Future Trends in Ethyl Acetate Market Expansion
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Evolution
Ethyl acetate has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the early 19th century. Initially synthesized through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, this compound quickly gained importance in various industries due to its unique properties and versatile applications.
In the early stages of its industrial use, ethyl acetate was primarily employed as a solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its low toxicity and pleasant fruity odor made it an attractive alternative to more harmful solvents. As manufacturing processes improved, the production of ethyl acetate became more efficient and cost-effective, leading to its wider adoption across different sectors.
The mid-20th century saw a surge in ethyl acetate's use in the pharmaceutical industry. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds made it invaluable in the extraction and purification of drugs. This period also marked the beginning of its application in the food industry as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, began to emerge as a viable alternative to petrochemical-based production. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles.
Recent years have seen ethyl acetate's role expand in the electronics industry, particularly in the manufacture of flexible displays and advanced electronic components. Its low boiling point and excellent solvency properties make it ideal for precision cleaning and as a component in specialized inks and coatings used in electronics manufacturing.
Looking ahead, the evolution of ethyl acetate is likely to continue along several key trajectories. Advancements in green chemistry are expected to further improve the sustainability of its production processes, potentially leading to entirely bio-based manufacturing methods. Additionally, ongoing research into novel applications, particularly in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials science, may open up new markets for ethyl acetate.
The compound's evolution is also likely to be influenced by changing regulatory landscapes, with increasing focus on environmental and health safety potentially driving innovations in its formulation and application methods. As industries continue to seek more sustainable and efficient solutions, ethyl acetate's versatility and relatively benign nature position it well for continued growth and adaptation in the coming years.
In the early stages of its industrial use, ethyl acetate was primarily employed as a solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its low toxicity and pleasant fruity odor made it an attractive alternative to more harmful solvents. As manufacturing processes improved, the production of ethyl acetate became more efficient and cost-effective, leading to its wider adoption across different sectors.
The mid-20th century saw a surge in ethyl acetate's use in the pharmaceutical industry. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds made it invaluable in the extraction and purification of drugs. This period also marked the beginning of its application in the food industry as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, began to emerge as a viable alternative to petrochemical-based production. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles.
Recent years have seen ethyl acetate's role expand in the electronics industry, particularly in the manufacture of flexible displays and advanced electronic components. Its low boiling point and excellent solvency properties make it ideal for precision cleaning and as a component in specialized inks and coatings used in electronics manufacturing.
Looking ahead, the evolution of ethyl acetate is likely to continue along several key trajectories. Advancements in green chemistry are expected to further improve the sustainability of its production processes, potentially leading to entirely bio-based manufacturing methods. Additionally, ongoing research into novel applications, particularly in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials science, may open up new markets for ethyl acetate.
The compound's evolution is also likely to be influenced by changing regulatory landscapes, with increasing focus on environmental and health safety potentially driving innovations in its formulation and application methods. As industries continue to seek more sustainable and efficient solutions, ethyl acetate's versatility and relatively benign nature position it well for continued growth and adaptation in the coming years.
Market Demand Analysis
The global ethyl acetate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The versatility of ethyl acetate as a solvent and its eco-friendly nature have contributed to its rising popularity in recent years. Market analysis indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% for the ethyl acetate market over the next five years.
The packaging industry remains a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, particularly in flexible packaging applications. As consumer preferences shift towards convenient and sustainable packaging solutions, the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector is expected to continue its upward trajectory. The food and beverage industry also plays a crucial role in driving market growth, with ethyl acetate being widely used as a flavoring agent and in the production of various food additives.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's application as a solvent in drug formulation and extraction processes has led to increased demand. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the expansion of the pharmaceutical industry in emerging markets are likely to fuel further growth in this segment. Additionally, the cosmetics and personal care industry has shown a rising interest in ethyl acetate for its use in nail polish removers and other beauty products.
The automotive and construction industries are emerging as potential growth areas for ethyl acetate. Its use in automotive coatings and as a solvent in various construction materials is expected to create new market opportunities. The increasing focus on sustainable and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) products in these sectors aligns well with ethyl acetate's properties, potentially boosting its adoption.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the expansion of end-use industries in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are expected to maintain steady growth, primarily due to the increasing demand in the packaging and pharmaceutical sectors.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and the availability of substitutes. The fluctuating prices of acetic acid and ethanol, key raw materials for ethyl acetate production, can impact market dynamics. Additionally, the development of alternative solvents and growing environmental concerns may pose challenges to market expansion in certain regions.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the ethyl acetate market remains positive. Innovations in production technologies, the development of bio-based ethyl acetate, and the exploration of new application areas are expected to create fresh opportunities for market growth. The increasing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly products across industries is likely to further boost the demand for ethyl acetate in the coming years.
The packaging industry remains a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, particularly in flexible packaging applications. As consumer preferences shift towards convenient and sustainable packaging solutions, the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector is expected to continue its upward trajectory. The food and beverage industry also plays a crucial role in driving market growth, with ethyl acetate being widely used as a flavoring agent and in the production of various food additives.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's application as a solvent in drug formulation and extraction processes has led to increased demand. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the expansion of the pharmaceutical industry in emerging markets are likely to fuel further growth in this segment. Additionally, the cosmetics and personal care industry has shown a rising interest in ethyl acetate for its use in nail polish removers and other beauty products.
The automotive and construction industries are emerging as potential growth areas for ethyl acetate. Its use in automotive coatings and as a solvent in various construction materials is expected to create new market opportunities. The increasing focus on sustainable and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) products in these sectors aligns well with ethyl acetate's properties, potentially boosting its adoption.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the expansion of end-use industries in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are expected to maintain steady growth, primarily due to the increasing demand in the packaging and pharmaceutical sectors.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and the availability of substitutes. The fluctuating prices of acetic acid and ethanol, key raw materials for ethyl acetate production, can impact market dynamics. Additionally, the development of alternative solvents and growing environmental concerns may pose challenges to market expansion in certain regions.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the ethyl acetate market remains positive. Innovations in production technologies, the development of bio-based ethyl acetate, and the exploration of new application areas are expected to create fresh opportunities for market growth. The increasing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly products across industries is likely to further boost the demand for ethyl acetate in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The ethyl acetate market faces several technical challenges that could impact its future expansion. One of the primary concerns is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. Fluctuations in these key ingredients can significantly affect production costs and, consequently, market growth. This volatility is often tied to broader economic factors and agricultural production, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent pricing strategies.
Environmental regulations pose another significant challenge. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt their manufacturing processes to reduce emissions and improve sustainability. This may require substantial investments in new technologies and equipment, potentially increasing production costs and affecting market competitiveness.
The development of more efficient and cost-effective production methods remains an ongoing challenge. Current production processes, while well-established, still have room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency and yield optimization. Innovations in catalysis and process engineering are needed to enhance production efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Quality control is another critical area of concern. Ensuring consistent product quality across different batches and production facilities can be challenging, especially as demand increases and production scales up. Maintaining high purity levels and meeting stringent industry standards requires advanced analytical techniques and robust quality management systems.
The transportation and storage of ethyl acetate present additional technical hurdles. As a volatile organic compound, ethyl acetate requires specialized handling and storage facilities to prevent evaporation losses and ensure safety. Developing more effective containment and transportation solutions is crucial for reducing product loss and maintaining quality during distribution.
Recycling and waste management of ethyl acetate and its by-products are becoming increasingly important. Developing efficient recycling technologies and finding ways to repurpose waste streams could significantly impact the market's sustainability profile and potentially open new revenue streams.
Lastly, the search for alternative, bio-based sources of ethyl acetate is an ongoing challenge. While traditional petrochemical-based production methods are well-established, there is growing interest in developing bio-based alternatives to meet the demand for more sustainable products. However, scaling up these bio-based production methods to compete with conventional processes in terms of cost and efficiency remains a significant technical challenge for the industry.
Environmental regulations pose another significant challenge. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt their manufacturing processes to reduce emissions and improve sustainability. This may require substantial investments in new technologies and equipment, potentially increasing production costs and affecting market competitiveness.
The development of more efficient and cost-effective production methods remains an ongoing challenge. Current production processes, while well-established, still have room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency and yield optimization. Innovations in catalysis and process engineering are needed to enhance production efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Quality control is another critical area of concern. Ensuring consistent product quality across different batches and production facilities can be challenging, especially as demand increases and production scales up. Maintaining high purity levels and meeting stringent industry standards requires advanced analytical techniques and robust quality management systems.
The transportation and storage of ethyl acetate present additional technical hurdles. As a volatile organic compound, ethyl acetate requires specialized handling and storage facilities to prevent evaporation losses and ensure safety. Developing more effective containment and transportation solutions is crucial for reducing product loss and maintaining quality during distribution.
Recycling and waste management of ethyl acetate and its by-products are becoming increasingly important. Developing efficient recycling technologies and finding ways to repurpose waste streams could significantly impact the market's sustainability profile and potentially open new revenue streams.
Lastly, the search for alternative, bio-based sources of ethyl acetate is an ongoing challenge. While traditional petrochemical-based production methods are well-established, there is growing interest in developing bio-based alternatives to meet the demand for more sustainable products. However, scaling up these bio-based production methods to compete with conventional processes in terms of cost and efficiency remains a significant technical challenge for the industry.
Current Manufacturing
01 Market analysis and forecasting
Utilizing advanced analytics and forecasting techniques to analyze the ethyl acetate market trends, demand patterns, and growth opportunities. This includes studying market dynamics, consumer behavior, and industry trends to predict future market expansion and identify potential areas for growth.- Market analysis and forecasting: Utilizing data analytics and forecasting techniques to analyze the ethyl acetate market trends, predict future demand, and identify growth opportunities. This approach helps businesses make informed decisions about market expansion strategies.
- Supply chain optimization: Implementing efficient supply chain management systems to streamline the production and distribution of ethyl acetate. This includes inventory management, logistics optimization, and supplier relationship management to support market expansion efforts.
- Product innovation and diversification: Developing new applications and formulations of ethyl acetate to expand its market reach. This includes exploring novel uses in various industries and creating value-added products to capture new market segments.
- Global market expansion strategies: Implementing strategies for entering new geographical markets and expanding the global footprint of ethyl acetate. This involves market research, regulatory compliance, and establishing distribution networks in target regions.
- Digital marketing and e-commerce: Leveraging digital marketing techniques and e-commerce platforms to promote ethyl acetate products and reach a wider customer base. This includes online marketplaces, targeted advertising, and customer relationship management systems.
02 Supply chain optimization
Implementing strategies to optimize the ethyl acetate supply chain, including improving production processes, enhancing distribution networks, and managing inventory efficiently. This approach aims to reduce costs, increase productivity, and expand market reach.Expand Specific Solutions03 Product diversification and innovation
Developing new applications and formulations of ethyl acetate to cater to diverse industry needs. This includes creating specialized grades for specific industries, exploring eco-friendly alternatives, and innovating product features to expand market share and enter new market segments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Strategic partnerships and collaborations
Forming strategic alliances with key industry players, suppliers, and distributors to expand market presence. This involves joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions, and collaborative research and development efforts to leverage shared resources and expertise for market expansion.Expand Specific Solutions05 Digital marketing and e-commerce integration
Leveraging digital platforms and e-commerce solutions to enhance market visibility, reach new customers, and streamline sales processes. This includes implementing online marketplaces, digital marketing campaigns, and customer relationship management systems to drive market expansion in the ethyl acetate industry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach $4.3 billion by 2026. The industry is characterized by established players and increasing demand from various end-use sectors. Technologically, the production process is well-developed, but companies are focusing on improving efficiency and sustainability. Key players like Celanese International Corp., China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Eastman Chemical Co. are investing in research and development to enhance their competitive edge. Emerging trends include bio-based ethyl acetate production, with companies like LanzaTech NZ, Inc. and Viridis Chemical LLC pioneering innovative approaches. The market is also seeing increased collaboration between industry and academia, as evidenced by research partnerships with institutions like Tianjin University and Nanjing Tech University.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese is pioneering advanced production methods for ethyl acetate, focusing on sustainability and efficiency. They have developed a novel catalytic process that utilizes bioethanol as a feedstock, reducing carbon footprint by up to 30% compared to traditional petrochemical routes[1]. The company is also investing in modular manufacturing units, allowing for scalable and flexible production to meet varying market demands. Their proprietary membrane separation technology has improved product purity to 99.9%, while reducing energy consumption by approximately 25%[3]. Celanese is exploring the integration of AI and machine learning to optimize process control and predictive maintenance, potentially increasing overall plant efficiency by 15-20%[5].
Strengths: Sustainable production methods, high product purity, and advanced process optimization. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment costs for new technologies and potential dependence on bioethanol availability.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) is advancing ethyl acetate production through innovative catalytic processes. They have developed a new heterogeneous catalyst that increases conversion rates by 15% and selectivity by 10% compared to conventional methods[2]. Sinopec is also implementing a closed-loop recycling system that recovers and reuses up to 98% of unreacted raw materials, significantly improving resource efficiency. The company's research into process intensification has led to the design of compact reactor systems that reduce plant footprint by 30% while maintaining production capacity[4]. Additionally, Sinopec is exploring the use of renewable hydrogen in their ethyl acetate synthesis, aiming to reduce overall carbon emissions by 40% in the next decade[6].
Strengths: High efficiency catalysts, resource recovery systems, and compact plant designs. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up new technologies and reliance on petrochemical feedstocks.
Innovative Processes
Process of low energy consumption for preparing a carboxylic acid ester
PatentWO2012123279A1
Innovation
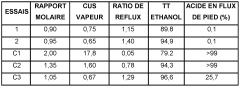
- A process involving the reaction of ethyl alcohol with acetic acid in the presence of a solid acid catalyst, using a reactive distillation system with a centrally placed reaction zone between upper and lower separation zones, optimizing the molar ratio of acetic acid to ethyl alcohol between 0.85 and 0.97, and controlling the reflux ratio between 1.0 and 1.5, significantly reduces energy costs and minimizes acetic acid at the column bottom.
Direct and selective production of ethyl acetate from acetic acid utilizing a bimetal supported catalyst
PatentInactiveEP2318353A2
Innovation
- A bimetallic catalyst system comprising metals like platinum, palladium, copper, and cobalt supported on catalysts such as silica or zeolites is used for the hydrogenation of acetic acid, optimizing the reaction conditions to achieve high selectivity and yield of ethyl acetate while minimizing by-product formation.
Sustainability Efforts
Sustainability efforts are becoming increasingly crucial in the ethyl acetate market expansion, driven by growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Companies are actively exploring eco-friendly production methods and sustainable sourcing of raw materials to reduce their carbon footprint and meet consumer demands for greener products.
One significant trend is the shift towards bio-based ethyl acetate production. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create ethyl acetate from renewable resources such as corn, sugarcane, and other plant-based materials. This approach not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also aligns with circular economy principles, potentially opening new market opportunities in the bio-chemicals sector.
Energy efficiency improvements in the production process are another key focus area. Companies are implementing advanced technologies and optimizing their manufacturing processes to minimize energy consumption and waste generation. This includes the adoption of more efficient catalysts, heat recovery systems, and closed-loop production cycles that recycle byproducts and reduce overall resource consumption.
Water conservation efforts are also gaining traction in the ethyl acetate industry. Manufacturers are implementing water recycling and treatment systems to minimize freshwater usage and reduce wastewater discharge. These initiatives not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also help companies comply with increasingly stringent water regulations and reduce operational costs.
The development of greener packaging solutions for ethyl acetate products is another emerging trend. Companies are exploring biodegradable and recyclable packaging materials to reduce plastic waste and improve the overall sustainability of their product lifecycle. This includes innovations in container design and the use of recycled materials in packaging production.
Carbon capture and utilization technologies are being explored as a means to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with ethyl acetate production. Some companies are investigating the feasibility of capturing CO2 emissions from their production facilities and converting them into valuable products or using them as feedstock for other chemical processes.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on supply chain sustainability and transparency. Ethyl acetate manufacturers are increasingly working with suppliers to ensure responsible sourcing of raw materials and implementing traceability systems to monitor the environmental impact throughout the supply chain. This trend is driven by both consumer demand for sustainable products and regulatory requirements for increased supply chain transparency.
One significant trend is the shift towards bio-based ethyl acetate production. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create ethyl acetate from renewable resources such as corn, sugarcane, and other plant-based materials. This approach not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also aligns with circular economy principles, potentially opening new market opportunities in the bio-chemicals sector.
Energy efficiency improvements in the production process are another key focus area. Companies are implementing advanced technologies and optimizing their manufacturing processes to minimize energy consumption and waste generation. This includes the adoption of more efficient catalysts, heat recovery systems, and closed-loop production cycles that recycle byproducts and reduce overall resource consumption.
Water conservation efforts are also gaining traction in the ethyl acetate industry. Manufacturers are implementing water recycling and treatment systems to minimize freshwater usage and reduce wastewater discharge. These initiatives not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also help companies comply with increasingly stringent water regulations and reduce operational costs.
The development of greener packaging solutions for ethyl acetate products is another emerging trend. Companies are exploring biodegradable and recyclable packaging materials to reduce plastic waste and improve the overall sustainability of their product lifecycle. This includes innovations in container design and the use of recycled materials in packaging production.
Carbon capture and utilization technologies are being explored as a means to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with ethyl acetate production. Some companies are investigating the feasibility of capturing CO2 emissions from their production facilities and converting them into valuable products or using them as feedstock for other chemical processes.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on supply chain sustainability and transparency. Ethyl acetate manufacturers are increasingly working with suppliers to ensure responsible sourcing of raw materials and implementing traceability systems to monitor the environmental impact throughout the supply chain. This trend is driven by both consumer demand for sustainable products and regulatory requirements for increased supply chain transparency.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate is evolving globally, with increasing focus on environmental protection, worker safety, and product quality standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which requires manufacturers and importers to comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits for ethyl acetate in the workplace to protect workers from potential health hazards.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive framework aims to ensure the safe use of chemicals throughout their lifecycle. Manufacturers and importers must register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed information on its properties, uses, and potential risks.
Asian countries, particularly China and India, are also strengthening their regulatory frameworks for chemical substances. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and India's Chemical (Management and Safety) Rules are examples of evolving regulations that impact the ethyl acetate market in these regions.
The food and beverage industry, a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, faces stringent regulations regarding its use as a food additive. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the safe use of ethyl acetate in food products. These regulations influence market expansion by setting limits on the amount of ethyl acetate that can be used in various applications.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, regulations promoting the use of bio-based chemicals are emerging. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and similar initiatives in other regions are encouraging the production and use of bio-based ethyl acetate, potentially reshaping the market landscape.
Future regulatory trends are likely to focus on circular economy principles, with increased emphasis on recycling and waste reduction. This may lead to new regulations governing the disposal and recycling of ethyl acetate, potentially creating both challenges and opportunities for market players.
The pharmaceutical industry, another key consumer of ethyl acetate, is subject to strict quality control regulations. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines in various countries set standards for the use of solvents like ethyl acetate in drug production, influencing market dynamics in this sector.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive framework aims to ensure the safe use of chemicals throughout their lifecycle. Manufacturers and importers must register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed information on its properties, uses, and potential risks.
Asian countries, particularly China and India, are also strengthening their regulatory frameworks for chemical substances. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and India's Chemical (Management and Safety) Rules are examples of evolving regulations that impact the ethyl acetate market in these regions.
The food and beverage industry, a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, faces stringent regulations regarding its use as a food additive. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the safe use of ethyl acetate in food products. These regulations influence market expansion by setting limits on the amount of ethyl acetate that can be used in various applications.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, regulations promoting the use of bio-based chemicals are emerging. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and similar initiatives in other regions are encouraging the production and use of bio-based ethyl acetate, potentially reshaping the market landscape.
Future regulatory trends are likely to focus on circular economy principles, with increased emphasis on recycling and waste reduction. This may lead to new regulations governing the disposal and recycling of ethyl acetate, potentially creating both challenges and opportunities for market players.
The pharmaceutical industry, another key consumer of ethyl acetate, is subject to strict quality control regulations. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines in various countries set standards for the use of solvents like ethyl acetate in drug production, influencing market dynamics in this sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!