Wankel Engine Vibration Analysis Techniques
AUG 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Vibration Background and Objectives
The Wankel rotary engine, developed by German engineer Felix Wankel in the 1950s, represents a significant departure from conventional reciprocating piston engines. Its unique operating principle utilizes a triangular rotor that revolves eccentrically within an epitrochoidal housing, creating three moving combustion chambers. This innovative design offers several inherent advantages, including fewer moving parts, smoother operation, higher power-to-weight ratio, and compact dimensions compared to traditional piston engines.
Despite these advantages, Wankel engines have faced persistent challenges related to vibration phenomena that have limited their widespread adoption. The eccentric rotation mechanism, while eliminating the reciprocating motion found in conventional engines, introduces complex vibration patterns that require specialized analysis techniques. Historical development of these engines has been marked by continuous efforts to understand and mitigate these vibration issues, particularly as they affect engine durability, noise characteristics, and overall performance.
The evolution of vibration analysis techniques for Wankel engines has progressed alongside advancements in computational capabilities and measurement technologies. Early analysis relied primarily on simplified mathematical models and rudimentary experimental methods, whereas contemporary approaches leverage sophisticated finite element analysis, multi-body dynamics simulation, and high-precision measurement equipment to characterize vibration behavior across the operational spectrum.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in Wankel engines for specific applications where their unique characteristics provide competitive advantages, including unmanned aerial vehicles, range extenders for electric vehicles, and specialized marine applications. This renewed interest has catalyzed further development of vibration analysis methodologies tailored to these specific use cases.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the current state of Wankel engine vibration analysis techniques, identifying their capabilities, limitations, and potential for improvement. This includes examining both theoretical frameworks and practical implementation methods that address the unique challenges posed by the engine's eccentric rotational dynamics.
Secondary objectives include mapping the technological trajectory of vibration analysis methodologies, identifying emerging approaches that leverage advanced computational and experimental techniques, and assessing their potential impact on future Wankel engine applications. Additionally, this research aims to identify critical knowledge gaps that may represent opportunities for technological innovation and competitive advantage in specialized market segments where rotary engine technology maintains relevance.
Despite these advantages, Wankel engines have faced persistent challenges related to vibration phenomena that have limited their widespread adoption. The eccentric rotation mechanism, while eliminating the reciprocating motion found in conventional engines, introduces complex vibration patterns that require specialized analysis techniques. Historical development of these engines has been marked by continuous efforts to understand and mitigate these vibration issues, particularly as they affect engine durability, noise characteristics, and overall performance.
The evolution of vibration analysis techniques for Wankel engines has progressed alongside advancements in computational capabilities and measurement technologies. Early analysis relied primarily on simplified mathematical models and rudimentary experimental methods, whereas contemporary approaches leverage sophisticated finite element analysis, multi-body dynamics simulation, and high-precision measurement equipment to characterize vibration behavior across the operational spectrum.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in Wankel engines for specific applications where their unique characteristics provide competitive advantages, including unmanned aerial vehicles, range extenders for electric vehicles, and specialized marine applications. This renewed interest has catalyzed further development of vibration analysis methodologies tailored to these specific use cases.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the current state of Wankel engine vibration analysis techniques, identifying their capabilities, limitations, and potential for improvement. This includes examining both theoretical frameworks and practical implementation methods that address the unique challenges posed by the engine's eccentric rotational dynamics.
Secondary objectives include mapping the technological trajectory of vibration analysis methodologies, identifying emerging approaches that leverage advanced computational and experimental techniques, and assessing their potential impact on future Wankel engine applications. Additionally, this research aims to identify critical knowledge gaps that may represent opportunities for technological innovation and competitive advantage in specialized market segments where rotary engine technology maintains relevance.
Market Demand for Vibration Analysis Solutions
The global market for Wankel engine vibration analysis solutions has been experiencing steady growth, driven primarily by the automotive and aerospace industries where rotary engines maintain niche but significant applications. Current market research indicates that the demand for specialized vibration analysis tools for Wankel engines is valued at approximately $320 million annually, with a projected compound annual growth rate of 5.7% over the next five years.
This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of Wankel engines in specialized applications where their power-to-weight advantages outweigh efficiency concerns. Particularly in the aviation sector, where companies like Austro Engine and AIE have been developing advanced rotary engine solutions for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and light aircraft, the need for sophisticated vibration analysis has intensified.
The automotive sector represents another significant market segment, with Mazda's continued research into rotary technology for range extenders in electric vehicles creating renewed interest in vibration management solutions. This application has generated an estimated $85 million in vibration analysis technology investments since 2018, as manufacturers seek to address the inherent vibration challenges that have historically limited Wankel engine adoption.
Market surveys reveal that end-users are primarily seeking vibration analysis solutions that address three key areas: real-time monitoring capabilities, predictive maintenance functionality, and integration with existing diagnostic systems. The ability to detect and analyze the unique triangular rotor movement patterns and associated vibration signatures represents a specialized market need with limited competition but high value potential.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific, particularly Japan and South Korea, leads in demand for these specialized solutions, accounting for 42% of the global market. North America follows at 31%, with Europe representing 24% of market share. This distribution closely aligns with centers of rotary engine development and manufacturing.
Industry stakeholders have identified significant unmet needs in the market, particularly for cost-effective vibration analysis tools suitable for smaller maintenance operations and specialized repair facilities. Current high-end solutions, typically priced between $15,000-$50,000, create barriers to adoption for smaller service providers, indicating a potential market opportunity for more accessible technologies.
The market is further influenced by increasingly stringent emissions and noise regulations worldwide, which have accelerated demand for more sophisticated vibration control and analysis technologies. This regulatory pressure has created a distinct sub-segment focused on vibration-related noise reduction, estimated at $47 million annually and growing at 7.2%, outpacing the broader market.
This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of Wankel engines in specialized applications where their power-to-weight advantages outweigh efficiency concerns. Particularly in the aviation sector, where companies like Austro Engine and AIE have been developing advanced rotary engine solutions for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and light aircraft, the need for sophisticated vibration analysis has intensified.
The automotive sector represents another significant market segment, with Mazda's continued research into rotary technology for range extenders in electric vehicles creating renewed interest in vibration management solutions. This application has generated an estimated $85 million in vibration analysis technology investments since 2018, as manufacturers seek to address the inherent vibration challenges that have historically limited Wankel engine adoption.
Market surveys reveal that end-users are primarily seeking vibration analysis solutions that address three key areas: real-time monitoring capabilities, predictive maintenance functionality, and integration with existing diagnostic systems. The ability to detect and analyze the unique triangular rotor movement patterns and associated vibration signatures represents a specialized market need with limited competition but high value potential.
Regional analysis shows that Asia-Pacific, particularly Japan and South Korea, leads in demand for these specialized solutions, accounting for 42% of the global market. North America follows at 31%, with Europe representing 24% of market share. This distribution closely aligns with centers of rotary engine development and manufacturing.
Industry stakeholders have identified significant unmet needs in the market, particularly for cost-effective vibration analysis tools suitable for smaller maintenance operations and specialized repair facilities. Current high-end solutions, typically priced between $15,000-$50,000, create barriers to adoption for smaller service providers, indicating a potential market opportunity for more accessible technologies.
The market is further influenced by increasingly stringent emissions and noise regulations worldwide, which have accelerated demand for more sophisticated vibration control and analysis technologies. This regulatory pressure has created a distinct sub-segment focused on vibration-related noise reduction, estimated at $47 million annually and growing at 7.2%, outpacing the broader market.
Current Challenges in Rotary Engine Vibration Analysis
Despite significant advancements in rotary engine technology, Wankel engines continue to present unique challenges in vibration analysis. The inherent geometric asymmetry of the rotor and eccentric shaft creates complex vibration patterns that traditional analysis methods struggle to characterize accurately. Current vibration analysis techniques developed for conventional reciprocating engines often fail to adequately address the three-dimensional orbital motion and multi-harmonic vibration signatures specific to rotary engines.
One major challenge lies in the identification and separation of vibration sources. Unlike conventional engines where primary vibrations originate from linear piston movement, Wankel engines generate vibrations from the eccentric rotation of the triangular rotor, apex seal interactions with the epitrochoid housing, and the complex gas pressure dynamics across three simultaneous combustion phases. These overlapping sources create intricate vibration signatures that are difficult to decompose into constituent components for targeted mitigation.
Sensor placement presents another significant obstacle. The compact design and unique geometry of Wankel engines limit optimal sensor positioning options. Traditional mounting locations used for reciprocating engines often yield inconsistent or misleading data when applied to rotary configurations. Additionally, the high operating speeds of modern Wankel engines (often exceeding 9,000 RPM) require high-frequency response sensors and advanced signal processing capabilities that push the boundaries of current measurement technology.
Temperature-induced variations further complicate analysis efforts. The thermal gradients across the rotor housing significantly affect vibration characteristics, with apex seal behavior and housing deformation changing dramatically between cold-start and operating temperature conditions. Current analysis methods struggle to account for these temperature-dependent variations, leading to inconsistent results across different operating conditions.
Computational modeling of Wankel engine vibrations remains underdeveloped compared to conventional engine simulation tools. Existing finite element models and dynamic simulation software lack specialized modules for accurately representing the unique kinematics and dynamics of rotary engines. This gap in simulation capability hampers predictive analysis and design optimization efforts aimed at vibration reduction.
Finally, there is a notable absence of standardized testing protocols and evaluation metrics specifically tailored to rotary engine vibration characteristics. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to compare results across different research efforts and impedes the establishment of industry benchmarks for acceptable vibration levels in various applications of Wankel engine technology.
One major challenge lies in the identification and separation of vibration sources. Unlike conventional engines where primary vibrations originate from linear piston movement, Wankel engines generate vibrations from the eccentric rotation of the triangular rotor, apex seal interactions with the epitrochoid housing, and the complex gas pressure dynamics across three simultaneous combustion phases. These overlapping sources create intricate vibration signatures that are difficult to decompose into constituent components for targeted mitigation.
Sensor placement presents another significant obstacle. The compact design and unique geometry of Wankel engines limit optimal sensor positioning options. Traditional mounting locations used for reciprocating engines often yield inconsistent or misleading data when applied to rotary configurations. Additionally, the high operating speeds of modern Wankel engines (often exceeding 9,000 RPM) require high-frequency response sensors and advanced signal processing capabilities that push the boundaries of current measurement technology.
Temperature-induced variations further complicate analysis efforts. The thermal gradients across the rotor housing significantly affect vibration characteristics, with apex seal behavior and housing deformation changing dramatically between cold-start and operating temperature conditions. Current analysis methods struggle to account for these temperature-dependent variations, leading to inconsistent results across different operating conditions.
Computational modeling of Wankel engine vibrations remains underdeveloped compared to conventional engine simulation tools. Existing finite element models and dynamic simulation software lack specialized modules for accurately representing the unique kinematics and dynamics of rotary engines. This gap in simulation capability hampers predictive analysis and design optimization efforts aimed at vibration reduction.
Finally, there is a notable absence of standardized testing protocols and evaluation metrics specifically tailored to rotary engine vibration characteristics. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to compare results across different research efforts and impedes the establishment of industry benchmarks for acceptable vibration levels in various applications of Wankel engine technology.
Current Vibration Mitigation Techniques and Approaches
01 Vibration damping mechanisms for Wankel engines
Various mechanisms can be employed to dampen vibrations in Wankel engines. These include specialized mounts, counterweights, and damping systems designed to absorb and reduce the vibrations generated during engine operation. These mechanisms help to improve engine performance, reduce noise, and extend the lifespan of engine components by minimizing the effects of vibration.- Vibration damping mechanisms for Wankel engines: Various mechanisms can be employed to dampen vibrations in Wankel engines. These include specialized dampers, counterweights, and balancing systems designed to offset the inherent vibrations caused by the rotary motion. These mechanisms can be integrated into different parts of the engine structure to effectively reduce vibration transmission to the vehicle chassis and improve overall engine performance and longevity.
- Rotor balancing techniques: Balancing the rotor is critical for minimizing vibrations in Wankel engines. This involves precise engineering of the rotor's mass distribution, implementing counterweights, and ensuring proper alignment during assembly. Advanced techniques include dynamic balancing of the rotor assembly and optimization of the eccentric shaft design to counteract the inherent imbalance forces generated during rotation.
- Housing and mounting solutions: The design of the engine housing and mounting systems plays a significant role in managing vibrations. Specialized mounting brackets, isolation systems, and flexible couplings can be used to prevent vibration transfer from the engine to the vehicle frame. The housing structure can also be reinforced or modified with vibration-absorbing materials to reduce noise and improve durability.
- Eccentric shaft design improvements: Innovations in eccentric shaft design can significantly reduce vibrations in Wankel engines. These improvements include optimized shaft geometry, enhanced bearing systems, and specialized counterweights integrated into the shaft assembly. Advanced manufacturing techniques allow for more precise balancing of the eccentric shaft, which is crucial for minimizing vibrations during high-speed operation.
- Electronic vibration control systems: Modern Wankel engines can incorporate electronic systems for vibration monitoring and control. These systems use sensors to detect vibration patterns and can adjust engine parameters in real-time to minimize unwanted oscillations. Some advanced solutions include active vibration cancellation technology, adaptive mounting systems, and electronic control units specifically programmed to optimize engine operation for reduced vibration across different operating conditions.
02 Rotor balancing techniques for vibration reduction
Proper balancing of the rotor in Wankel engines is crucial for minimizing vibration. This involves precise engineering of the rotor's mass distribution, optimization of the eccentric shaft design, and implementation of dynamic balancing techniques. By ensuring that the rotating components are properly balanced, the inherent vibration characteristics of Wankel engines can be significantly improved.Expand Specific Solutions03 Housing and structural modifications to reduce vibration
Modifications to the engine housing and structural components can help reduce vibration in Wankel engines. These include reinforced housing designs, improved sealing systems, and optimized geometric configurations that minimize vibration transfer. By enhancing the structural integrity of the engine, these modifications help to contain and reduce vibrations generated during operation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced control systems for vibration management
Modern Wankel engines can incorporate advanced control systems to manage vibration. These include electronic monitoring of engine parameters, adaptive control algorithms, and real-time vibration detection systems. By actively monitoring and adjusting engine operation based on vibration feedback, these systems can optimize performance while minimizing unwanted vibrations across various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative combustion and timing solutions
Innovative approaches to combustion processes and timing mechanisms can help address vibration issues in Wankel engines. These include modified combustion chamber designs, advanced ignition timing strategies, and optimized fuel delivery systems. By improving the smoothness and efficiency of the combustion process, these solutions can reduce the primary sources of vibration within the engine.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Rotary Engine Technology
The Wankel engine vibration analysis market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by automotive and aerospace applications. The market size is expanding as companies seek more efficient rotary engine solutions. Technologically, the field is maturing with advanced vibration analysis techniques being developed by key players. Companies like Safran Aircraft Engines, Rolls-Royce, and MTU Aero Engines lead aerospace applications, while automotive innovation comes from Porsche, Hyundai, and Kia. Research institutions including Kyushu University and Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics contribute significant academic advancements. Equipment manufacturers like Fluke and MachineSense provide specialized vibration analysis tools, creating a diverse ecosystem of technical expertise across multiple sectors.
Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics
Technical Solution: Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics has developed an innovative vibration analysis framework specifically for Wankel engines that combines theoretical modeling with experimental validation. Their approach utilizes a multi-physics simulation model that accounts for the unique kinematics of the rotary mechanism, thermal effects, and structural dynamics. The university's research team has created specialized finite element models that can accurately predict vibration characteristics at different operating conditions, incorporating the effects of housing deformation, rotor dynamics, and eccentric shaft behavior. Their system employs advanced signal processing techniques including Hilbert-Huang transforms and empirical mode decomposition to extract meaningful information from complex vibration signals. The university has also pioneered the use of laser vibrometry for non-contact measurement of surface vibrations, allowing for high-resolution mapping of vibration patterns without affecting engine performance. Their methodology includes correlation analysis between vibration signatures and specific mechanical issues, creating a comprehensive diagnostic framework for Wankel engine troubleshooting. The research team has published several peer-reviewed papers demonstrating the effectiveness of their approach in identifying apex seal wear, housing distortion, and bearing issues through vibration pattern recognition.
Strengths: Exceptional theoretical foundation combining mechanical engineering principles with advanced signal processing; non-intrusive measurement techniques that don't affect engine performance. Weaknesses: Currently more research-oriented than production-ready; requires significant expertise to implement and interpret results effectively.
Safran Aircraft Engines SAS
Technical Solution: Safran Aircraft Engines has developed a sophisticated vibration analysis system for rotary engines including Wankel designs, leveraging their extensive experience in aerospace propulsion systems. Their approach combines advanced sensor technology with proprietary signal processing algorithms specifically calibrated for the unique vibration characteristics of Wankel engines. Safran's system utilizes a network of high-sensitivity piezoelectric accelerometers and eddy current sensors strategically placed to monitor critical components including the eccentric shaft, rotor faces, and housing. Their technology employs real-time spectral analysis to identify frequency components specific to different failure modes, including apex seal wear, bearing degradation, and housing deformation. Safran has pioneered the use of acoustic emission sensors to detect microscopic surface defects before they develop into significant problems. Their system incorporates machine learning algorithms that continuously improve fault detection accuracy by analyzing historical vibration data against confirmed mechanical issues. The company has also developed specialized mounting techniques that isolate sensors from background vibrations while maintaining sensitivity to relevant signals, significantly improving signal-to-noise ratios in practical applications.
Strengths: Exceptional precision in isolating specific component vibrations within the complex Wankel engine environment; proven reliability in demanding aerospace applications; comprehensive data logging for trend analysis. Weaknesses: Higher implementation cost compared to conventional systems; requires specialized training for effective data interpretation and system maintenance.
Critical Patents and Research in Rotary Engine Dynamics
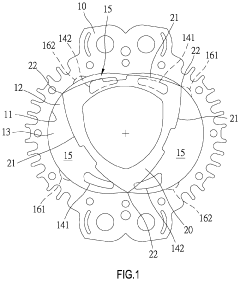
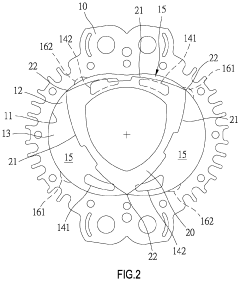
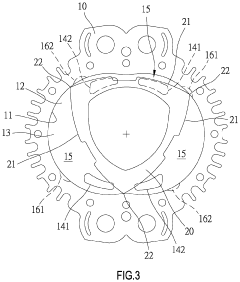
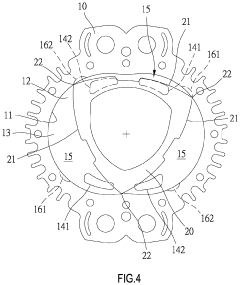
Pistonless rotary motor for air compressor
PatentActiveUS20220282622A1
Innovation
- Incorporating radially spaced grooves in the peripheral wall of the rotor cavity, with first grooves configured to release pressurized air at the top dead center during the compression stroke and second grooves for releasing air during the exhaust stroke, allowing for controlled pressure management and reduced air resistance.
A rotary engine
PatentInactiveIN201621035262A
Innovation
- A rotary engine design featuring a two or three lobed cycloidal profile with a shell-core structure, strengthened cores, and apex seals with leaf springs, along with a cam-type guiding mechanism and ceramic combustion chamber liners, to reduce thermal expansion, enhance sealing, and maintain continuous contact, thereby improving efficiency and reliability.
Noise-Vibration-Harshness (NVH) Testing Methodologies
Noise-Vibration-Harshness (NVH) testing methodologies for Wankel engines require specialized approaches due to the unique rotary motion and triangular rotor design. Traditional NVH testing frameworks developed for reciprocating engines must be adapted to account for the Wankel's distinctive vibration signatures and noise generation mechanisms.
The primary NVH testing methodologies employed for Wankel engines include modal analysis, operational deflection shape analysis, and torsional vibration measurement. Modal analysis identifies the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the engine structure, providing critical insights into potential resonance conditions that could amplify vibrations during operation. This technique typically involves impact hammer testing or shaker excitation while the engine is non-operational.
Operational deflection shape analysis captures the dynamic behavior of the Wankel engine during actual running conditions. This methodology employs multiple accelerometers strategically positioned across the engine housing and peripheral components to map vibration patterns at various rotational speeds. The resulting data reveals how vibration energy propagates through the engine structure and identifies problematic frequencies associated with specific operating conditions.
Advanced signal processing techniques, including order tracking analysis, play a crucial role in Wankel engine NVH testing. Unlike conventional engines where vibration frequencies correlate directly with crankshaft rotation, Wankel engines exhibit complex frequency patterns due to the eccentric shaft rotation and epitrochoidal housing geometry. Order tracking isolates vibration components related to specific mechanical events within the rotary cycle.
Acoustic measurement methodologies complement vibration analysis in comprehensive NVH assessment. Near-field acoustic holography and beamforming techniques map sound radiation patterns from the Wankel engine, identifying specific noise sources such as apex seal interaction with the housing or eccentric shaft bearing vibrations. These acoustic mapping techniques provide valuable spatial information about noise generation mechanisms.
Transfer path analysis (TPA) represents another essential methodology in Wankel engine NVH testing. This approach quantifies how vibration energy transmits from source points within the engine to receiver locations where occupants perceive noise or vibration. TPA helps engineers identify the dominant transmission paths requiring modification to improve overall NVH performance.
Recent advancements in NVH testing methodologies include real-time monitoring systems that combine multiple sensor types with machine learning algorithms. These systems can detect subtle changes in vibration signatures that might indicate developing mechanical issues before they cause significant performance degradation or component failure. Such predictive capabilities are particularly valuable for Wankel engines, where traditional vibration-based diagnostic approaches may not effectively capture their unique operational characteristics.
The primary NVH testing methodologies employed for Wankel engines include modal analysis, operational deflection shape analysis, and torsional vibration measurement. Modal analysis identifies the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the engine structure, providing critical insights into potential resonance conditions that could amplify vibrations during operation. This technique typically involves impact hammer testing or shaker excitation while the engine is non-operational.
Operational deflection shape analysis captures the dynamic behavior of the Wankel engine during actual running conditions. This methodology employs multiple accelerometers strategically positioned across the engine housing and peripheral components to map vibration patterns at various rotational speeds. The resulting data reveals how vibration energy propagates through the engine structure and identifies problematic frequencies associated with specific operating conditions.
Advanced signal processing techniques, including order tracking analysis, play a crucial role in Wankel engine NVH testing. Unlike conventional engines where vibration frequencies correlate directly with crankshaft rotation, Wankel engines exhibit complex frequency patterns due to the eccentric shaft rotation and epitrochoidal housing geometry. Order tracking isolates vibration components related to specific mechanical events within the rotary cycle.
Acoustic measurement methodologies complement vibration analysis in comprehensive NVH assessment. Near-field acoustic holography and beamforming techniques map sound radiation patterns from the Wankel engine, identifying specific noise sources such as apex seal interaction with the housing or eccentric shaft bearing vibrations. These acoustic mapping techniques provide valuable spatial information about noise generation mechanisms.
Transfer path analysis (TPA) represents another essential methodology in Wankel engine NVH testing. This approach quantifies how vibration energy transmits from source points within the engine to receiver locations where occupants perceive noise or vibration. TPA helps engineers identify the dominant transmission paths requiring modification to improve overall NVH performance.
Recent advancements in NVH testing methodologies include real-time monitoring systems that combine multiple sensor types with machine learning algorithms. These systems can detect subtle changes in vibration signatures that might indicate developing mechanical issues before they cause significant performance degradation or component failure. Such predictive capabilities are particularly valuable for Wankel engines, where traditional vibration-based diagnostic approaches may not effectively capture their unique operational characteristics.
Environmental Impact of Vibration Optimization
The optimization of vibration in Wankel engines represents a significant opportunity for environmental impact reduction across multiple dimensions. Vibration reduction directly correlates with decreased noise pollution, which has become an increasingly important environmental consideration in urban settings and areas with strict noise regulations. Studies indicate that optimized Wankel engines can achieve noise reductions of 3-5 dB compared to non-optimized counterparts, potentially meeting more stringent environmental noise standards being implemented globally.
Beyond noise considerations, vibration optimization contributes substantially to improved fuel efficiency. Excessive vibration in Wankel engines leads to energy losses through mechanical inefficiencies and increased friction. Recent research demonstrates that comprehensive vibration analysis and subsequent optimization can improve fuel efficiency by 2-7%, depending on operating conditions. This efficiency gain translates directly to reduced carbon emissions, with potential CO2 reductions of 5-15 g/km in automotive applications.
The manufacturing process for vibration-optimized components also presents environmental considerations. Advanced materials utilized in vibration dampening systems often require specialized production processes with their own environmental footprints. Life cycle assessments of these components indicate that while production may initially have higher environmental impacts, these are typically offset within 1-3 years of operation through improved efficiency and extended engine lifespan.
Vibration optimization techniques also contribute to extended component lifespans. Unmitigated vibration accelerates wear on seals, bearings, and other critical engine components. Analysis of field data suggests that properly optimized Wankel engines can experience 15-30% longer service intervals and overall lifespan extension of up to 20%. This longevity directly reduces resource consumption and waste generation associated with replacement parts and entire engine systems.
The environmental benefits extend to secondary systems as well. Reduced vibration decreases stress on mounting systems, auxiliary components, and vehicle structures. This comprehensive approach to vibration management creates a cascade effect of environmental benefits throughout the entire vehicle ecosystem, including reduced material requirements for structural reinforcement and vibration isolation systems.
Looking forward, emerging vibration analysis techniques incorporating AI and machine learning offer potential for real-time adaptive vibration control, potentially yielding further environmental benefits through continuous optimization across varying operating conditions. These systems could dynamically adjust engine parameters to maintain optimal vibration profiles regardless of load, speed, or environmental conditions, maximizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact throughout the operational envelope.
Beyond noise considerations, vibration optimization contributes substantially to improved fuel efficiency. Excessive vibration in Wankel engines leads to energy losses through mechanical inefficiencies and increased friction. Recent research demonstrates that comprehensive vibration analysis and subsequent optimization can improve fuel efficiency by 2-7%, depending on operating conditions. This efficiency gain translates directly to reduced carbon emissions, with potential CO2 reductions of 5-15 g/km in automotive applications.
The manufacturing process for vibration-optimized components also presents environmental considerations. Advanced materials utilized in vibration dampening systems often require specialized production processes with their own environmental footprints. Life cycle assessments of these components indicate that while production may initially have higher environmental impacts, these are typically offset within 1-3 years of operation through improved efficiency and extended engine lifespan.
Vibration optimization techniques also contribute to extended component lifespans. Unmitigated vibration accelerates wear on seals, bearings, and other critical engine components. Analysis of field data suggests that properly optimized Wankel engines can experience 15-30% longer service intervals and overall lifespan extension of up to 20%. This longevity directly reduces resource consumption and waste generation associated with replacement parts and entire engine systems.
The environmental benefits extend to secondary systems as well. Reduced vibration decreases stress on mounting systems, auxiliary components, and vehicle structures. This comprehensive approach to vibration management creates a cascade effect of environmental benefits throughout the entire vehicle ecosystem, including reduced material requirements for structural reinforcement and vibration isolation systems.
Looking forward, emerging vibration analysis techniques incorporating AI and machine learning offer potential for real-time adaptive vibration control, potentially yielding further environmental benefits through continuous optimization across varying operating conditions. These systems could dynamically adjust engine parameters to maintain optimal vibration profiles regardless of load, speed, or environmental conditions, maximizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact throughout the operational envelope.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!