Ethyl Acetate’s Role in Future Stylistic Trends
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, has been a staple in various industries for decades. This colorless liquid, characterized by its fruity odor, is produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid. Its widespread use stems from its unique properties, including low toxicity, high solvency, and rapid evaporation rate.
In the realm of industrial applications, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it indispensable in these sectors. The compound's low boiling point and fast evaporation rate contribute to its effectiveness in formulating quick-drying products, a feature highly valued in the manufacturing of lacquers and varnishes.
The food industry has long recognized ethyl acetate's potential, utilizing it as a flavoring agent due to its fruity essence. It occurs naturally in many fruits and is often employed to enhance or replicate fruit flavors in processed foods and beverages. Additionally, its role in decaffeinating coffee and tea has been significant, offering a less harmful alternative to traditional decaffeination methods.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various drugs and as a solvent in drug formulations. Its low toxicity and high purity standards make it suitable for use in the production of medicines and other health-related products. The compound's extractive properties are also leveraged in the isolation and purification of natural products and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's cleaning properties, using it to remove flux residues from printed circuit boards. Its effectiveness in dissolving various organic compounds without damaging sensitive electronic components has made it a preferred choice in this field. Furthermore, its application extends to the production of flexible packaging materials and in the manufacturing of photographic films and plates.
As environmental concerns grow, the role of ethyl acetate in green chemistry has gained attention. Its biodegradability and relatively low environmental impact compared to some other solvents have led to increased interest in its use as a more sustainable alternative in various applications. This shift aligns with global efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of industrial processes and products.
In the realm of industrial applications, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it indispensable in these sectors. The compound's low boiling point and fast evaporation rate contribute to its effectiveness in formulating quick-drying products, a feature highly valued in the manufacturing of lacquers and varnishes.
The food industry has long recognized ethyl acetate's potential, utilizing it as a flavoring agent due to its fruity essence. It occurs naturally in many fruits and is often employed to enhance or replicate fruit flavors in processed foods and beverages. Additionally, its role in decaffeinating coffee and tea has been significant, offering a less harmful alternative to traditional decaffeination methods.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various drugs and as a solvent in drug formulations. Its low toxicity and high purity standards make it suitable for use in the production of medicines and other health-related products. The compound's extractive properties are also leveraged in the isolation and purification of natural products and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's cleaning properties, using it to remove flux residues from printed circuit boards. Its effectiveness in dissolving various organic compounds without damaging sensitive electronic components has made it a preferred choice in this field. Furthermore, its application extends to the production of flexible packaging materials and in the manufacturing of photographic films and plates.
As environmental concerns grow, the role of ethyl acetate in green chemistry has gained attention. Its biodegradability and relatively low environmental impact compared to some other solvents have led to increased interest in its use as a more sustainable alternative in various applications. This shift aligns with global efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of industrial processes and products.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for ethyl acetate in the context of future stylistic trends is experiencing a significant upswing, driven by several key factors. The fragrance and flavor industry, in particular, is showing a growing interest in ethyl acetate due to its versatile properties and potential to create unique sensory experiences. This compound's fruity, sweet aroma makes it an attractive option for perfumers and flavorists seeking to develop innovative products that align with emerging consumer preferences.
In the cosmetics sector, ethyl acetate is gaining traction as a solvent in nail polish formulations, contributing to the development of long-lasting, quick-drying products. The increasing focus on personal grooming and self-expression through nail art is fueling demand for high-performance nail care products, thereby boosting the market for ethyl acetate in this segment.
The food and beverage industry is another major driver of ethyl acetate demand. As consumers seek novel taste experiences, food manufacturers are incorporating ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent in a wide range of products, from confectionery to beverages. The compound's ability to impart fruity notes, particularly reminiscent of pineapple and pear, aligns well with the growing consumer preference for natural and exotic flavors.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping the market demand for ethyl acetate. As a more environmentally friendly alternative to some traditional solvents, ethyl acetate is finding increased applications in various industries, including paints, coatings, and adhesives. This shift is driven by stringent regulations on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and a growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another significant market for ethyl acetate, where it is used as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients. The ongoing expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, coupled with the increasing focus on developing novel drug delivery systems, is expected to contribute to the sustained demand for ethyl acetate in this field.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. The region's burgeoning middle class, with its increasing disposable income and evolving preferences, is creating new opportunities for products that incorporate ethyl acetate across various sectors.
Looking ahead, the market demand for ethyl acetate is projected to continue its upward trajectory, supported by ongoing innovations in product formulations and manufacturing processes. The compound's versatility and alignment with current trends in sustainability and sensory experiences position it favorably in the evolving landscape of consumer preferences and industrial applications.
In the cosmetics sector, ethyl acetate is gaining traction as a solvent in nail polish formulations, contributing to the development of long-lasting, quick-drying products. The increasing focus on personal grooming and self-expression through nail art is fueling demand for high-performance nail care products, thereby boosting the market for ethyl acetate in this segment.
The food and beverage industry is another major driver of ethyl acetate demand. As consumers seek novel taste experiences, food manufacturers are incorporating ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent in a wide range of products, from confectionery to beverages. The compound's ability to impart fruity notes, particularly reminiscent of pineapple and pear, aligns well with the growing consumer preference for natural and exotic flavors.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping the market demand for ethyl acetate. As a more environmentally friendly alternative to some traditional solvents, ethyl acetate is finding increased applications in various industries, including paints, coatings, and adhesives. This shift is driven by stringent regulations on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and a growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another significant market for ethyl acetate, where it is used as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients. The ongoing expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, coupled with the increasing focus on developing novel drug delivery systems, is expected to contribute to the sustained demand for ethyl acetate in this field.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. The region's burgeoning middle class, with its increasing disposable income and evolving preferences, is creating new opportunities for products that incorporate ethyl acetate across various sectors.
Looking ahead, the market demand for ethyl acetate is projected to continue its upward trajectory, supported by ongoing innovations in product formulations and manufacturing processes. The compound's versatility and alignment with current trends in sustainability and sensory experiences position it favorably in the evolving landscape of consumer preferences and industrial applications.
Current Applications
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, plays a significant role in various industries and applications. In the realm of stylistic trends, its current applications are diverse and impactful. One of the primary uses of ethyl acetate is in the fragrance and flavor industry, where it serves as a key ingredient in perfumes, colognes, and food flavorings. Its fruity, sweet aroma makes it an essential component in creating scents that align with contemporary olfactory preferences.
In the cosmetics sector, ethyl acetate is widely utilized as a solvent in nail polish removers and other beauty products. Its ability to dissolve various substances effectively while being relatively mild on the skin has made it a popular choice among manufacturers. This application aligns with the growing consumer demand for gentler, less harsh beauty products that maintain efficacy.
The printing and packaging industry also heavily relies on ethyl acetate for its solvent properties. It is a crucial component in printing inks and adhesives, contributing to the visual appeal and durability of printed materials and packaging. As the demand for innovative and eye-catching packaging designs continues to rise, ethyl acetate's role in this sector remains significant.
In the textile industry, ethyl acetate finds application in the production of synthetic fabrics and as a cleaning agent for textiles. Its use in fabric finishing processes helps achieve desired textures and appearances, aligning with current fashion trends that emphasize unique material properties and finishes.
The automotive sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of car paints and coatings. Its fast-evaporating nature and ability to create smooth finishes make it valuable in achieving the high-gloss, durable paint jobs that are characteristic of modern vehicles. This application is particularly relevant as automotive design continues to be a key factor in consumer preferences.
In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate is employed in the manufacturing of circuit boards and electronic components. Its use as a cleaning agent and in the production of conductive inks contributes to the miniaturization and efficiency of electronic devices, aligning with the ongoing trend of sleeker, more powerful gadgets.
Lastly, ethyl acetate's application in the pharmaceutical industry is noteworthy. It is used as a solvent in the production of various medications and as an intermediate in the synthesis of certain drugs. This application is crucial in the development of new pharmaceutical products that cater to evolving health needs and treatment approaches.
In the cosmetics sector, ethyl acetate is widely utilized as a solvent in nail polish removers and other beauty products. Its ability to dissolve various substances effectively while being relatively mild on the skin has made it a popular choice among manufacturers. This application aligns with the growing consumer demand for gentler, less harsh beauty products that maintain efficacy.
The printing and packaging industry also heavily relies on ethyl acetate for its solvent properties. It is a crucial component in printing inks and adhesives, contributing to the visual appeal and durability of printed materials and packaging. As the demand for innovative and eye-catching packaging designs continues to rise, ethyl acetate's role in this sector remains significant.
In the textile industry, ethyl acetate finds application in the production of synthetic fabrics and as a cleaning agent for textiles. Its use in fabric finishing processes helps achieve desired textures and appearances, aligning with current fashion trends that emphasize unique material properties and finishes.
The automotive sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of car paints and coatings. Its fast-evaporating nature and ability to create smooth finishes make it valuable in achieving the high-gloss, durable paint jobs that are characteristic of modern vehicles. This application is particularly relevant as automotive design continues to be a key factor in consumer preferences.
In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate is employed in the manufacturing of circuit boards and electronic components. Its use as a cleaning agent and in the production of conductive inks contributes to the miniaturization and efficiency of electronic devices, aligning with the ongoing trend of sleeker, more powerful gadgets.
Lastly, ethyl acetate's application in the pharmaceutical industry is noteworthy. It is used as a solvent in the production of various medications and as an intermediate in the synthesis of certain drugs. This application is crucial in the development of new pharmaceutical products that cater to evolving health needs and treatment approaches.
Production Techniques
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The processes aim to optimize the production of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification reactions, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts or reactants to improve yield and purity.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds. Its applications span across different industries such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various substances. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, azeotropic distillation, and other separation techniques in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
- Ethyl acetate as a green solvent: The use of ethyl acetate as an environmentally friendly solvent is explored in various applications. Its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability make it a preferred choice in green chemistry processes and sustainable industrial practices.
- Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate: Methods and systems for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial processes are described. These include adsorption techniques, membrane separation, and other innovative approaches to minimize waste and improve process efficiency.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes and industries. It serves as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. Its versatility makes it valuable in diverse manufacturing applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, azeotropic distillation, and other separation techniques used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices to minimize risks associated with its flammability and volatility.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and formulations containing ethyl acetate
Innovative applications and formulations incorporating ethyl acetate are being developed. These include its use in advanced materials, coatings, adhesives, and specialized chemical products. Research focuses on exploiting ethyl acetate's properties to create new or improved products across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for ethyl acetate in future stylistic trends is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, with key players like Celanese International Corp., Eastman Chemical Co., and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. leading the competition. The technology is relatively mature, with established production processes, but innovation continues in application development. Companies such as BASF Corp. and L'Oréal SA are exploring new uses in cosmetics and personal care products, while research institutions like Nanjing Normal University and Tianjin University are contributing to advancements in synthesis and purification techniques. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical conglomerates and specialized manufacturers, with ongoing efforts to improve sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed advanced ethyl acetate production processes using innovative catalysts and reactor designs. Their technology allows for high-purity ethyl acetate production with improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact[1]. The company has also explored the use of bio-based feedstocks to produce sustainable ethyl acetate, aligning with future eco-friendly trends[2]. Celanese's research focuses on enhancing the solvent properties of ethyl acetate for various applications, including coatings, adhesives, and personal care products, which could influence future stylistic trends in these industries[3].
Strengths: Advanced production technology, focus on sustainability, and diverse application research. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs for bio-based ethyl acetate and dependency on volatile raw material prices.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical has developed a proprietary process for producing high-purity ethyl acetate using advanced distillation techniques[4]. Their research focuses on enhancing the performance of ethyl acetate in various applications, particularly in the field of coatings and inks, which could significantly impact future design trends[5]. The company has also invested in developing ethyl acetate-based formulations that offer improved durability and aesthetic properties for consumer products[6]. Additionally, Eastman is exploring the use of ethyl acetate as a green solvent in sustainable manufacturing processes, potentially influencing future eco-friendly product designs[7].
Strengths: High-purity production capabilities, extensive application research, and focus on sustainable solutions. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in scaling up new technologies and competition from alternative solvents.
Innovative Formulations
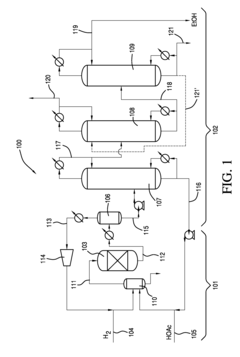
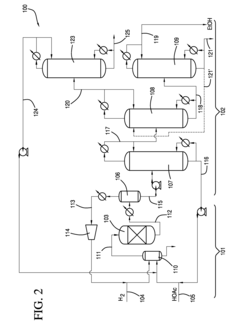
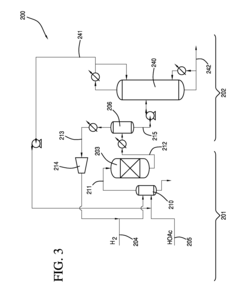
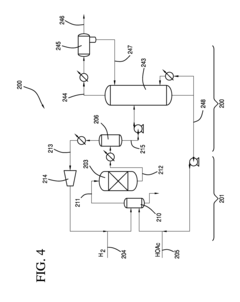
Process for producing an ethyl acetate solvent and co-production of ethanol
PatentInactiveUS20110190531A1
Innovation
- A process involving the hydrogenation of acetic acid in the presence of a catalyst, followed by a series of distillation columns to separate and recover ethanol and ethyl acetate solvent, with specific catalyst compositions and conditions to optimize ethanol and ethyl acetate production, including the use of platinum-based catalysts and modified silica supports.
Nail varnish comprising a cellulose ester and short ester solvents in a defined ratio
PatentInactiveUS20070154423A1
Innovation
- A nail varnish composition utilizing a solvent medium with a predominant ratio of ethyl acetate to butyl acetate, ranging from 87/25 to 100/1, along with a cellulose ester, to achieve rapid drying, smooth, glossy, and water-resistant films with improved adherence.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate in future stylistic trends is a critical consideration that requires thorough examination. As a solvent widely used in various industries, including cosmetics, fragrances, and coatings, ethyl acetate's role in shaping future styles must be balanced against its potential environmental consequences.
Ethyl acetate is generally considered less harmful to the environment compared to many other solvents. It has a relatively low toxicity profile and is biodegradable, breaking down into ethanol and acetic acid in the presence of water. This characteristic makes it a more environmentally friendly option in many applications. However, its widespread use still raises concerns about its cumulative impact on ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. VOCs can react with other pollutants in the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. As future stylistic trends may lead to increased use of ethyl acetate in consumer products, there is a need to address these emissions through improved manufacturing processes and product formulations.
Water pollution is another potential issue, as ethyl acetate can contaminate water sources if not properly managed during production and disposal processes. While it is less persistent in water compared to other solvents, large-scale industrial use could still pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if not adequately controlled.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, there is growing interest in developing more sustainable production methods, such as using bio-based feedstocks or employing green chemistry principles. These approaches could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of ethyl acetate production in the future.
As stylistic trends evolve, there is an opportunity to incorporate environmental considerations into product design and manufacturing processes. This could include developing formulations that use lower concentrations of ethyl acetate, exploring alternative solvents with even lower environmental impacts, or creating closed-loop systems that minimize solvent waste and emissions.
The regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate and other solvents is also likely to evolve in response to environmental concerns. Future stylistic trends may need to adapt to stricter regulations on VOC emissions, waste management, and product safety. This could drive innovation in formulation techniques and application methods that minimize environmental impact while maintaining desired aesthetic and functional properties.
Ethyl acetate is generally considered less harmful to the environment compared to many other solvents. It has a relatively low toxicity profile and is biodegradable, breaking down into ethanol and acetic acid in the presence of water. This characteristic makes it a more environmentally friendly option in many applications. However, its widespread use still raises concerns about its cumulative impact on ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. VOCs can react with other pollutants in the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. As future stylistic trends may lead to increased use of ethyl acetate in consumer products, there is a need to address these emissions through improved manufacturing processes and product formulations.
Water pollution is another potential issue, as ethyl acetate can contaminate water sources if not properly managed during production and disposal processes. While it is less persistent in water compared to other solvents, large-scale industrial use could still pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if not adequately controlled.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, there is growing interest in developing more sustainable production methods, such as using bio-based feedstocks or employing green chemistry principles. These approaches could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of ethyl acetate production in the future.
As stylistic trends evolve, there is an opportunity to incorporate environmental considerations into product design and manufacturing processes. This could include developing formulations that use lower concentrations of ethyl acetate, exploring alternative solvents with even lower environmental impacts, or creating closed-loop systems that minimize solvent waste and emissions.
The regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate and other solvents is also likely to evolve in response to environmental concerns. Future stylistic trends may need to adapt to stricter regulations on VOC emissions, waste management, and product safety. This could drive innovation in formulation techniques and application methods that minimize environmental impact while maintaining desired aesthetic and functional properties.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in shaping its future applications in stylistic trends. As a widely used solvent in various industries, including cosmetics, fragrances, and food flavorings, ethyl acetate is subject to a complex web of regulations that vary across different regions and sectors.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates ethyl acetate as a food additive and ingredient in cosmetics. It is classified as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) for use in food products, with specific limitations on its concentration in different applications. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees its use and potential environmental impact, particularly in industrial settings.
The European Union has established stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers of ethyl acetate must register the substance and provide detailed safety information. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which informs regulatory decisions and risk assessments.
In the cosmetics industry, the use of ethyl acetate is governed by the EU Cosmetics Regulation, which sets safety standards and labeling requirements. Similarly, its use in food products is regulated by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which has established specific purity criteria and maximum residue levels.
Emerging markets, such as China and India, are developing their regulatory frameworks to align with international standards while addressing local concerns. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and India's Food Safety and Standards Authority (FSSAI) have implemented regulations that impact the use of ethyl acetate in various consumer products.
The global trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly products is influencing regulatory approaches to ethyl acetate. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of chemicals, leading to stricter controls on emissions and waste management in production processes. This shift is likely to drive innovation in green chemistry alternatives and more sustainable production methods for ethyl acetate.
As consumer awareness grows, there is an increasing demand for transparency in product formulations. This has led to more stringent labeling requirements and restrictions on certain chemicals in consumer goods. Regulatory bodies are responding by implementing more comprehensive product safety assessments and encouraging the development of safer alternatives.
The future regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on harmonizing international standards, enhancing safety assessments, and promoting sustainable practices. This dynamic regulatory environment will significantly influence the role of ethyl acetate in future stylistic trends, driving innovation in formulation, application techniques, and production processes.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates ethyl acetate as a food additive and ingredient in cosmetics. It is classified as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) for use in food products, with specific limitations on its concentration in different applications. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees its use and potential environmental impact, particularly in industrial settings.
The European Union has established stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers of ethyl acetate must register the substance and provide detailed safety information. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which informs regulatory decisions and risk assessments.
In the cosmetics industry, the use of ethyl acetate is governed by the EU Cosmetics Regulation, which sets safety standards and labeling requirements. Similarly, its use in food products is regulated by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which has established specific purity criteria and maximum residue levels.
Emerging markets, such as China and India, are developing their regulatory frameworks to align with international standards while addressing local concerns. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and India's Food Safety and Standards Authority (FSSAI) have implemented regulations that impact the use of ethyl acetate in various consumer products.
The global trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly products is influencing regulatory approaches to ethyl acetate. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of chemicals, leading to stricter controls on emissions and waste management in production processes. This shift is likely to drive innovation in green chemistry alternatives and more sustainable production methods for ethyl acetate.
As consumer awareness grows, there is an increasing demand for transparency in product formulations. This has led to more stringent labeling requirements and restrictions on certain chemicals in consumer goods. Regulatory bodies are responding by implementing more comprehensive product safety assessments and encouraging the development of safer alternatives.
The future regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on harmonizing international standards, enhancing safety assessments, and promoting sustainable practices. This dynamic regulatory environment will significantly influence the role of ethyl acetate in future stylistic trends, driving innovation in formulation, application techniques, and production processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!