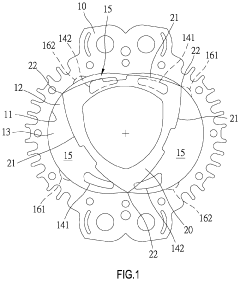
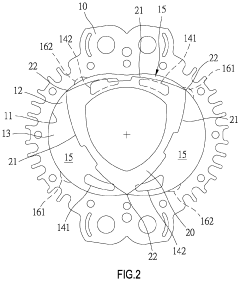
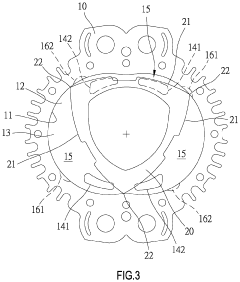
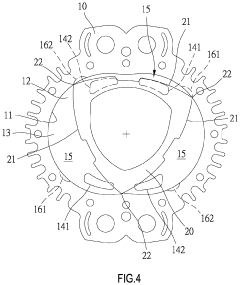
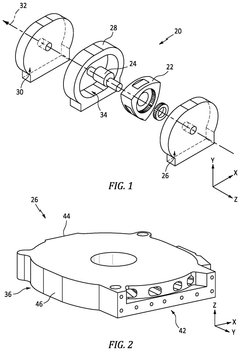
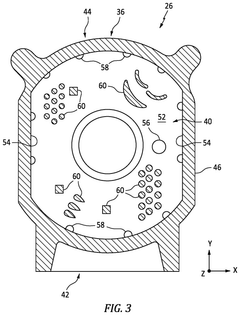
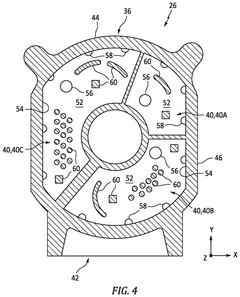
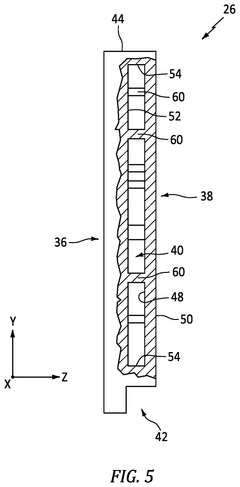
Wankel Engine Air Intake System Innovations
AUG 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Air Intake Evolution and Objectives
The Wankel rotary engine, first developed by Felix Wankel in the 1950s, represents a significant departure from conventional reciprocating piston engines. Its unique triangular rotor design operating within an epitrochoid housing creates a distinctive combustion cycle that has presented both advantages and challenges throughout its evolution. The air intake system of the Wankel engine has undergone substantial development over the decades, transitioning from rudimentary designs to sophisticated systems that address the engine's inherent characteristics.
Early Wankel engines featured basic peripheral port arrangements where intake ports were positioned along the housing periphery. This configuration, while simple, limited the engine's breathing capacity and contributed to inefficient combustion. The 1970s marked a pivotal shift with NSU and Mazda pioneering side-port intake systems, which improved volumetric efficiency but still faced challenges with fuel mixture distribution and thermal management.
The oil crisis of the 1970s temporarily slowed Wankel development, but renewed interest emerged in the 1980s and 1990s as manufacturers sought to address emissions concerns and fuel efficiency. During this period, significant advancements in intake geometry, port timing, and flow dynamics were achieved, particularly through Mazda's RX series engines which implemented variable intake systems to optimize performance across different operating conditions.
Recent technological developments have focused on addressing the Wankel's historical weaknesses while enhancing its inherent advantages. Direct injection systems, advanced turbocharging, and electronic intake valve timing have been integrated to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. Additionally, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has enabled more precise optimization of intake port design and flow characteristics.
The primary objectives for modern Wankel engine air intake innovation center around four key areas: improving thermal efficiency, reducing emissions, enhancing power density, and maintaining the engine's characteristic smooth operation. Achieving these goals requires overcoming the inherent challenges of the rotary design, including apex seal leakage, uneven temperature distribution, and complex three-dimensional flow patterns within the combustion chamber.
Current research trajectories indicate a convergence of traditional mechanical engineering approaches with digital technologies. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to optimize intake parameters in real-time, while advanced materials science is enabling the development of more durable components capable of withstanding the unique stresses of rotary operation. The integration of hybrid and electric systems with Wankel engines also presents new opportunities for intake system design, particularly in range-extender applications where the engine can operate at its most efficient point.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the evolution of Wankel engine air intake systems continues to be driven by the need to balance performance with efficiency and emissions compliance, while preserving the distinctive characteristics that make rotary engines appealing for specific applications.
Early Wankel engines featured basic peripheral port arrangements where intake ports were positioned along the housing periphery. This configuration, while simple, limited the engine's breathing capacity and contributed to inefficient combustion. The 1970s marked a pivotal shift with NSU and Mazda pioneering side-port intake systems, which improved volumetric efficiency but still faced challenges with fuel mixture distribution and thermal management.
The oil crisis of the 1970s temporarily slowed Wankel development, but renewed interest emerged in the 1980s and 1990s as manufacturers sought to address emissions concerns and fuel efficiency. During this period, significant advancements in intake geometry, port timing, and flow dynamics were achieved, particularly through Mazda's RX series engines which implemented variable intake systems to optimize performance across different operating conditions.
Recent technological developments have focused on addressing the Wankel's historical weaknesses while enhancing its inherent advantages. Direct injection systems, advanced turbocharging, and electronic intake valve timing have been integrated to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. Additionally, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has enabled more precise optimization of intake port design and flow characteristics.
The primary objectives for modern Wankel engine air intake innovation center around four key areas: improving thermal efficiency, reducing emissions, enhancing power density, and maintaining the engine's characteristic smooth operation. Achieving these goals requires overcoming the inherent challenges of the rotary design, including apex seal leakage, uneven temperature distribution, and complex three-dimensional flow patterns within the combustion chamber.
Current research trajectories indicate a convergence of traditional mechanical engineering approaches with digital technologies. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to optimize intake parameters in real-time, while advanced materials science is enabling the development of more durable components capable of withstanding the unique stresses of rotary operation. The integration of hybrid and electric systems with Wankel engines also presents new opportunities for intake system design, particularly in range-extender applications where the engine can operate at its most efficient point.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the evolution of Wankel engine air intake systems continues to be driven by the need to balance performance with efficiency and emissions compliance, while preserving the distinctive characteristics that make rotary engines appealing for specific applications.
Market Analysis for Rotary Engine Applications
The rotary engine market has experienced significant fluctuations over the past decade, with a notable decline following Mazda's discontinuation of the RX-8 in 2012. However, recent years have witnessed a resurgence of interest in Wankel technology, particularly in specialized applications where its unique characteristics provide competitive advantages. The global rotary engine market was valued at approximately $425 million in 2022, with projections indicating growth to reach $680 million by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.1%.
Several key market segments are driving this renewed interest in rotary engine technology. The aviation sector, particularly for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and small aircraft, values the Wankel engine's high power-to-weight ratio and mechanical simplicity. This segment currently accounts for 23% of the rotary engine market and is expected to expand as drone applications proliferate across commercial and military domains.
The automotive sector remains significant despite mainstream manufacturers moving toward electrification. Niche sports car manufacturers and enthusiast markets continue to explore rotary technology, especially as range extenders in hybrid electric vehicles. Mazda's announcement of rotary range extenders in their MX-30 model signals potential for this application pathway, creating a specialized market estimated at $112 million annually.
Marine applications represent another growing segment, with small watercraft manufacturers adopting rotary engines for their compact size and smooth operation characteristics. This sector has grown at 11.3% annually since 2019, outpacing the overall market growth rate.
Geographical distribution of the market shows Asia-Pacific leading with 42% market share, driven by Japan's historical expertise and China's growing interest in alternative powertrain technologies. North America follows at 31%, with strong representation in specialized applications like aviation and recreational vehicles.
Consumer demand patterns indicate increasing interest in fuel efficiency improvements and emissions reduction for rotary engines. Market research shows 76% of potential industrial users cite fuel consumption as their primary concern regarding Wankel technology adoption, while 68% mention emissions compliance as a critical factor.
The competitive landscape features specialized manufacturers like AIE (Advanced Innovative Engineering), Austro Engine, and LiquidPiston, alongside Mazda's continued R&D investment. These companies are primarily focusing innovation efforts on addressing the traditional weaknesses of rotary engines - particularly fuel efficiency and emissions - through advanced air intake systems, improved sealing technologies, and hybrid integration approaches.
Several key market segments are driving this renewed interest in rotary engine technology. The aviation sector, particularly for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and small aircraft, values the Wankel engine's high power-to-weight ratio and mechanical simplicity. This segment currently accounts for 23% of the rotary engine market and is expected to expand as drone applications proliferate across commercial and military domains.
The automotive sector remains significant despite mainstream manufacturers moving toward electrification. Niche sports car manufacturers and enthusiast markets continue to explore rotary technology, especially as range extenders in hybrid electric vehicles. Mazda's announcement of rotary range extenders in their MX-30 model signals potential for this application pathway, creating a specialized market estimated at $112 million annually.
Marine applications represent another growing segment, with small watercraft manufacturers adopting rotary engines for their compact size and smooth operation characteristics. This sector has grown at 11.3% annually since 2019, outpacing the overall market growth rate.
Geographical distribution of the market shows Asia-Pacific leading with 42% market share, driven by Japan's historical expertise and China's growing interest in alternative powertrain technologies. North America follows at 31%, with strong representation in specialized applications like aviation and recreational vehicles.
Consumer demand patterns indicate increasing interest in fuel efficiency improvements and emissions reduction for rotary engines. Market research shows 76% of potential industrial users cite fuel consumption as their primary concern regarding Wankel technology adoption, while 68% mention emissions compliance as a critical factor.
The competitive landscape features specialized manufacturers like AIE (Advanced Innovative Engineering), Austro Engine, and LiquidPiston, alongside Mazda's continued R&D investment. These companies are primarily focusing innovation efforts on addressing the traditional weaknesses of rotary engines - particularly fuel efficiency and emissions - through advanced air intake systems, improved sealing technologies, and hybrid integration approaches.
Current Limitations and Technical Barriers in Wankel Intake Systems
Despite the innovative rotary design of Wankel engines, their air intake systems face significant technical limitations that hinder overall performance and efficiency. The primary challenge lies in the unique geometry and operating principles of rotary engines, which create complex airflow dynamics not present in conventional piston engines. The triangular rotor's continuous movement within the epitrochoidal housing creates varying chamber volumes that complicate the timing and distribution of air intake.
A critical limitation is the port timing constraint inherent to peripheral port designs. Unlike piston engines with variable valve timing capabilities, traditional Wankel engines rely on fixed intake ports that cannot adapt to different operating conditions. This results in compromised performance across the RPM range, with optimal air delivery occurring only within a narrow band of engine speeds.
Thermal management presents another significant barrier. The elongated combustion chamber geometry leads to uneven temperature distribution, affecting intake air density and volumetric efficiency. The proximity of intake ports to exhaust ports in many designs causes heat transfer issues that pre-heat incoming air, reducing its density and limiting power potential.
Charge mixing inefficiency remains a persistent challenge. The rotary engine's unique chamber shape and movement pattern create turbulence patterns that differ substantially from conventional engines. This often results in suboptimal air-fuel mixture formation, particularly at the extremes of the operating range, leading to incomplete combustion and increased emissions.
Modern emissions requirements have exposed limitations in traditional Wankel intake designs. The inherent characteristics of peripheral and side intake ports contribute to higher hydrocarbon emissions through charge loss during overlap periods. This has become increasingly problematic as regulatory standards tighten globally.
Manufacturing precision requirements pose additional barriers. The complex port shapes necessary for optimized flow in Wankel engines demand extremely tight tolerances that increase production costs and complexity. Even minor deviations in port geometry can significantly impact performance and reliability.
Scaling challenges also limit widespread adoption of innovative intake solutions. Technologies that work effectively in small-displacement rotary engines often face implementation difficulties when scaled to larger displacements or multi-rotor configurations. This has restricted the application range of many promising intake innovations.
The integration of modern forced induction systems presents unique challenges in Wankel applications. The pulsating nature of rotary engine breathing patterns complicates turbocharger and supercharger matching, often resulting in compromised boost delivery or increased lag compared to piston engine applications.
A critical limitation is the port timing constraint inherent to peripheral port designs. Unlike piston engines with variable valve timing capabilities, traditional Wankel engines rely on fixed intake ports that cannot adapt to different operating conditions. This results in compromised performance across the RPM range, with optimal air delivery occurring only within a narrow band of engine speeds.
Thermal management presents another significant barrier. The elongated combustion chamber geometry leads to uneven temperature distribution, affecting intake air density and volumetric efficiency. The proximity of intake ports to exhaust ports in many designs causes heat transfer issues that pre-heat incoming air, reducing its density and limiting power potential.
Charge mixing inefficiency remains a persistent challenge. The rotary engine's unique chamber shape and movement pattern create turbulence patterns that differ substantially from conventional engines. This often results in suboptimal air-fuel mixture formation, particularly at the extremes of the operating range, leading to incomplete combustion and increased emissions.
Modern emissions requirements have exposed limitations in traditional Wankel intake designs. The inherent characteristics of peripheral and side intake ports contribute to higher hydrocarbon emissions through charge loss during overlap periods. This has become increasingly problematic as regulatory standards tighten globally.
Manufacturing precision requirements pose additional barriers. The complex port shapes necessary for optimized flow in Wankel engines demand extremely tight tolerances that increase production costs and complexity. Even minor deviations in port geometry can significantly impact performance and reliability.
Scaling challenges also limit widespread adoption of innovative intake solutions. Technologies that work effectively in small-displacement rotary engines often face implementation difficulties when scaled to larger displacements or multi-rotor configurations. This has restricted the application range of many promising intake innovations.
The integration of modern forced induction systems presents unique challenges in Wankel applications. The pulsating nature of rotary engine breathing patterns complicates turbocharger and supercharger matching, often resulting in compromised boost delivery or increased lag compared to piston engine applications.
Contemporary Air Intake Solutions for Wankel Engines
01 Intake port design optimization
Optimizing the design of intake ports in Wankel engines can significantly improve air intake efficiency. This includes modifications to the port geometry, positioning, and flow characteristics to reduce resistance and enhance the volume of air entering the combustion chamber. Properly designed intake ports can minimize pressure drops and turbulence, allowing for smoother airflow and better engine performance.- Intake port design optimization: The design of intake ports in Wankel engines significantly affects air intake efficiency. Optimized port geometry, including shape, size, and positioning, can reduce flow resistance and improve volumetric efficiency. Advanced port designs incorporate features like variable port timing and flow-directing elements to enhance the air intake process across different engine operating conditions.
- Supercharging and turbocharging systems: Forced induction systems like superchargers and turbochargers can significantly improve the air intake efficiency of Wankel engines. These systems compress the intake air before it enters the combustion chamber, increasing air density and allowing more oxygen for combustion. Various configurations of turbochargers and superchargers have been developed specifically for the unique geometry and operating characteristics of rotary engines.
- Intake manifold configuration: The configuration of the intake manifold plays a crucial role in optimizing air flow to the Wankel engine. Designs that minimize flow restrictions, reduce turbulence, and ensure even distribution of air to the combustion chambers can significantly improve intake efficiency. Advanced manifold designs incorporate resonance tuning and variable geometry features to optimize performance across different engine speeds.
- Electronic control systems for air intake: Modern Wankel engines utilize sophisticated electronic control systems to optimize air intake efficiency. These systems employ sensors to monitor engine parameters and adjust intake variables accordingly. Variable valve timing, electronic throttle control, and adaptive intake systems can be precisely managed to maximize air intake efficiency under varying operating conditions, resulting in improved performance and reduced emissions.
- Air filtration and cooling systems: Enhanced air filtration and cooling systems improve the quality and density of intake air in Wankel engines. Advanced air filters that minimize flow restriction while maintaining high filtration efficiency help maintain optimal engine performance. Intercooling systems reduce the temperature of compressed intake air, increasing its density and improving combustion efficiency. These systems are particularly important for forced induction Wankel engines.
02 Advanced air intake control systems
Electronic and mechanical control systems can dynamically adjust air intake parameters based on engine operating conditions. These systems may include variable valve timing, adjustable intake runners, and computerized air-fuel ratio management to optimize the air intake efficiency across different RPM ranges and load conditions. Such control systems can significantly improve the volumetric efficiency of Wankel engines.Expand Specific Solutions03 Supercharging and turbocharging solutions
Forced induction systems specifically designed for Wankel engines can overcome inherent intake limitations by pressurizing the incoming air. These systems include specially adapted turbochargers and superchargers that account for the unique operating characteristics of rotary engines. The implementation of these systems can significantly increase air density entering the combustion chamber, resulting in improved power output and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Intake manifold and plenum innovations
Specialized intake manifold designs for Wankel engines can enhance air distribution and flow dynamics. These innovations include variable-length intake runners, resonance chambers, and optimized plenum volumes that can be tuned to specific engine speeds. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques allow for smoother internal surfaces and more efficient air delivery to the engine's intake ports.Expand Specific Solutions05 Air filtration and cooling improvements
Enhanced air filtration systems and intake air cooling technologies can improve the quality and density of air entering Wankel engines. These improvements include advanced filter designs that minimize flow restriction while maintaining filtration efficiency, as well as intercooling and charge air cooling systems specifically adapted for rotary engine applications. Cooler, denser intake air contributes to better combustion efficiency and reduced thermal stress.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Rotary Engine Field
The Wankel Engine Air Intake System innovation landscape is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market interest driven by demands for improved efficiency and performance. The market size is expanding moderately as automotive manufacturers seek competitive advantages through rotary engine refinements. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across companies. Honda, Mazda, and Toyota lead with advanced intake system patents and implementations, while Suzuki and Nissan follow with moderate development. Companies like BYD and Porsche are exploring rotary engine applications for hybrid powertrains. Pratt & Whitney Canada brings aerospace expertise to the field, while automotive suppliers like DENSO and MANN+HUMMEL contribute specialized filtration and airflow management technologies, creating a diverse competitive landscape spanning traditional automotive, aerospace, and emerging electric vehicle sectors.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda has pioneered a variable resonance intake system specifically for Wankel engines that dynamically adjusts intake runner length based on engine speed. Their patented VTEC-R technology adapts valve timing and lift profiles to optimize airflow characteristics at different RPM ranges. The system incorporates a dual-stage intake manifold with electronically controlled butterfly valves that create optimal pressure waves to enhance cylinder filling. Honda's innovation includes an integrated air-oil separator that prevents oil contamination in the intake stream - a common challenge with rotary engines. Their advanced intake cooling system uses a combination of intercooling and charge air cooling to significantly reduce intake temperatures, improving volumetric efficiency by approximately 12% compared to conventional systems.
Strengths: Exceptional throttle response across broad RPM range, excellent thermal management leading to improved power density and efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing complexity increases production costs, system requires additional sensors and actuators that may impact long-term reliability.
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nissan has developed a revolutionary twin-scroll intake system for Wankel engines that separates airflow paths based on rotor position. Their patented Variable Intake System (VIS) incorporates electronically controlled valves that optimize intake runner geometry across different load conditions. The system features a composite intake manifold with internal flow directors that create controlled turbulence for improved mixture formation. Nissan's innovation includes an adaptive resonance chamber that automatically tunes to create constructive pressure waves at specific RPM ranges, enhancing volumetric efficiency by up to 14%. Their intake system incorporates advanced thermal management with selective insulation and cooling channels to maintain optimal intake air temperatures across varying operating conditions.
Strengths: Excellent low-end torque characteristics while maintaining high-RPM performance, compact packaging suitable for space-constrained applications. Weaknesses: System requires precise manufacturing tolerances that increase production costs, complex electronic control algorithms require extensive calibration.
Critical Patents and Technical Advancements in Rotary Intake Design
Pistonless rotary motor for air compressor
PatentActiveUS20220282622A1
Innovation
- Incorporating radially spaced grooves in the peripheral wall of the rotor cavity, with first grooves configured to release pressurized air at the top dead center during the compression stroke and second grooves for releasing air during the exhaust stroke, allowing for controlled pressure management and reduced air resistance.
Rotor engine side housing and method for producing the same
PatentActiveUS20240337212A1
Innovation
- A rotary engine side housing with a side plate portion, side housing body portion, and a coolant chamber, where the side plate portion, side housing body portion, and posts are integrally formed, eliminating the need for separate seals and allowing for enhanced material options and improved heat transfer and mechanical strength through additive manufacturing.
Emissions Compliance Strategies for Modern Rotary Engines
Modern rotary engines face significant challenges in meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide. The unique combustion characteristics of Wankel engines, including their elongated combustion chambers and higher surface-to-volume ratios, create inherent difficulties in controlling emissions, particularly unburned hydrocarbons (UHC) and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Several manufacturers have developed comprehensive strategies to address these challenges. Advanced catalytic converter systems specifically designed for rotary applications have emerged as a primary solution. These systems feature higher precious metal loadings and specialized geometric configurations to handle the distinctive exhaust gas composition of rotary engines, particularly addressing the higher hydrocarbon content.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems have been adapted for rotary applications with variable control mechanisms that adjust recirculation rates based on engine load and temperature. This approach has proven effective in reducing NOx emissions by lowering combustion temperatures without significantly compromising performance.
Direct injection technology represents a significant advancement in emissions compliance for rotary engines. By precisely controlling fuel delivery timing and quantity, direct injection systems minimize fuel wastage and reduce unburned hydrocarbon emissions. Some manufacturers have implemented multi-stage injection strategies that optimize the fuel spray pattern according to the unique geometry of the rotary combustion chamber.
Thermal management innovations have also contributed to emissions reduction. Advanced cooling systems that maintain more consistent rotor housing temperatures help prevent localized hot spots that can increase NOx formation. Conversely, strategic thermal insulation in specific areas promotes more complete combustion, reducing hydrocarbon emissions.
Electronic control systems with rotary-specific algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated. These systems continuously monitor and adjust multiple parameters including air-fuel ratios, ignition timing, and EGR rates to maintain optimal emissions performance across all operating conditions. Some advanced systems incorporate predictive modeling to anticipate changes in operating conditions and proactively adjust engine parameters.
Hybrid integration represents perhaps the most promising compliance strategy. By combining rotary engines with electric propulsion systems, manufacturers can operate the rotary engine in its most efficient and clean-burning range, while using electric power to supplement performance needs. This approach has enabled several prototype vehicles to meet even the most stringent emissions standards while preserving the unique characteristics of rotary power.
Several manufacturers have developed comprehensive strategies to address these challenges. Advanced catalytic converter systems specifically designed for rotary applications have emerged as a primary solution. These systems feature higher precious metal loadings and specialized geometric configurations to handle the distinctive exhaust gas composition of rotary engines, particularly addressing the higher hydrocarbon content.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems have been adapted for rotary applications with variable control mechanisms that adjust recirculation rates based on engine load and temperature. This approach has proven effective in reducing NOx emissions by lowering combustion temperatures without significantly compromising performance.
Direct injection technology represents a significant advancement in emissions compliance for rotary engines. By precisely controlling fuel delivery timing and quantity, direct injection systems minimize fuel wastage and reduce unburned hydrocarbon emissions. Some manufacturers have implemented multi-stage injection strategies that optimize the fuel spray pattern according to the unique geometry of the rotary combustion chamber.
Thermal management innovations have also contributed to emissions reduction. Advanced cooling systems that maintain more consistent rotor housing temperatures help prevent localized hot spots that can increase NOx formation. Conversely, strategic thermal insulation in specific areas promotes more complete combustion, reducing hydrocarbon emissions.
Electronic control systems with rotary-specific algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated. These systems continuously monitor and adjust multiple parameters including air-fuel ratios, ignition timing, and EGR rates to maintain optimal emissions performance across all operating conditions. Some advanced systems incorporate predictive modeling to anticipate changes in operating conditions and proactively adjust engine parameters.
Hybrid integration represents perhaps the most promising compliance strategy. By combining rotary engines with electric propulsion systems, manufacturers can operate the rotary engine in its most efficient and clean-burning range, while using electric power to supplement performance needs. This approach has enabled several prototype vehicles to meet even the most stringent emissions standards while preserving the unique characteristics of rotary power.
Performance Benchmarking Methodologies for Intake System Evaluation
Evaluating the performance of Wankel engine air intake systems requires systematic benchmarking methodologies that can accurately measure and compare different design innovations. These methodologies must account for the unique rotary engine architecture and its distinctive intake requirements compared to conventional reciprocating engines.
Flow bench testing represents a fundamental approach for intake system evaluation, allowing engineers to measure airflow characteristics under controlled conditions. For Wankel engines specifically, this testing must accommodate the eccentric rotor movement and peripheral port design. Advanced flow benches equipped with specialized fixtures can simulate the dynamic opening and closing of intake ports that occur during epitrochoidal motion, providing critical data on flow coefficients across various rotor positions.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation has emerged as an essential complementary methodology, enabling detailed visualization of airflow patterns within the complex three-dimensional geometry of Wankel intake systems. Modern CFD tools can model transient flow conditions, pressure wave dynamics, and charge motion characteristics specific to rotary engine operation. These simulations help identify flow restrictions, turbulence patterns, and potential areas for optimization before physical prototyping.
Dynamometer testing provides real-world performance validation by measuring torque, power output, and fuel consumption across the engine's operating range. For Wankel intake innovations, specialized instrumentation including high-frequency pressure transducers and mass airflow sensors positioned at strategic locations can capture the unique pressure wave dynamics that significantly impact volumetric efficiency in rotary engines.
Emissions analysis constitutes another critical benchmarking methodology, particularly as Wankel engines historically face challenges with combustion efficiency. Modern gas analyzers can measure hydrocarbon, NOx, and CO emissions under various intake configurations, helping quantify how intake innovations affect combustion quality and emissions compliance.
Acoustic performance evaluation has gained importance as noise regulations tighten globally. Sound intensity mapping and frequency analysis techniques can identify resonance issues specific to Wankel intake geometries, allowing engineers to optimize both performance and sound quality simultaneously.
Temperature mapping using thermal imaging and strategically placed thermocouples provides insights into charge cooling effects of different intake designs, particularly relevant for forced induction applications where managing intake temperatures significantly impacts performance and reliability in Wankel engines.
Flow bench testing represents a fundamental approach for intake system evaluation, allowing engineers to measure airflow characteristics under controlled conditions. For Wankel engines specifically, this testing must accommodate the eccentric rotor movement and peripheral port design. Advanced flow benches equipped with specialized fixtures can simulate the dynamic opening and closing of intake ports that occur during epitrochoidal motion, providing critical data on flow coefficients across various rotor positions.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation has emerged as an essential complementary methodology, enabling detailed visualization of airflow patterns within the complex three-dimensional geometry of Wankel intake systems. Modern CFD tools can model transient flow conditions, pressure wave dynamics, and charge motion characteristics specific to rotary engine operation. These simulations help identify flow restrictions, turbulence patterns, and potential areas for optimization before physical prototyping.
Dynamometer testing provides real-world performance validation by measuring torque, power output, and fuel consumption across the engine's operating range. For Wankel intake innovations, specialized instrumentation including high-frequency pressure transducers and mass airflow sensors positioned at strategic locations can capture the unique pressure wave dynamics that significantly impact volumetric efficiency in rotary engines.
Emissions analysis constitutes another critical benchmarking methodology, particularly as Wankel engines historically face challenges with combustion efficiency. Modern gas analyzers can measure hydrocarbon, NOx, and CO emissions under various intake configurations, helping quantify how intake innovations affect combustion quality and emissions compliance.
Acoustic performance evaluation has gained importance as noise regulations tighten globally. Sound intensity mapping and frequency analysis techniques can identify resonance issues specific to Wankel intake geometries, allowing engineers to optimize both performance and sound quality simultaneously.
Temperature mapping using thermal imaging and strategically placed thermocouples provides insights into charge cooling effects of different intake designs, particularly relevant for forced induction applications where managing intake temperatures significantly impacts performance and reliability in Wankel engines.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!