How to Optimize Wankel Engine RPM Performance?
AUG 25, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Development History and Performance Objectives
The Wankel engine, a revolutionary rotary internal combustion engine design, was first conceived by German engineer Felix Wankel in the 1920s and developed into a working prototype by 1957. Unlike conventional reciprocating piston engines, the Wankel engine utilizes a triangular rotor that revolves within an epitrochoid-shaped housing, creating compression and expansion spaces through its motion. This unique design offers several inherent advantages for high-RPM performance, including fewer moving parts, smoother operation due to the absence of reciprocating mass, and a higher power-to-weight ratio.
The historical development of Wankel engine technology has been marked by significant milestones. After NSU obtained the first running prototype in 1957, they licensed the technology to various manufacturers including Mazda, which became the most committed developer of Wankel engines. Mazda's first rotary-powered production car, the Cosmo Sport, debuted in 1967, followed by a series of successful rotary vehicles including the iconic RX-7 and RX-8 sports cars. These vehicles demonstrated the Wankel engine's capability to achieve high RPM performance, with some racing variants exceeding 10,000 RPM.
Throughout its evolution, the Wankel engine has faced persistent technical challenges affecting RPM optimization. These include apex seal durability, rotor housing distortion at high temperatures, and combustion chamber shape inefficiencies. Early designs suffered from premature apex seal wear and poor fuel efficiency, particularly at high RPMs where thermal expansion created sealing issues. The oil crisis of the 1970s further highlighted the fuel consumption disadvantages of rotary engines, leading many manufacturers to abandon the technology.
Despite these challenges, continuous engineering improvements have been made to enhance Wankel engine RPM performance. Advancements in materials science have yielded more durable apex seals using ceramic composites and improved coating technologies. Cooling system innovations have addressed thermal management issues, while electronic engine management systems have optimized fuel delivery and ignition timing across the RPM range. Mazda's RENESIS engine, introduced in the RX-8, represented a significant leap forward with side intake and exhaust ports that improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
The performance objectives for modern Wankel engine development focus on several key areas: increasing thermal efficiency to compete with conventional engines, extending apex seal longevity to match piston ring durability, optimizing combustion chamber geometry to reduce emissions, and enhancing lubrication systems to maintain seal integrity at extreme RPMs. Additionally, researchers are exploring hybrid rotary systems and alternative fuels to address efficiency concerns while capitalizing on the Wankel's inherent high-RPM capabilities and compact design.
The historical development of Wankel engine technology has been marked by significant milestones. After NSU obtained the first running prototype in 1957, they licensed the technology to various manufacturers including Mazda, which became the most committed developer of Wankel engines. Mazda's first rotary-powered production car, the Cosmo Sport, debuted in 1967, followed by a series of successful rotary vehicles including the iconic RX-7 and RX-8 sports cars. These vehicles demonstrated the Wankel engine's capability to achieve high RPM performance, with some racing variants exceeding 10,000 RPM.
Throughout its evolution, the Wankel engine has faced persistent technical challenges affecting RPM optimization. These include apex seal durability, rotor housing distortion at high temperatures, and combustion chamber shape inefficiencies. Early designs suffered from premature apex seal wear and poor fuel efficiency, particularly at high RPMs where thermal expansion created sealing issues. The oil crisis of the 1970s further highlighted the fuel consumption disadvantages of rotary engines, leading many manufacturers to abandon the technology.
Despite these challenges, continuous engineering improvements have been made to enhance Wankel engine RPM performance. Advancements in materials science have yielded more durable apex seals using ceramic composites and improved coating technologies. Cooling system innovations have addressed thermal management issues, while electronic engine management systems have optimized fuel delivery and ignition timing across the RPM range. Mazda's RENESIS engine, introduced in the RX-8, represented a significant leap forward with side intake and exhaust ports that improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
The performance objectives for modern Wankel engine development focus on several key areas: increasing thermal efficiency to compete with conventional engines, extending apex seal longevity to match piston ring durability, optimizing combustion chamber geometry to reduce emissions, and enhancing lubrication systems to maintain seal integrity at extreme RPMs. Additionally, researchers are exploring hybrid rotary systems and alternative fuels to address efficiency concerns while capitalizing on the Wankel's inherent high-RPM capabilities and compact design.
Market Analysis for High-RPM Rotary Engine Applications
The Wankel rotary engine market for high-RPM applications represents a specialized but significant segment within the broader automotive and powertrain industry. Current market analysis indicates that while rotary engines occupy a niche position, their unique characteristics create distinct opportunities in sectors where high-RPM performance is valued. The global market for high-performance engines is estimated at $12.5 billion, with rotary engines capturing approximately 3% of this specialized market.
Racing and motorsport applications continue to drive significant demand for high-RPM rotary engines. The lightweight design and compact form factor make these engines particularly attractive for competitive environments where power-to-weight ratio is critical. Market research shows the motorsport segment growing at 4.7% annually, with rotary applications experiencing even stronger growth at 5.9% due to their performance characteristics at high RPM ranges.
Aviation represents another promising market segment, particularly in the ultralight and experimental aircraft categories. The rotary engine's smooth operation at high RPMs and favorable power-to-weight ratio align well with aviation requirements. This segment is projected to grow at 6.2% annually through 2028, outpacing conventional piston engine growth in the same category.
Consumer demand for high-performance vehicles with distinctive characteristics has created a persistent niche market for rotary-powered sports cars. While mainstream automotive manufacturers have largely moved away from rotary technology due to emissions challenges, specialized manufacturers and aftermarket conversion companies report steady demand growth of 3.8% annually for high-RPM rotary applications in premium sports vehicles.
Marine applications represent an emerging opportunity, with high-RPM rotary engines finding application in personal watercraft and specialized racing boats. This segment has shown 7.1% growth over the past three years, albeit from a relatively small base. The smooth power delivery and compact design make rotary engines particularly suitable for certain marine applications where space constraints and power density are important considerations.
Market barriers include emissions regulations, which have become increasingly stringent across most developed markets. This has limited mass-market adoption despite the performance advantages at high RPM. Additionally, fuel efficiency concerns have restricted broader market penetration, though this is less significant in specialized high-performance applications where efficiency is secondary to power delivery characteristics.
Consumer awareness and technical familiarity with rotary technology remain limited outside enthusiast circles, creating marketing challenges for manufacturers. However, this also presents an opportunity for differentiation in crowded high-performance markets where distinctive technology can command premium pricing. Market research indicates consumers are willing to pay 15-20% premiums for vehicles with unique powertrain technologies that deliver exceptional high-RPM performance characteristics.
Racing and motorsport applications continue to drive significant demand for high-RPM rotary engines. The lightweight design and compact form factor make these engines particularly attractive for competitive environments where power-to-weight ratio is critical. Market research shows the motorsport segment growing at 4.7% annually, with rotary applications experiencing even stronger growth at 5.9% due to their performance characteristics at high RPM ranges.
Aviation represents another promising market segment, particularly in the ultralight and experimental aircraft categories. The rotary engine's smooth operation at high RPMs and favorable power-to-weight ratio align well with aviation requirements. This segment is projected to grow at 6.2% annually through 2028, outpacing conventional piston engine growth in the same category.
Consumer demand for high-performance vehicles with distinctive characteristics has created a persistent niche market for rotary-powered sports cars. While mainstream automotive manufacturers have largely moved away from rotary technology due to emissions challenges, specialized manufacturers and aftermarket conversion companies report steady demand growth of 3.8% annually for high-RPM rotary applications in premium sports vehicles.
Marine applications represent an emerging opportunity, with high-RPM rotary engines finding application in personal watercraft and specialized racing boats. This segment has shown 7.1% growth over the past three years, albeit from a relatively small base. The smooth power delivery and compact design make rotary engines particularly suitable for certain marine applications where space constraints and power density are important considerations.
Market barriers include emissions regulations, which have become increasingly stringent across most developed markets. This has limited mass-market adoption despite the performance advantages at high RPM. Additionally, fuel efficiency concerns have restricted broader market penetration, though this is less significant in specialized high-performance applications where efficiency is secondary to power delivery characteristics.
Consumer awareness and technical familiarity with rotary technology remain limited outside enthusiast circles, creating marketing challenges for manufacturers. However, this also presents an opportunity for differentiation in crowded high-performance markets where distinctive technology can command premium pricing. Market research indicates consumers are willing to pay 15-20% premiums for vehicles with unique powertrain technologies that deliver exceptional high-RPM performance characteristics.
Current Limitations and Technical Challenges in Wankel RPM Optimization
Despite significant advancements in Wankel rotary engine technology since its inception in the 1950s, several persistent limitations continue to challenge RPM optimization efforts. The fundamental design of the Wankel engine, while elegant in its simplicity, creates inherent constraints that affect high-RPM performance. The triangular rotor design creates varying compression ratios throughout the rotation cycle, leading to combustion inefficiencies that become more pronounced at higher RPM ranges.
Sealing technology remains perhaps the most critical challenge in Wankel RPM optimization. The apex seals, which maintain compression between the rotor and housing, experience extreme thermal and mechanical stress at high RPMs. Current materials struggle to maintain effective sealing while withstanding these conditions, resulting in increased friction, wear, and eventual performance degradation. This sealing issue directly impacts compression efficiency and power output at elevated RPM levels.
Thermal management presents another significant obstacle. The elongated combustion chamber geometry creates uneven heat distribution, with concentrated hot spots that can lead to thermal distortion of the housing at sustained high RPMs. This thermal expansion affects the critical tolerances between the rotor and housing, further compromising seal effectiveness and overall efficiency. Current cooling systems struggle to adequately address these thermal gradients, particularly in high-performance applications.
Lubrication systems face unique challenges in the Wankel architecture. The oil must effectively lubricate the apex seals and bearings while withstanding high temperatures and avoiding contamination of the combustion chamber. At higher RPMs, oil consumption typically increases, creating both environmental concerns and potential carbon buildup that can further degrade performance over time.
The eccentric shaft and bearing system that translates the rotor's motion into rotational output faces mechanical limitations at extreme RPMs. Bearing design and durability become critical factors, as does the balance of the eccentric mechanism. Vibration and harmonics at high RPMs can accelerate wear and potentially lead to catastrophic failure if not properly managed.
Fuel delivery and mixture formation present additional challenges at high RPMs. The unique geometry and flow characteristics of the Wankel engine require precisely timed and directed fuel injection to achieve optimal combustion. As RPM increases, the window for effective mixture formation narrows, often resulting in incomplete combustion, increased emissions, and reduced efficiency.
Electronic control systems for Wankel engines lag behind their piston counterparts in sophistication and adaptability. The complex three-dimensional flame propagation patterns and varying combustion conditions throughout the RPM range require advanced modeling and control algorithms that are still being developed and refined by researchers and manufacturers.
Sealing technology remains perhaps the most critical challenge in Wankel RPM optimization. The apex seals, which maintain compression between the rotor and housing, experience extreme thermal and mechanical stress at high RPMs. Current materials struggle to maintain effective sealing while withstanding these conditions, resulting in increased friction, wear, and eventual performance degradation. This sealing issue directly impacts compression efficiency and power output at elevated RPM levels.
Thermal management presents another significant obstacle. The elongated combustion chamber geometry creates uneven heat distribution, with concentrated hot spots that can lead to thermal distortion of the housing at sustained high RPMs. This thermal expansion affects the critical tolerances between the rotor and housing, further compromising seal effectiveness and overall efficiency. Current cooling systems struggle to adequately address these thermal gradients, particularly in high-performance applications.
Lubrication systems face unique challenges in the Wankel architecture. The oil must effectively lubricate the apex seals and bearings while withstanding high temperatures and avoiding contamination of the combustion chamber. At higher RPMs, oil consumption typically increases, creating both environmental concerns and potential carbon buildup that can further degrade performance over time.
The eccentric shaft and bearing system that translates the rotor's motion into rotational output faces mechanical limitations at extreme RPMs. Bearing design and durability become critical factors, as does the balance of the eccentric mechanism. Vibration and harmonics at high RPMs can accelerate wear and potentially lead to catastrophic failure if not properly managed.
Fuel delivery and mixture formation present additional challenges at high RPMs. The unique geometry and flow characteristics of the Wankel engine require precisely timed and directed fuel injection to achieve optimal combustion. As RPM increases, the window for effective mixture formation narrows, often resulting in incomplete combustion, increased emissions, and reduced efficiency.
Electronic control systems for Wankel engines lag behind their piston counterparts in sophistication and adaptability. The complex three-dimensional flame propagation patterns and varying combustion conditions throughout the RPM range require advanced modeling and control algorithms that are still being developed and refined by researchers and manufacturers.
Current RPM Enhancement Solutions and Methodologies
01 High RPM performance characteristics of Wankel engines
Wankel engines are known for their ability to achieve high RPM performance due to their rotary design which eliminates reciprocating mass. This allows for smoother operation at high speeds with less vibration compared to conventional piston engines. The rotary design enables Wankel engines to reach higher operational RPMs, making them suitable for applications requiring high-speed performance. The unique combustion cycle of Wankel engines contributes to their capability to maintain stable performance at elevated RPM ranges.- High RPM capabilities and performance characteristics: Wankel engines are known for their ability to achieve high RPM levels due to their rotary design, which eliminates the reciprocating motion found in conventional piston engines. This design allows for smoother operation at high speeds, reduced vibration, and better power-to-weight ratio. The rotary motion enables Wankel engines to reach higher RPM thresholds than traditional internal combustion engines, contributing to their performance advantages in certain applications.
- RPM monitoring and control systems: Advanced monitoring and control systems are essential for optimizing Wankel engine RPM performance. These systems include electronic control units that regulate fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture based on RPM readings. Sensors throughout the engine provide real-time data to ensure optimal performance across various operating conditions. Implementing sophisticated RPM control mechanisms helps maintain engine efficiency, prevent overrevving, and extend engine lifespan while maximizing power output.
- Rotor design improvements for RPM optimization: Innovations in rotor design significantly impact the RPM performance of Wankel engines. Modified rotor geometries, improved apex seal configurations, and advanced materials contribute to reduced friction and enhanced sealing at high rotational speeds. Optimized rotor profiles allow for better combustion chamber shaping, improving thermal efficiency and power delivery across the RPM range. These design improvements enable more reliable operation at elevated RPM levels while addressing traditional challenges associated with rotary engines.
- Cooling and lubrication systems for high-RPM operation: Specialized cooling and lubrication systems are crucial for sustaining high-RPM performance in Wankel engines. Enhanced oil delivery mechanisms ensure proper lubrication of apex seals and bearings during high-speed operation. Advanced cooling solutions address the thermal challenges associated with the concentrated combustion area of rotary engines. These systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures, prevent overheating, and ensure consistent performance during extended high-RPM operation.
- Electronic and hybrid integration for RPM management: Integration of electronic systems and hybrid technologies with Wankel engines offers new approaches to RPM management and performance enhancement. Electronic control units provide precise management of engine parameters based on operating conditions. Hybrid configurations combine rotary engines with electric motors to optimize the RPM range where each power source operates most efficiently. These integrations allow for improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced torque characteristics across the entire RPM band.
02 RPM monitoring and control systems for Wankel engines
Advanced monitoring and control systems have been developed specifically for Wankel engines to optimize their RPM performance. These systems include electronic control units that regulate fuel injection, ignition timing, and air intake based on real-time RPM data. Sensors throughout the engine provide feedback to ensure optimal performance across various RPM ranges. Some systems incorporate adaptive algorithms that learn from operational patterns to further enhance RPM stability and response. These monitoring solutions help maintain ideal operating conditions while preventing damage from excessive RPM.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mechanical improvements for RPM enhancement
Various mechanical innovations have been developed to enhance the RPM performance of Wankel engines. These include redesigned rotor housings with improved sealing systems that reduce friction and maintain compression at high rotational speeds. Advanced materials for rotors and housings provide better thermal management and reduced weight, allowing for higher operational RPMs. Modified apex seal designs help maintain compression while reducing friction at elevated speeds. Optimized intake and exhaust port configurations improve gas flow dynamics, particularly at high RPM ranges.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cooling and lubrication systems for high-RPM operation
Specialized cooling and lubrication systems have been developed to support Wankel engines operating at high RPMs. Enhanced oil delivery systems ensure proper lubrication of critical components during high-speed operation. Advanced cooling channels and heat management solutions prevent overheating when the engine is running at elevated RPMs for extended periods. Some designs incorporate targeted cooling for specific high-stress areas of the engine. These systems are crucial for maintaining reliability and longevity while allowing the Wankel engine to perform at high rotational speeds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Performance optimization across RPM ranges
Technologies have been developed to optimize Wankel engine performance across various RPM ranges rather than just at peak RPM. Variable intake systems adjust airflow characteristics based on engine speed to maintain torque throughout the RPM band. Electronic ignition timing systems that adapt to different RPM levels ensure optimal combustion efficiency. Fuel delivery systems with RPM-dependent mapping provide appropriate fuel-air mixtures at different rotational speeds. These innovations help Wankel engines deliver more consistent power output and improved efficiency across their entire operational RPM range.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Rotary Engine Development
The Wankel engine RPM performance optimization market is in a growth phase, with increasing interest from both automotive and aerospace sectors. The market size is expanding as companies seek more efficient rotary engine solutions for various applications. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with significant innovation potential. Key players include Audi AG, which has historical experience with rotary engines, and specialized entities like Shaanxi New Year Power Technology Group, which has made breakthroughs addressing traditional Wankel engine limitations. Academic institutions including Northwestern Polytechnical University, Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, and Beihang University are contributing significant research. The collaboration between industry players like Chery Automobile and academic institutions indicates growing technological convergence and commercialization opportunities in high-RPM rotary engine applications.
Pratt & Whitney Canada Corp.
Technical Solution: Pratt & Whitney Canada has leveraged their extensive aerospace engineering expertise to develop advanced Wankel engine RPM optimization technologies. Their approach centers on precision-balanced rotors manufactured using aerospace-grade materials with optimized mass distribution to minimize vibration at extremely high RPM ranges. P&WC engineers implemented a proprietary apex seal design utilizing carbon-ceramic composite materials with specialized coating technology that maintains sealing integrity while significantly reducing friction across all RPM ranges. Their system incorporates active cooling oil jets that adjust flow rates based on real-time RPM data, targeting specific housing areas prone to thermal distortion during high-speed operation. Additionally, P&WC developed an advanced electronic engine management system that utilizes predictive algorithms to optimize ignition timing and fuel delivery based on RPM acceleration patterns rather than just current RPM values. This system incorporates multiple sensors monitoring housing temperatures, rotor position, and combustion pressure to make microsecond adjustments to operating parameters specifically optimized for different RPM bands.
Strengths: Aerospace-derived materials and manufacturing techniques enable exceptional balance and durability at extreme RPM ranges. Advanced carbon-ceramic apex seals significantly reduce friction while maintaining compression. Weaknesses: Specialized materials and precision manufacturing requirements result in substantially higher production costs. The technology is primarily focused on specialized applications rather than mass-market implementation.
AUDI AG
Technical Solution: Audi has developed advanced Wankel engine RPM optimization through their e-tron rotary range extender program. Their approach focuses on variable apex seal technology that dynamically adjusts pressure against the housing based on RPM ranges, reducing friction at high speeds while maintaining compression. Audi engineers implemented a dual-stage intake system with electronically controlled valves that optimize air-fuel mixture delivery across different RPM bands. The system transitions between efficiency-focused low-RPM operation and performance-oriented high-RPM combustion cycles. Additionally, Audi's thermal management system uses targeted cooling channels and ceramic apex seals to maintain optimal operating temperatures even at sustained high RPM, preventing housing distortion that typically limits Wankel performance. Their electronic control unit continuously adjusts ignition timing based on a comprehensive RPM-specific map to maximize power output while minimizing fuel consumption.
Strengths: Superior thermal management allows sustained high-RPM operation without performance degradation. Variable apex seal technology significantly reduces friction losses at high RPM. Weaknesses: System complexity increases manufacturing costs and potential maintenance issues. The technology remains primarily focused on range extender applications rather than primary propulsion.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Rotary Engine Performance
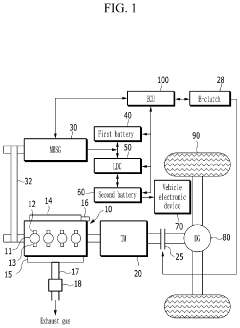
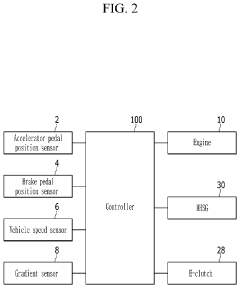
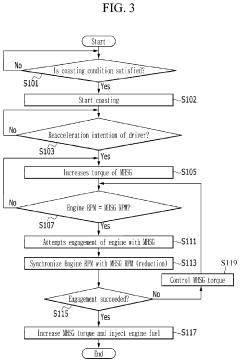
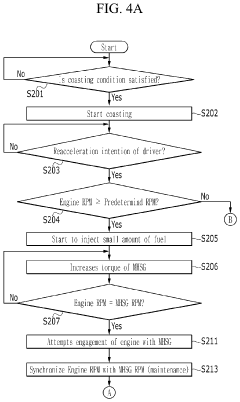
Control method and apparatus for mild hybrid electric vehicle
PatentInactiveUS10821818B2
Innovation
- A control method that synchronizes the RPM of the MHSG with the engine for a predetermined period before reacceleration, adjusting torque to match the engine's RPM and ensuring smooth engagement, thereby reducing rapid RPM variations and providing a stable driving experience.
Engine RPM compensating method for RPM drop
PatentInactiveKR1019980017320A
Innovation
- A method involving a control unit that subdivides engine speed bands and uses a microcomputer to detect and store engine speed changes, controlling the amount of air flowing into the throttle valve based on these stored signals to compensate for speed drops or increases.
Thermal Management Strategies for High-RPM Rotary Operations
Thermal management represents a critical challenge in optimizing Wankel engine RPM performance, particularly during high-speed operations where heat generation increases exponentially. The rotary engine's unique geometry creates distinct thermal patterns that differ significantly from conventional piston engines, requiring specialized cooling strategies to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
The primary thermal challenge in high-RPM rotary operations stems from the concentrated heat generation at the rotor housing, particularly near the combustion area. Temperature differentials between the rotor housing, side housings, and eccentric shaft can reach up to 200°C during sustained high-RPM operation, creating thermal expansion issues that affect apex seal integrity and combustion chamber geometry.
Advanced cooling jacket designs have emerged as a leading solution, with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling enabling precision-engineered coolant pathways that target high-temperature zones. Recent developments include variable-flow cooling systems that adjust coolant distribution based on real-time temperature monitoring, ensuring optimal thermal balance across different engine components during varying RPM ranges.
Oil cooling systems play a dual role in thermal management, simultaneously lubricating moving components and transferring heat away from critical areas. High-performance rotary engines increasingly employ dedicated oil jets directed at the rotor interior, reducing internal temperatures by up to 15% compared to traditional splash lubrication methods. Synthetic oils with improved thermal stability have shown particular efficacy in maintaining viscosity characteristics under extreme temperature conditions.
Material science advancements have introduced ceramic-coated apex seals and rotor housings that provide superior thermal barrier properties. These coatings, typically composed of yttria-stabilized zirconia or similar compounds, reduce heat transfer into the cooling system by reflecting thermal energy back into the combustion chamber, improving thermodynamic efficiency while reducing cooling system load.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, when precisely calibrated for rotary applications, offer another thermal management avenue by moderating combustion temperatures. Advanced EGR implementations with dedicated cooling circuits can reduce peak combustion temperatures by 50-100°C, mitigating thermal stress on engine components while simultaneously addressing NOx emissions concerns.
Integrated thermal management control systems represent the frontier of high-RPM rotary engine optimization, utilizing multiple temperature sensors and adaptive algorithms to orchestrate cooling system responses based on operating conditions. These systems continuously adjust coolant flow rates, oil circulation patterns, and even combustion parameters to maintain optimal thermal equilibrium across the entire RPM range.
The primary thermal challenge in high-RPM rotary operations stems from the concentrated heat generation at the rotor housing, particularly near the combustion area. Temperature differentials between the rotor housing, side housings, and eccentric shaft can reach up to 200°C during sustained high-RPM operation, creating thermal expansion issues that affect apex seal integrity and combustion chamber geometry.
Advanced cooling jacket designs have emerged as a leading solution, with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling enabling precision-engineered coolant pathways that target high-temperature zones. Recent developments include variable-flow cooling systems that adjust coolant distribution based on real-time temperature monitoring, ensuring optimal thermal balance across different engine components during varying RPM ranges.
Oil cooling systems play a dual role in thermal management, simultaneously lubricating moving components and transferring heat away from critical areas. High-performance rotary engines increasingly employ dedicated oil jets directed at the rotor interior, reducing internal temperatures by up to 15% compared to traditional splash lubrication methods. Synthetic oils with improved thermal stability have shown particular efficacy in maintaining viscosity characteristics under extreme temperature conditions.
Material science advancements have introduced ceramic-coated apex seals and rotor housings that provide superior thermal barrier properties. These coatings, typically composed of yttria-stabilized zirconia or similar compounds, reduce heat transfer into the cooling system by reflecting thermal energy back into the combustion chamber, improving thermodynamic efficiency while reducing cooling system load.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, when precisely calibrated for rotary applications, offer another thermal management avenue by moderating combustion temperatures. Advanced EGR implementations with dedicated cooling circuits can reduce peak combustion temperatures by 50-100°C, mitigating thermal stress on engine components while simultaneously addressing NOx emissions concerns.
Integrated thermal management control systems represent the frontier of high-RPM rotary engine optimization, utilizing multiple temperature sensors and adaptive algorithms to orchestrate cooling system responses based on operating conditions. These systems continuously adjust coolant flow rates, oil circulation patterns, and even combustion parameters to maintain optimal thermal equilibrium across the entire RPM range.
Environmental Compliance and Emissions Control for Modern Wankel Engines
Environmental compliance represents a significant challenge for modern Wankel engine development, particularly when optimizing RPM performance. The inherent design characteristics of Wankel engines, including their epitrochoidal housing and triangular rotor, create unique combustion dynamics that historically result in higher hydrocarbon (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) emissions compared to conventional piston engines. These emissions challenges stem from the elongated combustion chamber geometry and the inherent difficulty in maintaining complete combustion across all operating RPM ranges.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including Euro 6d, EPA Tier 3, and California's CARB standards, have established increasingly stringent emissions limits that directly impact Wankel engine viability. Meeting these standards while maintaining optimal RPM performance requires sophisticated technological solutions that address the fundamental combustion characteristics of rotary engines.
Direct injection systems have emerged as a critical technology for emissions control in modern Wankel applications. By precisely timing fuel delivery at various RPM ranges, these systems can significantly reduce unburned hydrocarbon emissions—a persistent challenge in rotary engine design. Advanced direct injection strategies, particularly those employing multiple injection events per combustion cycle, have demonstrated up to 30% reduction in HC emissions while preserving high-RPM performance characteristics.
Thermal management systems represent another crucial development area. The asymmetric heating patterns in Wankel engines contribute to emissions challenges, particularly at variable RPM operations. Advanced cooling systems that maintain optimal operating temperatures across the epitrochoidal housing help ensure more complete combustion and reduced emissions. Ceramic apex seals and housing coatings have shown particular promise in managing thermal gradients while withstanding the mechanical stresses of high-RPM operation.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, specifically calibrated for Wankel's unique operating characteristics, have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions without significantly compromising RPM performance. Variable EGR rates, adjusted according to engine load and RPM, maintain compliance while preserving the rotary engine's characteristic power delivery.
Catalytic converter technologies specifically engineered for Wankel applications represent perhaps the most significant advancement in emissions control. These systems must contend with higher exhaust temperatures and different emission profiles compared to reciprocating engines. Multi-stage catalytic systems with specialized coatings have proven effective at managing the unique emission characteristics of Wankel engines across their operating RPM range.
The integration of these environmental compliance technologies must be carefully balanced with performance objectives. Advanced engine control units (ECUs) with sophisticated mapping capabilities allow for dynamic adjustments to combustion parameters based on RPM, load, and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including Euro 6d, EPA Tier 3, and California's CARB standards, have established increasingly stringent emissions limits that directly impact Wankel engine viability. Meeting these standards while maintaining optimal RPM performance requires sophisticated technological solutions that address the fundamental combustion characteristics of rotary engines.
Direct injection systems have emerged as a critical technology for emissions control in modern Wankel applications. By precisely timing fuel delivery at various RPM ranges, these systems can significantly reduce unburned hydrocarbon emissions—a persistent challenge in rotary engine design. Advanced direct injection strategies, particularly those employing multiple injection events per combustion cycle, have demonstrated up to 30% reduction in HC emissions while preserving high-RPM performance characteristics.
Thermal management systems represent another crucial development area. The asymmetric heating patterns in Wankel engines contribute to emissions challenges, particularly at variable RPM operations. Advanced cooling systems that maintain optimal operating temperatures across the epitrochoidal housing help ensure more complete combustion and reduced emissions. Ceramic apex seals and housing coatings have shown particular promise in managing thermal gradients while withstanding the mechanical stresses of high-RPM operation.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, specifically calibrated for Wankel's unique operating characteristics, have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions without significantly compromising RPM performance. Variable EGR rates, adjusted according to engine load and RPM, maintain compliance while preserving the rotary engine's characteristic power delivery.
Catalytic converter technologies specifically engineered for Wankel applications represent perhaps the most significant advancement in emissions control. These systems must contend with higher exhaust temperatures and different emission profiles compared to reciprocating engines. Multi-stage catalytic systems with specialized coatings have proven effective at managing the unique emission characteristics of Wankel engines across their operating RPM range.
The integration of these environmental compliance technologies must be carefully balanced with performance objectives. Advanced engine control units (ECUs) with sophisticated mapping capabilities allow for dynamic adjustments to combustion parameters based on RPM, load, and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!