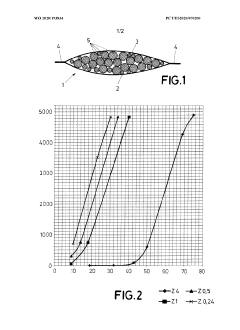
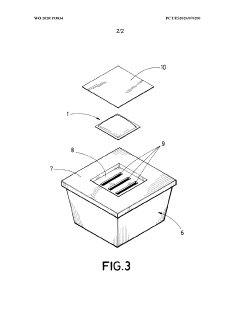
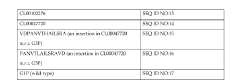
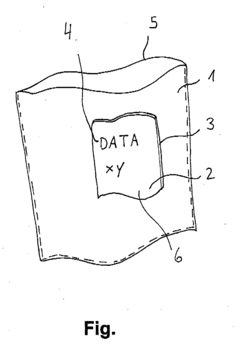
How to Integrate Ethyl Acetate in Sustainable Packaging?
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate in Packaging: Background and Objectives
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has emerged as a promising candidate for sustainable packaging solutions. This colorless liquid, with its fruity odor and low toxicity, has been traditionally used in various industries, including as a solvent in paints and adhesives. However, its potential in the packaging sector has gained significant attention in recent years due to its biodegradable nature and renewable sourcing possibilities.
The evolution of packaging materials has been driven by the growing demand for environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. As global awareness of plastic pollution and its detrimental effects on ecosystems increases, there is a pressing need for innovative, sustainable packaging solutions. Ethyl acetate, derived from ethanol and acetic acid, both of which can be obtained from renewable resources, aligns well with this sustainability trend.
The primary objective of integrating ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging is to develop materials that maintain the functional properties of traditional packaging while significantly reducing environmental impact. This includes creating packaging that is biodegradable, recyclable, and produced from renewable resources. Additionally, the integration aims to address concerns related to food safety, as ethyl acetate is already approved for use in food contact materials in many jurisdictions.
Another key goal is to leverage ethyl acetate's unique properties to enhance packaging performance. Its excellent solvent properties can potentially improve the barrier characteristics of packaging materials, extending product shelf life and reducing food waste. Furthermore, its low toxicity and pleasant odor make it an attractive option for consumer-facing packaging applications.
The technical evolution in this field is expected to focus on developing novel polymer blends and composites that incorporate ethyl acetate as a key component. This may involve creating new manufacturing processes or modifying existing ones to effectively utilize ethyl acetate in packaging production. Research efforts are likely to concentrate on optimizing the material properties, such as strength, flexibility, and barrier performance, while maintaining or improving the sustainability profile.
As the packaging industry continues to seek alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, the integration of ethyl acetate presents an opportunity to address multiple challenges simultaneously. It offers the potential to reduce carbon footprint, minimize waste, and create packaging solutions that align with circular economy principles. The success of this integration could have far-reaching implications for various sectors, from food and beverage to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, potentially reshaping the landscape of sustainable packaging technologies.
The evolution of packaging materials has been driven by the growing demand for environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. As global awareness of plastic pollution and its detrimental effects on ecosystems increases, there is a pressing need for innovative, sustainable packaging solutions. Ethyl acetate, derived from ethanol and acetic acid, both of which can be obtained from renewable resources, aligns well with this sustainability trend.
The primary objective of integrating ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging is to develop materials that maintain the functional properties of traditional packaging while significantly reducing environmental impact. This includes creating packaging that is biodegradable, recyclable, and produced from renewable resources. Additionally, the integration aims to address concerns related to food safety, as ethyl acetate is already approved for use in food contact materials in many jurisdictions.
Another key goal is to leverage ethyl acetate's unique properties to enhance packaging performance. Its excellent solvent properties can potentially improve the barrier characteristics of packaging materials, extending product shelf life and reducing food waste. Furthermore, its low toxicity and pleasant odor make it an attractive option for consumer-facing packaging applications.
The technical evolution in this field is expected to focus on developing novel polymer blends and composites that incorporate ethyl acetate as a key component. This may involve creating new manufacturing processes or modifying existing ones to effectively utilize ethyl acetate in packaging production. Research efforts are likely to concentrate on optimizing the material properties, such as strength, flexibility, and barrier performance, while maintaining or improving the sustainability profile.
As the packaging industry continues to seek alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, the integration of ethyl acetate presents an opportunity to address multiple challenges simultaneously. It offers the potential to reduce carbon footprint, minimize waste, and create packaging solutions that align with circular economy principles. The success of this integration could have far-reaching implications for various sectors, from food and beverage to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, potentially reshaping the landscape of sustainable packaging technologies.
Market Demand for Sustainable Packaging Solutions
The demand for sustainable packaging solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and changing consumer preferences. This trend has created a significant market opportunity for innovative packaging materials that can reduce environmental impact while maintaining product integrity. Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has emerged as a potential candidate for integration into sustainable packaging solutions.
Consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a shift in purchasing behavior, with many customers actively seeking products with eco-friendly packaging. This has prompted major retailers and brands to commit to sustainability goals, including the use of recyclable, biodegradable, or compostable packaging materials. As a result, the global sustainable packaging market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years.
The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown strong interest in sustainable packaging solutions. This sector faces unique challenges in balancing product freshness and safety with environmental considerations. Ethyl acetate's potential applications in food-safe coatings and as a component in biodegradable plastics make it an attractive option for this market segment.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, there is a growing demand for packaging that aligns with the natural and organic product trends. Ethyl acetate's role in creating bio-based plastics and its potential as a safer alternative to certain petrochemical-derived solvents positions it well to meet this market need.
The e-commerce sector, which has seen explosive growth, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, presents another significant market opportunity for sustainable packaging solutions. As online retailers seek to reduce their environmental footprint, there is increasing interest in lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of shipping while minimizing waste.
Regulatory pressures and government initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles are also driving the demand for sustainable packaging. Many countries have implemented or are considering policies that incentivize the use of environmentally friendly packaging materials, creating a favorable market environment for innovations in this space.
However, the market demand for sustainable packaging solutions incorporating ethyl acetate must be balanced against cost considerations. While consumers express a preference for eco-friendly options, price sensitivity remains a factor. Successful integration of ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging will require solutions that are not only environmentally beneficial but also economically viable for both manufacturers and end-users.
Consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a shift in purchasing behavior, with many customers actively seeking products with eco-friendly packaging. This has prompted major retailers and brands to commit to sustainability goals, including the use of recyclable, biodegradable, or compostable packaging materials. As a result, the global sustainable packaging market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years.
The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown strong interest in sustainable packaging solutions. This sector faces unique challenges in balancing product freshness and safety with environmental considerations. Ethyl acetate's potential applications in food-safe coatings and as a component in biodegradable plastics make it an attractive option for this market segment.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, there is a growing demand for packaging that aligns with the natural and organic product trends. Ethyl acetate's role in creating bio-based plastics and its potential as a safer alternative to certain petrochemical-derived solvents positions it well to meet this market need.
The e-commerce sector, which has seen explosive growth, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, presents another significant market opportunity for sustainable packaging solutions. As online retailers seek to reduce their environmental footprint, there is increasing interest in lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of shipping while minimizing waste.
Regulatory pressures and government initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles are also driving the demand for sustainable packaging. Many countries have implemented or are considering policies that incentivize the use of environmentally friendly packaging materials, creating a favorable market environment for innovations in this space.
However, the market demand for sustainable packaging solutions incorporating ethyl acetate must be balanced against cost considerations. While consumers express a preference for eco-friendly options, price sensitivity remains a factor. Successful integration of ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging will require solutions that are not only environmentally beneficial but also economically viable for both manufacturers and end-users.
Current State and Challenges of Ethyl Acetate Integration
The integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging is currently at a nascent stage, with significant potential for growth and innovation. Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has garnered attention in the packaging industry due to its biodegradable nature and potential to replace conventional petroleum-based materials. However, the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging faces several challenges that need to be addressed.
One of the primary obstacles is the cost-effectiveness of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions. While the compound itself is relatively inexpensive, the processes required to incorporate it into packaging materials can be costly. This economic barrier has limited its adoption, particularly among smaller manufacturers who may struggle to justify the initial investment.
Technical challenges also persist in the integration of ethyl acetate into packaging materials. The compound's volatile nature can lead to issues with material stability and shelf life. Researchers and engineers are working to develop methods to stabilize ethyl acetate within packaging structures without compromising its biodegradability or sustainability benefits.
Another significant challenge lies in scaling up production to meet potential demand. Current manufacturing processes for ethyl acetate-based packaging are not yet optimized for large-scale production, which is crucial for widespread adoption in the packaging industry. This scalability issue is closely tied to the need for more efficient and cost-effective production methods.
Regulatory hurdles also present a challenge to the integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging. While the compound is generally recognized as safe for food contact, varying regulations across different regions can complicate its use in global supply chains. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance and market access.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate production is another area of concern. While the end product is biodegradable, the current production methods for ethyl acetate often rely on petrochemical feedstocks. This contradiction poses a challenge to its positioning as a truly sustainable alternative. Research is ongoing to develop more environmentally friendly production methods, such as using bio-based feedstocks.
Despite these challenges, there are promising developments in the field. Innovative companies are exploring novel applications of ethyl acetate in packaging, such as its use in biodegradable coatings and adhesives. These applications show potential for enhancing the sustainability profile of various packaging types without requiring a complete overhaul of existing manufacturing processes.
Collaboration between academic institutions, industry players, and regulatory bodies is crucial to overcoming the current challenges. Interdisciplinary research efforts are focusing on improving the stability of ethyl acetate in packaging materials, developing more sustainable production methods, and creating standardized testing protocols to assess the performance and environmental impact of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions.
One of the primary obstacles is the cost-effectiveness of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions. While the compound itself is relatively inexpensive, the processes required to incorporate it into packaging materials can be costly. This economic barrier has limited its adoption, particularly among smaller manufacturers who may struggle to justify the initial investment.
Technical challenges also persist in the integration of ethyl acetate into packaging materials. The compound's volatile nature can lead to issues with material stability and shelf life. Researchers and engineers are working to develop methods to stabilize ethyl acetate within packaging structures without compromising its biodegradability or sustainability benefits.
Another significant challenge lies in scaling up production to meet potential demand. Current manufacturing processes for ethyl acetate-based packaging are not yet optimized for large-scale production, which is crucial for widespread adoption in the packaging industry. This scalability issue is closely tied to the need for more efficient and cost-effective production methods.
Regulatory hurdles also present a challenge to the integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging. While the compound is generally recognized as safe for food contact, varying regulations across different regions can complicate its use in global supply chains. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance and market access.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate production is another area of concern. While the end product is biodegradable, the current production methods for ethyl acetate often rely on petrochemical feedstocks. This contradiction poses a challenge to its positioning as a truly sustainable alternative. Research is ongoing to develop more environmentally friendly production methods, such as using bio-based feedstocks.
Despite these challenges, there are promising developments in the field. Innovative companies are exploring novel applications of ethyl acetate in packaging, such as its use in biodegradable coatings and adhesives. These applications show potential for enhancing the sustainability profile of various packaging types without requiring a complete overhaul of existing manufacturing processes.
Collaboration between academic institutions, industry players, and regulatory bodies is crucial to overcoming the current challenges. Interdisciplinary research efforts are focusing on improving the stability of ethyl acetate in packaging materials, developing more sustainable production methods, and creating standardized testing protocols to assess the performance and environmental impact of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions.
Existing Ethyl Acetate Integration Methods
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the production of other compounds. Its applications span across industries such as pharmaceuticals, coatings, and specialty chemicals.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various substances, including natural products, pharmaceuticals, and other organic compounds. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction and chromatographic techniques.
- Ethyl acetate as a component in formulations: Ethyl acetate is used as an ingredient in various formulations, including adhesives, coatings, inks, and personal care products. Its properties as a solvent and its compatibility with other ingredients make it valuable in these applications.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, such as solvent extraction, as a reaction medium, and in the production of various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for use in pharmaceuticals, coatings, and other industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science
Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer synthesis, material processing, and the development of novel materials. It is used in the preparation of polymers, as a solvent in material formulations, and in the modification of material properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Research focuses on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for ethyl acetate
Various analytical techniques and methods are developed for the detection, quantification, and characterization of ethyl acetate in different matrices. These methods are crucial for quality control, process monitoring, and research applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Packaging Industry
The integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging is gaining traction in an industry transitioning towards eco-friendly solutions. The market is experiencing moderate growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are making significant strides. Companies like Kuraray Co., Ltd., BASF Corp., and Wacker Chemie AG are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing to develop innovative, sustainable packaging solutions incorporating ethyl acetate. The market is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts, with collaborations between industry leaders and academic institutions like the University of Campinas and Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee contributing to technological advancements.
Kuraray Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kuraray has developed a sustainable packaging solution that incorporates ethyl acetate through its PLANTIC™ bio-based barrier films. This innovative technology uses ethyl acetate as a solvent in the production of high-barrier, compostable films made from renewable resources[7]. The PLANTIC™ films consist of a unique layer structure that combines ethyl acetate-processed starch-based polymers with other biodegradable materials, resulting in packaging with excellent oxygen and moisture barrier properties[8]. Kuraray's approach optimizes the use of ethyl acetate to enhance film formation and improve the overall performance of the packaging. The company has also implemented a solvent recovery system to recycle ethyl acetate, minimizing waste and environmental impact[9].
Strengths: Bio-based and compostable, excellent barrier properties, suitable for food packaging. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, limited heat resistance compared to conventional plastics.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has integrated ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging through its CelFX™ Matrix Technology. This innovative approach uses ethyl acetate as a key component in producing high-performance, recyclable packaging materials. The CelFX™ technology incorporates ethyl acetate-based polymers into a matrix structure, resulting in films with enhanced barrier properties and mechanical strength[10]. Celanese's process optimizes the use of ethyl acetate to improve film formation and increase the overall sustainability of the packaging solution. The company has also developed a closed-loop system for ethyl acetate recovery and reuse, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact[11]. Additionally, Celanese has explored the use of bio-based ethyl acetate in their packaging solutions, further enhancing the sustainability profile of their products[12].
Strengths: High-performance films, recyclable, potential for bio-based raw materials. Weaknesses: Complex production process, may require specialized recycling facilities.
Innovative Approaches to Ethyl Acetate Utilization
Sachet that absorbs ethylene or other gases for containers of fresh produce intended for the retail market
PatentWO2020193834A1
Innovation
- Development of an absorbent sachet with granules composed of a high purity natural clay base impregnated with low concentrations of potassium or sodium permanganate (0.25-2%), optionally mixed with active carbon, to effectively absorb ethylene and other volatiles while minimizing the risk of staining and contamination, and designed for large production volumes and diverse packaging formats.
EVA bag with a stuck-on EVA sticker
PatentInactiveEP2168884A1
Innovation
- A bag made of ethyl vinyl acetate with a captively attached label film, glued using an acrylate adhesive, allowing for reliable melting and ensuring accurate additive assignment in production processes.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment to ensure its viability and long-term sustainability. This assessment begins with an analysis of the raw material sourcing for ethyl acetate production, considering the environmental implications of its extraction or synthesis processes. The carbon footprint associated with these processes must be carefully evaluated, taking into account energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and potential resource depletion.
Furthermore, the manufacturing phase of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials requires scrutiny. This includes examining the energy efficiency of production facilities, water usage, and waste generation. The assessment should also consider the potential for implementing closed-loop systems or circular economy principles to minimize environmental impact during production.
The use phase of ethyl acetate in packaging presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, its potential to enhance the barrier properties of packaging materials may lead to extended product shelf life, reducing food waste and associated environmental burdens. On the other hand, the assessment must address concerns regarding the migration of ethyl acetate into packaged products and its potential effects on human health and the environment.
End-of-life considerations are crucial in this environmental impact assessment. The recyclability and biodegradability of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials should be thoroughly investigated. This includes assessing the compatibility of these materials with existing recycling infrastructure and exploring innovative recycling technologies that may be required. Additionally, the potential for composting or biodegradation in various environmental conditions must be evaluated to understand the long-term ecological impact.
The assessment should also consider the broader ecosystem impacts of ethyl acetate integration in packaging. This includes potential effects on air and water quality, soil health, and biodiversity. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies can be employed to quantify these impacts across the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment must address the potential for ethyl acetate to contribute to the reduction of plastic waste and pollution. By comparing the environmental footprint of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions with conventional plastic packaging, the assessment can provide valuable insights into the overall sustainability benefits and trade-offs associated with this innovative approach to packaging.
Furthermore, the manufacturing phase of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials requires scrutiny. This includes examining the energy efficiency of production facilities, water usage, and waste generation. The assessment should also consider the potential for implementing closed-loop systems or circular economy principles to minimize environmental impact during production.
The use phase of ethyl acetate in packaging presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, its potential to enhance the barrier properties of packaging materials may lead to extended product shelf life, reducing food waste and associated environmental burdens. On the other hand, the assessment must address concerns regarding the migration of ethyl acetate into packaged products and its potential effects on human health and the environment.
End-of-life considerations are crucial in this environmental impact assessment. The recyclability and biodegradability of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials should be thoroughly investigated. This includes assessing the compatibility of these materials with existing recycling infrastructure and exploring innovative recycling technologies that may be required. Additionally, the potential for composting or biodegradation in various environmental conditions must be evaluated to understand the long-term ecological impact.
The assessment should also consider the broader ecosystem impacts of ethyl acetate integration in packaging. This includes potential effects on air and water quality, soil health, and biodiversity. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies can be employed to quantify these impacts across the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment must address the potential for ethyl acetate to contribute to the reduction of plastic waste and pollution. By comparing the environmental footprint of ethyl acetate-based packaging solutions with conventional plastic packaging, the assessment can provide valuable insights into the overall sustainability benefits and trade-offs associated with this innovative approach to packaging.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Considerations
The integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging requires careful consideration of regulatory compliance and safety aspects. Packaging manufacturers must adhere to strict guidelines set by various regulatory bodies to ensure the safety of consumers and the environment.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of ethyl acetate in food packaging materials. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, ethyl acetate is classified as a "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) substance when used as a synthetic flavoring agent and solvent. However, its use in packaging must comply with specific limitations and conditions outlined in FDA regulations.
The European Union (EU) also has stringent regulations concerning the use of chemicals in food contact materials. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated ethyl acetate and established specific migration limits for its use in packaging. Manufacturers must ensure that the migration of ethyl acetate from the packaging into food does not exceed these limits under normal or foreseeable conditions of use.
Safety considerations are paramount when incorporating ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging. Ethyl acetate is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Therefore, proper handling, storage, and processing procedures must be implemented to minimize fire and explosion risks during manufacturing processes. Adequate ventilation systems and fire suppression measures should be in place at production facilities.
Occupational safety is another crucial aspect. Workers involved in the production of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and safety goggles. Regular safety training and risk assessments should be conducted to ensure compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, as ethyl acetate is classified as a VOC. Manufacturers must employ emission control technologies and implement best practices to minimize the release of ethyl acetate into the atmosphere during production and use.
The disposal and recycling of packaging materials containing ethyl acetate must align with waste management regulations. Proper labeling and documentation are essential to ensure that end-users and recycling facilities can handle the materials appropriately. Some jurisdictions may require specific disposal methods or recycling processes for packaging containing certain chemical compounds.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, manufacturers must also consider eco-labeling and certification requirements. Various voluntary certification schemes, such as the EU Ecolabel or the Cradle to Cradle Certified™ Product Standard, may have specific criteria related to the use of chemicals like ethyl acetate in packaging materials.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of ethyl acetate in food packaging materials. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, ethyl acetate is classified as a "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) substance when used as a synthetic flavoring agent and solvent. However, its use in packaging must comply with specific limitations and conditions outlined in FDA regulations.
The European Union (EU) also has stringent regulations concerning the use of chemicals in food contact materials. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated ethyl acetate and established specific migration limits for its use in packaging. Manufacturers must ensure that the migration of ethyl acetate from the packaging into food does not exceed these limits under normal or foreseeable conditions of use.
Safety considerations are paramount when incorporating ethyl acetate into sustainable packaging. Ethyl acetate is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Therefore, proper handling, storage, and processing procedures must be implemented to minimize fire and explosion risks during manufacturing processes. Adequate ventilation systems and fire suppression measures should be in place at production facilities.
Occupational safety is another crucial aspect. Workers involved in the production of ethyl acetate-based packaging materials must be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and safety goggles. Regular safety training and risk assessments should be conducted to ensure compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the integration of ethyl acetate in sustainable packaging. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, as ethyl acetate is classified as a VOC. Manufacturers must employ emission control technologies and implement best practices to minimize the release of ethyl acetate into the atmosphere during production and use.
The disposal and recycling of packaging materials containing ethyl acetate must align with waste management regulations. Proper labeling and documentation are essential to ensure that end-users and recycling facilities can handle the materials appropriately. Some jurisdictions may require specific disposal methods or recycling processes for packaging containing certain chemical compounds.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, manufacturers must also consider eco-labeling and certification requirements. Various voluntary certification schemes, such as the EU Ecolabel or the Cradle to Cradle Certified™ Product Standard, may have specific criteria related to the use of chemicals like ethyl acetate in packaging materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!