650°C and 950°C, depending on the specific chloride being treated[3]. Andritz's system incorporates advanced heat recovery mechanisms, significantly improving overall energy efficiency. The recovered HCl gas is then absorbed in water to produce high-purity hydrochloric acid with concentrations up to 32%[4]. This technology has been successfully implemented in several large-scale plants, demonstrating its commercial viability.
Strengths: High-purity acid recovery, suitable for metallurgical waste streams, energy-efficient design. Weaknesses: High operating temperatures may lead to increased maintenance costs, limited applicability outside metallurgical industry.
Innovative HCl Recovery Technologies
Methods for the recovery of hcl and for the production of carbohydrates
PatentInactiveUS20130047979A1
Innovation
- A method utilizing an organic phase composition comprising quaternary amines, specific organic acids, and hydrocarbons, which selectively extracts HCl from aqueous solutions at controlled temperatures, minimizing solvent use and maintaining product integrity, and a process for recovering HCl through solvent extraction and distillation, ensuring high purity and minimal product loss.
Method and plant for regenerating a hydrochloric solution
PatentWO1986003521A1
Innovation
- A process and installation utilizing a stirred liquid medium at atmospheric pressure or under vacuum, with a heating device for solid-liquid contact, allowing hydrolysis at 130-190°C, followed by condensation to recover a mixture of hydrochloric acid vapor and water, and incorporating a filtration unit to recycle iron precipitate and concentrate ferrous chloride, optimizing energy use and reducing maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact of HCl Recovery
The environmental impact of hydrochloric acid (HCl) recovery is a critical consideration in the development and implementation of emerging technologies. Traditional HCl production and disposal methods have been associated with significant environmental concerns, including air pollution, water contamination, and soil degradation. However, the advent of new recovery technologies offers promising solutions to mitigate these issues.
One of the primary environmental benefits of HCl recovery is the reduction of waste and emissions. By reclaiming and reusing HCl, industries can significantly decrease the volume of acid that needs to be neutralized or disposed of as waste. This not only reduces the environmental burden but also minimizes the consumption of raw materials required for fresh acid production. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with HCl manufacturing and transportation is substantially lowered.
Advanced recovery technologies, such as membrane-based systems and distillation processes, have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in reducing energy consumption compared to conventional methods. This energy efficiency translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global efforts in combating climate change. Moreover, these technologies often operate in closed-loop systems, minimizing the risk of accidental releases and spills that could harm local ecosystems.
Water conservation is another significant environmental advantage of HCl recovery. Many emerging technologies incorporate water recycling mechanisms, drastically reducing the freshwater demand in industrial processes. This is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions where industrial water usage competes with other essential needs.
The implementation of HCl recovery systems also leads to improved air quality in industrial areas. By capturing and reprocessing acid vapors that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere, these technologies help reduce the formation of acid rain and mitigate the associated impacts on vegetation, aquatic life, and infrastructure.
Furthermore, the recovery of HCl from waste streams often results in the removal of other contaminants, such as heavy metals and organic compounds. This multi-pollutant control approach enhances the overall environmental performance of industrial facilities, contributing to cleaner soil and water resources in surrounding communities.
However, it is important to note that the environmental benefits of HCl recovery technologies must be weighed against potential drawbacks. The production and disposal of materials used in recovery systems, such as membranes or adsorbents, need to be carefully managed to prevent creating new environmental challenges. Additionally, the energy requirements for some advanced recovery processes may offset some of the environmental gains if not sourced from renewable energy.
In conclusion, emerging technologies for HCl recovery offer substantial environmental benefits, including waste reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, and improved air and water quality. As these technologies continue to evolve, their integration into industrial processes promises to significantly enhance environmental sustainability in sectors reliant on hydrochloric acid.
One of the primary environmental benefits of HCl recovery is the reduction of waste and emissions. By reclaiming and reusing HCl, industries can significantly decrease the volume of acid that needs to be neutralized or disposed of as waste. This not only reduces the environmental burden but also minimizes the consumption of raw materials required for fresh acid production. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with HCl manufacturing and transportation is substantially lowered.
Advanced recovery technologies, such as membrane-based systems and distillation processes, have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in reducing energy consumption compared to conventional methods. This energy efficiency translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global efforts in combating climate change. Moreover, these technologies often operate in closed-loop systems, minimizing the risk of accidental releases and spills that could harm local ecosystems.
Water conservation is another significant environmental advantage of HCl recovery. Many emerging technologies incorporate water recycling mechanisms, drastically reducing the freshwater demand in industrial processes. This is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions where industrial water usage competes with other essential needs.
The implementation of HCl recovery systems also leads to improved air quality in industrial areas. By capturing and reprocessing acid vapors that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere, these technologies help reduce the formation of acid rain and mitigate the associated impacts on vegetation, aquatic life, and infrastructure.
Furthermore, the recovery of HCl from waste streams often results in the removal of other contaminants, such as heavy metals and organic compounds. This multi-pollutant control approach enhances the overall environmental performance of industrial facilities, contributing to cleaner soil and water resources in surrounding communities.
However, it is important to note that the environmental benefits of HCl recovery technologies must be weighed against potential drawbacks. The production and disposal of materials used in recovery systems, such as membranes or adsorbents, need to be carefully managed to prevent creating new environmental challenges. Additionally, the energy requirements for some advanced recovery processes may offset some of the environmental gains if not sourced from renewable energy.
In conclusion, emerging technologies for HCl recovery offer substantial environmental benefits, including waste reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, and improved air and water quality. As these technologies continue to evolve, their integration into industrial processes promises to significantly enhance environmental sustainability in sectors reliant on hydrochloric acid.
Economic Feasibility of HCl Recovery
The economic feasibility of hydrochloric acid (HCl) recovery is a critical factor in determining the viability of emerging technologies in this field. As industries seek to reduce waste and optimize resource utilization, the recovery of HCl has become increasingly important. The economic analysis of HCl recovery technologies must consider several key factors to provide a comprehensive assessment.
Capital expenditure (CAPEX) is a primary consideration in evaluating the economic feasibility of HCl recovery systems. This includes the initial investment in equipment, infrastructure, and installation costs. The scale of the recovery operation significantly impacts CAPEX, with larger systems often benefiting from economies of scale. However, the complexity of some emerging technologies may lead to higher upfront costs, which must be weighed against long-term benefits.
Operating expenses (OPEX) play a crucial role in determining the ongoing economic viability of HCl recovery. This encompasses energy consumption, maintenance requirements, labor costs, and consumables. Advanced recovery technologies may offer lower OPEX through improved energy efficiency and reduced chemical consumption, potentially offsetting higher initial investments.
The market value of recovered HCl is a key driver of economic feasibility. High-purity recovered acid can command premium prices, especially in industries requiring stringent quality standards. The ability to produce consistent, high-quality HCl can significantly enhance the economic attractiveness of recovery technologies.
Regulatory factors also influence the economic landscape of HCl recovery. Stringent environmental regulations may necessitate investment in recovery technologies, turning what might otherwise be a cost center into a potential source of value. Tax incentives or penalties related to waste management can further alter the economic equation.
The integration of HCl recovery systems into existing industrial processes is another critical economic consideration. Technologies that can be seamlessly incorporated into current operations without major disruptions or modifications to existing infrastructure may have a competitive edge in terms of implementation costs and operational efficiency.
Lifecycle cost analysis is essential for a comprehensive economic assessment. This involves evaluating the total cost of ownership over the expected lifespan of the recovery system, including initial investment, operational costs, maintenance, and eventual decommissioning or replacement expenses.
Finally, the potential for byproduct valorization can significantly enhance the economic feasibility of HCl recovery. Some emerging technologies may enable the recovery of valuable co-products or the conversion of waste streams into marketable materials, creating additional revenue streams that improve the overall economic proposition.
Capital expenditure (CAPEX) is a primary consideration in evaluating the economic feasibility of HCl recovery systems. This includes the initial investment in equipment, infrastructure, and installation costs. The scale of the recovery operation significantly impacts CAPEX, with larger systems often benefiting from economies of scale. However, the complexity of some emerging technologies may lead to higher upfront costs, which must be weighed against long-term benefits.
Operating expenses (OPEX) play a crucial role in determining the ongoing economic viability of HCl recovery. This encompasses energy consumption, maintenance requirements, labor costs, and consumables. Advanced recovery technologies may offer lower OPEX through improved energy efficiency and reduced chemical consumption, potentially offsetting higher initial investments.
The market value of recovered HCl is a key driver of economic feasibility. High-purity recovered acid can command premium prices, especially in industries requiring stringent quality standards. The ability to produce consistent, high-quality HCl can significantly enhance the economic attractiveness of recovery technologies.
Regulatory factors also influence the economic landscape of HCl recovery. Stringent environmental regulations may necessitate investment in recovery technologies, turning what might otherwise be a cost center into a potential source of value. Tax incentives or penalties related to waste management can further alter the economic equation.
The integration of HCl recovery systems into existing industrial processes is another critical economic consideration. Technologies that can be seamlessly incorporated into current operations without major disruptions or modifications to existing infrastructure may have a competitive edge in terms of implementation costs and operational efficiency.
Lifecycle cost analysis is essential for a comprehensive economic assessment. This involves evaluating the total cost of ownership over the expected lifespan of the recovery system, including initial investment, operational costs, maintenance, and eventual decommissioning or replacement expenses.
Finally, the potential for byproduct valorization can significantly enhance the economic feasibility of HCl recovery. Some emerging technologies may enable the recovery of valuable co-products or the conversion of waste streams into marketable materials, creating additional revenue streams that improve the overall economic proposition.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!