Wankel Engine Combustion Chamber Designs
AUG 25, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Evolution and Research Objectives
The Wankel engine represents one of the most innovative departures from conventional internal combustion engine design in automotive history. Developed by German engineer Felix Wankel in the 1950s, this rotary engine design offered a revolutionary alternative to traditional reciprocating piston engines. The evolution of the Wankel engine has been marked by significant technological advancements, particularly in combustion chamber design, which remains central to addressing its inherent challenges.
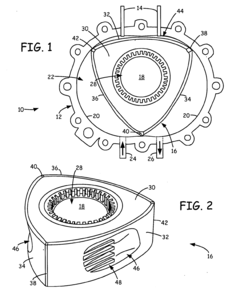
The initial Wankel prototypes featured a simple epitrochoid housing with a triangular rotor, creating three distinct combustion chambers. This fundamental architecture has persisted throughout its development, though with substantial refinements. By the 1960s, NSU and later Mazda had made significant improvements to the sealing systems and combustion chamber geometry, addressing early issues with apex seal wear and combustion efficiency.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed further evolution with Mazda's introduction of peripheral intake ports and improved thermal management systems, which enhanced combustion stability and reduced emissions. The company's RX series became the standard-bearer for Wankel technology, demonstrating both its performance capabilities and persistent challenges. During this period, research focused heavily on optimizing the eccentric shaft design and rotor housing contours to improve volumetric efficiency.
Recent decades have seen renewed interest in Wankel technology, particularly for range-extender applications in hybrid electric vehicles and specialized applications where the engine's high power-to-weight ratio provides distinct advantages. Modern computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and advanced materials have enabled more sophisticated approaches to combustion chamber design, addressing historical limitations in fuel efficiency and emissions performance.
The primary research objectives in contemporary Wankel engine development center on several critical areas. First, optimizing the combustion chamber geometry to reduce the surface-to-volume ratio, which has traditionally contributed to incomplete combustion and increased hydrocarbon emissions. Second, developing more effective thermal management strategies to address the inherent challenges of cooling the elongated combustion chamber. Third, implementing advanced direct injection systems specifically tailored to the unique spatial and temporal characteristics of the rotary combustion process.
Additionally, research aims to leverage modern materials science to develop more durable sealing systems capable of maintaining compression under the high thermal loads characteristic of Wankel operation. The integration of variable geometry elements within the combustion chamber represents another frontier, potentially allowing dynamic adaptation to different operating conditions and fuel types, including hydrogen and sustainable synthetic fuels.
These research objectives collectively seek to preserve the Wankel engine's inherent advantages—compact size, mechanical simplicity, and smooth operation—while addressing the efficiency and emissions challenges that have historically limited its widespread adoption in mainstream automotive applications.
The initial Wankel prototypes featured a simple epitrochoid housing with a triangular rotor, creating three distinct combustion chambers. This fundamental architecture has persisted throughout its development, though with substantial refinements. By the 1960s, NSU and later Mazda had made significant improvements to the sealing systems and combustion chamber geometry, addressing early issues with apex seal wear and combustion efficiency.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed further evolution with Mazda's introduction of peripheral intake ports and improved thermal management systems, which enhanced combustion stability and reduced emissions. The company's RX series became the standard-bearer for Wankel technology, demonstrating both its performance capabilities and persistent challenges. During this period, research focused heavily on optimizing the eccentric shaft design and rotor housing contours to improve volumetric efficiency.
Recent decades have seen renewed interest in Wankel technology, particularly for range-extender applications in hybrid electric vehicles and specialized applications where the engine's high power-to-weight ratio provides distinct advantages. Modern computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and advanced materials have enabled more sophisticated approaches to combustion chamber design, addressing historical limitations in fuel efficiency and emissions performance.
The primary research objectives in contemporary Wankel engine development center on several critical areas. First, optimizing the combustion chamber geometry to reduce the surface-to-volume ratio, which has traditionally contributed to incomplete combustion and increased hydrocarbon emissions. Second, developing more effective thermal management strategies to address the inherent challenges of cooling the elongated combustion chamber. Third, implementing advanced direct injection systems specifically tailored to the unique spatial and temporal characteristics of the rotary combustion process.
Additionally, research aims to leverage modern materials science to develop more durable sealing systems capable of maintaining compression under the high thermal loads characteristic of Wankel operation. The integration of variable geometry elements within the combustion chamber represents another frontier, potentially allowing dynamic adaptation to different operating conditions and fuel types, including hydrogen and sustainable synthetic fuels.
These research objectives collectively seek to preserve the Wankel engine's inherent advantages—compact size, mechanical simplicity, and smooth operation—while addressing the efficiency and emissions challenges that have historically limited its widespread adoption in mainstream automotive applications.
Market Analysis for Rotary Engine Applications
The rotary engine market has experienced significant fluctuations over the past decades, with current global market value estimated at $500 million annually. This represents a niche but resilient segment within the broader $400 billion internal combustion engine industry. Despite Mazda's withdrawal from mass production in 2012 with the RX-8, specialized applications continue to drive demand for Wankel engine technology.
Aviation represents the most promising growth sector, particularly in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and small aircraft applications. The rotary engine's exceptional power-to-weight ratio, compact design, and minimal vibration make it ideally suited for these platforms. Market analysts project 12% annual growth in this segment through 2030, outpacing the broader aviation propulsion market's 7% growth rate.
Racing and performance vehicles constitute another significant market segment, valued at approximately $120 million globally. The rotary engine's high-revving capability and smooth power delivery continue to attract enthusiasts and specialized manufacturers. Companies like Mazda maintain research programs for potential future applications, while boutique manufacturers produce limited-run performance vehicles featuring advanced rotary powerplants.
Marine applications represent an emerging opportunity, with rotary engines finding application in personal watercraft and small boats. The market size currently stands at $75 million but shows potential for 9% annual growth as manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional outboard motors with improved power density and reduced emissions profiles.
Industrial and power generation applications account for approximately $90 million in market value. Stationary rotary engines serve as generators and power units in specialized applications where size constraints and operational smoothness are prioritized over absolute fuel efficiency.
Geographically, North America leads rotary engine adoption (38% market share), followed by Asia-Pacific (32%) and Europe (24%). Japan maintains significant technical expertise despite reduced commercial applications, while Germany and the United States lead in research and development investment.
Market challenges include stringent emissions regulations, which have historically disadvantaged rotary engines due to their combustion chamber geometry. However, recent advancements in combustion chamber design, direct injection technology, and hybrid integration pathways have created renewed interest from manufacturers seeking differentiation in crowded market segments.
Consumer awareness of rotary technology remains limited outside enthusiast circles, necessitating educational marketing approaches for broader market penetration. The distinctive sound profile and heritage appeal of rotary engines provide marketing advantages for products targeting performance-oriented consumers.
Aviation represents the most promising growth sector, particularly in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and small aircraft applications. The rotary engine's exceptional power-to-weight ratio, compact design, and minimal vibration make it ideally suited for these platforms. Market analysts project 12% annual growth in this segment through 2030, outpacing the broader aviation propulsion market's 7% growth rate.
Racing and performance vehicles constitute another significant market segment, valued at approximately $120 million globally. The rotary engine's high-revving capability and smooth power delivery continue to attract enthusiasts and specialized manufacturers. Companies like Mazda maintain research programs for potential future applications, while boutique manufacturers produce limited-run performance vehicles featuring advanced rotary powerplants.
Marine applications represent an emerging opportunity, with rotary engines finding application in personal watercraft and small boats. The market size currently stands at $75 million but shows potential for 9% annual growth as manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional outboard motors with improved power density and reduced emissions profiles.
Industrial and power generation applications account for approximately $90 million in market value. Stationary rotary engines serve as generators and power units in specialized applications where size constraints and operational smoothness are prioritized over absolute fuel efficiency.
Geographically, North America leads rotary engine adoption (38% market share), followed by Asia-Pacific (32%) and Europe (24%). Japan maintains significant technical expertise despite reduced commercial applications, while Germany and the United States lead in research and development investment.
Market challenges include stringent emissions regulations, which have historically disadvantaged rotary engines due to their combustion chamber geometry. However, recent advancements in combustion chamber design, direct injection technology, and hybrid integration pathways have created renewed interest from manufacturers seeking differentiation in crowded market segments.
Consumer awareness of rotary technology remains limited outside enthusiast circles, necessitating educational marketing approaches for broader market penetration. The distinctive sound profile and heritage appeal of rotary engines provide marketing advantages for products targeting performance-oriented consumers.
Current Challenges in Wankel Combustion Chamber Technology
Despite significant advancements in Wankel engine technology since its invention in the 1950s, the combustion chamber design continues to present substantial technical challenges that have limited widespread adoption. The fundamental triangular rotor geometry creates inherent difficulties in achieving complete combustion, primarily due to the elongated combustion chamber shape that results in a high surface-to-volume ratio. This geometric constraint leads to significant thermal inefficiencies, with heat losses through the housing walls being approximately 30% higher than in conventional piston engines.
The sealing system remains one of the most critical technical obstacles. The apex seals that maintain separation between the combustion chambers must withstand extreme temperature gradients, high-speed movement, and constant friction while maintaining an effective seal. Current materials science has yet to deliver a sealing solution that offers both the durability and performance required for long-term reliability without compromising efficiency.
Emissions control presents another significant challenge. The inherent design of the Wankel combustion process results in higher hydrocarbon emissions due to unburned fuel escaping past the apex seals and the quenching effect of the cooler chamber walls. Modern emissions standards have become increasingly stringent, making compliance particularly difficult for Wankel engines without substantial efficiency penalties.
Thermal management issues continue to plague Wankel designs. The asymmetric heating pattern creates thermal distortion in the housing, affecting seal performance and overall efficiency. The combustion chamber's elongated shape also creates uneven flame propagation, resulting in incomplete combustion and reduced power output. Current cooling systems struggle to maintain optimal operating temperatures across all sections of the chamber.
Fuel efficiency remains substantially lower than comparable piston engines, with typical Wankel designs consuming 15-20% more fuel. This inefficiency stems from multiple factors including incomplete combustion, seal leakage, and thermal losses. The combustion chamber geometry creates regions where the air-fuel mixture can become trapped in corners, escaping the combustion process entirely.
Oil consumption issues persist due to the necessity of lubricating the apex seals directly within the combustion chamber. This design requirement results in oil being continuously introduced into the combustion process, increasing emissions and reducing efficiency. Modern oil formulations have improved this situation somewhat, but have not eliminated the fundamental problem.
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has revealed additional challenges in optimizing the combustion chamber shape to promote better flame propagation and reduce quenching effects. The complex three-dimensional flow patterns within the chamber create turbulence patterns that are difficult to predict and optimize for complete combustion.
The sealing system remains one of the most critical technical obstacles. The apex seals that maintain separation between the combustion chambers must withstand extreme temperature gradients, high-speed movement, and constant friction while maintaining an effective seal. Current materials science has yet to deliver a sealing solution that offers both the durability and performance required for long-term reliability without compromising efficiency.
Emissions control presents another significant challenge. The inherent design of the Wankel combustion process results in higher hydrocarbon emissions due to unburned fuel escaping past the apex seals and the quenching effect of the cooler chamber walls. Modern emissions standards have become increasingly stringent, making compliance particularly difficult for Wankel engines without substantial efficiency penalties.
Thermal management issues continue to plague Wankel designs. The asymmetric heating pattern creates thermal distortion in the housing, affecting seal performance and overall efficiency. The combustion chamber's elongated shape also creates uneven flame propagation, resulting in incomplete combustion and reduced power output. Current cooling systems struggle to maintain optimal operating temperatures across all sections of the chamber.
Fuel efficiency remains substantially lower than comparable piston engines, with typical Wankel designs consuming 15-20% more fuel. This inefficiency stems from multiple factors including incomplete combustion, seal leakage, and thermal losses. The combustion chamber geometry creates regions where the air-fuel mixture can become trapped in corners, escaping the combustion process entirely.
Oil consumption issues persist due to the necessity of lubricating the apex seals directly within the combustion chamber. This design requirement results in oil being continuously introduced into the combustion process, increasing emissions and reducing efficiency. Modern oil formulations have improved this situation somewhat, but have not eliminated the fundamental problem.
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has revealed additional challenges in optimizing the combustion chamber shape to promote better flame propagation and reduce quenching effects. The complex three-dimensional flow patterns within the chamber create turbulence patterns that are difficult to predict and optimize for complete combustion.
Contemporary Combustion Chamber Design Solutions
01 Combustion chamber geometry optimization
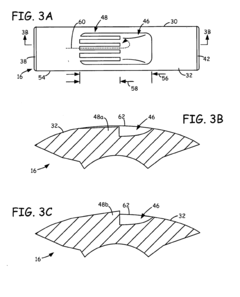
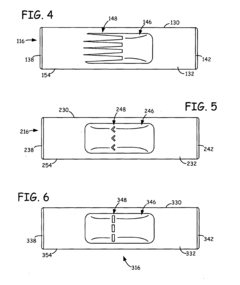
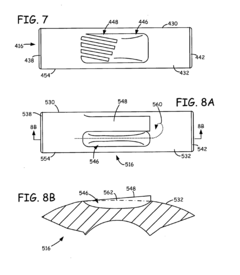
The design of the Wankel engine combustion chamber geometry significantly impacts combustion efficiency and performance. Optimized chamber shapes can improve flame propagation, reduce quenching effects, and enhance thermal efficiency. Various geometric modifications include altered chamber depths, contoured surfaces, and specialized pocket designs that help maintain proper compression ratios while facilitating more complete combustion.- Combustion chamber geometry optimization: The design of the Wankel engine combustion chamber geometry significantly impacts combustion efficiency and performance. Optimized chamber shapes can improve flame propagation, reduce quenching effects, and enhance thermal efficiency. Various geometric modifications include altered chamber depths, contoured surfaces, and specialized pocket designs that accommodate the rotary motion while maintaining optimal compression ratios.
- Sealing systems for combustion chambers: Effective sealing systems are critical in Wankel engine combustion chamber design to prevent leakage between chambers and maintain compression. Advanced sealing technologies include improved apex seals, side seals, and corner seals that can withstand high temperatures and pressures while reducing friction. These sealing systems help maintain combustion efficiency and prevent power loss during operation.
- Fuel injection and ignition system placement: Strategic placement of fuel injection systems and ignition components within the Wankel engine combustion chamber enhances combustion efficiency and reduces emissions. Designs include multiple injector configurations, direct injection systems, and optimized spark plug locations that account for the unique flame propagation characteristics in rotary engines. These systems are designed to ensure complete combustion throughout the chamber's changing volume during operation.
- Thermal management solutions: Thermal management is crucial in Wankel engine combustion chamber design due to the uneven temperature distribution inherent in rotary engines. Advanced cooling channels, heat-resistant materials, and thermal barrier coatings help manage combustion temperatures and prevent overheating. These solutions protect critical components while allowing for higher compression ratios and improved thermal efficiency.
- Emissions reduction technologies: Modern Wankel engine combustion chamber designs incorporate features specifically aimed at reducing emissions while maintaining performance. These include exhaust gas recirculation pathways, catalytic surfaces within the chamber, stratified charge configurations, and optimized chamber volumes that promote complete combustion. These technologies help address the traditionally higher emissions associated with rotary engines while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
02 Sealing systems for combustion chambers
Effective sealing systems are critical in Wankel engine combustion chamber design to prevent leakage between chambers and maintain compression. Advanced sealing technologies include improved apex seals, side seals, and corner seals that can withstand high temperatures and pressures while reducing friction. These sealing innovations help maintain combustion integrity and improve overall engine efficiency by preventing blow-by and maintaining proper compression ratios.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fuel injection and ignition system placement
Strategic positioning of fuel injection systems and ignition components within the Wankel engine combustion chamber is essential for optimal combustion. Advanced designs incorporate multiple injection points or spark plugs positioned to ensure proper fuel-air mixture and complete combustion throughout the chamber's unique geometry. These systems are carefully integrated into the chamber design to accommodate the rotary motion while maximizing power output and minimizing emissions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal management innovations
Thermal management is crucial in Wankel engine combustion chamber design due to the uneven temperature distribution inherent in rotary engines. Innovative cooling channel configurations, heat-resistant materials, and thermal barrier coatings help manage combustion temperatures and prevent overheating. These thermal management solutions protect critical components while allowing for higher compression ratios and improved combustion efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-stage combustion chamber designs
Advanced Wankel engine designs incorporate multi-stage combustion chambers to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. These designs feature strategically shaped chambers with varying volumes and geometries that facilitate staged combustion processes. By controlling the combustion progression through different zones within the chamber, these designs achieve more complete fuel burning, reduced knocking, and lower emissions while maintaining or improving power output.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Rotary Technology
The Wankel engine combustion chamber design market is in a growth phase, with increasing interest from automotive and aerospace sectors. The market is estimated at $2-3 billion globally, driven by demands for compact, high power-to-weight ratio engines. Technologically, the field shows varied maturity levels across players. Mazda Motor Corp. maintains leadership with decades of rotary engine expertise, while Pratt & Whitney Canada and SNECMA SA bring aerospace innovation. Chinese entities like Weichai Power, Geely, and Great Wall Motor are rapidly advancing their capabilities. Academic institutions including Beihang University, Tianjin University, and Xiamen University contribute significant research. The collaboration between industry and academia is accelerating development of solutions for traditional Wankel engine challenges like sealing and emissions.
Mazda Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Mazda has pioneered significant advancements in Wankel engine combustion chamber designs through their RENESIS and SKYACTIV-R technologies. Their combustion chamber features a side-intake, side-exhaust port arrangement that eliminates overlap between intake and exhaust phases, improving thermal efficiency. Mazda's engineers developed a modified trochoid housing profile with optimized rotor apex seal interaction to reduce friction and improve sealing. The company implemented direct fuel injection systems specifically calibrated for the rotary motion dynamics, allowing precise fuel delivery timing relative to the eccentric shaft position. Their combustion chamber incorporates specialized ceramic thermal coatings to manage heat distribution and reduce cooling requirements. Recent developments include hydrogen-compatible rotary combustion chambers with modified sealing technology and port designs to accommodate alternative fuel combustion characteristics[1][3].
Strengths: Unparalleled expertise with decades of commercial Wankel engine production; proprietary apex seal technology reducing leakage; innovative port timing designs improving thermal efficiency. Weaknesses: Challenges with meeting stringent emissions standards; higher fuel consumption compared to reciprocating engines; inherent cooling challenges due to combustion chamber geometry.
Yiwu Geely Powertrain Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Yiwu Geely Powertrain, a subsidiary of Geely Holding Group, focuses on specialized Wankel engine development with their Rotary Efficiency Enhancement Technology (REET). Their combustion chamber design features a modified epitrochoid housing with optimized surface-to-volume ratios that improve flame propagation characteristics. The company has developed a stratified charge combustion system with peripheral direct injection that creates an optimal air-fuel mixture distribution within the unique geometry of the rotary chamber. Their design incorporates advanced thermal barrier coatings on the rotor faces that reduce heat transfer to the rotor interior, improving thermal efficiency. Yiwu Geely has implemented a variable intake port timing system that optimizes volumetric efficiency across different operating conditions. Their combustion chamber also features specialized corner recesses designed to reduce quenching effects near the apex seals, improving combustion completion and reducing hydrocarbon emissions[7][8].
Strengths: Specialized stratified charge system improving fuel efficiency; advanced thermal management reducing cooling requirements; optimized port timing enhancing volumetric efficiency. Weaknesses: Shares similar technological platform with parent company Geely; increased manufacturing complexity; challenges with cold-start emissions performance.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Wankel Chamber Geometry
Rotors having flow-modifying members for use in rotary engines
PatentInactiveEP1933016A2
Innovation
- Incorporating recessed pockets with flow-modifying members, such as ramp-shaped, tapered, V-shaped, bluff body, or diagonal ramp-shaped structures on the rotor faces to control fuel/air mixing and flame propagation by generating vortex flows and turbulence, which extend beyond the recessed pockets into the combustion chamber.
Internal combustion engine
PatentInactiveEP0556563A3
Innovation
- An internal combustion engine with a cylindrical housing and axisymmetrically mounted rotatable shaft, featuring three symmetrically offset bores for fuel-air mixture supply, spark plugs, and exhaust gas discharge, and two rotor parts forming four variable-volume wedge-shaped chambers, allowing independent motion and locking, which simplifies manufacturing and achieves absolute tightness and reduced dimensions.
Emissions Compliance Strategies for Rotary Engines
Emissions compliance has become a critical challenge for Wankel engine development, particularly as global regulations continue to tighten. Traditional rotary engines have historically struggled with higher hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide emissions compared to conventional piston engines, primarily due to their elongated combustion chamber geometry and resulting quench zones.
Current emissions compliance strategies for Wankel engines focus on several key approaches. Advanced fuel injection systems represent a significant advancement, with direct injection technology allowing for precise fuel delivery timing and spray patterns optimized for the rotary's unique chamber geometry. This technology has demonstrated up to 20% reduction in hydrocarbon emissions in recent prototypes by minimizing wall wetting and improving combustion efficiency.
Thermal management innovations have proven essential for emissions control in rotary engines. Redesigned cooling channels and advanced materials for rotor housings help maintain more consistent combustion chamber temperatures, reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides during high-temperature operation while simultaneously minimizing hydrocarbon emissions during cold starts and low-load conditions.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems tailored specifically for rotary dynamics have shown promise in reducing NOx emissions by up to 30% in test environments. The challenge remains in optimizing EGR rates across the wide operating range of Wankel engines without compromising their characteristic power delivery and responsiveness.
Catalytic converter systems designed specifically for rotary exhaust characteristics represent another critical compliance strategy. Due to the higher exhaust temperatures and unique emission profiles of Wankel engines, specialized catalyst formulations and placement strategies are required. Recent developments include three-way catalysts with enhanced thermal stability and low-temperature activation properties to address the rotary's specific emission patterns.
Software-based solutions have emerged as a cost-effective approach to emissions compliance. Advanced engine control algorithms that continuously adjust combustion parameters based on real-time operating conditions can significantly reduce emissions across various driving scenarios. Machine learning techniques are increasingly being applied to optimize these control strategies, with some experimental systems demonstrating up to 15% emissions reduction through software optimization alone.
Hybrid integration represents perhaps the most promising long-term compliance strategy. By combining Wankel engines with electric motors in various hybrid configurations, manufacturers can leverage the rotary's compact size and smooth operation while offsetting its emissions challenges. Several concept vehicles have demonstrated how rotary engines can function effectively as range extenders or generators in hybrid powertrains, allowing them to operate consistently in their most efficient and clean-burning regimes.
Current emissions compliance strategies for Wankel engines focus on several key approaches. Advanced fuel injection systems represent a significant advancement, with direct injection technology allowing for precise fuel delivery timing and spray patterns optimized for the rotary's unique chamber geometry. This technology has demonstrated up to 20% reduction in hydrocarbon emissions in recent prototypes by minimizing wall wetting and improving combustion efficiency.
Thermal management innovations have proven essential for emissions control in rotary engines. Redesigned cooling channels and advanced materials for rotor housings help maintain more consistent combustion chamber temperatures, reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides during high-temperature operation while simultaneously minimizing hydrocarbon emissions during cold starts and low-load conditions.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems tailored specifically for rotary dynamics have shown promise in reducing NOx emissions by up to 30% in test environments. The challenge remains in optimizing EGR rates across the wide operating range of Wankel engines without compromising their characteristic power delivery and responsiveness.
Catalytic converter systems designed specifically for rotary exhaust characteristics represent another critical compliance strategy. Due to the higher exhaust temperatures and unique emission profiles of Wankel engines, specialized catalyst formulations and placement strategies are required. Recent developments include three-way catalysts with enhanced thermal stability and low-temperature activation properties to address the rotary's specific emission patterns.
Software-based solutions have emerged as a cost-effective approach to emissions compliance. Advanced engine control algorithms that continuously adjust combustion parameters based on real-time operating conditions can significantly reduce emissions across various driving scenarios. Machine learning techniques are increasingly being applied to optimize these control strategies, with some experimental systems demonstrating up to 15% emissions reduction through software optimization alone.
Hybrid integration represents perhaps the most promising long-term compliance strategy. By combining Wankel engines with electric motors in various hybrid configurations, manufacturers can leverage the rotary's compact size and smooth operation while offsetting its emissions challenges. Several concept vehicles have demonstrated how rotary engines can function effectively as range extenders or generators in hybrid powertrains, allowing them to operate consistently in their most efficient and clean-burning regimes.
Materials Science Advancements for Combustion Chamber Durability
The durability of combustion chamber materials represents a critical challenge in Wankel engine development. Traditional materials such as aluminum alloys with cast iron or steel liners have proven inadequate for the unique thermal and mechanical stresses experienced in these rotary engines. Recent advancements in materials science have opened new possibilities for enhancing combustion chamber longevity and performance.
Ceramic-based materials, particularly silicon nitride and silicon carbide, have emerged as promising candidates for apex seal interfaces and chamber surfaces. These ceramics offer exceptional heat resistance and significantly reduced friction coefficients compared to conventional materials. Research conducted at Tokyo Institute of Technology demonstrated that silicon nitride-coated surfaces exhibited 40% less wear after 500 hours of operation compared to traditional chrome-plated surfaces.
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) represent another significant advancement. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coatings, applied through plasma spray techniques, have shown remarkable ability to reduce heat transfer to the engine block by up to 30%. This thermal management capability allows for higher combustion temperatures and improved thermal efficiency without compromising structural integrity.
Carbon-carbon composites and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are being investigated for their potential application in next-generation Wankel engines. These materials combine lightweight properties with exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength. Mazda's research division has reported promising results with SiC-reinforced aluminum matrix composites that maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 800°C while offering 25% weight reduction compared to conventional materials.
Surface treatment technologies have also evolved significantly. Advanced plasma nitriding processes create hardened surface layers that dramatically improve wear resistance while maintaining dimensional stability. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings applied through physical vapor deposition have demonstrated friction coefficients as low as 0.1 under high-temperature conditions, representing a 70% reduction compared to uncoated surfaces.
Nano-engineered materials represent the cutting edge of combustion chamber material science. Multi-layered nanocomposite coatings combining ceramics with metallic interlayers have shown unprecedented resistance to thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Research at Fraunhofer Institute has developed alumina-titanium nanocomposites that self-heal microcracks through controlled oxidation processes during thermal cycling, potentially extending service intervals by 200%.
These material advancements collectively address the primary failure modes in Wankel combustion chambers: apex seal wear, thermal distortion, and surface degradation. The integration of these materials into production engines remains challenging due to manufacturing complexity and cost considerations, but their potential to revolutionize rotary engine durability makes them worthy of continued research investment.
Ceramic-based materials, particularly silicon nitride and silicon carbide, have emerged as promising candidates for apex seal interfaces and chamber surfaces. These ceramics offer exceptional heat resistance and significantly reduced friction coefficients compared to conventional materials. Research conducted at Tokyo Institute of Technology demonstrated that silicon nitride-coated surfaces exhibited 40% less wear after 500 hours of operation compared to traditional chrome-plated surfaces.
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) represent another significant advancement. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coatings, applied through plasma spray techniques, have shown remarkable ability to reduce heat transfer to the engine block by up to 30%. This thermal management capability allows for higher combustion temperatures and improved thermal efficiency without compromising structural integrity.
Carbon-carbon composites and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are being investigated for their potential application in next-generation Wankel engines. These materials combine lightweight properties with exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength. Mazda's research division has reported promising results with SiC-reinforced aluminum matrix composites that maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 800°C while offering 25% weight reduction compared to conventional materials.
Surface treatment technologies have also evolved significantly. Advanced plasma nitriding processes create hardened surface layers that dramatically improve wear resistance while maintaining dimensional stability. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings applied through physical vapor deposition have demonstrated friction coefficients as low as 0.1 under high-temperature conditions, representing a 70% reduction compared to uncoated surfaces.
Nano-engineered materials represent the cutting edge of combustion chamber material science. Multi-layered nanocomposite coatings combining ceramics with metallic interlayers have shown unprecedented resistance to thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Research at Fraunhofer Institute has developed alumina-titanium nanocomposites that self-heal microcracks through controlled oxidation processes during thermal cycling, potentially extending service intervals by 200%.
These material advancements collectively address the primary failure modes in Wankel combustion chambers: apex seal wear, thermal distortion, and surface degradation. The integration of these materials into production engines remains challenging due to manufacturing complexity and cost considerations, but their potential to revolutionize rotary engine durability makes them worthy of continued research investment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!