How to Leverage Ethyl Acetate Properties in R&D?
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate R&D Objectives
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, presents numerous opportunities for research and development across various industries. The primary objective of leveraging ethyl acetate properties in R&D is to exploit its unique characteristics for innovative applications and process improvements. One key focus area is enhancing the solvent properties of ethyl acetate, which can lead to more efficient extraction and purification processes in pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
Another significant R&D objective is to optimize ethyl acetate's role as a reaction medium. Its moderate polarity and low boiling point make it an attractive solvent for many organic reactions. Researchers aim to develop novel reaction protocols that take advantage of these properties, potentially leading to more sustainable and cost-effective synthetic routes for valuable compounds.
Improving the production methods of ethyl acetate is also a crucial R&D goal. Current efforts are directed towards developing more environmentally friendly and economically viable manufacturing processes. This includes exploring bio-based production routes, which align with the growing demand for sustainable chemical alternatives.
The fragrance and flavor industry represents another important area for ethyl acetate R&D. Given its fruity aroma, researchers are working on new formulations that incorporate ethyl acetate to create unique scent profiles and enhance existing products. This objective extends to the food industry, where ethyl acetate's potential as a natural flavor enhancer is being investigated.
In materials science, leveraging ethyl acetate's properties for advanced coating technologies is a key R&D focus. Scientists are exploring its use in developing high-performance adhesives, paints, and protective coatings with improved durability and environmental resistance. The low toxicity of ethyl acetate makes it an attractive option for eco-friendly coating solutions.
Researchers are also targeting the development of ethyl acetate-based composite materials. By exploiting its solvent properties and compatibility with various polymers, there is potential to create novel composites with enhanced mechanical and chemical properties. This could lead to breakthroughs in lightweight materials for aerospace and automotive applications.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry is exploring ethyl acetate's potential in drug delivery systems. Its ability to form stable emulsions and its relatively low toxicity make it an interesting candidate for developing new drug formulations and controlled-release mechanisms. R&D efforts in this area aim to improve drug efficacy and patient compliance through innovative delivery methods.
Another significant R&D objective is to optimize ethyl acetate's role as a reaction medium. Its moderate polarity and low boiling point make it an attractive solvent for many organic reactions. Researchers aim to develop novel reaction protocols that take advantage of these properties, potentially leading to more sustainable and cost-effective synthetic routes for valuable compounds.
Improving the production methods of ethyl acetate is also a crucial R&D goal. Current efforts are directed towards developing more environmentally friendly and economically viable manufacturing processes. This includes exploring bio-based production routes, which align with the growing demand for sustainable chemical alternatives.
The fragrance and flavor industry represents another important area for ethyl acetate R&D. Given its fruity aroma, researchers are working on new formulations that incorporate ethyl acetate to create unique scent profiles and enhance existing products. This objective extends to the food industry, where ethyl acetate's potential as a natural flavor enhancer is being investigated.
In materials science, leveraging ethyl acetate's properties for advanced coating technologies is a key R&D focus. Scientists are exploring its use in developing high-performance adhesives, paints, and protective coatings with improved durability and environmental resistance. The low toxicity of ethyl acetate makes it an attractive option for eco-friendly coating solutions.
Researchers are also targeting the development of ethyl acetate-based composite materials. By exploiting its solvent properties and compatibility with various polymers, there is potential to create novel composites with enhanced mechanical and chemical properties. This could lead to breakthroughs in lightweight materials for aerospace and automotive applications.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry is exploring ethyl acetate's potential in drug delivery systems. Its ability to form stable emulsions and its relatively low toxicity make it an interesting candidate for developing new drug formulations and controlled-release mechanisms. R&D efforts in this area aim to improve drug efficacy and patient compliance through innovative delivery methods.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Acetate Applications
The global ethyl acetate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key solvent and intermediate in chemical processes, ethyl acetate's market demand is closely tied to industrial production and consumer goods manufacturing. The market size for ethyl acetate was valued at approximately $3.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.9 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of around 5.2% during the forecast period.
The primary drivers of market growth include the expanding packaging industry, increasing demand for flexible packaging solutions, and the rising adoption of eco-friendly products. Ethyl acetate's properties make it an ideal choice for use in adhesives, coatings, and inks, which are essential components in the packaging sector. The food and beverage industry, in particular, has been a significant contributor to the market's expansion, as ethyl acetate is widely used in food packaging materials and as a flavoring agent.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate finds applications in the production of various drugs and as a solvent in drug formulations. The growing pharmaceutical industry, especially in emerging economies, is expected to create new opportunities for ethyl acetate manufacturers. Additionally, the cosmetics and personal care industry utilizes ethyl acetate in nail polish removers and other beauty products, further driving market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the ethyl acetate market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with steady demand from established industries.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and environmental concerns associated with the production and use of ethyl acetate. To address these issues, manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production processes and develop bio-based alternatives. The shift towards sustainable and green chemistry is expected to shape the future of the ethyl acetate market, with bio-ethyl acetate gaining traction as an environmentally friendly option.
In conclusion, the ethyl acetate market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. Companies looking to leverage ethyl acetate properties in R&D should focus on developing sustainable production methods, exploring new applications in emerging industries, and optimizing formulations to meet evolving regulatory standards and consumer preferences. By addressing these market trends and challenges, businesses can position themselves for success in the dynamic ethyl acetate market landscape.
The primary drivers of market growth include the expanding packaging industry, increasing demand for flexible packaging solutions, and the rising adoption of eco-friendly products. Ethyl acetate's properties make it an ideal choice for use in adhesives, coatings, and inks, which are essential components in the packaging sector. The food and beverage industry, in particular, has been a significant contributor to the market's expansion, as ethyl acetate is widely used in food packaging materials and as a flavoring agent.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate finds applications in the production of various drugs and as a solvent in drug formulations. The growing pharmaceutical industry, especially in emerging economies, is expected to create new opportunities for ethyl acetate manufacturers. Additionally, the cosmetics and personal care industry utilizes ethyl acetate in nail polish removers and other beauty products, further driving market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the ethyl acetate market, accounting for the largest share of global consumption. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with steady demand from established industries.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and environmental concerns associated with the production and use of ethyl acetate. To address these issues, manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production processes and develop bio-based alternatives. The shift towards sustainable and green chemistry is expected to shape the future of the ethyl acetate market, with bio-ethyl acetate gaining traction as an environmentally friendly option.
In conclusion, the ethyl acetate market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. Companies looking to leverage ethyl acetate properties in R&D should focus on developing sustainable production methods, exploring new applications in emerging industries, and optimizing formulations to meet evolving regulatory standards and consumer preferences. By addressing these market trends and challenges, businesses can position themselves for success in the dynamic ethyl acetate market landscape.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Acetate Utilization
Despite the widespread use of ethyl acetate in various industries, several challenges persist in its utilization, particularly in research and development contexts. One of the primary issues is the solvent's high volatility, which can lead to rapid evaporation during experimental procedures. This characteristic, while beneficial in some applications, can pose difficulties in maintaining consistent concentrations and may require specialized handling techniques to prevent loss of material.
Another significant challenge is the flammability of ethyl acetate. Its low flash point necessitates stringent safety measures in laboratory settings, including proper storage, handling, and disposal protocols. This can increase operational costs and complexity in R&D processes, especially when scaling up experiments or transitioning to industrial applications.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate usage is also a growing concern. Although it is considered less harmful than many other organic solvents, its production and disposal still contribute to environmental pollution. Researchers are faced with the challenge of developing more sustainable alternatives or improving recycling methods to mitigate these effects.
In the pharmaceutical and food industries, the presence of trace impurities in ethyl acetate can be problematic. Even small amounts of contaminants can affect product quality and safety, necessitating additional purification steps or the use of higher-grade, more expensive ethyl acetate in research and production processes.
The reactivity of ethyl acetate with certain compounds presents both opportunities and challenges in R&D. While this property is exploited in various synthetic reactions, it can also lead to unwanted side reactions or degradation of sensitive materials. Researchers must carefully consider these interactions when designing experiments or formulating products.
Stability issues arise when ethyl acetate is used in long-term storage of research materials or products. Its tendency to hydrolyze in the presence of moisture can alter the composition of stored solutions over time, potentially compromising experimental results or product integrity.
Lastly, the optimization of ethyl acetate recovery and recycling processes remains a challenge in both research and industrial settings. Developing efficient and cost-effective methods for purifying and reusing the solvent could significantly reduce waste and operational costs, but current techniques often require substantial energy input or produce additional waste streams.
Another significant challenge is the flammability of ethyl acetate. Its low flash point necessitates stringent safety measures in laboratory settings, including proper storage, handling, and disposal protocols. This can increase operational costs and complexity in R&D processes, especially when scaling up experiments or transitioning to industrial applications.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate usage is also a growing concern. Although it is considered less harmful than many other organic solvents, its production and disposal still contribute to environmental pollution. Researchers are faced with the challenge of developing more sustainable alternatives or improving recycling methods to mitigate these effects.
In the pharmaceutical and food industries, the presence of trace impurities in ethyl acetate can be problematic. Even small amounts of contaminants can affect product quality and safety, necessitating additional purification steps or the use of higher-grade, more expensive ethyl acetate in research and production processes.
The reactivity of ethyl acetate with certain compounds presents both opportunities and challenges in R&D. While this property is exploited in various synthetic reactions, it can also lead to unwanted side reactions or degradation of sensitive materials. Researchers must carefully consider these interactions when designing experiments or formulating products.
Stability issues arise when ethyl acetate is used in long-term storage of research materials or products. Its tendency to hydrolyze in the presence of moisture can alter the composition of stored solutions over time, potentially compromising experimental results or product integrity.
Lastly, the optimization of ethyl acetate recovery and recycling processes remains a challenge in both research and industrial settings. Developing efficient and cost-effective methods for purifying and reusing the solvent could significantly reduce waste and operational costs, but current techniques often require substantial energy input or produce additional waste streams.
Existing Ethyl Acetate R&D Solutions
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification reactions, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts or reactants to improve yield and purity.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification reactions, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts or reactants to improve yield and purity.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, including as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate in the production of other compounds. Its applications span across industries such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: The use of ethyl acetate in various extraction and separation processes is explored. This includes its role in liquid-liquid extraction, azeotropic distillation, and as a component in separation membranes or adsorbents.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Methods for handling, storing, and disposing of ethyl acetate safely are discussed. This includes techniques for reducing emissions, recovering and recycling ethyl acetate, and developing more environmentally friendly processes involving its use.
- Novel formulations and compositions containing ethyl acetate: Innovative formulations and compositions incorporating ethyl acetate are presented. These include its use in cleaning solutions, coatings, adhesives, and other specialized products where its unique properties are leveraged for improved performance.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds. Its applications span across multiple industries such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various substances. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, azeotropic distillation, and other separation techniques in industrial and laboratory settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ethyl acetate-based formulations and compositions
Formulations and compositions containing ethyl acetate are developed for specific applications. These may include adhesives, coatings, cleaning solutions, or pharmaceutical preparations where ethyl acetate serves as a key component or solvent.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate use
Research and development efforts focus on addressing environmental and safety concerns related to ethyl acetate use. This includes developing greener production methods, improving handling and storage practices, and exploring alternatives in certain applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to exceed $3 billion by 2025. The competitive landscape is characterized by established players like Celanese International Corp., Eastman Chemical Co., and SABIC, alongside emerging companies such as Viridis Chemical LLC. Technological maturity varies, with major corporations focusing on process optimization and sustainability, while research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Nanjing Normal University are exploring novel applications and production methods. The industry is seeing a shift towards bio-based ethyl acetate, with companies like Viridis Chemical leading in renewable production. Collaborations between industry and academia are driving innovation, as seen in partnerships between universities and chemical manufacturers.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese leverages ethyl acetate properties in R&D through innovative solvent applications. They have developed a proprietary process for producing high-purity ethyl acetate using advanced catalysts and reactive distillation technology[1]. This method results in a product with 99.9% purity, suitable for electronic and pharmaceutical applications. Celanese also focuses on sustainable production, implementing a closed-loop system that recycles byproducts and reduces waste[2]. Their R&D efforts extend to exploring ethyl acetate as a green solvent in various chemical processes, particularly in the synthesis of polymers and coatings[3].
Strengths: High-purity product, sustainable production methods, versatile applications in multiple industries. Weaknesses: Dependence on acetate market fluctuations, potential competition from bio-based alternatives.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical Co. utilizes ethyl acetate properties in their R&D efforts, focusing on sustainable solutions and performance materials. They have developed a novel process for producing ethyl acetate from bioethanol, reducing carbon footprint by up to 50% compared to traditional methods[4]. Eastman's research also explores the use of ethyl acetate as a key component in advanced coating formulations, particularly for automotive and aerospace applications[5]. Their proprietary solvent systems, incorporating ethyl acetate, have shown improved performance in paint stripping and industrial cleaning processes, reducing environmental impact and improving worker safety[6].
Strengths: Bio-based production capabilities, diverse application portfolio, strong focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for bio-based ethyl acetate, potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
Innovative Ethyl Acetate Properties Exploitation
Ethyl Acetate Production
PatentActiveUS20120178962A1
Innovation
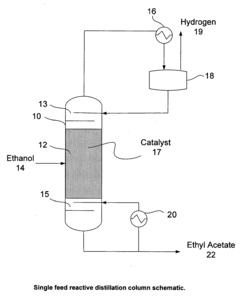
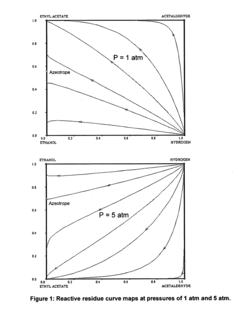
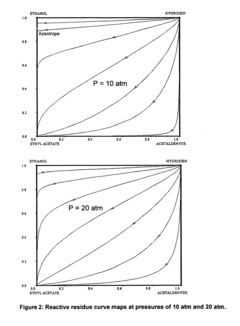
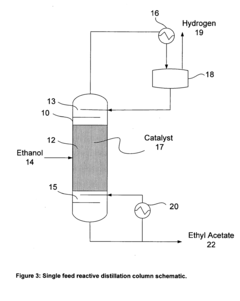
- A reactive distillation process using a single reactive distillation column where ethanol is dehydrogenated over a catalyst to produce ethyl acetate and hydrogen, with optional hydrogenation of byproducts to simplify separation and achieve high purity ethyl acetate, utilizing catalysts like copper, ruthenium, and platinum supported on materials like carbon or alumina.
Process of low energy consumption for preparing a carboxylic acid ester
PatentWO2012123279A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of ethyl alcohol with acetic acid in the presence of a solid acid catalyst, using a reactive distillation system with a centrally placed reaction zone between upper and lower separation zones, optimizing the molar ratio of acetic acid to ethyl alcohol between 0.85 and 0.97, and controlling the reflux ratio between 1.0 and 1.5, significantly reduces energy costs and minimizes acetic acid at the column bottom.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl acetate in R&D applications is a critical consideration for sustainable development and responsible innovation. Ethyl acetate, while widely used in various industries, poses potential risks to the environment that must be carefully evaluated and mitigated.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its volatile organic compound (VOC) status. When released into the atmosphere, ethyl acetate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Research and development facilities must implement proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies to minimize the release of ethyl acetate vapors into the environment.
Water pollution is another significant environmental risk associated with ethyl acetate usage in R&D settings. Although ethyl acetate has limited solubility in water, improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies. This can adversely affect aquatic ecosystems and potentially impact drinking water sources. Implementing robust waste management protocols and spill prevention measures is essential to mitigate these risks.
The production and disposal of ethyl acetate also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process typically involves the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, which requires energy inputs and may generate byproducts. Sustainable production methods, such as using renewable feedstocks or optimizing reaction conditions, should be explored to reduce the overall environmental impact.
Biodegradability is a positive aspect of ethyl acetate's environmental profile. Under aerobic conditions, ethyl acetate can be broken down by microorganisms into harmless components, primarily ethanol and acetic acid. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, and high concentrations may still pose short-term risks to ecosystems.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies should be conducted to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of ethyl acetate throughout its entire life cycle, from production to disposal. This approach can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable practices in R&D applications.
To leverage ethyl acetate properties in R&D while minimizing environmental impact, several strategies can be employed. These include implementing closed-loop systems to recover and recycle ethyl acetate, exploring alternative green solvents for specific applications, and optimizing processes to reduce overall solvent consumption. Additionally, investing in advanced treatment technologies for ethyl acetate-containing waste streams can significantly reduce environmental risks associated with disposal.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its volatile organic compound (VOC) status. When released into the atmosphere, ethyl acetate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Research and development facilities must implement proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies to minimize the release of ethyl acetate vapors into the environment.
Water pollution is another significant environmental risk associated with ethyl acetate usage in R&D settings. Although ethyl acetate has limited solubility in water, improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies. This can adversely affect aquatic ecosystems and potentially impact drinking water sources. Implementing robust waste management protocols and spill prevention measures is essential to mitigate these risks.
The production and disposal of ethyl acetate also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process typically involves the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, which requires energy inputs and may generate byproducts. Sustainable production methods, such as using renewable feedstocks or optimizing reaction conditions, should be explored to reduce the overall environmental impact.
Biodegradability is a positive aspect of ethyl acetate's environmental profile. Under aerobic conditions, ethyl acetate can be broken down by microorganisms into harmless components, primarily ethanol and acetic acid. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, and high concentrations may still pose short-term risks to ecosystems.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies should be conducted to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of ethyl acetate throughout its entire life cycle, from production to disposal. This approach can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable practices in R&D applications.
To leverage ethyl acetate properties in R&D while minimizing environmental impact, several strategies can be employed. These include implementing closed-loop systems to recover and recycle ethyl acetate, exploring alternative green solvents for specific applications, and optimizing processes to reduce overall solvent consumption. Additionally, investing in advanced treatment technologies for ethyl acetate-containing waste streams can significantly reduce environmental risks associated with disposal.
Intellectual Property Landscape
The intellectual property landscape surrounding ethyl acetate in R&D is characterized by a diverse array of patents and innovations across multiple industries. A significant portion of these patents focus on novel synthesis methods, aiming to improve the efficiency and sustainability of ethyl acetate production. For instance, several patents describe catalytic processes that reduce energy consumption and increase yield, addressing both economic and environmental concerns.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's properties as a solvent have led to numerous patents for drug formulation and delivery systems. These innovations often leverage ethyl acetate's ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, making it valuable in the development of controlled-release medications and improved bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The electronics industry has also contributed to the ethyl acetate IP landscape, particularly in the realm of semiconductor manufacturing. Patents in this area frequently involve the use of ethyl acetate in cleaning and etching processes, taking advantage of its low toxicity and high solvency power for removing organic residues from sensitive electronic components.
In the field of materials science, there is a growing trend of patents related to the use of ethyl acetate in the production of advanced polymers and composites. These innovations often exploit ethyl acetate's role as a reaction medium or as a key component in polymer synthesis, leading to materials with enhanced properties for applications in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods industries.
The food and beverage sector has seen a surge in patents leveraging ethyl acetate's natural occurrence in fruits and its GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status. These patents often focus on extraction techniques for natural flavors and fragrances, as well as methods for enhancing the shelf life of food products through ethyl acetate-based preservative systems.
Notably, there is an emerging trend in green chemistry patents that utilize ethyl acetate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional solvents. These innovations span various industries and often highlight ethyl acetate's biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to other organic solvents.
The geographical distribution of ethyl acetate-related patents shows a concentration in major chemical and pharmaceutical hubs, with significant activity in the United States, Europe, and Asia. Recent years have seen an increase in patent filings from emerging economies, particularly in applications related to agricultural and food processing technologies.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's properties as a solvent have led to numerous patents for drug formulation and delivery systems. These innovations often leverage ethyl acetate's ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, making it valuable in the development of controlled-release medications and improved bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The electronics industry has also contributed to the ethyl acetate IP landscape, particularly in the realm of semiconductor manufacturing. Patents in this area frequently involve the use of ethyl acetate in cleaning and etching processes, taking advantage of its low toxicity and high solvency power for removing organic residues from sensitive electronic components.
In the field of materials science, there is a growing trend of patents related to the use of ethyl acetate in the production of advanced polymers and composites. These innovations often exploit ethyl acetate's role as a reaction medium or as a key component in polymer synthesis, leading to materials with enhanced properties for applications in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods industries.
The food and beverage sector has seen a surge in patents leveraging ethyl acetate's natural occurrence in fruits and its GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status. These patents often focus on extraction techniques for natural flavors and fragrances, as well as methods for enhancing the shelf life of food products through ethyl acetate-based preservative systems.
Notably, there is an emerging trend in green chemistry patents that utilize ethyl acetate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional solvents. These innovations span various industries and often highlight ethyl acetate's biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to other organic solvents.
The geographical distribution of ethyl acetate-related patents shows a concentration in major chemical and pharmaceutical hubs, with significant activity in the United States, Europe, and Asia. Recent years have seen an increase in patent filings from emerging economies, particularly in applications related to agricultural and food processing technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!