Wankel Engine Fuel Injection Advances
AUG 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Evolution and Fuel Efficiency Goals
The Wankel rotary engine, first developed by Felix Wankel in the 1950s, represents a significant departure from conventional reciprocating piston engines. Its evolution has been marked by several distinct phases, each characterized by technological advancements aimed at improving performance and efficiency. The initial commercial implementation by NSU in the 1960s demonstrated the rotary engine's potential for high power-to-weight ratios and mechanical simplicity, but also revealed inherent challenges in fuel efficiency and emissions control.
Mazda's subsequent development efforts from the 1970s through the 2000s established the company as the primary champion of Wankel technology. Their RX series vehicles showcased the engine's capabilities while continuously refining the design to address efficiency concerns. The introduction of the 13B-REW engine in the RX-7 FD represented a significant milestone, incorporating twin sequential turbocharging to enhance both power delivery and fuel economy.
Despite these advancements, Wankel engines have historically suffered from inherent thermodynamic inefficiencies. The elongated combustion chamber creates challenges for complete fuel combustion, while the rotor housing's geometry leads to unfavorable surface-to-volume ratios. These factors have contributed to fuel consumption rates typically 20-40% higher than comparable piston engines, presenting a persistent challenge for manufacturers.
Current fuel efficiency goals for Wankel engines are ambitious but necessary in the context of increasingly stringent global emissions standards. The primary target is to achieve thermal efficiency comparable to modern gasoline direct injection piston engines, which typically operate at 35-40% efficiency. This represents a significant improvement from traditional Wankel designs that often struggled to exceed 25% thermal efficiency.
Secondary efficiency goals include reducing oil consumption, which has historically been a challenge due to the need for oil injection to lubricate rotor apex seals. Modern designs aim to reduce oil consumption to less than 0.1 liters per 1000 kilometers, comparable to contemporary piston engines. Additionally, cold-start emissions reduction has become a critical focus area, with targets to meet Euro 6d and equivalent global standards.
The evolution trajectory suggests several promising approaches to meeting these efficiency goals. Direct fuel injection technology, particularly stratified charge configurations, has demonstrated potential to improve combustion efficiency by 15-20%. Advanced rotor apex seal designs utilizing ceramic composites and improved coating technologies are reducing friction losses while extending service intervals. Furthermore, hybrid integration strategies are emerging as a compelling approach, using the Wankel engine as a range extender operating at its optimal efficiency point while electric motors handle variable load demands.
Mazda's subsequent development efforts from the 1970s through the 2000s established the company as the primary champion of Wankel technology. Their RX series vehicles showcased the engine's capabilities while continuously refining the design to address efficiency concerns. The introduction of the 13B-REW engine in the RX-7 FD represented a significant milestone, incorporating twin sequential turbocharging to enhance both power delivery and fuel economy.
Despite these advancements, Wankel engines have historically suffered from inherent thermodynamic inefficiencies. The elongated combustion chamber creates challenges for complete fuel combustion, while the rotor housing's geometry leads to unfavorable surface-to-volume ratios. These factors have contributed to fuel consumption rates typically 20-40% higher than comparable piston engines, presenting a persistent challenge for manufacturers.
Current fuel efficiency goals for Wankel engines are ambitious but necessary in the context of increasingly stringent global emissions standards. The primary target is to achieve thermal efficiency comparable to modern gasoline direct injection piston engines, which typically operate at 35-40% efficiency. This represents a significant improvement from traditional Wankel designs that often struggled to exceed 25% thermal efficiency.
Secondary efficiency goals include reducing oil consumption, which has historically been a challenge due to the need for oil injection to lubricate rotor apex seals. Modern designs aim to reduce oil consumption to less than 0.1 liters per 1000 kilometers, comparable to contemporary piston engines. Additionally, cold-start emissions reduction has become a critical focus area, with targets to meet Euro 6d and equivalent global standards.
The evolution trajectory suggests several promising approaches to meeting these efficiency goals. Direct fuel injection technology, particularly stratified charge configurations, has demonstrated potential to improve combustion efficiency by 15-20%. Advanced rotor apex seal designs utilizing ceramic composites and improved coating technologies are reducing friction losses while extending service intervals. Furthermore, hybrid integration strategies are emerging as a compelling approach, using the Wankel engine as a range extender operating at its optimal efficiency point while electric motors handle variable load demands.
Market Analysis for Rotary Engine Applications
The global market for rotary engine applications has experienced significant shifts over the past decade, primarily driven by evolving emission standards and changing consumer preferences. While Wankel engines once held promise across multiple sectors due to their compact size, high power-to-weight ratio, and mechanical simplicity, their market presence has contracted substantially since their peak in the 1970s and early 2000s.
Currently, the automotive sector represents the most visible but contracting market for rotary engine technology. Mazda, historically the largest commercial producer of Wankel engines, has shifted its strategy from using rotary engines as primary powerplants to employing them as range extenders in hybrid electric vehicles, as demonstrated in their MX-30 R-EV model launched in 2023. This strategic pivot reflects broader market trends toward electrification while leveraging the rotary engine's compact size and operational efficiency in specialized applications.
The aviation sector presents a more promising growth market for advanced rotary engine applications. Small aircraft manufacturers value the Wankel engine's favorable power-to-weight ratio and reduced vibration characteristics. Companies like Austro Engine and AIE (Advanced Innovative Engineering) have developed modern rotary engines specifically for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and light aircraft, with the global UAV market projected to grow at 14.1% CAGR through 2028.
Marine applications constitute another niche but stable market segment, where rotary engines' compact profile and smooth operation provide advantages in certain watercraft designs. The recreational boating sector in particular has shown interest in lightweight propulsion solutions that maximize cabin space.
The military and defense sector represents a specialized market with significant research investment in advanced rotary engine technologies. Military applications value the Wankel engine's reduced infrared signature, compact size, and multi-fuel capabilities, particularly for portable power generation and unmanned systems.
Regional market distribution shows concentrated development activities in Japan, Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom, with emerging interest in China and South Korea. Japan maintains leadership through Mazda's continued refinement of rotary technology, while European and American markets focus on specialized applications in aviation and military sectors.
Market forecasts indicate that while rotary engines will remain a niche technology, advancements in fuel injection systems could expand their applicability in hybrid powertrains, specialized industrial equipment, and next-generation UAVs. The global market value for specialized rotary engine applications is expected to grow moderately as fuel efficiency improvements address historical limitations.
Currently, the automotive sector represents the most visible but contracting market for rotary engine technology. Mazda, historically the largest commercial producer of Wankel engines, has shifted its strategy from using rotary engines as primary powerplants to employing them as range extenders in hybrid electric vehicles, as demonstrated in their MX-30 R-EV model launched in 2023. This strategic pivot reflects broader market trends toward electrification while leveraging the rotary engine's compact size and operational efficiency in specialized applications.
The aviation sector presents a more promising growth market for advanced rotary engine applications. Small aircraft manufacturers value the Wankel engine's favorable power-to-weight ratio and reduced vibration characteristics. Companies like Austro Engine and AIE (Advanced Innovative Engineering) have developed modern rotary engines specifically for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and light aircraft, with the global UAV market projected to grow at 14.1% CAGR through 2028.
Marine applications constitute another niche but stable market segment, where rotary engines' compact profile and smooth operation provide advantages in certain watercraft designs. The recreational boating sector in particular has shown interest in lightweight propulsion solutions that maximize cabin space.
The military and defense sector represents a specialized market with significant research investment in advanced rotary engine technologies. Military applications value the Wankel engine's reduced infrared signature, compact size, and multi-fuel capabilities, particularly for portable power generation and unmanned systems.
Regional market distribution shows concentrated development activities in Japan, Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom, with emerging interest in China and South Korea. Japan maintains leadership through Mazda's continued refinement of rotary technology, while European and American markets focus on specialized applications in aviation and military sectors.
Market forecasts indicate that while rotary engines will remain a niche technology, advancements in fuel injection systems could expand their applicability in hybrid powertrains, specialized industrial equipment, and next-generation UAVs. The global market value for specialized rotary engine applications is expected to grow moderately as fuel efficiency improvements address historical limitations.
Current Challenges in Wankel Engine Fuel Injection
Despite significant advancements in rotary engine technology, Wankel engines continue to face persistent challenges in fuel injection systems that limit their widespread adoption. The unique geometry and operating principles of rotary engines create combustion chamber conditions fundamentally different from conventional reciprocating engines, resulting in incomplete fuel combustion and higher emissions. The elongated combustion chamber shape leads to flame propagation issues, while the eccentric rotor motion creates varying compression ratios throughout the rotation cycle.
The primary technical hurdle remains achieving optimal fuel-air mixture distribution within the irregularly shaped combustion chamber. Unlike piston engines with relatively predictable combustion dynamics, the constantly changing geometry of the Wankel's combustion chamber makes uniform fuel delivery exceptionally difficult. This challenge is exacerbated by the engine's high operating speeds, which leave minimal time for proper atomization and mixing.
Thermal management presents another significant obstacle. The concentrated heat in specific regions of the rotor housing creates thermal gradients that affect fuel vaporization and combustion efficiency. These temperature variations can lead to inconsistent fuel atomization, contributing to increased hydrocarbon emissions and reduced thermal efficiency. Current injection systems struggle to compensate for these thermal variations across different operating conditions.
Sealing technology limitations compound these challenges. Despite improvements in apex seal materials and designs, the inherent leakage between chambers affects compression and consequently the fuel injection timing and pressure requirements. Engineers must balance injection parameters to account for these seal-related pressure losses, often resulting in compromised performance or efficiency.
Modern emissions standards have placed additional pressure on Wankel engine development. The inherently higher hydrocarbon emissions due to incomplete combustion and oil consumption make meeting stringent regulations particularly challenging. Direct injection systems show promise but introduce new complexities related to injector positioning and durability in the high-temperature, high-stress rotary environment.
The transition to alternative fuels presents both opportunities and challenges. While hydrogen and other alternative fuels might address some emissions concerns, they require fundamentally different injection strategies and hardware. Existing fuel injection systems optimized for gasoline operation require significant redesign to accommodate these alternative energy carriers effectively.
Manufacturing complexity and cost considerations further constrain innovation in this space. The precision required for effective rotary engine fuel injection systems, combined with relatively low production volumes, creates economic barriers to implementing cutting-edge solutions that might otherwise address the technical challenges.
The primary technical hurdle remains achieving optimal fuel-air mixture distribution within the irregularly shaped combustion chamber. Unlike piston engines with relatively predictable combustion dynamics, the constantly changing geometry of the Wankel's combustion chamber makes uniform fuel delivery exceptionally difficult. This challenge is exacerbated by the engine's high operating speeds, which leave minimal time for proper atomization and mixing.
Thermal management presents another significant obstacle. The concentrated heat in specific regions of the rotor housing creates thermal gradients that affect fuel vaporization and combustion efficiency. These temperature variations can lead to inconsistent fuel atomization, contributing to increased hydrocarbon emissions and reduced thermal efficiency. Current injection systems struggle to compensate for these thermal variations across different operating conditions.
Sealing technology limitations compound these challenges. Despite improvements in apex seal materials and designs, the inherent leakage between chambers affects compression and consequently the fuel injection timing and pressure requirements. Engineers must balance injection parameters to account for these seal-related pressure losses, often resulting in compromised performance or efficiency.
Modern emissions standards have placed additional pressure on Wankel engine development. The inherently higher hydrocarbon emissions due to incomplete combustion and oil consumption make meeting stringent regulations particularly challenging. Direct injection systems show promise but introduce new complexities related to injector positioning and durability in the high-temperature, high-stress rotary environment.
The transition to alternative fuels presents both opportunities and challenges. While hydrogen and other alternative fuels might address some emissions concerns, they require fundamentally different injection strategies and hardware. Existing fuel injection systems optimized for gasoline operation require significant redesign to accommodate these alternative energy carriers effectively.
Manufacturing complexity and cost considerations further constrain innovation in this space. The precision required for effective rotary engine fuel injection systems, combined with relatively low production volumes, creates economic barriers to implementing cutting-edge solutions that might otherwise address the technical challenges.
Contemporary Fuel Injection Solutions for Rotary Engines
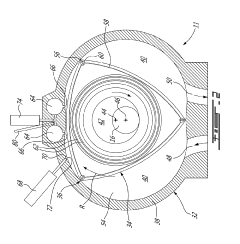
01 Direct fuel injection systems for Wankel engines
Direct fuel injection systems specifically designed for Wankel rotary engines improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. These systems inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber at precise timing, allowing for better fuel atomization and mixing with air. The specialized injector placement accommodates the unique geometry of the Wankel engine's rotor housing, optimizing the fuel spray pattern for the moving rotor.- Direct fuel injection systems for Wankel engines: Direct fuel injection systems specifically designed for Wankel rotary engines that inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber. These systems improve fuel efficiency and combustion control by precisely timing the fuel delivery according to the rotary engine's unique geometry and operating cycle. The direct injection approach helps overcome traditional challenges of fuel mixing in Wankel engines and reduces emissions while enhancing power output.
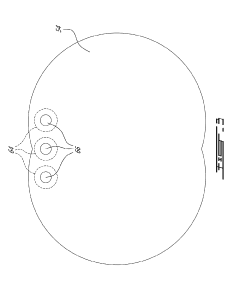
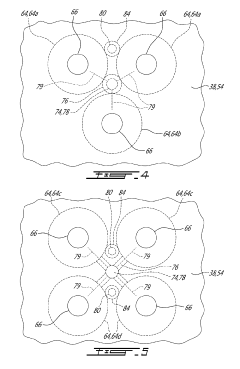
- Fuel injector positioning and arrangement in Wankel engines: Strategic positioning and arrangement of fuel injectors in Wankel rotary engines to optimize fuel delivery and combustion. This includes specific mounting locations on the housing, orientation angles, and specialized nozzle designs that account for the unique combustion chamber geometry. Proper injector positioning ensures optimal fuel spray patterns that follow the rotational movement of the rotor and improve the air-fuel mixture formation.
- Multi-stage and variable fuel injection for Wankel engines: Multi-stage and variable fuel injection systems that adapt to different operating conditions of Wankel engines. These systems can adjust injection timing, duration, and pressure based on engine load, speed, and temperature. Some implementations include multiple injectors per chamber that activate sequentially or simultaneously depending on performance requirements, enabling better combustion control across the engine's operating range.
- Electronic control systems for Wankel engine fuel injection: Advanced electronic control systems specifically designed to manage fuel injection in Wankel rotary engines. These systems use sensors to monitor engine parameters and precisely control injection timing, duration, and pressure. The electronic controllers compensate for the unique rotational dynamics of Wankel engines and implement sophisticated algorithms to optimize combustion efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance performance across various operating conditions.
- Alternative fuel injection technologies for Wankel engines: Specialized fuel injection technologies adapted for alternative fuels in Wankel rotary engines. These include systems designed for hydrogen, natural gas, alcohol-based fuels, and dual-fuel operations. The injection systems account for the different combustion characteristics of alternative fuels and may incorporate modified injector designs, altered spray patterns, and specialized sealing technologies to maintain efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
02 Multi-point fuel injection for rotary engines
Multi-point fuel injection systems for Wankel engines feature multiple injectors positioned at strategic locations around the rotor housing. This configuration ensures more uniform fuel distribution throughout the combustion chamber, improving power output and thermal efficiency. The system can be designed to inject fuel at different phases of the combustion cycle, adapting to various engine operating conditions and load requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electronic control systems for Wankel engine fuel injection
Advanced electronic control systems manage fuel injection in Wankel engines by precisely controlling injection timing, duration, and pressure based on various operating parameters. These systems utilize sensors to monitor engine speed, temperature, throttle position, and exhaust composition to optimize the air-fuel mixture. The electronic control units can adjust injection parameters in real-time to improve performance, fuel economy, and emissions across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 High-pressure fuel injection for improved combustion
High-pressure fuel injection systems for Wankel engines deliver fuel at elevated pressures, resulting in finer atomization and more complete combustion. These systems can operate at pressures significantly higher than conventional injection systems, allowing for better penetration of fuel into the combustion chamber. The improved atomization leads to more efficient burning, reduced fuel consumption, and lower emissions, particularly at high engine speeds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Dual-fuel and alternative fuel injection systems
Specialized fuel injection systems for Wankel engines that accommodate dual-fuel operation or alternative fuels such as hydrogen, natural gas, or alcohol-based fuels. These systems may include modified injectors, fuel rails, and control algorithms to handle the different combustion characteristics of alternative fuels. Some designs incorporate separate injection systems for different fuels, allowing the engine to switch between fuel types or use them simultaneously for optimal performance and emissions control.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The Wankel engine fuel injection market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing technological advancements and expanding applications. The market size is projected to grow steadily as automotive manufacturers seek more efficient rotary engine solutions. Technologically, the field is reaching maturity with significant innovations from key players. Robert Bosch GmbH leads with advanced direct injection systems, while DENSO Corp. and Continental Automotive GmbH have developed specialized electronic control units for rotary applications. Nissan Motor and Mazda have historically invested in Wankel technology, with Mercedes-Benz and Ford Global Technologies pursuing efficiency improvements. BYD and Hitachi are advancing in electrification integration, while university partnerships with North Carolina State and Beijing Institute of Technology are driving fundamental research in combustion optimization.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed advanced direct injection systems specifically optimized for Wankel rotary engines that address the unique combustion chamber geometry challenges. Their technology incorporates high-precision piezoelectric injectors capable of multiple injections per combustion cycle with pressures exceeding 200 bar, allowing for precise fuel delivery timing and spray pattern optimization. The system utilizes sophisticated electronic control units that continuously adjust injection parameters based on engine load, speed, and temperature data collected from multiple sensors. Bosch's solution includes specialized injector positioning that targets the fuel spray directly into the moving combustion chamber, compensating for the rotary motion to achieve optimal air-fuel mixture formation. Their system also integrates with exhaust gas recirculation to reduce emissions while maintaining the Wankel engine's characteristic power density advantages.
Strengths: Superior atomization quality and precise injection timing control leads to improved fuel efficiency (up to 15% compared to conventional port injection systems for Wankel engines) and significantly reduced hydrocarbon emissions. Weaknesses: Higher system complexity and cost compared to traditional injection systems, requiring specialized maintenance and calibration expertise.
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nissan has pioneered a multi-stage direct injection system specifically for Wankel rotary engines that addresses the unique challenges of the elongated combustion chamber. Their technology features strategically positioned multiple injectors that activate sequentially as the rotor moves through its cycle, ensuring optimal fuel distribution throughout the combustion process. The system incorporates variable pressure control (ranging from 50-180 bar) that adjusts based on engine load and speed conditions. Nissan's approach includes proprietary spray pattern designs that account for the three-dimensional flow dynamics within the rotary housing. Their fuel delivery system is integrated with advanced electronic control units that utilize predictive algorithms to anticipate combustion conditions based on driver input and engine parameters. This technology was notably implemented in prototype RX-series vehicles developed in partnership with Mazda, demonstrating significant improvements in both power delivery and emissions control.
Strengths: Exceptional fuel distribution throughout the unique rotary combustion chamber geometry, resulting in more complete combustion and reduced fuel consumption (approximately 20% improvement over previous rotary injection systems). Weaknesses: Requires complex calibration across various operating conditions and additional injector components that increase system cost and potential failure points.
Critical Patents in Wankel Engine Fuel Delivery Systems
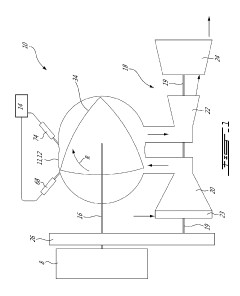
Rotary engine with pilot subchambers
PatentActiveUS20190162108A1
Innovation
- The implementation of at least two pilot subchambers in parallel fluid communication with the combustion chambers, where a pilot quantity of fuel is ignited and directed into the combustion chamber through transfer holes that partially restrict the flow, enhancing the ignition of the main fuel quantity and achieving a lean fuel-air mixture.
Internal combustion engine with rotating pistons
PatentInactiveEP0020335A1
Innovation
- A redesigned rotary piston engine with a central permanent compression system and a turbo-gas-air mixture that enhances combustion efficiency, combined with a unique bearing mechanism and spring locking system to minimize friction and optimize power transmission, allowing for circular movement and efficient combustion chamber filling.
Emissions Compliance Strategies for Wankel Engines
The Wankel rotary engine faces unique challenges in meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide. Traditional compliance strategies for reciprocating engines cannot be directly applied due to the rotary engine's distinctive combustion chamber geometry and operating characteristics. The elongated combustion chamber and inherent quenching zones create conditions that promote incomplete combustion and higher hydrocarbon emissions.
Recent advances in fuel injection technology have enabled significant improvements in emissions control for Wankel engines. Direct injection systems, particularly those utilizing multiple injection points around the rotor housing, have demonstrated substantial reductions in unburned hydrocarbon emissions by optimizing fuel delivery timing relative to the rotary cycle. These systems can precisely target fuel delivery to avoid the quenching zones that traditionally contribute to emissions challenges.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) strategies have been adapted specifically for rotary applications, with variable EGR rates controlled according to engine load and speed profiles unique to Wankel operation. This approach has proven effective in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions while maintaining acceptable thermal efficiency.
Catalytic converter technology has evolved to address the higher exhaust temperatures and different emission profiles of rotary engines. Specialized catalyst formulations with enhanced thermal stability and optimized precious metal loadings have been developed to handle the higher hydrocarbon concentrations typical in rotary exhaust streams.
Advanced electronic control units (ECUs) with rotary-specific algorithms represent another critical compliance strategy. These systems continuously monitor combustion parameters and adjust fuel injection timing, duration, and pressure to maintain optimal combustion efficiency across all operating conditions. Some manufacturers have implemented predictive control models that anticipate combustion behavior based on historical data and sensor inputs.
Low-temperature combustion strategies, including homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) adaptations for rotary architecture, have shown promise in laboratory testing. These approaches significantly reduce both NOx and particulate emissions simultaneously by operating at lower peak combustion temperatures while maintaining efficient combustion.
Hydrogen-assisted combustion represents an emerging compliance strategy, where small amounts of hydrogen are introduced to enhance flame propagation and reduce cycle-to-cycle variations. This approach has demonstrated particular effectiveness in addressing the cold-start emissions that have traditionally been problematic for Wankel engines.
Material science advancements have also contributed to emissions compliance through improved apex seal designs that maintain better compression and reduce oil consumption, directly addressing one source of particulate emissions in rotary engines.
Recent advances in fuel injection technology have enabled significant improvements in emissions control for Wankel engines. Direct injection systems, particularly those utilizing multiple injection points around the rotor housing, have demonstrated substantial reductions in unburned hydrocarbon emissions by optimizing fuel delivery timing relative to the rotary cycle. These systems can precisely target fuel delivery to avoid the quenching zones that traditionally contribute to emissions challenges.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) strategies have been adapted specifically for rotary applications, with variable EGR rates controlled according to engine load and speed profiles unique to Wankel operation. This approach has proven effective in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions while maintaining acceptable thermal efficiency.
Catalytic converter technology has evolved to address the higher exhaust temperatures and different emission profiles of rotary engines. Specialized catalyst formulations with enhanced thermal stability and optimized precious metal loadings have been developed to handle the higher hydrocarbon concentrations typical in rotary exhaust streams.
Advanced electronic control units (ECUs) with rotary-specific algorithms represent another critical compliance strategy. These systems continuously monitor combustion parameters and adjust fuel injection timing, duration, and pressure to maintain optimal combustion efficiency across all operating conditions. Some manufacturers have implemented predictive control models that anticipate combustion behavior based on historical data and sensor inputs.
Low-temperature combustion strategies, including homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) adaptations for rotary architecture, have shown promise in laboratory testing. These approaches significantly reduce both NOx and particulate emissions simultaneously by operating at lower peak combustion temperatures while maintaining efficient combustion.
Hydrogen-assisted combustion represents an emerging compliance strategy, where small amounts of hydrogen are introduced to enhance flame propagation and reduce cycle-to-cycle variations. This approach has demonstrated particular effectiveness in addressing the cold-start emissions that have traditionally been problematic for Wankel engines.
Material science advancements have also contributed to emissions compliance through improved apex seal designs that maintain better compression and reduce oil consumption, directly addressing one source of particulate emissions in rotary engines.
Materials Science Advancements for Injection Components
The evolution of materials science has been pivotal in advancing Wankel engine fuel injection systems. Traditional injection components faced significant challenges in the rotary engine environment, including extreme thermal cycling, high-speed operation, and exposure to combustion byproducts. Recent developments in ceramic-metal composites (cermets) have revolutionized injector nozzle durability, with silicon nitride and aluminum oxide matrices providing up to 300% longer service life compared to conventional steel alloys.
Advanced surface engineering techniques, particularly diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, have dramatically improved the wear resistance of moving components within fuel injectors. These coatings, typically 2-5 μm thick, reduce friction coefficients by up to 70% while providing exceptional chemical resistance against increasingly complex fuel formulations containing biofuel components.
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) derived from aerospace applications have been successfully adapted for Wankel engine injection systems. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coatings enable injector tips to withstand the unique thermal profile of rotary combustion chambers, where temperatures can fluctuate more rapidly than in reciprocating engines. This thermal management capability has been crucial for maintaining precise spray patterns throughout the engine's operating range.
Nano-structured materials represent the cutting edge of injection component development. Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology have pioneered nickel-tungsten nanocomposites that exhibit self-healing properties at the microscopic level, extending component lifespan by redistributing material during operation to counteract wear patterns. These materials show particular promise for the high-frequency operation characteristic of direct injection systems in modern Wankel applications.
Additive manufacturing has enabled previously impossible geometries in fuel delivery systems. Selective laser melting (SLM) processes can now produce injection components with internal cooling channels and optimized fluid dynamics that were previously unachievable with traditional manufacturing methods. These components feature wall thicknesses as low as 0.2 mm while maintaining structural integrity under operating pressures exceeding 200 MPa.
Biodegradable polymers and elastomers derived from renewable resources are being investigated for sealing components in fuel delivery systems. These materials address environmental concerns while offering improved compatibility with alternative fuels. Preliminary testing shows that modified cellulose-based composites can maintain sealing integrity for up to 5,000 operating hours in ethanol-rich fuel environments, representing a significant advancement over conventional fluoroelastomers.
Advanced surface engineering techniques, particularly diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, have dramatically improved the wear resistance of moving components within fuel injectors. These coatings, typically 2-5 μm thick, reduce friction coefficients by up to 70% while providing exceptional chemical resistance against increasingly complex fuel formulations containing biofuel components.
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) derived from aerospace applications have been successfully adapted for Wankel engine injection systems. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coatings enable injector tips to withstand the unique thermal profile of rotary combustion chambers, where temperatures can fluctuate more rapidly than in reciprocating engines. This thermal management capability has been crucial for maintaining precise spray patterns throughout the engine's operating range.
Nano-structured materials represent the cutting edge of injection component development. Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology have pioneered nickel-tungsten nanocomposites that exhibit self-healing properties at the microscopic level, extending component lifespan by redistributing material during operation to counteract wear patterns. These materials show particular promise for the high-frequency operation characteristic of direct injection systems in modern Wankel applications.
Additive manufacturing has enabled previously impossible geometries in fuel delivery systems. Selective laser melting (SLM) processes can now produce injection components with internal cooling channels and optimized fluid dynamics that were previously unachievable with traditional manufacturing methods. These components feature wall thicknesses as low as 0.2 mm while maintaining structural integrity under operating pressures exceeding 200 MPa.
Biodegradable polymers and elastomers derived from renewable resources are being investigated for sealing components in fuel delivery systems. These materials address environmental concerns while offering improved compatibility with alternative fuels. Preliminary testing shows that modified cellulose-based composites can maintain sealing integrity for up to 5,000 operating hours in ethanol-rich fuel environments, representing a significant advancement over conventional fluoroelastomers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!