Ethyl Acetate’s Advantages in Photographic Materials
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate in Photography: Background and Objectives
Ethyl acetate has played a significant role in the development of photographic materials since the early days of photography. This versatile organic compound, with its unique chemical properties, has been instrumental in advancing various aspects of photographic technology. The evolution of ethyl acetate's use in photography can be traced back to the mid-19th century when the wet collodion process was introduced, revolutionizing the field of photography.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl acetate in photographic materials is to enhance the quality, durability, and versatility of photographic products. Its excellent solvent properties make it an ideal component in the formulation of photographic emulsions, film bases, and developing solutions. Ethyl acetate's low boiling point and rapid evaporation rate contribute to its effectiveness in these applications, allowing for quick drying and uniform coating of photographic materials.
One of the key advantages of ethyl acetate in photography is its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, including cellulose derivatives and various resins. This property has been crucial in the development of flexible film bases, which replaced glass plates as the primary support for photographic emulsions. The introduction of flexible film bases marked a significant milestone in the history of photography, enabling the production of roll films and eventually leading to the development of portable cameras.
In addition to its role in film base production, ethyl acetate has been extensively used in the formulation of photographic developers and fixers. Its solvent properties facilitate the dissolution of developing agents and other chemicals, ensuring uniform distribution and efficient processing of photographic materials. The use of ethyl acetate in these solutions has contributed to improved image quality, faster processing times, and enhanced stability of photographic prints.
The ongoing technological advancements in digital photography have not diminished the importance of ethyl acetate in the field. In fact, its applications have expanded to include the production of high-quality inkjet papers and specialty printing materials. The compound's ability to interact with various polymers and coatings continues to be valuable in creating surfaces that can accurately reproduce digital images with vibrant colors and sharp details.
As the photography industry continues to evolve, the objectives for using ethyl acetate in photographic materials have broadened. Current research focuses on developing more environmentally friendly formulations, improving the archival quality of photographic prints, and enhancing the compatibility of traditional photographic materials with digital imaging technologies. These objectives align with the growing demand for sustainable and high-performance photographic products in both professional and consumer markets.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl acetate in photographic materials is to enhance the quality, durability, and versatility of photographic products. Its excellent solvent properties make it an ideal component in the formulation of photographic emulsions, film bases, and developing solutions. Ethyl acetate's low boiling point and rapid evaporation rate contribute to its effectiveness in these applications, allowing for quick drying and uniform coating of photographic materials.
One of the key advantages of ethyl acetate in photography is its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, including cellulose derivatives and various resins. This property has been crucial in the development of flexible film bases, which replaced glass plates as the primary support for photographic emulsions. The introduction of flexible film bases marked a significant milestone in the history of photography, enabling the production of roll films and eventually leading to the development of portable cameras.
In addition to its role in film base production, ethyl acetate has been extensively used in the formulation of photographic developers and fixers. Its solvent properties facilitate the dissolution of developing agents and other chemicals, ensuring uniform distribution and efficient processing of photographic materials. The use of ethyl acetate in these solutions has contributed to improved image quality, faster processing times, and enhanced stability of photographic prints.
The ongoing technological advancements in digital photography have not diminished the importance of ethyl acetate in the field. In fact, its applications have expanded to include the production of high-quality inkjet papers and specialty printing materials. The compound's ability to interact with various polymers and coatings continues to be valuable in creating surfaces that can accurately reproduce digital images with vibrant colors and sharp details.
As the photography industry continues to evolve, the objectives for using ethyl acetate in photographic materials have broadened. Current research focuses on developing more environmentally friendly formulations, improving the archival quality of photographic prints, and enhancing the compatibility of traditional photographic materials with digital imaging technologies. These objectives align with the growing demand for sustainable and high-performance photographic products in both professional and consumer markets.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Acetate in Photographic Materials
The market for ethyl acetate in photographic materials has shown significant growth and potential in recent years. This versatile solvent plays a crucial role in various photographic applications, contributing to the overall quality and performance of photographic products. The demand for ethyl acetate in this sector is primarily driven by its excellent solvency properties, low toxicity, and compatibility with a wide range of photographic chemicals.
In the photographic materials market, ethyl acetate is extensively used in the production of photographic films, papers, and plates. It serves as an essential component in the formulation of photographic emulsions, acting as a carrier for light-sensitive materials and other additives. The solvent's ability to dissolve various organic compounds makes it ideal for creating uniform and stable photographic coatings.
The global photographic materials market has been experiencing steady growth, with a particular emphasis on digital printing and specialty photographic products. As the demand for high-quality photographic materials continues to rise, the market for ethyl acetate in this sector is expected to expand correspondingly. The increasing popularity of instant photography and the resurgence of analog photography among enthusiasts have also contributed to the sustained demand for ethyl acetate in photographic applications.
One of the key factors driving the market growth is the superior performance of ethyl acetate compared to alternative solvents. Its low boiling point and rapid evaporation rate make it particularly suitable for fast-drying photographic coatings, improving production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, ethyl acetate's low toxicity and relatively mild odor make it a preferred choice for manufacturers concerned with worker safety and environmental regulations.
The market for ethyl acetate in photographic materials is also influenced by technological advancements in the photography industry. As new photographic techniques and materials are developed, the demand for specialized solvents like ethyl acetate is likely to increase. This trend is particularly evident in the growing market for high-performance photographic films and papers used in professional and artistic applications.
Geographically, the market for ethyl acetate in photographic materials is well-established in North America and Europe, where the photography industry has a long-standing presence. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to drive significant growth in the coming years. These regions are witnessing rapid industrialization and increasing disposable incomes, leading to a growing demand for high-quality photographic products.
In the photographic materials market, ethyl acetate is extensively used in the production of photographic films, papers, and plates. It serves as an essential component in the formulation of photographic emulsions, acting as a carrier for light-sensitive materials and other additives. The solvent's ability to dissolve various organic compounds makes it ideal for creating uniform and stable photographic coatings.
The global photographic materials market has been experiencing steady growth, with a particular emphasis on digital printing and specialty photographic products. As the demand for high-quality photographic materials continues to rise, the market for ethyl acetate in this sector is expected to expand correspondingly. The increasing popularity of instant photography and the resurgence of analog photography among enthusiasts have also contributed to the sustained demand for ethyl acetate in photographic applications.
One of the key factors driving the market growth is the superior performance of ethyl acetate compared to alternative solvents. Its low boiling point and rapid evaporation rate make it particularly suitable for fast-drying photographic coatings, improving production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, ethyl acetate's low toxicity and relatively mild odor make it a preferred choice for manufacturers concerned with worker safety and environmental regulations.
The market for ethyl acetate in photographic materials is also influenced by technological advancements in the photography industry. As new photographic techniques and materials are developed, the demand for specialized solvents like ethyl acetate is likely to increase. This trend is particularly evident in the growing market for high-performance photographic films and papers used in professional and artistic applications.
Geographically, the market for ethyl acetate in photographic materials is well-established in North America and Europe, where the photography industry has a long-standing presence. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to drive significant growth in the coming years. These regions are witnessing rapid industrialization and increasing disposable incomes, leading to a growing demand for high-quality photographic products.
Current Applications and Challenges in Photographic Industry
Ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the photographic industry, serving as a versatile solvent and component in various applications. In film production, it is widely used as a solvent for cellulose acetate, the primary material for photographic film base. This application leverages ethyl acetate's excellent solvency properties and low toxicity, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing processes that require stringent safety standards.
In photographic emulsions, ethyl acetate acts as a dispersing agent, helping to create uniform and stable suspensions of light-sensitive materials. This property is essential for producing high-quality photographic films and papers with consistent sensitivity and image quality. Additionally, ethyl acetate is employed in the formulation of photographic developers, where it aids in the dissolution and stabilization of developing agents.
The printing and coating processes in photography also benefit from ethyl acetate's rapid evaporation rate. It is used in coating solutions for photographic papers and films, allowing for quick drying and efficient production. This characteristic is particularly valuable in high-speed manufacturing environments, where fast processing times are critical.
Despite its widespread use, the photographic industry faces several challenges related to ethyl acetate. One significant issue is the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with its use. As environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers are under pressure to reduce VOC emissions, leading to a search for alternative solvents or improved containment methods.
Another challenge is the increasing shift towards digital photography, which has reduced the demand for traditional film and paper products. This transition has prompted the industry to explore new applications for ethyl acetate in emerging photographic technologies, such as advanced printing processes for digital images or specialized coatings for electronic display devices.
The industry also grapples with the need for higher purity ethyl acetate in certain applications. Trace impurities can affect the quality and stability of photographic materials, necessitating more sophisticated purification processes. This challenge is particularly acute in the production of high-performance films for scientific and industrial applications.
Lastly, the fluctuating costs of raw materials used to produce ethyl acetate pose a challenge for manufacturers. Price volatility can impact production costs and, ultimately, the affordability of photographic products. The industry is exploring ways to optimize ethyl acetate usage and investigating alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate these economic pressures.
In photographic emulsions, ethyl acetate acts as a dispersing agent, helping to create uniform and stable suspensions of light-sensitive materials. This property is essential for producing high-quality photographic films and papers with consistent sensitivity and image quality. Additionally, ethyl acetate is employed in the formulation of photographic developers, where it aids in the dissolution and stabilization of developing agents.
The printing and coating processes in photography also benefit from ethyl acetate's rapid evaporation rate. It is used in coating solutions for photographic papers and films, allowing for quick drying and efficient production. This characteristic is particularly valuable in high-speed manufacturing environments, where fast processing times are critical.
Despite its widespread use, the photographic industry faces several challenges related to ethyl acetate. One significant issue is the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with its use. As environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers are under pressure to reduce VOC emissions, leading to a search for alternative solvents or improved containment methods.
Another challenge is the increasing shift towards digital photography, which has reduced the demand for traditional film and paper products. This transition has prompted the industry to explore new applications for ethyl acetate in emerging photographic technologies, such as advanced printing processes for digital images or specialized coatings for electronic display devices.
The industry also grapples with the need for higher purity ethyl acetate in certain applications. Trace impurities can affect the quality and stability of photographic materials, necessitating more sophisticated purification processes. This challenge is particularly acute in the production of high-performance films for scientific and industrial applications.
Lastly, the fluctuating costs of raw materials used to produce ethyl acetate pose a challenge for manufacturers. Price volatility can impact production costs and, ultimately, the affordability of photographic products. The industry is exploring ways to optimize ethyl acetate usage and investigating alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate these economic pressures.
Ethyl Acetate-based Solutions for Photographic Materials
01 Solvent properties
Ethyl acetate is an excellent solvent for a wide range of organic compounds. It has high solvency power and is particularly useful in dissolving various resins, plastics, and polymers. Its low boiling point and fast evaporation rate make it ideal for applications where quick drying is required, such as in paints, coatings, and adhesives.- Solvent properties: Ethyl acetate is an excellent solvent with a wide range of applications. It has the ability to dissolve various substances, making it useful in industries such as paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its low boiling point and fast evaporation rate contribute to its effectiveness as a solvent in many processes.
- Use in extraction processes: Ethyl acetate is advantageous in extraction processes due to its selective solubility. It is particularly useful in the extraction of organic compounds from aqueous solutions. This property makes it valuable in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing for isolating and purifying various substances.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate has relatively low toxicity and is considered more environmentally friendly. It has a lower impact on air quality and ozone depletion potential. These characteristics make it a preferred choice in many applications where environmental and safety concerns are paramount.
- Use in chemical synthesis: Ethyl acetate serves as a valuable reagent and intermediate in various chemical synthesis processes. Its reactivity and functional group make it useful in the production of esters, as well as in other organic reactions. This versatility in chemical synthesis contributes to its widespread use in the chemical industry.
- Application in cleaning and degreasing: The solvent properties of ethyl acetate make it effective for cleaning and degreasing applications. It can dissolve oils, greases, and other contaminants, making it useful in industrial cleaning processes, electronics manufacturing, and surface preparation. Its relatively low toxicity and quick evaporation rate are advantageous in these applications.
02 Environmental and safety advantages
Ethyl acetate is considered a more environmentally friendly solvent compared to many alternatives. It has low toxicity, is biodegradable, and has a relatively low impact on air quality. These properties make it a preferred choice in industries where environmental concerns are paramount, such as food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in extraction processes
Ethyl acetate is widely used in extraction processes, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Its selective solubility properties make it effective for extracting specific compounds from complex mixtures. It is commonly used in the extraction of natural products, flavors, and fragrances from plant materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in chemical synthesis
Ethyl acetate serves as an important reagent and intermediate in various chemical synthesis processes. It is used in the production of other esters, as a raw material for pharmaceuticals, and in the synthesis of various organic compounds. Its reactivity and stability make it a versatile building block in organic chemistry.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial cleaning and degreasing
Ethyl acetate is an effective cleaning and degreasing agent in industrial applications. Its ability to dissolve oils, fats, and other organic residues makes it useful in cleaning electronic components, machinery parts, and precision instruments. It leaves minimal residue after evaporation, which is advantageous in many cleaning processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Suppliers of Ethyl Acetate
The competitive landscape for ethyl acetate in photographic materials is characterized by a mature industry with established players and moderate market growth. Key companies like Eastman Kodak, Canon, and FUJIFILM dominate the sector, leveraging their extensive experience and technological capabilities. The market size is substantial but faces challenges from digital photography advancements. Technologically, ethyl acetate's application in photographic materials is well-established, with companies focusing on incremental improvements rather than disruptive innovations. Smaller players like Kuraray and Clariant also contribute specialized solutions, while research institutions like MIT continue to explore novel applications, ensuring ongoing development in this field.
Eastman Kodak Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Kodak has developed advanced photographic materials utilizing ethyl acetate as a key solvent. Their technology incorporates ethyl acetate in film coatings and emulsions, enhancing image quality and stability. The company's approach involves using ethyl acetate to dissolve light-sensitive compounds and polymers, creating uniform layers that improve color reproduction and longevity[1]. Kodak's process also leverages ethyl acetate's low boiling point for rapid drying, enabling faster production speeds while maintaining coating integrity[3]. Additionally, they have implemented ethyl acetate recycling systems in their manufacturing to reduce environmental impact and costs[5].
Strengths: Improved image quality, faster production, and environmental sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential volatility issues and the need for specialized handling equipment.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has pioneered the use of ethyl acetate in their advanced photographic film technologies. Their approach involves incorporating ethyl acetate as a primary solvent in their film emulsion formulations, which has led to significant improvements in image sharpness and color accuracy[2]. FUJIFILM's proprietary process utilizes ethyl acetate's excellent solvency properties to create ultra-thin, uniform coating layers, resulting in enhanced light sensitivity and reduced grain in their photographic materials[4]. The company has also developed innovative ethyl acetate-based coating techniques that improve the film's resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations[6].
Strengths: Superior image quality, improved film durability, and enhanced light sensitivity. Weaknesses: Potential cost implications and the need for specialized manufacturing equipment.
Innovative Uses of Ethyl Acetate in Photography
Photoresist composition
PatentInactiveUS7014980B2
Innovation
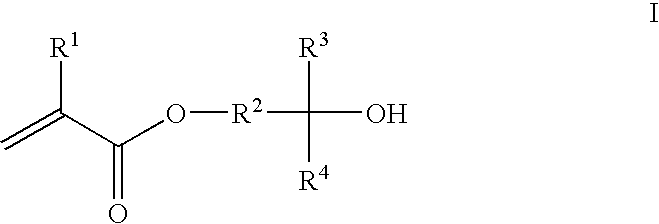
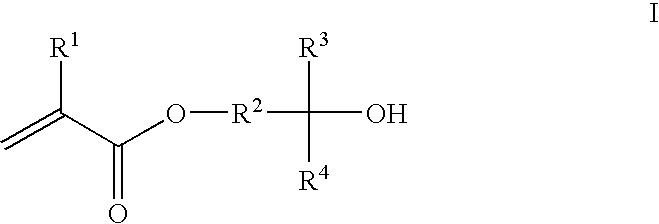
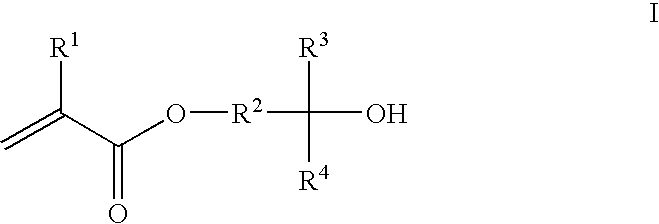
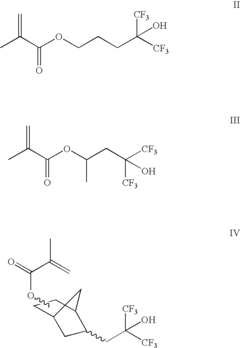
- A photoresist composition incorporating acrylate or methacrylate monomers with fluoro alcohol groups, which provide similar pKa values to phenolic materials, allowing for uniform dissolution in TMAH and enabling high resolution patterning with 193 nm optical radiation, along with the inclusion of crosslinking agents and acid labile groups for negative and positive tone photoresists respectively.
Photoacid generator and photoreactive composition
PatentInactiveUS20100233621A1
Innovation
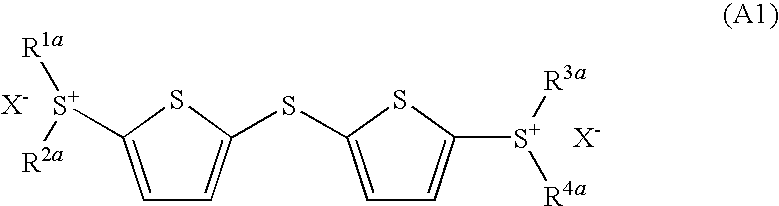
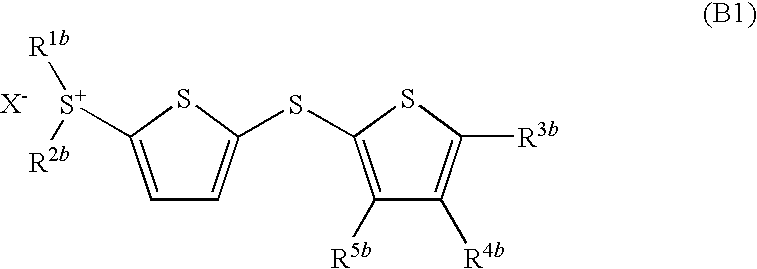
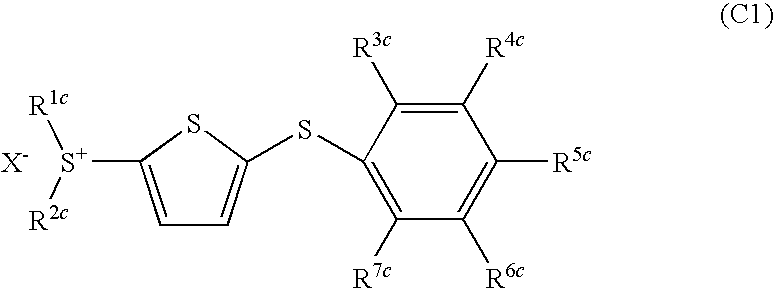
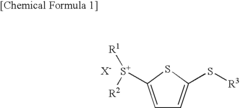
- Development of (5-arylthio-thiophen-2-yl)-diaryl sulfonium salts, specifically dithienyl sulfide disulfonium, dithienyl sulfide sulfonium, and phenylthiothiophene sulfonium salts, which serve as photoacid generators, enhancing sensitivity and reaction rates in the near ultraviolet range by incorporating these salts into photoreactive compositions.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Acetate in Photography
The use of ethyl acetate in photographic materials has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a solvent widely used in film base production and photographic processing, ethyl acetate's environmental impact extends throughout its lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal.
During production, ethyl acetate synthesis typically involves the reaction of ethanol with acetic acid. This process requires energy input and may result in emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. However, compared to some alternative solvents, ethyl acetate production generally has a lower carbon footprint and reduced potential for ozone depletion.
In photographic applications, ethyl acetate's relatively low toxicity and high volatility contribute to its favorable environmental profile. Its rapid evaporation reduces the risk of long-term environmental contamination, especially when compared to slower-evaporating solvents. This characteristic also minimizes worker exposure during handling and processing of photographic materials.
Ethyl acetate is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, breaking down into ethanol and acetic acid, which are naturally occurring substances. This property significantly reduces its potential for bioaccumulation and long-term ecological harm. However, improper disposal or large-scale releases could still lead to short-term aquatic toxicity and contribute to air quality issues.
The recycling and recovery of ethyl acetate from photographic processes present opportunities for reducing environmental impact. Modern distillation and membrane separation techniques allow for efficient solvent recovery, minimizing waste and reducing the need for fresh solvent production. This closed-loop approach aligns with principles of green chemistry and circular economy practices.
From a broader perspective, the shift towards digital photography has led to a decrease in traditional film and chemical processing, indirectly reducing the overall environmental footprint associated with ethyl acetate in photography. However, this transition brings its own set of environmental challenges, such as electronic waste and energy consumption of digital devices.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers several environmental advantages in photographic applications, its use still requires careful management to minimize potential negative impacts. Continued research into greener alternatives and improved recycling technologies will be crucial in further reducing the environmental footprint of photographic materials and processes.
During production, ethyl acetate synthesis typically involves the reaction of ethanol with acetic acid. This process requires energy input and may result in emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. However, compared to some alternative solvents, ethyl acetate production generally has a lower carbon footprint and reduced potential for ozone depletion.
In photographic applications, ethyl acetate's relatively low toxicity and high volatility contribute to its favorable environmental profile. Its rapid evaporation reduces the risk of long-term environmental contamination, especially when compared to slower-evaporating solvents. This characteristic also minimizes worker exposure during handling and processing of photographic materials.
Ethyl acetate is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, breaking down into ethanol and acetic acid, which are naturally occurring substances. This property significantly reduces its potential for bioaccumulation and long-term ecological harm. However, improper disposal or large-scale releases could still lead to short-term aquatic toxicity and contribute to air quality issues.
The recycling and recovery of ethyl acetate from photographic processes present opportunities for reducing environmental impact. Modern distillation and membrane separation techniques allow for efficient solvent recovery, minimizing waste and reducing the need for fresh solvent production. This closed-loop approach aligns with principles of green chemistry and circular economy practices.
From a broader perspective, the shift towards digital photography has led to a decrease in traditional film and chemical processing, indirectly reducing the overall environmental footprint associated with ethyl acetate in photography. However, this transition brings its own set of environmental challenges, such as electronic waste and energy consumption of digital devices.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers several environmental advantages in photographic applications, its use still requires careful management to minimize potential negative impacts. Continued research into greener alternatives and improved recycling technologies will be crucial in further reducing the environmental footprint of photographic materials and processes.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Solvents
Ethyl acetate stands out as a preferred solvent in photographic materials due to its unique properties and advantages over alternative solvents. When compared to other commonly used solvents in the photographic industry, ethyl acetate demonstrates superior performance in several key aspects.
One of the primary advantages of ethyl acetate is its excellent solvency power for a wide range of photographic chemicals and polymers. This characteristic allows for efficient dissolution of various components used in photographic emulsions and coatings. In contrast, alternative solvents such as methanol or isopropanol may not provide the same level of versatility in dissolving different substances, potentially limiting their applicability across various photographic processes.
Ethyl acetate also exhibits a favorable evaporation rate, which is crucial for the drying and setting of photographic layers. This property enables precise control over the drying process, resulting in uniform and high-quality film formation. Solvents with slower evaporation rates, like butyl acetate, may lead to longer processing times and potential issues with film consistency.
From an environmental and safety perspective, ethyl acetate presents advantages over more hazardous alternatives. It has lower toxicity compared to solvents such as methylene chloride or toluene, reducing potential health risks for workers in the photographic industry. Additionally, ethyl acetate's relatively low environmental impact and biodegradability make it a more sustainable choice compared to some chlorinated solvents or aromatic hydrocarbons.
The low water solubility of ethyl acetate is another beneficial characteristic for photographic applications. This property helps maintain the integrity of water-sensitive photographic materials during processing and storage. In comparison, highly water-soluble solvents like acetone may cause unwanted interactions with aqueous components in photographic systems.
Ethyl acetate's moderate boiling point (77.1°C) provides a good balance between effective solvency and ease of removal during processing. This characteristic allows for efficient coating and drying processes while minimizing the risk of thermal damage to sensitive photographic materials. Solvents with significantly higher boiling points, such as dimethylformamide, may require more energy for removal and potentially compromise heat-sensitive components.
In terms of cost-effectiveness and availability, ethyl acetate offers advantages over some specialty solvents. Its widespread use in various industries ensures a stable supply chain and competitive pricing, making it an economically viable choice for large-scale photographic production. This aspect gives ethyl acetate an edge over more niche or expensive solvents that may have limited availability or higher costs.
One of the primary advantages of ethyl acetate is its excellent solvency power for a wide range of photographic chemicals and polymers. This characteristic allows for efficient dissolution of various components used in photographic emulsions and coatings. In contrast, alternative solvents such as methanol or isopropanol may not provide the same level of versatility in dissolving different substances, potentially limiting their applicability across various photographic processes.
Ethyl acetate also exhibits a favorable evaporation rate, which is crucial for the drying and setting of photographic layers. This property enables precise control over the drying process, resulting in uniform and high-quality film formation. Solvents with slower evaporation rates, like butyl acetate, may lead to longer processing times and potential issues with film consistency.
From an environmental and safety perspective, ethyl acetate presents advantages over more hazardous alternatives. It has lower toxicity compared to solvents such as methylene chloride or toluene, reducing potential health risks for workers in the photographic industry. Additionally, ethyl acetate's relatively low environmental impact and biodegradability make it a more sustainable choice compared to some chlorinated solvents or aromatic hydrocarbons.
The low water solubility of ethyl acetate is another beneficial characteristic for photographic applications. This property helps maintain the integrity of water-sensitive photographic materials during processing and storage. In comparison, highly water-soluble solvents like acetone may cause unwanted interactions with aqueous components in photographic systems.
Ethyl acetate's moderate boiling point (77.1°C) provides a good balance between effective solvency and ease of removal during processing. This characteristic allows for efficient coating and drying processes while minimizing the risk of thermal damage to sensitive photographic materials. Solvents with significantly higher boiling points, such as dimethylformamide, may require more energy for removal and potentially compromise heat-sensitive components.
In terms of cost-effectiveness and availability, ethyl acetate offers advantages over some specialty solvents. Its widespread use in various industries ensures a stable supply chain and competitive pricing, making it an economically viable choice for large-scale photographic production. This aspect gives ethyl acetate an edge over more niche or expensive solvents that may have limited availability or higher costs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!