How Ethyl Acetate Advances Inks and Paints Technology?
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate in Inks and Paints: Evolution and Objectives
Ethyl acetate has played a pivotal role in the evolution of inks and paints technology, revolutionizing the industry over the past century. This versatile organic compound, with its unique properties, has become an indispensable component in various formulations, driving innovation and enhancing performance across multiple applications.
The journey of ethyl acetate in inks and paints began in the early 20th century when manufacturers recognized its potential as a solvent. Its low boiling point, high solvency power, and rapid evaporation rate made it an ideal candidate for improving the drying time and flow characteristics of inks and paints. As the industry progressed, ethyl acetate's role expanded beyond that of a mere solvent.
In the realm of inks, ethyl acetate has been instrumental in developing fast-drying formulations for flexographic and gravure printing. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of resins and pigments while maintaining low viscosity has enabled the production of high-quality, vibrant prints on various substrates. The compound's low toxicity compared to other solvents has also contributed to its widespread adoption in food packaging inks, aligning with increasing safety regulations.
For the paints industry, ethyl acetate has been a game-changer in the development of high-performance coatings. Its excellent solvency for cellulose-based resins has been crucial in the formulation of nitrocellulose lacquers, widely used in automotive and wood finishes. The compound's rapid evaporation rate has allowed for faster drying times, increased productivity, and improved surface finish quality.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the inks and paints industry faced the challenge of reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Ethyl acetate, with its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability, emerged as a preferred alternative to more harmful solvents. This shift has driven research into water-based and high-solids formulations where ethyl acetate serves as a co-solvent or coalescent agent, helping to bridge the gap between performance and environmental sustainability.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ethyl acetate in inks and paints technology are multifaceted. Researchers are exploring ways to further optimize its use in eco-friendly formulations, aiming to reduce VOC content while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. There is also a growing interest in developing bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, to align with circular economy principles and reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks.
Another key objective is to enhance the functional properties of inks and paints through synergistic combinations of ethyl acetate with other additives. This includes improving adhesion, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. Additionally, the industry is focusing on tailoring ethyl acetate-based formulations for emerging applications, such as 3D printing inks and smart coatings with self-healing or color-changing properties.
The journey of ethyl acetate in inks and paints began in the early 20th century when manufacturers recognized its potential as a solvent. Its low boiling point, high solvency power, and rapid evaporation rate made it an ideal candidate for improving the drying time and flow characteristics of inks and paints. As the industry progressed, ethyl acetate's role expanded beyond that of a mere solvent.
In the realm of inks, ethyl acetate has been instrumental in developing fast-drying formulations for flexographic and gravure printing. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of resins and pigments while maintaining low viscosity has enabled the production of high-quality, vibrant prints on various substrates. The compound's low toxicity compared to other solvents has also contributed to its widespread adoption in food packaging inks, aligning with increasing safety regulations.
For the paints industry, ethyl acetate has been a game-changer in the development of high-performance coatings. Its excellent solvency for cellulose-based resins has been crucial in the formulation of nitrocellulose lacquers, widely used in automotive and wood finishes. The compound's rapid evaporation rate has allowed for faster drying times, increased productivity, and improved surface finish quality.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the inks and paints industry faced the challenge of reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Ethyl acetate, with its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability, emerged as a preferred alternative to more harmful solvents. This shift has driven research into water-based and high-solids formulations where ethyl acetate serves as a co-solvent or coalescent agent, helping to bridge the gap between performance and environmental sustainability.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ethyl acetate in inks and paints technology are multifaceted. Researchers are exploring ways to further optimize its use in eco-friendly formulations, aiming to reduce VOC content while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. There is also a growing interest in developing bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, to align with circular economy principles and reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks.
Another key objective is to enhance the functional properties of inks and paints through synergistic combinations of ethyl acetate with other additives. This includes improving adhesion, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. Additionally, the industry is focusing on tailoring ethyl acetate-based formulations for emerging applications, such as 3D printing inks and smart coatings with self-healing or color-changing properties.
Market Demand Analysis for Ethyl Acetate-Based Products
The market demand for ethyl acetate-based products in the inks and paints industry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by several key factors. The global ethyl acetate market size was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period.
In the inks sector, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The increasing demand for packaging materials, especially in the food and beverage industry, has led to a surge in the use of ethyl acetate-based inks for flexible packaging printing. This trend is particularly prominent in emerging economies where rapid urbanization and changing consumer preferences are driving the growth of the packaged food market.
The paints and coatings industry is another significant consumer of ethyl acetate-based products. The construction sector's expansion, particularly in developing countries, has fueled the demand for architectural paints and coatings. Ethyl acetate's fast-evaporating properties make it an ideal solvent for quick-drying paints, which are increasingly preferred in both residential and commercial applications.
Automotive coatings represent another growth area for ethyl acetate-based products. As the automotive industry continues to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for high-performance coatings with superior finish and durability is expected to rise. Ethyl acetate's role in formulating these advanced coatings positions it well to benefit from this trend.
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions have also influenced the market dynamics. Ethyl acetate, being a relatively low-VOC solvent compared to some alternatives, has gained favor among manufacturers looking to comply with stricter environmental standards without compromising on performance.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the ethyl acetate market, accounting for over 40% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with the growth of end-user industries such as packaging, textiles, and automotive. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on innovation and sustainability in ethyl acetate-based products.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl acetate in inks and paints is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Innovations in bio-based ethyl acetate production methods are likely to open up new opportunities, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and manufacturers alike. Additionally, the ongoing research into improving the performance characteristics of ethyl acetate-based formulations promises to expand its applications in high-tech coatings and specialty inks.
In the inks sector, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The increasing demand for packaging materials, especially in the food and beverage industry, has led to a surge in the use of ethyl acetate-based inks for flexible packaging printing. This trend is particularly prominent in emerging economies where rapid urbanization and changing consumer preferences are driving the growth of the packaged food market.
The paints and coatings industry is another significant consumer of ethyl acetate-based products. The construction sector's expansion, particularly in developing countries, has fueled the demand for architectural paints and coatings. Ethyl acetate's fast-evaporating properties make it an ideal solvent for quick-drying paints, which are increasingly preferred in both residential and commercial applications.
Automotive coatings represent another growth area for ethyl acetate-based products. As the automotive industry continues to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for high-performance coatings with superior finish and durability is expected to rise. Ethyl acetate's role in formulating these advanced coatings positions it well to benefit from this trend.
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions have also influenced the market dynamics. Ethyl acetate, being a relatively low-VOC solvent compared to some alternatives, has gained favor among manufacturers looking to comply with stricter environmental standards without compromising on performance.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the ethyl acetate market, accounting for over 40% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with the growth of end-user industries such as packaging, textiles, and automotive. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on innovation and sustainability in ethyl acetate-based products.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl acetate in inks and paints is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Innovations in bio-based ethyl acetate production methods are likely to open up new opportunities, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and manufacturers alike. Additionally, the ongoing research into improving the performance characteristics of ethyl acetate-based formulations promises to expand its applications in high-tech coatings and specialty inks.
Current Applications and Challenges in Inks and Paints
Ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in advancing inks and paints technology, with its current applications spanning various sectors of the industry. In the realm of inks, ethyl acetate serves as a primary solvent for flexographic and gravure printing inks, offering rapid evaporation rates that facilitate quick drying and improved print quality. Its low toxicity and mild odor make it a preferred choice for food packaging applications, where safety is paramount.
In the paints sector, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent and diluent in both industrial and decorative coatings. Its excellent solvency properties enable it to dissolve a wide range of resins and binders, contributing to the formulation of high-performance paints with enhanced durability and finish. Additionally, ethyl acetate's compatibility with various pigments allows for vibrant color development in paint formulations.
Despite its widespread use, the application of ethyl acetate in inks and paints faces several challenges. One significant issue is its volatility, which can lead to rapid evaporation during application, potentially affecting the consistency and quality of the final product. This volatility also raises environmental concerns, as it contributes to the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
Another challenge lies in the balance between performance and environmental sustainability. While ethyl acetate is considered less harmful than many other solvents, there is growing pressure to reduce VOC emissions in industrial processes. This has led to increased research into water-based and low-VOC formulations, which may potentially limit the use of ethyl acetate in certain applications.
The cost and availability of ethyl acetate can also pose challenges for manufacturers. As a petroleum-derived product, its price is subject to fluctuations in the global oil market, which can impact production costs and pricing strategies for inks and paints. Furthermore, the push towards bio-based alternatives has sparked interest in developing sustainable sources of ethyl acetate, though these alternatives often face hurdles in terms of cost-effectiveness and scalability.
In the realm of product performance, while ethyl acetate offers many advantages, it may not be suitable for all applications. For instance, its fast evaporation rate can be problematic in hot or humid environments, potentially leading to issues such as blushing or poor flow in paint applications. Additionally, its limited resistance to certain chemicals may restrict its use in specialized coatings that require high chemical resistance.
As the industry continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for maximizing the potential of ethyl acetate in advancing inks and paints technology. This will likely involve a combination of innovative formulation techniques, process optimizations, and the development of complementary or alternative technologies to overcome the current limitations while leveraging the benefits that ethyl acetate brings to the table.
In the paints sector, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent and diluent in both industrial and decorative coatings. Its excellent solvency properties enable it to dissolve a wide range of resins and binders, contributing to the formulation of high-performance paints with enhanced durability and finish. Additionally, ethyl acetate's compatibility with various pigments allows for vibrant color development in paint formulations.
Despite its widespread use, the application of ethyl acetate in inks and paints faces several challenges. One significant issue is its volatility, which can lead to rapid evaporation during application, potentially affecting the consistency and quality of the final product. This volatility also raises environmental concerns, as it contributes to the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
Another challenge lies in the balance between performance and environmental sustainability. While ethyl acetate is considered less harmful than many other solvents, there is growing pressure to reduce VOC emissions in industrial processes. This has led to increased research into water-based and low-VOC formulations, which may potentially limit the use of ethyl acetate in certain applications.
The cost and availability of ethyl acetate can also pose challenges for manufacturers. As a petroleum-derived product, its price is subject to fluctuations in the global oil market, which can impact production costs and pricing strategies for inks and paints. Furthermore, the push towards bio-based alternatives has sparked interest in developing sustainable sources of ethyl acetate, though these alternatives often face hurdles in terms of cost-effectiveness and scalability.
In the realm of product performance, while ethyl acetate offers many advantages, it may not be suitable for all applications. For instance, its fast evaporation rate can be problematic in hot or humid environments, potentially leading to issues such as blushing or poor flow in paint applications. Additionally, its limited resistance to certain chemicals may restrict its use in specialized coatings that require high chemical resistance.
As the industry continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for maximizing the potential of ethyl acetate in advancing inks and paints technology. This will likely involve a combination of innovative formulation techniques, process optimizations, and the development of complementary or alternative technologies to overcome the current limitations while leveraging the benefits that ethyl acetate brings to the table.
Innovative Ethyl Acetate Solutions in Inks and Paints
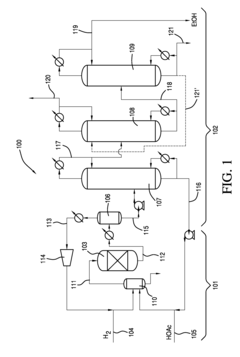
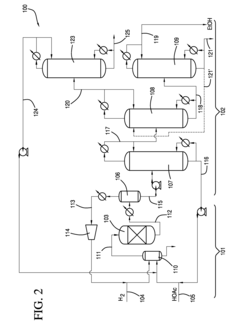
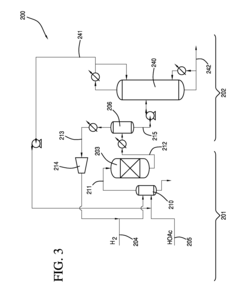
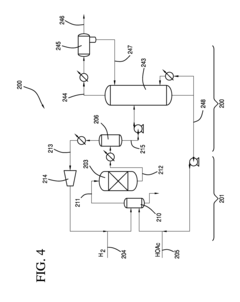
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of catalysts. These processes aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification reactions, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The processes aim to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes and industries. It serves as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. Its versatility makes it valuable in diverse applications across different sectors.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography, and other separation techniques. These processes are used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemical manufacturing.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices to minimize risks associated with its flammability and volatility.
- Novel applications and formulations containing ethyl acetate: Innovative applications and formulations incorporating ethyl acetate are being developed. These include its use in specialized coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. Research is ongoing to explore new potential uses and improve existing applications across various industries.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, such as solvent extraction, as a reaction medium, and in the production of various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for use in industries like pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in coating and adhesive formulations
Ethyl acetate is employed in the formulation of coatings, paints, and adhesives. Its fast evaporation rate and solvency properties make it useful for improving the application and performance of these products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ethyl acetate as a green solvent
The use of ethyl acetate as an environmentally friendly solvent is explored in various applications. Its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability make it a suitable alternative to more hazardous solvents in industrial processes and consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate
Methods for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial processes are developed to improve sustainability and reduce waste. These techniques include adsorption, membrane separation, and advanced distillation processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Market Dynamics
The ethyl acetate market for inks and paints technology is in a mature growth stage, with a steady global market size driven by increasing demand in various industries. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of major chemical companies like BASF, Celanese, and Eastman Kodak, who have established production capabilities and product lines. Smaller specialized firms such as Nantong Baichuan New Material and Jiangsu Baichuan High-Tech New Materials are also contributing to innovation in this field. Research institutions like Tianjin University and South China University of Technology are actively involved in advancing the technology, indicating ongoing development and refinement of ethyl acetate applications in inks and paints.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced ethyl acetate production technologies to enhance inks and paints. Their process utilizes a reactive distillation method, which combines reaction and separation in a single unit, improving efficiency and product quality[1]. This method allows for continuous production of high-purity ethyl acetate (>99.5%) with reduced energy consumption. Sinopec's technology also incorporates a novel catalyst system that increases selectivity and yield, minimizing byproduct formation[2]. The company has implemented this technology in large-scale plants, producing ethyl acetate with a capacity of over 100,000 tons per year[3].
Strengths: High-purity product, energy-efficient process, large-scale production capability. Weaknesses: Potential dependency on petroleum-based feedstocks, which may face sustainability challenges in the future.
Nissin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nissin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. has developed a proprietary ethyl acetate-based solvent system for high-performance inks and coatings. Their technology focuses on optimizing the solvent blend to enhance pigment dispersion and film formation properties. The company's approach involves using ethyl acetate as a primary solvent, combined with carefully selected co-solvents and additives to improve drying speed and adhesion[4]. Nissin's formulations are designed to reduce VOC emissions while maintaining excellent print quality and durability. They have also developed specialized ethyl acetate-based solutions for UV-curable inks, which offer rapid curing and improved scratch resistance[5].
Strengths: Tailored solutions for specific ink and paint applications, improved environmental profile. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal performance, potentially higher cost compared to conventional solvent systems.
Breakthrough Patents in Ethyl Acetate Technology
Process for producing an ethyl acetate solvent and co-production of ethanol
PatentInactiveUS20110190531A1
Innovation
- A process involving the hydrogenation of acetic acid in the presence of a catalyst, followed by a series of distillation columns to separate and recover ethanol and ethyl acetate solvent, with specific catalyst compositions and conditions to optimize ethanol and ethyl acetate production, including the use of platinum-based catalysts and modified silica supports.
Solvent composition
PatentInactiveUS7648651B2
Innovation
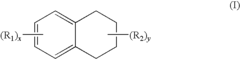
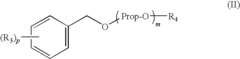
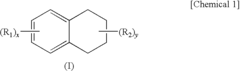
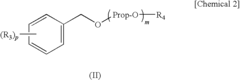
- A solvent composition combining a tetralin compound and a specific polyether compound, which enhances solute dissolution and substrate affinity while being safe and odorless, is developed, with specific formulations and usage ratios optimized for various applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The use of ethyl acetate in inks and paints technology has significant environmental and sustainability implications that warrant careful consideration. As a solvent, ethyl acetate offers several advantages over traditional petroleum-based alternatives, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint in the coatings industry.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ethyl acetate is its lower toxicity compared to many other solvents. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, breaking down relatively quickly into harmless components. This characteristic reduces the long-term impact on ecosystems and minimizes the risk of soil and water contamination.
Furthermore, ethyl acetate has a lower volatile organic compound (VOC) content than many conventional solvents. VOCs contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. By utilizing ethyl acetate, manufacturers can develop low-VOC or VOC-compliant formulations, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and improving air quality.
From a sustainability perspective, ethyl acetate can be derived from renewable resources, such as fermented sugars or ethanol produced from biomass. This bio-based production route offers an alternative to petrochemical-based solvents, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and potentially lowering the carbon footprint of ink and paint products.
However, it is essential to consider the entire lifecycle of ethyl acetate in assessing its environmental impact. While it offers advantages in use and disposal, the production process still requires energy and resources. Manufacturers must evaluate the overall sustainability of their supply chains, including the sourcing of raw materials and energy efficiency in production.
In terms of waste management, ethyl acetate's high volatility allows for easier recovery and recycling in industrial processes. This property enables the implementation of solvent recovery systems, reducing waste and promoting a more circular economy in the coatings industry.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, ethyl acetate plays a role in enabling water-based and high-solids formulations. These advanced coating technologies typically have lower environmental impacts than traditional solvent-based systems, and ethyl acetate's properties make it a valuable component in their development.
While ethyl acetate offers numerous environmental benefits, it is crucial to maintain a balanced perspective. Continuous research and development efforts are necessary to further improve its production efficiency, explore even more sustainable alternatives, and optimize its use in various applications to maximize its positive environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ethyl acetate is its lower toxicity compared to many other solvents. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, breaking down relatively quickly into harmless components. This characteristic reduces the long-term impact on ecosystems and minimizes the risk of soil and water contamination.
Furthermore, ethyl acetate has a lower volatile organic compound (VOC) content than many conventional solvents. VOCs contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. By utilizing ethyl acetate, manufacturers can develop low-VOC or VOC-compliant formulations, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and improving air quality.
From a sustainability perspective, ethyl acetate can be derived from renewable resources, such as fermented sugars or ethanol produced from biomass. This bio-based production route offers an alternative to petrochemical-based solvents, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and potentially lowering the carbon footprint of ink and paint products.
However, it is essential to consider the entire lifecycle of ethyl acetate in assessing its environmental impact. While it offers advantages in use and disposal, the production process still requires energy and resources. Manufacturers must evaluate the overall sustainability of their supply chains, including the sourcing of raw materials and energy efficiency in production.
In terms of waste management, ethyl acetate's high volatility allows for easier recovery and recycling in industrial processes. This property enables the implementation of solvent recovery systems, reducing waste and promoting a more circular economy in the coatings industry.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, ethyl acetate plays a role in enabling water-based and high-solids formulations. These advanced coating technologies typically have lower environmental impacts than traditional solvent-based systems, and ethyl acetate's properties make it a valuable component in their development.
While ethyl acetate offers numerous environmental benefits, it is crucial to maintain a balanced perspective. Continuous research and development efforts are necessary to further improve its production efficiency, explore even more sustainable alternatives, and optimize its use in various applications to maximize its positive environmental impact.
Regulatory Framework for Ethyl Acetate Usage
The regulatory framework for ethyl acetate usage in inks and paints is a critical aspect of the industry, ensuring safety, environmental protection, and quality standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which requires manufacturers and importers to report production volumes, uses, and potential exposures. The EPA has established a reportable quantity of 5,000 pounds for ethyl acetate under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA).
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ethyl acetate in the workplace. The current PEL is 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. This regulation aims to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to ethyl acetate vapors.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Manufacturers and importers are required to register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data sheets to downstream users. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation also applies, ensuring that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
For inks and paints specifically, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the EU have established guidelines for the use of ethyl acetate in food packaging materials and printing inks that may come into contact with food. These regulations set limits on the migration of ethyl acetate from packaging materials into food products.
The volatile organic compound (VOC) content of paints and inks is another area of regulatory focus. Many jurisdictions have implemented VOC regulations to reduce air pollution and improve indoor air quality. While ethyl acetate is considered a VOC, its relatively low toxicity and high volatility make it a preferred solvent in many low-VOC formulations.
Industry associations, such as the European Printing Ink Association (EuPIA) and the American Coatings Association (ACA), have developed voluntary guidelines and best practices for the use of solvents, including ethyl acetate, in inks and paints. These guidelines often go beyond regulatory requirements and address issues such as product stewardship and sustainability.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulatory frameworks are evolving to promote the use of more sustainable and less harmful solvents. This trend may lead to increased scrutiny of ethyl acetate usage in the future, potentially driving innovation in bio-based alternatives or water-based formulations for inks and paints.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ethyl acetate in the workplace. The current PEL is 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. This regulation aims to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to ethyl acetate vapors.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Manufacturers and importers are required to register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data sheets to downstream users. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation also applies, ensuring that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
For inks and paints specifically, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the EU have established guidelines for the use of ethyl acetate in food packaging materials and printing inks that may come into contact with food. These regulations set limits on the migration of ethyl acetate from packaging materials into food products.
The volatile organic compound (VOC) content of paints and inks is another area of regulatory focus. Many jurisdictions have implemented VOC regulations to reduce air pollution and improve indoor air quality. While ethyl acetate is considered a VOC, its relatively low toxicity and high volatility make it a preferred solvent in many low-VOC formulations.
Industry associations, such as the European Printing Ink Association (EuPIA) and the American Coatings Association (ACA), have developed voluntary guidelines and best practices for the use of solvents, including ethyl acetate, in inks and paints. These guidelines often go beyond regulatory requirements and address issues such as product stewardship and sustainability.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulatory frameworks are evolving to promote the use of more sustainable and less harmful solvents. This trend may lead to increased scrutiny of ethyl acetate usage in the future, potentially driving innovation in bio-based alternatives or water-based formulations for inks and paints.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!