How To Enhance Tungsten Processing Techniques?
Tungsten Processing Evolution and Objectives
Tungsten processing has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the 16th century. Initially, the metal was primarily used in its natural form, with limited processing techniques available. The 20th century saw a revolution in tungsten processing, driven by its increasing importance in industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing of high-strength alloys and filaments for incandescent light bulbs.
The development of powder metallurgy techniques in the mid-20th century marked a pivotal moment in tungsten processing. This method allowed for the production of dense, high-purity tungsten components, significantly expanding its applications in aerospace, electronics, and defense industries. Concurrently, advancements in chemical processing enabled more efficient extraction of tungsten from its ores, improving yield and reducing environmental impact.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of tungsten processing. Key objectives include reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and developing more environmentally friendly extraction methods. The industry is also exploring novel techniques for recycling tungsten from scrap materials, addressing the growing concern of resource scarcity.
Current technological trends in tungsten processing are centered around precision control of microstructure and properties. Advanced techniques such as spark plasma sintering and additive manufacturing are being investigated to produce tungsten components with tailored properties for specific applications. These methods offer the potential for creating complex geometries and gradient structures that were previously unattainable.
Looking ahead, the objectives for enhancing tungsten processing techniques are multifaceted. There is a strong push towards developing more efficient refining processes that can handle lower-grade ores, as high-grade deposits become increasingly scarce. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring alternative processing routes that could reduce the reliance on energy-intensive thermal treatments.
Another key objective is the integration of digital technologies and artificial intelligence into tungsten processing. This includes the development of smart manufacturing systems that can optimize process parameters in real-time, leading to improved product quality and reduced variability. Machine learning algorithms are being employed to predict material properties based on processing conditions, potentially revolutionizing alloy design and process optimization.
As the demand for tungsten in emerging technologies such as quantum computing and fusion reactors grows, there is an increasing need for ultra-high purity tungsten. Consequently, research is being directed towards developing advanced purification techniques that can achieve purity levels beyond current standards, opening up new possibilities for tungsten applications in cutting-edge fields.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Tungsten Products
The global market for advanced tungsten products has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. Tungsten's unique properties, including high melting point, density, and hardness, make it indispensable in numerous applications, from aerospace and automotive to electronics and energy sectors.
In the aerospace industry, there is a growing need for high-performance materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Advanced tungsten alloys are being increasingly utilized in aircraft engines, rocket nozzles, and heat shields, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and overall performance. The automotive sector is also witnessing a surge in demand for tungsten-based products, particularly in the production of wear-resistant components and high-performance engine parts.
The electronics industry continues to be a significant driver of tungsten demand, with the material playing a crucial role in the manufacture of integrated circuits, semiconductors, and LED lighting. As consumer electronics become more sophisticated and miniaturized, the need for tungsten's thermal management properties and electrical conductivity is expected to grow further.
In the energy sector, tungsten is gaining prominence in both traditional and renewable energy applications. Its use in drilling equipment for oil and gas exploration remains strong, while its potential in nuclear fusion reactors and solar panel production is being actively explored. The growing focus on sustainable energy solutions is likely to create new opportunities for advanced tungsten products in the coming years.
The medical industry represents another promising market for tungsten products. The material's high density makes it ideal for radiation shielding applications in medical imaging equipment and cancer treatment devices. As healthcare technologies continue to advance, the demand for specialized tungsten components is expected to increase.
Market analysts project that the global tungsten market will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4-5% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing industrialization in emerging economies, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and the development of new applications for tungsten-based materials.
However, the market faces challenges related to the limited global supply of tungsten and environmental concerns associated with its mining and processing. These factors are driving research into more efficient extraction methods and recycling technologies to ensure a sustainable supply chain for advanced tungsten products.
Current Challenges in Tungsten Processing Technologies
Tungsten processing technologies face several significant challenges that hinder the efficient production and utilization of this critical metal. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption associated with tungsten extraction and refining processes. The extreme temperatures required for tungsten reduction and the subsequent energy-intensive purification steps contribute to increased production costs and environmental concerns.
Another major challenge lies in the limited availability of high-grade tungsten ores. As easily accessible deposits become depleted, mining operations are forced to exploit lower-grade ores, which necessitate more complex and costly processing techniques. This situation is further exacerbated by the geopolitical concentration of tungsten resources, with China dominating global production and influencing market dynamics.
The environmental impact of tungsten processing remains a pressing concern. Traditional extraction methods often involve the use of harmful chemicals and generate substantial waste, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Developing more environmentally friendly processing techniques while maintaining economic viability is a significant challenge for the industry.
Recycling and recovery of tungsten from scrap and end-of-life products present both an opportunity and a challenge. While recycling can reduce reliance on primary ore extraction, the complex nature of tungsten-containing products and the lack of efficient separation technologies make large-scale recycling efforts difficult and often economically unfeasible.
The development of advanced tungsten alloys and composites for specialized applications is hindered by limitations in current processing technologies. Achieving precise control over microstructure and properties during manufacturing processes remains a challenge, particularly for applications in aerospace, defense, and high-temperature industries.
Lastly, the tungsten industry faces challenges in scaling up novel processing technologies from laboratory to industrial levels. Many promising techniques for enhancing tungsten production efficiency or reducing environmental impact struggle to demonstrate economic viability at commercial scales, creating a barrier to widespread adoption and technological advancement in the field.
State-of-the-Art Tungsten Processing Methods
01 Chemical vapor deposition of tungsten
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a widely used technique for depositing tungsten films. This process involves the reaction of tungsten-containing gases on a substrate surface to form a thin film. CVD can produce high-quality, uniform tungsten coatings with excellent step coverage and is commonly used in semiconductor manufacturing.- Chemical vapor deposition of tungsten: Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a widely used technique for depositing tungsten films. This process involves the reaction of tungsten-containing gases on a substrate surface to form a solid tungsten layer. CVD can produce high-quality, uniform tungsten coatings with excellent step coverage and is commonly used in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Tungsten powder production: Various methods are employed to produce tungsten powder, including reduction of tungsten oxides, mechanical alloying, and chemical processes. These techniques aim to create fine, uniform tungsten particles with specific characteristics suitable for different applications, such as in the production of tungsten alloys or as raw material for other tungsten processing methods.
- Tungsten alloy formation: Tungsten alloys are created by combining tungsten with other metals to enhance its properties or create materials with specific characteristics. Common alloying elements include nickel, iron, and copper. These alloys are often produced through powder metallurgy techniques, involving mixing, compacting, and sintering of metal powders.
- Tungsten thin film deposition: Thin films of tungsten are deposited using various techniques such as sputtering, e-beam evaporation, and atomic layer deposition. These methods allow for precise control of film thickness and properties, making them suitable for applications in microelectronics, optical coatings, and other advanced technologies.
- Tungsten recycling and recovery: Recycling and recovery of tungsten from scrap and waste materials is an important aspect of tungsten processing. Techniques include hydrometallurgical processes, pyrometallurgical methods, and mechanical separation. These processes aim to recover valuable tungsten from end-of-life products and manufacturing waste, contributing to resource conservation and sustainability in the tungsten industry.
02 Tungsten powder production
Various methods are employed to produce tungsten powder, including reduction of tungsten oxides, mechanical alloying, and chemical processes. These techniques aim to create fine, uniform tungsten particles with specific characteristics suitable for different applications, such as in the production of tungsten alloys or as raw material for other tungsten products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Tungsten etching and patterning
Etching and patterning techniques are crucial in tungsten processing, especially in the semiconductor industry. These processes involve selectively removing tungsten material to create desired patterns or structures. Various methods, including wet etching, dry etching, and plasma etching, are used depending on the specific requirements of the application.Expand Specific Solutions04 Tungsten thin film deposition
Tungsten thin films are deposited using various techniques such as sputtering, e-beam evaporation, and atomic layer deposition. These methods allow for precise control over film thickness and properties, making them suitable for applications in microelectronics, optical coatings, and other advanced technologies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tungsten alloy processing
Processing techniques for tungsten alloys involve methods such as powder metallurgy, sintering, and hot isostatic pressing. These processes aim to create alloys with improved properties, such as increased strength, hardness, or heat resistance, for use in various industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Tungsten Processing Industry
The tungsten processing techniques market is in a mature stage, with ongoing research and development efforts to enhance efficiency and performance. The global tungsten market size is projected to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand in various industries. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Applied Materials, Inc., Starck GmbH, and Toshiba Corp. leading innovation. These firms, along with research institutions such as Central South University and Beijing University of Technology, are focusing on improving processing methods, developing new alloys, and optimizing tungsten's properties for diverse applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established industrial players and emerging research-driven entities, all striving to push the boundaries of tungsten processing capabilities.
Applied Materials, Inc.
A.L.M.T. Corp.
Innovative Patents in Tungsten Processing
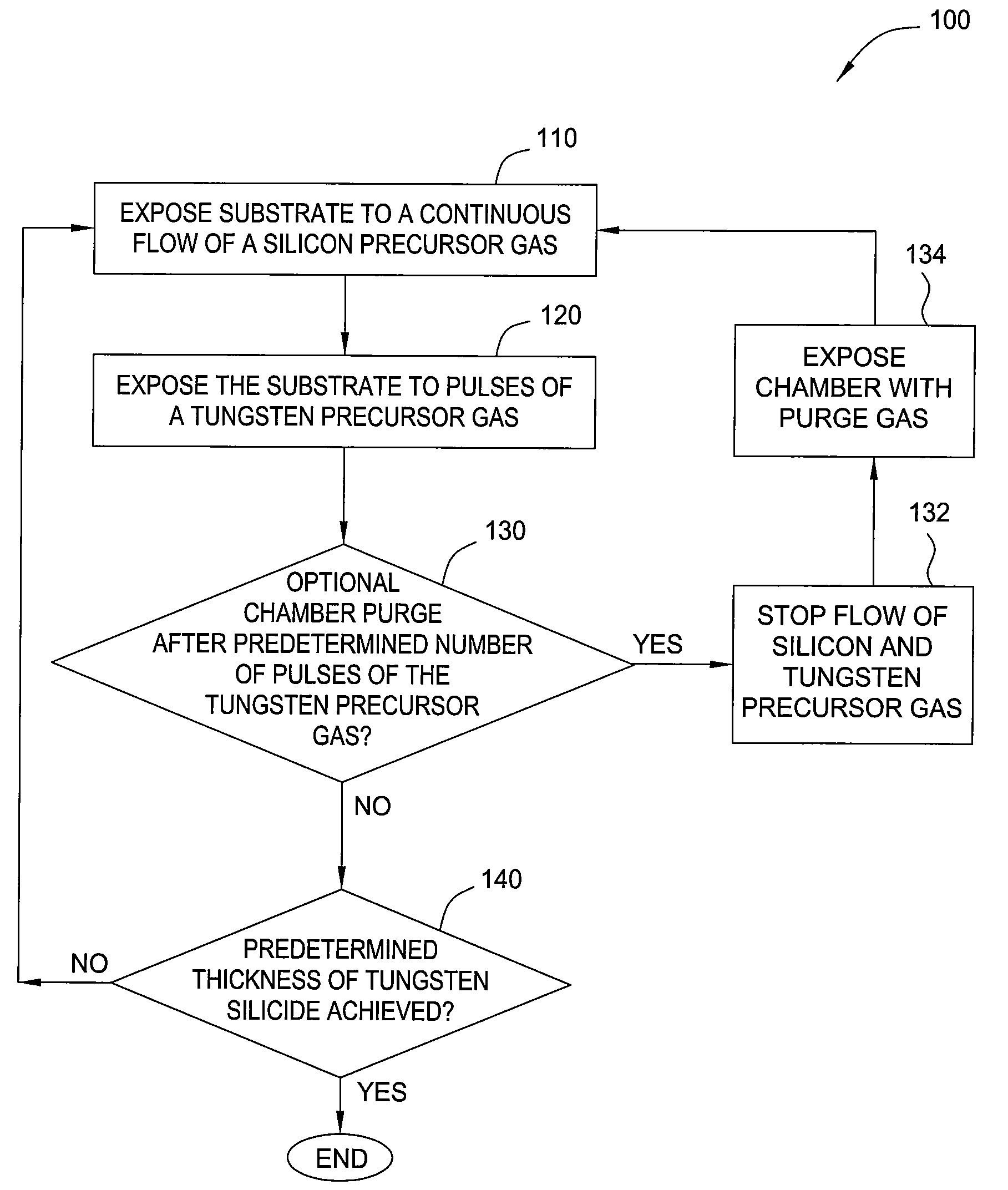
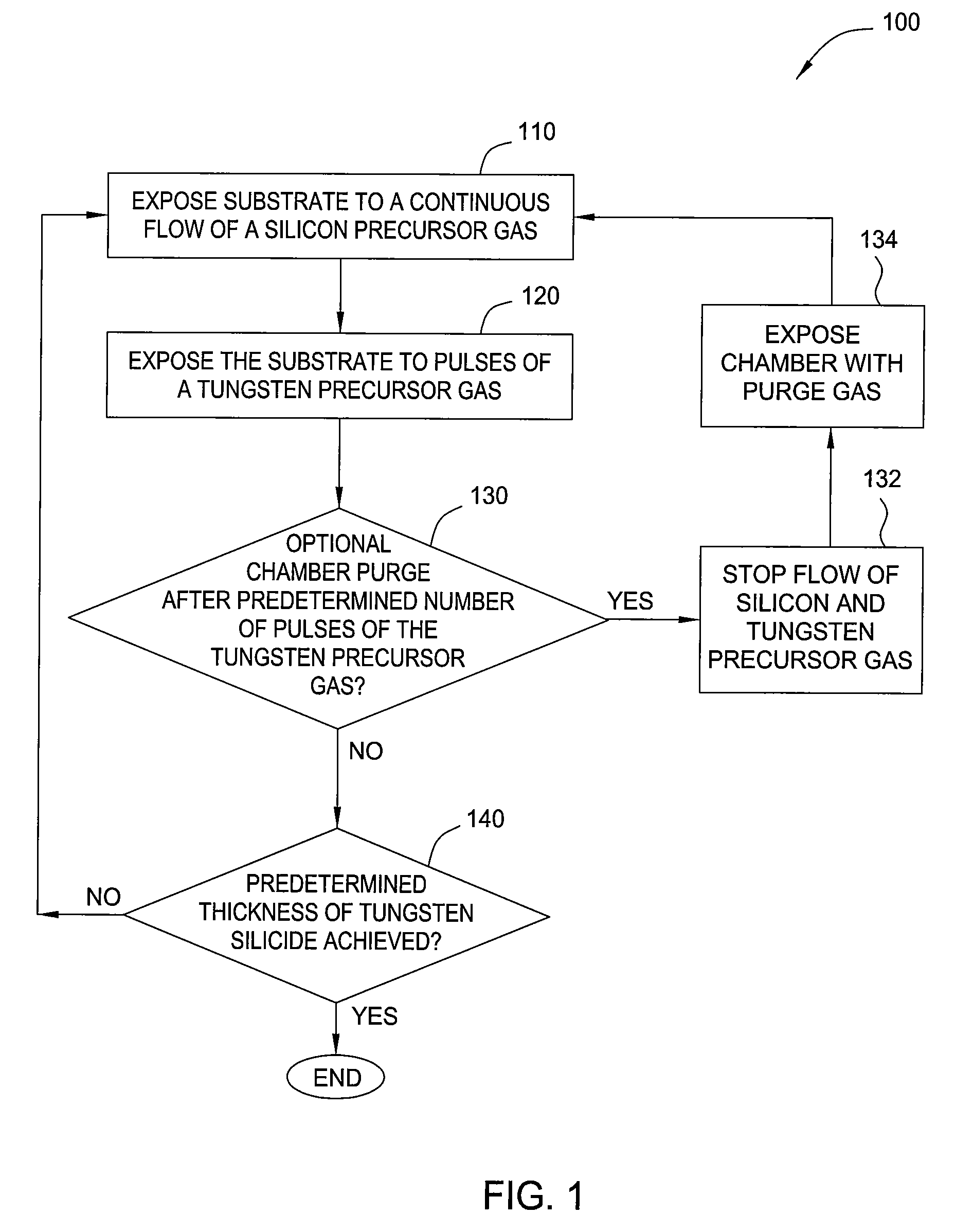
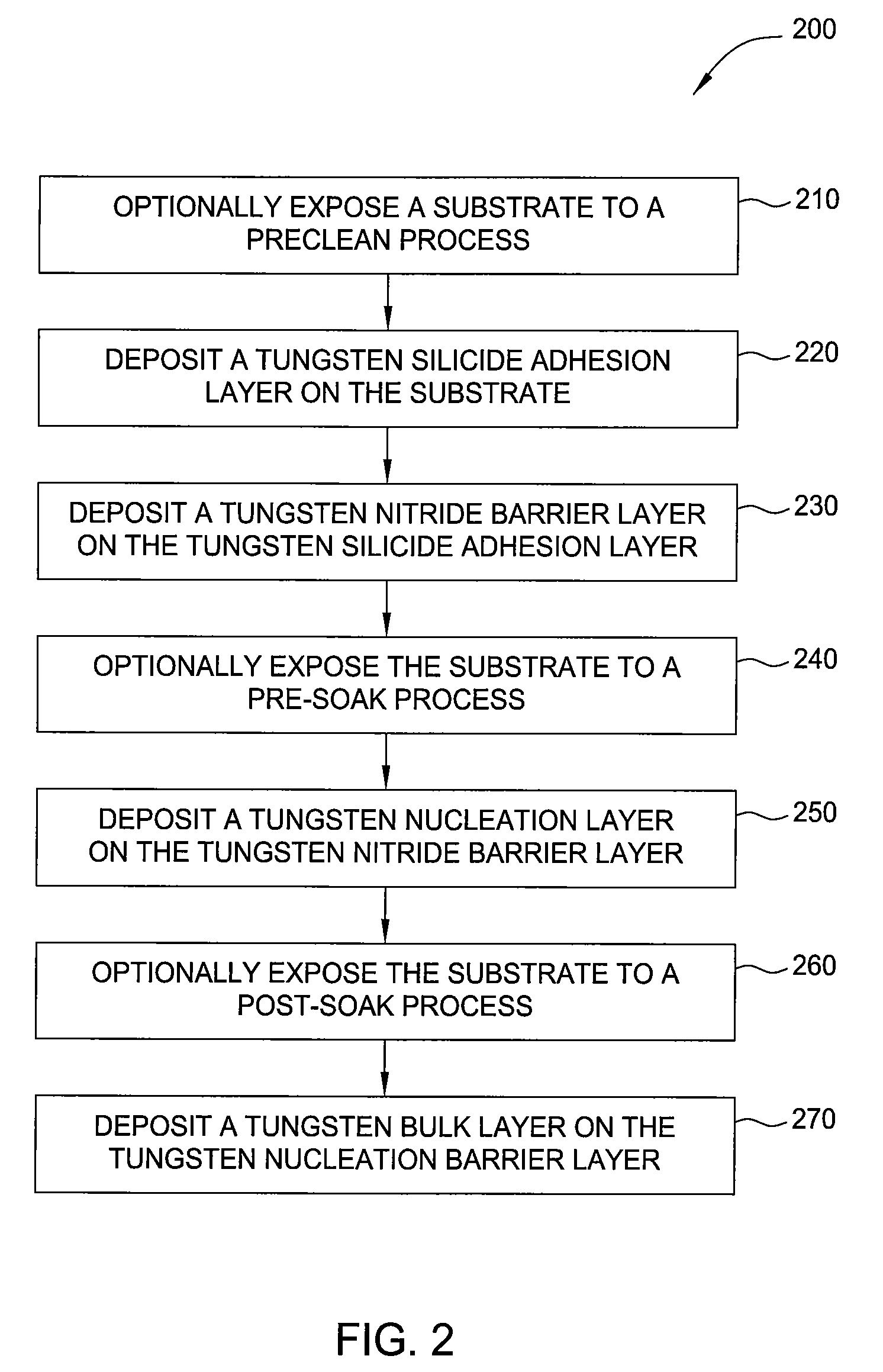
- A vapor deposition process involving intermittent pulses of tungsten precursor gas with a continuous flow of silicon precursor gas, along with soak processes using reducing agents, to form tungsten silicide, nitride, and bulk layers, optimizing the silicon/tungsten precursor flow rate ratio and processing conditions for improved conductivity and uniformity.
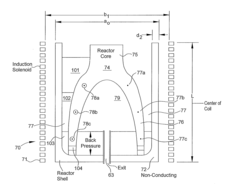
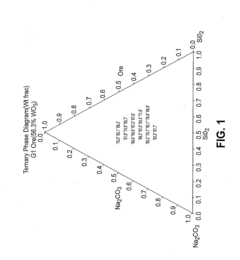
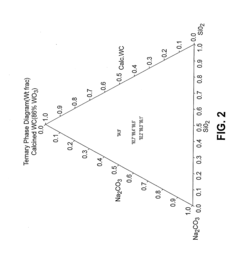
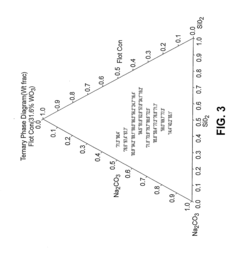
- A process involving the combination of a metal source with an alkali metal salt and silicon dioxide to form a melt flux, allowing for phase separation into a purified alkali metal metalate phase and a silica glass phase, which can be further processed to achieve high purity tungsten metal, utilizing a unique reactor system for continuous operation and efficient heat transfer.
Environmental Impact of Tungsten Processing
Tungsten processing techniques, while essential for various industries, have significant environmental implications that require careful consideration and mitigation strategies. The extraction and refining of tungsten ore can lead to substantial environmental degradation, including soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat destruction. Mining activities often result in the removal of large quantities of earth, altering landscapes and potentially disrupting local ecosystems. The use of heavy machinery in these operations contributes to air pollution through emissions and dust generation.
Water pollution is a major concern in tungsten processing. The beneficiation process, which involves separating tungsten from other minerals, typically requires large volumes of water. This can lead to the contamination of local water sources with heavy metals and other pollutants. Acid mine drainage is another significant issue, occurring when sulfide minerals in the ore are exposed to air and water, creating acidic runoff that can harm aquatic life and render water sources unusable for long periods.
Energy consumption in tungsten processing is another environmental factor to consider. The high temperatures required for smelting and refining tungsten contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. Additionally, the production of tungsten carbide, a common form of processed tungsten, involves the use of cobalt as a binder, which has its own set of environmental concerns related to mining and processing.
Waste management is a critical aspect of tungsten processing's environmental impact. Tailings, the materials left over after the extraction of tungsten from its ore, can contain hazardous substances and pose long-term environmental risks if not properly managed. These tailings can leach toxic compounds into soil and groundwater, potentially affecting both human health and local ecosystems.
To address these environmental challenges, the tungsten industry has been developing more sustainable processing techniques. These include implementing closed-loop water systems to reduce water consumption and prevent contamination, utilizing more efficient extraction methods to minimize waste generation, and exploring cleaner energy sources for processing operations. Some companies are also investigating ways to recycle tungsten from end-of-life products, which could significantly reduce the need for new mining activities and their associated environmental impacts.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of tungsten processing. Many countries have implemented stricter environmental standards for mining and processing operations, requiring companies to conduct thorough environmental impact assessments and implement robust management plans. These regulations often mandate the use of best available technologies to minimize pollution and ensure responsible resource management.
Tungsten Supply Chain Analysis
The tungsten supply chain is a complex network of global actors involved in the extraction, processing, and distribution of this critical metal. The chain begins with mining operations, predominantly located in China, which accounts for over 80% of global tungsten production. Other significant producers include Vietnam, Russia, and Bolivia. The raw ore undergoes initial processing at or near the mining sites to produce tungsten concentrates.
These concentrates are then transported to processing facilities, where they are converted into intermediate products such as ammonium paratungstate (APT) or tungsten oxide. China dominates this stage of the supply chain as well, with a significant portion of global APT production capacity. However, countries like Vietnam, Austria, and the United States also have notable processing capabilities.
The next stage involves the production of tungsten powders and tungsten carbide, which are essential for manufacturing various end products. This stage is more geographically diverse, with major producers in China, Japan, Germany, and the United States. The supply chain then branches out to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, mining, and electronics.
A key challenge in the tungsten supply chain is its vulnerability to disruptions due to the concentration of production in a few countries, particularly China. This has led to efforts to diversify supply sources and develop alternative processing techniques. Recycling has also become an increasingly important part of the supply chain, with tungsten scrap recovery and reprocessing contributing significantly to the global supply.
The tungsten supply chain is further complicated by geopolitical factors and trade policies. Export restrictions, tariffs, and regulations on conflict minerals can impact the flow of tungsten materials across borders. Additionally, environmental concerns and sustainability requirements are shaping the future of tungsten processing and supply chain management.
To enhance tungsten processing techniques, it is crucial to consider the entire supply chain. Improvements in extraction efficiency, processing technologies, and recycling methods can all contribute to a more robust and sustainable tungsten supply. Developing alternative sources and processing capabilities outside of China is also a key strategy for many countries and companies seeking to secure their tungsten supply.