How to Enhance Industrial Output with Hydrochloric Acid?
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl in Industry: Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) has been a cornerstone in industrial processes for over a century, playing a crucial role in various sectors including chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and water treatment. The evolution of HCl usage in industry has been marked by continuous improvements in production methods, safety protocols, and application techniques. As global industrial output continues to grow, the demand for efficient and sustainable use of HCl has become increasingly important.
The primary objective of enhancing industrial output with HCl is to optimize its utilization while minimizing environmental impact and maximizing economic benefits. This involves developing innovative approaches to HCl production, recovery, and recycling, as well as exploring novel applications across different industries. By improving the efficiency of HCl-based processes, industries can reduce costs, increase productivity, and meet stringent environmental regulations.
One of the key trends in HCl technology is the shift towards more sustainable production methods. Traditional processes, such as the direct synthesis of hydrogen and chlorine, are being supplemented or replaced by more environmentally friendly alternatives. These include the recovery of HCl from waste streams and the development of closed-loop systems that minimize HCl consumption and emissions.
In the chemical industry, HCl serves as a vital reagent in the production of various compounds, including PVC, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Enhancing industrial output in this sector involves improving reaction efficiencies, developing more selective catalysts, and implementing advanced process control systems. The metal processing industry, another major consumer of HCl, is focusing on optimizing pickling processes to reduce acid consumption and improve surface quality of treated metals.
Water treatment represents another significant area where HCl plays a critical role. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is a growing emphasis on developing more efficient water treatment technologies that utilize HCl. This includes advanced membrane systems for desalination and innovative approaches to pH adjustment in industrial wastewater treatment.
The future of HCl in enhancing industrial output lies in the integration of digital technologies and sustainable practices. Industry 4.0 concepts, such as IoT sensors and AI-driven process optimization, are being applied to HCl-based processes to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing green chemistry alternatives that can complement or partially replace HCl in certain applications, further driving innovation in this field.
The primary objective of enhancing industrial output with HCl is to optimize its utilization while minimizing environmental impact and maximizing economic benefits. This involves developing innovative approaches to HCl production, recovery, and recycling, as well as exploring novel applications across different industries. By improving the efficiency of HCl-based processes, industries can reduce costs, increase productivity, and meet stringent environmental regulations.
One of the key trends in HCl technology is the shift towards more sustainable production methods. Traditional processes, such as the direct synthesis of hydrogen and chlorine, are being supplemented or replaced by more environmentally friendly alternatives. These include the recovery of HCl from waste streams and the development of closed-loop systems that minimize HCl consumption and emissions.
In the chemical industry, HCl serves as a vital reagent in the production of various compounds, including PVC, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Enhancing industrial output in this sector involves improving reaction efficiencies, developing more selective catalysts, and implementing advanced process control systems. The metal processing industry, another major consumer of HCl, is focusing on optimizing pickling processes to reduce acid consumption and improve surface quality of treated metals.
Water treatment represents another significant area where HCl plays a critical role. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is a growing emphasis on developing more efficient water treatment technologies that utilize HCl. This includes advanced membrane systems for desalination and innovative approaches to pH adjustment in industrial wastewater treatment.
The future of HCl in enhancing industrial output lies in the integration of digital technologies and sustainable practices. Industry 4.0 concepts, such as IoT sensors and AI-driven process optimization, are being applied to HCl-based processes to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing green chemistry alternatives that can complement or partially replace HCl in certain applications, further driving innovation in this field.
Market Analysis for HCl-Enhanced Production
The global market for hydrochloric acid (HCl) in industrial applications has shown steady growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various sectors. The use of HCl to enhance industrial output has become a significant trend, particularly in the chemical, metallurgy, and oil and gas industries. Market analysis indicates that the HCl market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be robust over the next five years.
In the chemical industry, HCl plays a crucial role in the production of various chemicals, including PVC, polyurethane, and other polymers. The growing demand for these materials in construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors is a key driver for HCl-enhanced production. Additionally, the steel industry's use of HCl for pickling and descaling processes has contributed significantly to market growth.
The oil and gas sector represents another major market for HCl-enhanced production. Hydraulic fracturing operations, which require large volumes of HCl for well stimulation and acidizing, have boosted demand in regions with active shale gas and oil exploration. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and is expected to expand to other regions as unconventional oil and gas extraction methods gain traction globally.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the market for HCl-enhanced industrial production, primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. The region's expanding manufacturing sector, coupled with increasing investments in infrastructure development, has created a substantial demand for HCl-based processes. North America follows closely, driven by its robust chemical industry and the aforementioned shale gas boom.
Market analysis also reveals a growing interest in recycling and regeneration of HCl in industrial processes. This trend is partly driven by environmental concerns and regulations aimed at reducing waste and emissions. Companies are increasingly investing in technologies that allow for the recovery and reuse of HCl, which not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainability goals.
The competitive landscape of the HCl market for industrial enhancement is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and regional players. Key market participants are focusing on expanding their production capacities and developing innovative applications for HCl to gain a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships and collaborations between HCl producers and end-users are becoming more common, aiming to optimize supply chains and develop tailored solutions for specific industrial processes.
In the chemical industry, HCl plays a crucial role in the production of various chemicals, including PVC, polyurethane, and other polymers. The growing demand for these materials in construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors is a key driver for HCl-enhanced production. Additionally, the steel industry's use of HCl for pickling and descaling processes has contributed significantly to market growth.
The oil and gas sector represents another major market for HCl-enhanced production. Hydraulic fracturing operations, which require large volumes of HCl for well stimulation and acidizing, have boosted demand in regions with active shale gas and oil exploration. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and is expected to expand to other regions as unconventional oil and gas extraction methods gain traction globally.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the market for HCl-enhanced industrial production, primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. The region's expanding manufacturing sector, coupled with increasing investments in infrastructure development, has created a substantial demand for HCl-based processes. North America follows closely, driven by its robust chemical industry and the aforementioned shale gas boom.
Market analysis also reveals a growing interest in recycling and regeneration of HCl in industrial processes. This trend is partly driven by environmental concerns and regulations aimed at reducing waste and emissions. Companies are increasingly investing in technologies that allow for the recovery and reuse of HCl, which not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainability goals.
The competitive landscape of the HCl market for industrial enhancement is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and regional players. Key market participants are focusing on expanding their production capacities and developing innovative applications for HCl to gain a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships and collaborations between HCl producers and end-users are becoming more common, aiming to optimize supply chains and develop tailored solutions for specific industrial processes.
Current HCl Applications and Challenges
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) plays a crucial role in various industrial processes, contributing significantly to global manufacturing output. Its versatility and reactivity make it indispensable in sectors ranging from chemical production to metal processing. However, the current applications of HCl face several challenges that need to be addressed to enhance industrial output further.
In the chemical industry, HCl is widely used as a catalyst and reagent in the production of various compounds, including PVC, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Its ability to control pH levels and facilitate reactions is essential for maintaining product quality and process efficiency. Nevertheless, the corrosive nature of HCl poses significant challenges in terms of equipment maintenance and worker safety, necessitating robust containment systems and stringent safety protocols.
The metal processing sector heavily relies on HCl for pickling and descaling operations, particularly in steel manufacturing. While effective in removing oxide layers and improving surface quality, the use of HCl in these applications often results in substantial acid consumption and generates large volumes of waste. This not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns, prompting the need for more efficient acid recovery and recycling technologies.
In the oil and gas industry, HCl is employed for well stimulation and scale removal in drilling operations. Its effectiveness in dissolving carbonate formations enhances oil and gas recovery rates. However, the unpredictable nature of subsurface conditions can lead to inconsistent results and potential formation damage if not properly controlled. Additionally, the transportation and handling of large quantities of HCl in remote locations present logistical and safety challenges.
The water treatment sector utilizes HCl for pH adjustment and chlorine production. While essential for ensuring water quality, the storage and handling of HCl in municipal water treatment facilities pose significant safety risks. Moreover, the potential for accidental releases and their environmental impact necessitates stringent regulatory compliance and advanced containment measures.
A major challenge across all industries is the management of HCl emissions and waste streams. Stringent environmental regulations require industries to implement effective scrubbing systems and waste treatment processes, which can be costly and energy-intensive. The development of more efficient and cost-effective emission control technologies remains a priority for enhancing the sustainability of HCl-dependent processes.
The global supply chain for HCl also presents challenges, with production often tied to chlor-alkali processes. Fluctuations in demand for caustic soda can impact HCl availability and pricing, affecting industries that rely heavily on this acid. This interdependence highlights the need for more flexible production methods and improved supply chain management strategies to ensure a stable and cost-effective HCl supply.
In the chemical industry, HCl is widely used as a catalyst and reagent in the production of various compounds, including PVC, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Its ability to control pH levels and facilitate reactions is essential for maintaining product quality and process efficiency. Nevertheless, the corrosive nature of HCl poses significant challenges in terms of equipment maintenance and worker safety, necessitating robust containment systems and stringent safety protocols.
The metal processing sector heavily relies on HCl for pickling and descaling operations, particularly in steel manufacturing. While effective in removing oxide layers and improving surface quality, the use of HCl in these applications often results in substantial acid consumption and generates large volumes of waste. This not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns, prompting the need for more efficient acid recovery and recycling technologies.
In the oil and gas industry, HCl is employed for well stimulation and scale removal in drilling operations. Its effectiveness in dissolving carbonate formations enhances oil and gas recovery rates. However, the unpredictable nature of subsurface conditions can lead to inconsistent results and potential formation damage if not properly controlled. Additionally, the transportation and handling of large quantities of HCl in remote locations present logistical and safety challenges.
The water treatment sector utilizes HCl for pH adjustment and chlorine production. While essential for ensuring water quality, the storage and handling of HCl in municipal water treatment facilities pose significant safety risks. Moreover, the potential for accidental releases and their environmental impact necessitates stringent regulatory compliance and advanced containment measures.
A major challenge across all industries is the management of HCl emissions and waste streams. Stringent environmental regulations require industries to implement effective scrubbing systems and waste treatment processes, which can be costly and energy-intensive. The development of more efficient and cost-effective emission control technologies remains a priority for enhancing the sustainability of HCl-dependent processes.
The global supply chain for HCl also presents challenges, with production often tied to chlor-alkali processes. Fluctuations in demand for caustic soda can impact HCl availability and pricing, affecting industries that rely heavily on this acid. This interdependence highlights the need for more flexible production methods and improved supply chain management strategies to ensure a stable and cost-effective HCl supply.
Existing HCl-Based Industrial Solutions
01 Production methods for hydrochloric acid
Various methods are employed in the industrial production of hydrochloric acid, including the reaction of hydrogen and chlorine, the chlorination of organic compounds, and as a byproduct in chlor-alkali processes. These methods are optimized for efficiency and yield in industrial settings.- Production methods for hydrochloric acid: Various methods are employed in the industrial production of hydrochloric acid. These include the direct synthesis from hydrogen and chlorine, as a byproduct in chlorination processes, and through the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. Each method has its own advantages and is used based on specific industrial requirements and available resources.
- Purification and concentration techniques: Industrial hydrochloric acid production often involves purification and concentration steps to meet specific quality standards. This may include distillation, absorption processes, and the use of specialized equipment to remove impurities and adjust the acid concentration. These techniques are crucial for producing high-purity hydrochloric acid for various industrial applications.
- Recycling and waste management in HCl production: Efficient recycling and waste management are important aspects of industrial hydrochloric acid production. This includes recovering and reusing excess acid, treating waste streams, and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact. Such practices not only improve the overall efficiency of the production process but also contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Equipment and process optimization: Continuous improvement in equipment design and process optimization plays a crucial role in enhancing the industrial output of hydrochloric acid. This includes the development of corrosion-resistant materials, advanced reactor designs, and automated control systems. These innovations aim to increase production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and improve product quality.
- Safety and environmental considerations: Industrial hydrochloric acid production requires strict adherence to safety protocols and environmental regulations. This involves implementing robust containment systems, emission control measures, and worker safety procedures. Additionally, there is a focus on developing greener production methods and reducing the carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid manufacturing processes.
02 Purification and concentration techniques
Industrial processes focus on purifying and concentrating hydrochloric acid to meet specific quality standards. This involves distillation, absorption, and membrane separation techniques to remove impurities and achieve desired concentration levels for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and waste management
Efficient recycling of hydrochloric acid from industrial processes and proper waste management are crucial for sustainable production. This includes recovering acid from waste streams, neutralization processes, and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Equipment and process optimization
Specialized equipment and process optimizations are employed to enhance hydrochloric acid production efficiency and safety. This includes corrosion-resistant materials, advanced reactor designs, and automated control systems for improved output and quality control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications and market demand
The industrial output of hydrochloric acid is driven by its diverse applications in various sectors, including chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and water treatment. Market demand influences production scales and specialized grades of hydrochloric acid for different industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HCl Production and Application
The hydrochloric acid market for industrial output enhancement is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to exceed $7 billion by 2027. The technology's maturity is evident from its widespread use across various industries. Key players like BASF Corp., Covestro Deutschland AG, and Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. have established strong positions in the market, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. Emerging companies such as Fluid Energy Group Ltd. and Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE are introducing innovative solutions, focusing on environmentally friendly and high-performance products. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical conglomerates and specialized manufacturers, with ongoing research at institutions like The University of Queensland driving further advancements in hydrochloric acid applications for industrial processes.
Fluid Energy Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fluid Energy Group has developed a range of innovative hydrochloric acid-based products for enhancing industrial output, particularly in the oil and gas sector. Their HCl-based stimulation fluids, such as the ENVIRO-SYNTM product line, are designed to improve well productivity while minimizing environmental impact[6]. These fluids utilize a unique blend of hydrochloric acid and proprietary additives to effectively dissolve scale and stimulate formation permeability. The company has also implemented advanced manufacturing processes that allow for precise control of acid concentration and purity, ensuring consistent product quality and performance across various applications[7].
Strengths: Environmentally friendly formulations, improved well productivity, and consistent product quality. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on oil and gas industry, which may limit applicability in other industrial sectors.
Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE
Technical Solution: Dorf Ketal has developed advanced hydrochloric acid-based solutions for enhancing industrial output in refinery and petrochemical operations. Their technology focuses on using hydrochloric acid in combination with proprietary inhibitors and catalysts to improve process efficiency and equipment reliability. One of their key innovations is a hydrochloric acid-based system for crude unit overhead corrosion control, which effectively neutralizes basic compounds and reduces fouling in distillation columns[8]. Additionally, Dorf Ketal has developed specialized HCl-based chemical cleaning solutions that can be used at higher temperatures and pressures, allowing for more effective removal of deposits and scale in industrial equipment[9].
Strengths: Improved process efficiency, enhanced equipment reliability, and specialized solutions for refinery and petrochemical industries. Weaknesses: Limited focus on specific industrial sectors may restrict broader application of their technologies.
Innovations in HCl Handling and Utilization
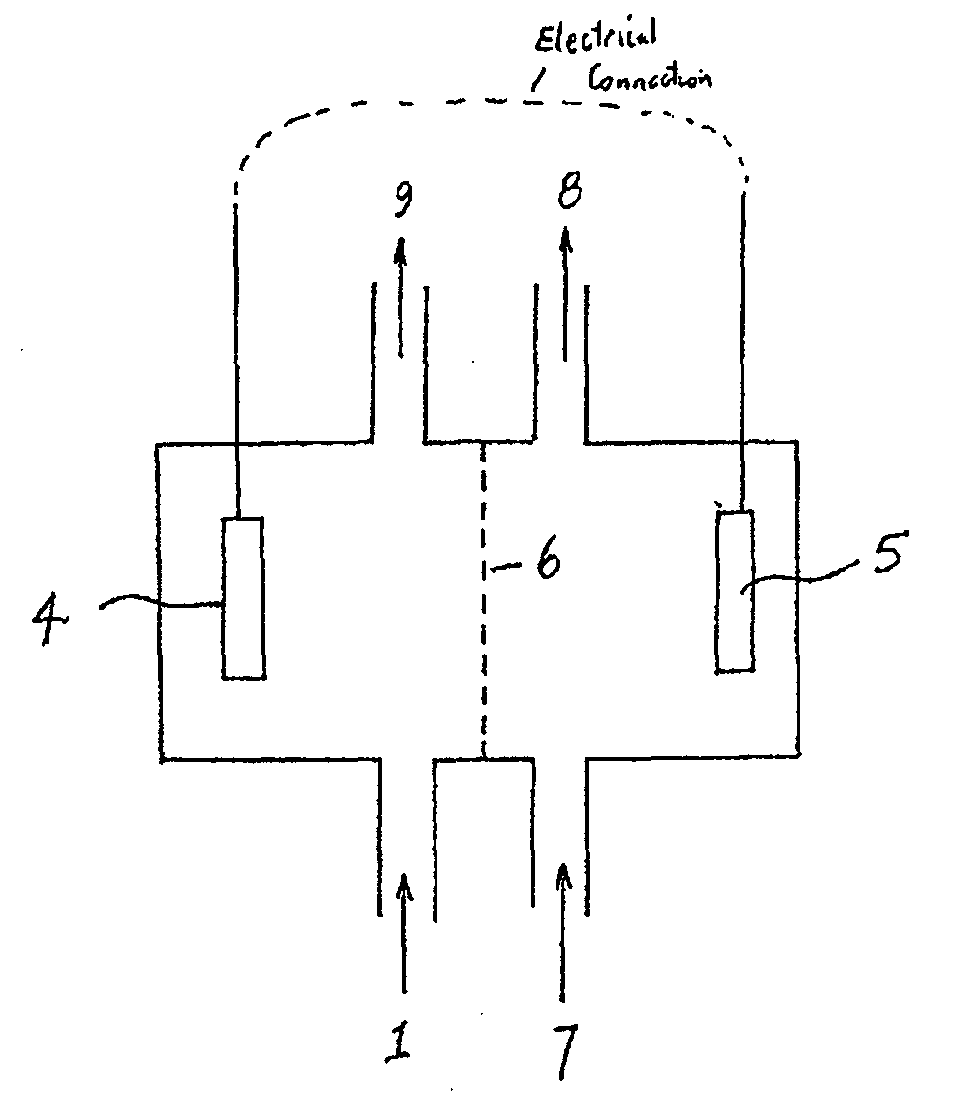
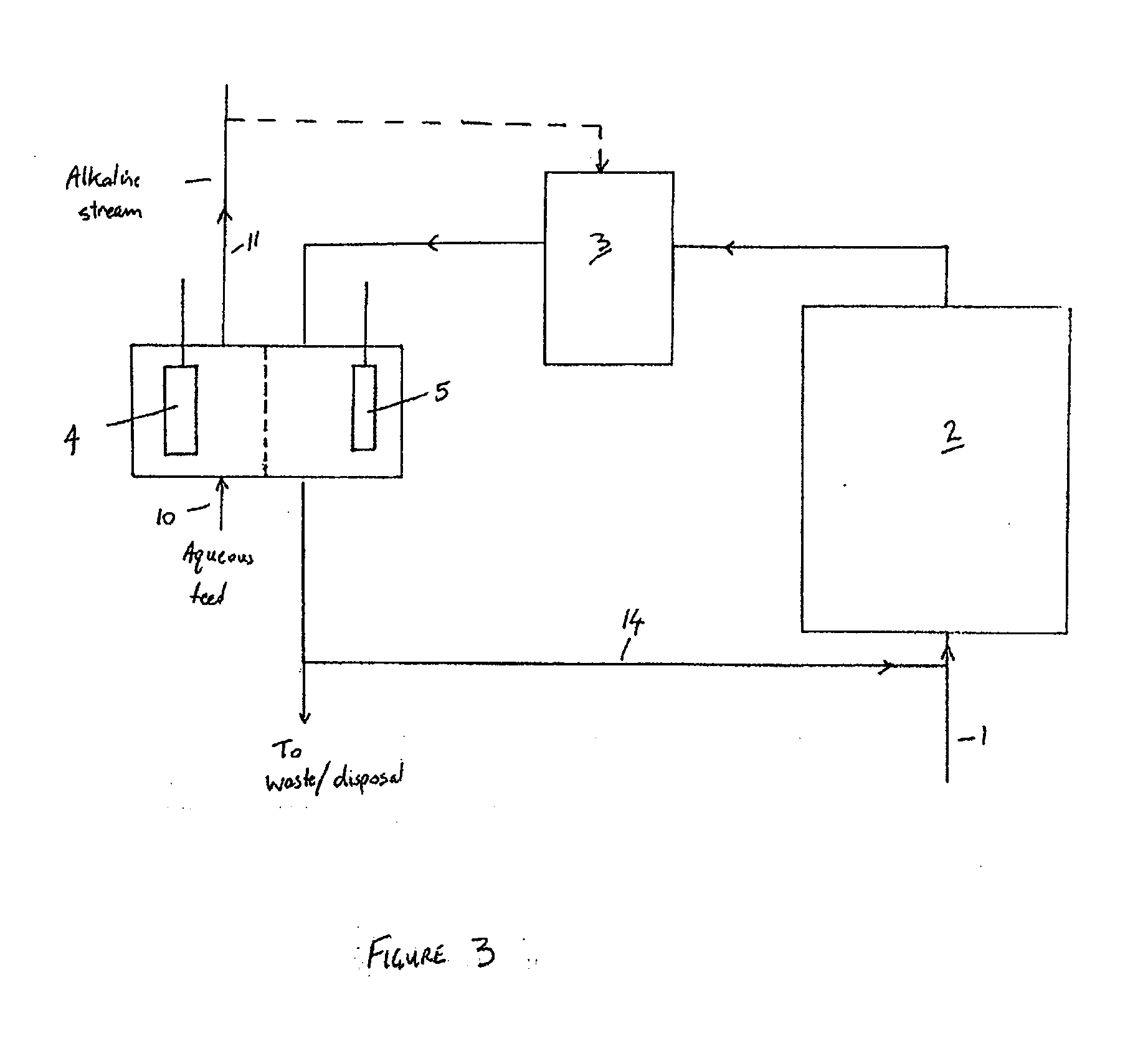
Treatment of solutions or wastewater
PatentInactiveUS20110315561A1
Innovation
- A method involving a bioelectrochemical system with an anode and cathode separated by an ion permeable membrane, where the pH of the wastewater stream is altered by passing it through the anode or cathode to reduce cation precipitation or produce acidic or alkaline solutions, utilizing electrochemically active microorganisms to control pH and facilitate ion transport.
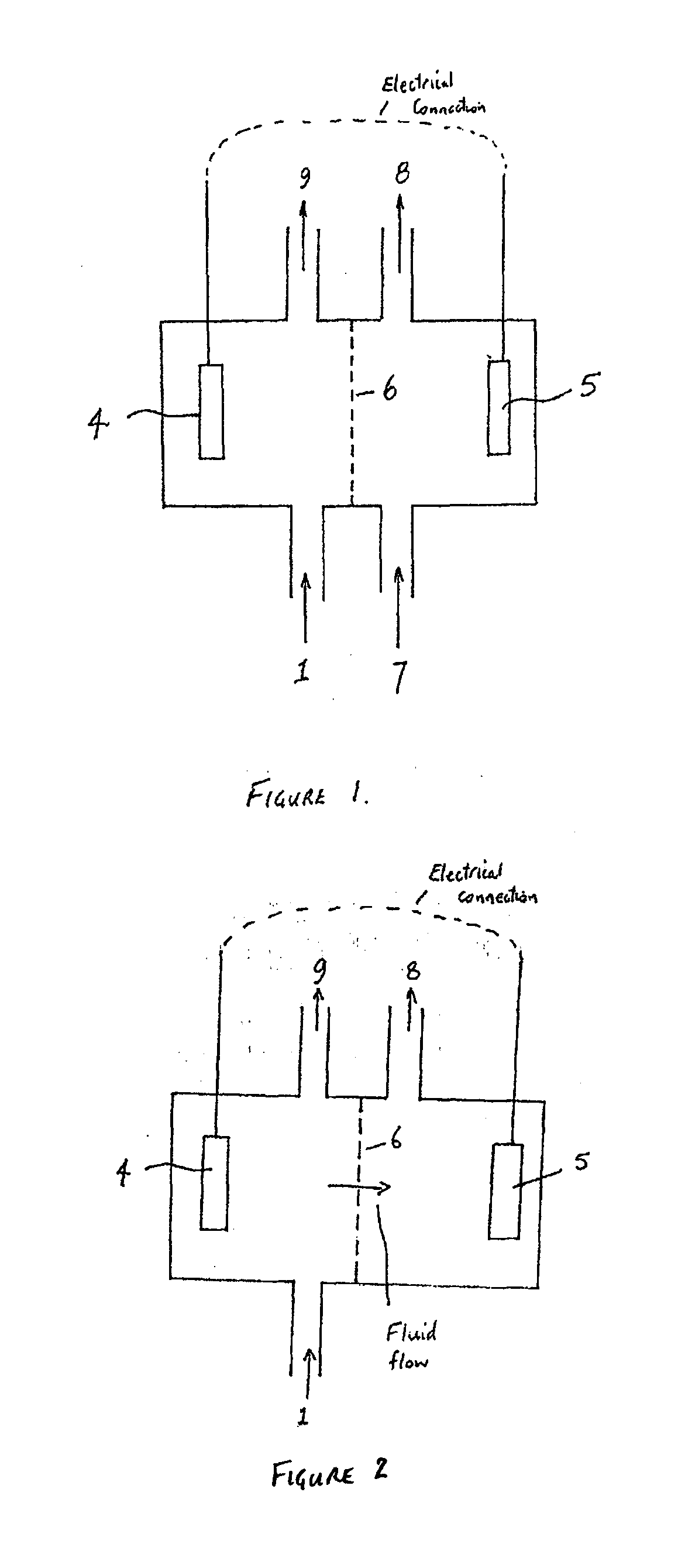
Treatment of solutions or wastewater
PatentInactiveEP2365941A1
Innovation
- A method involving a bioelectrochemical system with an anode and cathode separated by an ion-permeable membrane, where the pH of the wastewater stream is altered by passing it through the anode or cathode compartments to reduce cation precipitation, produce an alkaline stream, or generate acidic solutions, using electrochemically active microorganisms to control pH and facilitate the transport of ions, thereby maintaining electroneutrality and preventing scaling.
Environmental Impact of HCl Use
The use of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in industrial processes has significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered and managed. While HCl can enhance industrial output in various sectors, its potential environmental impact is a critical concern for sustainable manufacturing practices.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with HCl use is air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, HCl can form acid rain, contributing to the acidification of ecosystems and damaging vegetation, aquatic life, and infrastructure. Industrial facilities using HCl must implement robust emission control systems to minimize atmospheric releases and comply with stringent air quality regulations.
Water pollution is another major concern. Improper disposal or accidental spills of HCl can lead to the contamination of water bodies, altering pH levels and potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. Industries must establish comprehensive wastewater treatment protocols to neutralize and safely dispose of HCl-containing effluents, ensuring compliance with environmental protection standards.
The production and transportation of HCl also carry environmental risks. Manufacturing processes for HCl can generate greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the transportation of this corrosive substance poses potential hazards in case of accidents, necessitating strict safety measures and emergency response plans to mitigate environmental damage.
Soil contamination is a further environmental concern associated with HCl use. Accidental spills or improper storage can lead to soil acidification, affecting soil fertility and potentially contaminating groundwater. Industries must implement proper containment measures and have remediation strategies in place to address any soil contamination incidents promptly.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries are increasingly adopting cleaner production techniques and circular economy principles. This includes exploring alternatives to HCl where possible, implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and investing in advanced treatment technologies to reduce emissions and effluents.
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in managing the environmental impact of HCl use. Industries must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations, which often require regular monitoring, reporting, and continuous improvement of environmental performance. Many companies are going beyond compliance, implementing voluntary environmental management systems to proactively address potential impacts.
In conclusion, while HCl remains an important industrial chemical, its use necessitates a comprehensive approach to environmental management. Balancing the benefits of enhanced industrial output with environmental protection requires ongoing research, innovation in cleaner technologies, and a commitment to sustainable practices across the industrial sector.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with HCl use is air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, HCl can form acid rain, contributing to the acidification of ecosystems and damaging vegetation, aquatic life, and infrastructure. Industrial facilities using HCl must implement robust emission control systems to minimize atmospheric releases and comply with stringent air quality regulations.
Water pollution is another major concern. Improper disposal or accidental spills of HCl can lead to the contamination of water bodies, altering pH levels and potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. Industries must establish comprehensive wastewater treatment protocols to neutralize and safely dispose of HCl-containing effluents, ensuring compliance with environmental protection standards.
The production and transportation of HCl also carry environmental risks. Manufacturing processes for HCl can generate greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the transportation of this corrosive substance poses potential hazards in case of accidents, necessitating strict safety measures and emergency response plans to mitigate environmental damage.
Soil contamination is a further environmental concern associated with HCl use. Accidental spills or improper storage can lead to soil acidification, affecting soil fertility and potentially contaminating groundwater. Industries must implement proper containment measures and have remediation strategies in place to address any soil contamination incidents promptly.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries are increasingly adopting cleaner production techniques and circular economy principles. This includes exploring alternatives to HCl where possible, implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and investing in advanced treatment technologies to reduce emissions and effluents.
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in managing the environmental impact of HCl use. Industries must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations, which often require regular monitoring, reporting, and continuous improvement of environmental performance. Many companies are going beyond compliance, implementing voluntary environmental management systems to proactively address potential impacts.
In conclusion, while HCl remains an important industrial chemical, its use necessitates a comprehensive approach to environmental management. Balancing the benefits of enhanced industrial output with environmental protection requires ongoing research, innovation in cleaner technologies, and a commitment to sustainable practices across the industrial sector.
Safety Protocols for HCl in Manufacturing
The implementation of robust safety protocols for hydrochloric acid (HCl) in manufacturing is crucial for enhancing industrial output while ensuring worker protection and environmental compliance. These protocols encompass a comprehensive set of guidelines, procedures, and preventive measures designed to mitigate risks associated with HCl handling, storage, and usage.
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) forms the foundation of HCl safety. Workers must be equipped with acid-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection, such as appropriate respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus, is essential in areas with potential HCl vapor exposure. Regular inspection and maintenance of PPE ensure its effectiveness in preventing chemical burns and inhalation hazards.
Engineering controls play a vital role in minimizing HCl exposure. Adequate ventilation systems, including fume hoods and local exhaust ventilation, must be installed to remove acid vapors from work areas. Closed systems for HCl transfer and handling reduce the risk of spills and worker exposure. Additionally, emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in all areas where HCl is used or stored.
Proper storage and handling procedures are critical components of HCl safety protocols. HCl must be stored in corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials. Secondary containment systems should be implemented to prevent spills from spreading. Clear labeling of containers and storage areas, along with regular inspections for leaks or damage, helps maintain a safe working environment.
Employee training is essential for the effective implementation of safety protocols. Comprehensive training programs should cover HCl properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the correct use of PPE. Regular refresher courses and safety drills ensure that workers remain vigilant and prepared to respond to potential incidents.
Emergency response planning is a crucial aspect of HCl safety protocols. Detailed procedures for spill containment, neutralization, and disposal must be established and regularly practiced. Emergency communication systems, evacuation routes, and coordination with local emergency services should be clearly defined and periodically tested.
Continuous monitoring and assessment of HCl-related processes help identify potential hazards and areas for improvement. Regular safety audits, incident reporting systems, and analysis of near-misses contribute to the ongoing refinement of safety protocols. Implementation of advanced monitoring technologies, such as real-time HCl vapor detectors, can provide early warning of potential leaks or exposure risks.
By implementing and consistently enforcing these comprehensive safety protocols, manufacturers can significantly enhance their industrial output while maintaining a safe and compliant working environment for HCl-related processes.
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) forms the foundation of HCl safety. Workers must be equipped with acid-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection, such as appropriate respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus, is essential in areas with potential HCl vapor exposure. Regular inspection and maintenance of PPE ensure its effectiveness in preventing chemical burns and inhalation hazards.
Engineering controls play a vital role in minimizing HCl exposure. Adequate ventilation systems, including fume hoods and local exhaust ventilation, must be installed to remove acid vapors from work areas. Closed systems for HCl transfer and handling reduce the risk of spills and worker exposure. Additionally, emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in all areas where HCl is used or stored.
Proper storage and handling procedures are critical components of HCl safety protocols. HCl must be stored in corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials. Secondary containment systems should be implemented to prevent spills from spreading. Clear labeling of containers and storage areas, along with regular inspections for leaks or damage, helps maintain a safe working environment.
Employee training is essential for the effective implementation of safety protocols. Comprehensive training programs should cover HCl properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the correct use of PPE. Regular refresher courses and safety drills ensure that workers remain vigilant and prepared to respond to potential incidents.
Emergency response planning is a crucial aspect of HCl safety protocols. Detailed procedures for spill containment, neutralization, and disposal must be established and regularly practiced. Emergency communication systems, evacuation routes, and coordination with local emergency services should be clearly defined and periodically tested.
Continuous monitoring and assessment of HCl-related processes help identify potential hazards and areas for improvement. Regular safety audits, incident reporting systems, and analysis of near-misses contribute to the ongoing refinement of safety protocols. Implementation of advanced monitoring technologies, such as real-time HCl vapor detectors, can provide early warning of potential leaks or exposure risks.
By implementing and consistently enforcing these comprehensive safety protocols, manufacturers can significantly enhance their industrial output while maintaining a safe and compliant working environment for HCl-related processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!