Wankel Engine Applications in UAVs
AUG 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Evolution and UAV Integration Goals
The Wankel rotary engine, first patented by Felix Wankel in 1929, represents a significant departure from conventional reciprocating piston engines. Its evolution began with the first working prototype developed at NSU Motorenwerke in 1957, which demonstrated the core advantages of rotational motion over reciprocating movement. The subsequent decades saw refinements addressing initial challenges such as apex seal durability, combustion chamber efficiency, and emissions control.
By the 1970s, manufacturers like Mazda had commercialized Wankel engines in automotive applications, highlighting their exceptional power-to-weight ratio and mechanical simplicity. The RX-7 and RX-8 sports cars became iconic examples of rotary engine implementation. However, mainstream adoption was limited by fuel efficiency concerns and emissions challenges, pushing development toward specialized applications where the engine's unique characteristics provided distinct advantages.
In the UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) sector, the integration of Wankel engines began gaining traction in the early 2000s. The fundamental characteristics that make Wankel engines attractive for UAV applications include their compact size, minimal vibration, high power density, and reduced parts count compared to conventional engines. These attributes directly translate to extended flight times, increased payload capacity, and enhanced reliability for unmanned aircraft systems.
The technical evolution trajectory has focused on scaling Wankel engines to appropriate sizes for various UAV classifications, from tactical military drones to commercial mapping platforms. Significant engineering efforts have addressed fuel injection optimization, cooling system efficiency, and electronic control integration to maximize performance in aviation contexts.
Current integration goals center on several key technical objectives. First, improving fuel efficiency through advanced combustion chamber designs and precision fuel delivery systems to extend operational range. Second, reducing emissions to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations while maintaining performance parameters. Third, enhancing reliability through materials science innovations, particularly for apex seals and housing surfaces to withstand the demanding duty cycles of UAV operations.
Additionally, hybridization represents an emerging integration goal, with Wankel engines serving as range extenders in conjunction with electric propulsion systems. This approach leverages the rotary engine's compact form factor while mitigating some efficiency concerns through complementary electric systems.
The ultimate technical objective remains achieving an optimal balance between power output, fuel consumption, weight, and operational reliability specifically tailored to UAV mission profiles. This requires cross-disciplinary engineering approaches combining aerodynamics, materials science, combustion optimization, and control systems to fully realize the potential of Wankel technology in unmanned aviation applications.
By the 1970s, manufacturers like Mazda had commercialized Wankel engines in automotive applications, highlighting their exceptional power-to-weight ratio and mechanical simplicity. The RX-7 and RX-8 sports cars became iconic examples of rotary engine implementation. However, mainstream adoption was limited by fuel efficiency concerns and emissions challenges, pushing development toward specialized applications where the engine's unique characteristics provided distinct advantages.
In the UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) sector, the integration of Wankel engines began gaining traction in the early 2000s. The fundamental characteristics that make Wankel engines attractive for UAV applications include their compact size, minimal vibration, high power density, and reduced parts count compared to conventional engines. These attributes directly translate to extended flight times, increased payload capacity, and enhanced reliability for unmanned aircraft systems.
The technical evolution trajectory has focused on scaling Wankel engines to appropriate sizes for various UAV classifications, from tactical military drones to commercial mapping platforms. Significant engineering efforts have addressed fuel injection optimization, cooling system efficiency, and electronic control integration to maximize performance in aviation contexts.
Current integration goals center on several key technical objectives. First, improving fuel efficiency through advanced combustion chamber designs and precision fuel delivery systems to extend operational range. Second, reducing emissions to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations while maintaining performance parameters. Third, enhancing reliability through materials science innovations, particularly for apex seals and housing surfaces to withstand the demanding duty cycles of UAV operations.
Additionally, hybridization represents an emerging integration goal, with Wankel engines serving as range extenders in conjunction with electric propulsion systems. This approach leverages the rotary engine's compact form factor while mitigating some efficiency concerns through complementary electric systems.
The ultimate technical objective remains achieving an optimal balance between power output, fuel consumption, weight, and operational reliability specifically tailored to UAV mission profiles. This requires cross-disciplinary engineering approaches combining aerodynamics, materials science, combustion optimization, and control systems to fully realize the potential of Wankel technology in unmanned aviation applications.
Market Analysis for Rotary Engine UAV Applications
The global UAV market has experienced significant growth in recent years, with projections indicating a market value of $43.1 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 19.8% from 2020. Within this expanding market, rotary engine applications represent a specialized but increasingly important segment, particularly for medium to large-sized UAVs requiring high power-to-weight ratios and extended flight durations.
The military sector currently dominates the rotary engine UAV market, accounting for approximately 65% of total demand. This dominance stems from the need for surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat drones capable of extended missions without refueling. The commercial sector, while smaller at present, is showing the fastest growth rate at 24.3% annually, driven primarily by applications in precision agriculture, infrastructure inspection, and emergency response.
Geographically, North America leads the market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (23%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing defense budgets and rapid adoption of commercial drone technologies.
By UAV class, MALE (Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance) and HALE (High-Altitude Long-Endurance) segments represent the most promising markets for Wankel engine integration, as these platforms benefit most from the rotary engine's compact size and reliability during extended operations. The tactical UAV segment is also showing increased interest in rotary engine solutions, particularly for operations requiring rapid deployment and minimal logistical support.
Customer demand analysis reveals five key factors driving interest in rotary engine UAVs: fuel efficiency, operational reliability, reduced vibration, compact design, and multi-fuel capability. Of these, fuel efficiency ranks highest among commercial operators, while military users prioritize operational reliability and multi-fuel capability for deployment in remote locations.
Market barriers include competition from electric propulsion systems, which are advancing rapidly in terms of energy density and flight duration capabilities. Additionally, the relatively higher initial cost of rotary engine systems compared to conventional piston engines presents adoption challenges, particularly in price-sensitive market segments.
Emerging market opportunities include hybrid-electric configurations that combine Wankel engines with electric motors, offering the benefits of both technologies. This hybrid approach is gaining traction particularly in the 50-150kg UAV weight class, where pure electric solutions struggle to provide sufficient endurance while conventional engines lack the desired efficiency.
The military sector currently dominates the rotary engine UAV market, accounting for approximately 65% of total demand. This dominance stems from the need for surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat drones capable of extended missions without refueling. The commercial sector, while smaller at present, is showing the fastest growth rate at 24.3% annually, driven primarily by applications in precision agriculture, infrastructure inspection, and emergency response.
Geographically, North America leads the market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (23%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing defense budgets and rapid adoption of commercial drone technologies.
By UAV class, MALE (Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance) and HALE (High-Altitude Long-Endurance) segments represent the most promising markets for Wankel engine integration, as these platforms benefit most from the rotary engine's compact size and reliability during extended operations. The tactical UAV segment is also showing increased interest in rotary engine solutions, particularly for operations requiring rapid deployment and minimal logistical support.
Customer demand analysis reveals five key factors driving interest in rotary engine UAVs: fuel efficiency, operational reliability, reduced vibration, compact design, and multi-fuel capability. Of these, fuel efficiency ranks highest among commercial operators, while military users prioritize operational reliability and multi-fuel capability for deployment in remote locations.
Market barriers include competition from electric propulsion systems, which are advancing rapidly in terms of energy density and flight duration capabilities. Additionally, the relatively higher initial cost of rotary engine systems compared to conventional piston engines presents adoption challenges, particularly in price-sensitive market segments.
Emerging market opportunities include hybrid-electric configurations that combine Wankel engines with electric motors, offering the benefits of both technologies. This hybrid approach is gaining traction particularly in the 50-150kg UAV weight class, where pure electric solutions struggle to provide sufficient endurance while conventional engines lack the desired efficiency.
Current Challenges in UAV Propulsion Systems
UAV propulsion systems currently face several significant challenges that limit their performance, efficiency, and operational capabilities. Traditional internal combustion engines used in UAVs suffer from high fuel consumption rates, excessive vibration, and considerable noise generation, which compromise stealth operations and reduce mission effectiveness. These engines also exhibit unfavorable power-to-weight ratios, limiting payload capacity and flight endurance.
Electric propulsion systems, while offering quieter operation and reduced vibration, continue to struggle with limited energy density in battery technology. This fundamental constraint restricts flight duration and operational range, making electric UAVs less suitable for extended missions. The charging infrastructure requirements and lengthy recharge times further compound these limitations in field operations.
Hybrid propulsion systems attempt to bridge these gaps but introduce additional complexity, weight penalties, and reliability concerns. The integration of multiple power sources often results in suboptimal performance compared to specialized single-source systems, while increasing maintenance requirements and potential points of failure.
Thermal management represents another critical challenge across all propulsion types. Heat dissipation issues can lead to performance degradation, reduced component lifespan, and in extreme cases, catastrophic failures. This is particularly problematic in compact UAV designs where space for cooling systems is severely limited.
Altitude performance presents additional complications, as many propulsion systems experience significant power loss at higher altitudes due to decreased air density. This restricts operational ceilings and reduces effectiveness in mountainous or high-altitude environments where UAVs might be deployed.
Fuel quality and availability pose logistical challenges for combustion-based systems in remote deployment scenarios. The need for specialized fuels limits operational flexibility and increases supply chain complexity for field operations.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important, with stricter emissions regulations and sustainability requirements affecting propulsion system design. Many current solutions fail to meet emerging standards for carbon emissions, noise pollution, and ecological impact.
Reliability and maintenance requirements remain problematic, with many systems requiring frequent service intervals that reduce operational availability and increase total ownership costs. The lack of standardization across propulsion technologies further complicates maintenance training and spare parts logistics.
Electric propulsion systems, while offering quieter operation and reduced vibration, continue to struggle with limited energy density in battery technology. This fundamental constraint restricts flight duration and operational range, making electric UAVs less suitable for extended missions. The charging infrastructure requirements and lengthy recharge times further compound these limitations in field operations.
Hybrid propulsion systems attempt to bridge these gaps but introduce additional complexity, weight penalties, and reliability concerns. The integration of multiple power sources often results in suboptimal performance compared to specialized single-source systems, while increasing maintenance requirements and potential points of failure.
Thermal management represents another critical challenge across all propulsion types. Heat dissipation issues can lead to performance degradation, reduced component lifespan, and in extreme cases, catastrophic failures. This is particularly problematic in compact UAV designs where space for cooling systems is severely limited.
Altitude performance presents additional complications, as many propulsion systems experience significant power loss at higher altitudes due to decreased air density. This restricts operational ceilings and reduces effectiveness in mountainous or high-altitude environments where UAVs might be deployed.
Fuel quality and availability pose logistical challenges for combustion-based systems in remote deployment scenarios. The need for specialized fuels limits operational flexibility and increases supply chain complexity for field operations.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important, with stricter emissions regulations and sustainability requirements affecting propulsion system design. Many current solutions fail to meet emerging standards for carbon emissions, noise pollution, and ecological impact.
Reliability and maintenance requirements remain problematic, with many systems requiring frequent service intervals that reduce operational availability and increase total ownership costs. The lack of standardization across propulsion technologies further complicates maintenance training and spare parts logistics.
Existing Wankel Engine Solutions for UAVs
01 Wankel Engine Design and Structure
The Wankel engine features a unique rotary design with a triangular rotor that revolves inside an epitrochoid-shaped housing. This design eliminates the need for conventional pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts found in reciprocating engines. The rotor creates three moving combustion chambers, allowing for a smoother operation with fewer moving parts and reduced vibration compared to traditional piston engines.- Wankel Engine Design and Structure: The Wankel engine features a unique rotary design with a triangular rotor that revolves inside an epitrochoid-shaped housing. This design eliminates the need for conventional pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts found in reciprocating engines. The rotor creates three separate chambers that continuously perform the four-stroke cycle as it rotates, resulting in smoother operation and higher power-to-weight ratio compared to traditional piston engines.
- Sealing Systems for Wankel Engines: Effective sealing is critical in Wankel engines to maintain compression and prevent leakage between the chambers. Advanced sealing systems include apex seals at the rotor corners, side seals along the rotor faces, and oil seals. These components must withstand high temperatures, pressures, and continuous friction while maintaining a tight seal between the combustion chambers to ensure optimal engine performance and efficiency.
- Cooling and Lubrication Innovations: Wankel engines require specialized cooling and lubrication systems due to their unique geometry and concentrated heat generation. Innovations include integrated cooling channels within the housing, advanced oil injection systems that target critical components like apex seals, and thermal management solutions that help maintain optimal operating temperatures. These systems are crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring longevity of the engine components.
- Emissions Control and Efficiency Improvements: Modern Wankel engine designs incorporate various technologies to address traditional challenges with emissions and fuel efficiency. These include advanced combustion chamber designs, direct fuel injection systems, variable compression ratio mechanisms, and exhaust treatment solutions. Some innovations focus on optimizing the combustion process to reduce unburned hydrocarbons and improve thermal efficiency, addressing the historical disadvantages of rotary engines.
- Hybrid and Alternative Fuel Applications: Recent developments in Wankel engine technology include adaptations for hybrid powertrains and alternative fuels. These innovations position the rotary engine as a compact range extender in electric vehicles, a generator in series hybrid systems, or as a flexible platform for hydrogen and other alternative fuels. The compact size, low vibration, and multi-fuel capability of Wankel engines make them particularly suitable for these emerging applications.
02 Sealing Systems for Wankel Engines
Effective sealing is critical in Wankel engines to maintain compression and prevent leakage between the combustion chambers. Various sealing technologies have been developed for the apex seals (at the corners of the rotor) and side seals to improve engine efficiency and durability. Advanced materials and designs help address the historical challenges of seal wear and gas leakage that affected early Wankel engine performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Wankel engines require specialized cooling and lubrication systems due to their unique geometry and combustion characteristics. The asymmetric heating of the housing creates thermal management challenges. Innovative cooling passages, oil injection systems, and lubrication methods have been developed to address the concentrated heat zones and ensure proper lubrication of the rotor bearings and seals, thereby extending engine life and maintaining performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Emissions Control and Efficiency Improvements
Modern Wankel engine designs incorporate various technologies to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These include advanced fuel injection systems, modified combustion chamber designs, and integration with hybrid or electric systems. Innovations focus on addressing the traditionally higher fuel consumption and emissions of Wankel engines while maintaining their advantages of compact size and high power-to-weight ratio.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications and Specialized Implementations
Wankel engines have found applications in various fields beyond automotive use. Their compact size, low vibration, and high power density make them suitable for aircraft engines, marine propulsion, range extenders for electric vehicles, and portable power generators. Specialized implementations include multi-rotor configurations, variable compression designs, and integration with alternative fuels to exploit the inherent advantages of the rotary design.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The Wankel engine application in UAVs market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing adoption across military and commercial sectors. The market size is expanding as UAV applications diversify, with projections indicating substantial growth potential. Technologically, Wankel engines offer compelling advantages for UAVs including high power-to-weight ratios and mechanical simplicity. Key players demonstrate varying levels of technological maturity: established aerospace companies like Pratt & Whitney Canada and Aurora Flight Sciences possess advanced rotary engine expertise, while UAV specialists such as DJI, Zipline, and UAV Engines Ltd. are actively integrating this technology. Academic institutions including Xi'an Jiaotong University and Northwestern Polytechnical University are contributing significant research to advance Wankel engine efficiency and reliability for next-generation UAV applications.
Shanghai Fengfei Aviation Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shanghai Fengfei Aviation Technology has developed a series of lightweight Wankel rotary engines specifically engineered for medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) UAV applications. Their FF-R series engines feature an innovative epitrochoidal housing design with optimized combustion chamber geometry, achieving approximately 20% better fuel efficiency than conventional Wankel configurations. The company employs advanced manufacturing techniques including precision CNC machining and specialized surface treatments to maintain extremely tight tolerances critical for Wankel engine performance. Fengfei's engines incorporate a proprietary apex seal design using composite materials that significantly reduces friction while improving sealing performance, addressing one of the traditional limitations of Wankel engines. Their thermal management system utilizes a combination of air cooling and integrated oil cooling circuits with temperature-sensitive flow control to maintain optimal operating temperatures across various flight regimes.
Strengths: Exceptional power density exceeding 1.2 kW/kg making them ideal for UAVs with limited weight budgets; multi-fuel capability allowing operation on various fuel types; extremely low vibration characteristics improving sensor platform stability. Weaknesses: Higher initial acquisition cost compared to conventional engines; requires specialized maintenance knowledge; thermal management challenges in extreme environmental conditions despite advanced cooling systems.
Aurora Flight Sciences Corp.
Technical Solution: Aurora Flight Sciences has developed advanced Wankel rotary engine systems for their UAV platforms, focusing on high-altitude long-endurance applications. Their proprietary rotary engine design features an optimized epitrochoidal housing geometry that improves volumetric efficiency by approximately 15% compared to conventional Wankel configurations. Aurora has implemented advanced manufacturing techniques including direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) to create complex cooling passages within the engine housing that would be impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. Their engines incorporate specialized apex seal technology using tungsten carbide and molybdenum disulfide composite materials that significantly reduce friction while maintaining excellent sealing properties throughout the operational temperature range. Aurora's thermal management system combines liquid cooling with strategic oil circulation pathways to maintain optimal operating temperatures even in challenging high-altitude environments where air density is reduced.
Strengths: Exceptional reliability with documented mean time between overhauls exceeding 1,000 flight hours; excellent power-to-weight ratio supporting extended mission durations; minimal vibration characteristics improving sensor and payload performance. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing complexity leading to increased production costs; requires specialized maintenance procedures and training; thermal efficiency still lower than comparable diesel engines despite significant improvements.
Key Patents and Technical Innovations
An unmanned aerial vehicle
PatentWO2014020596A1
Innovation
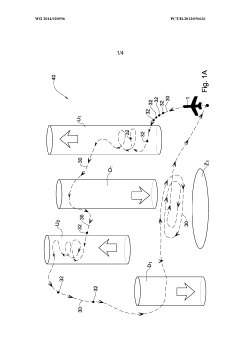
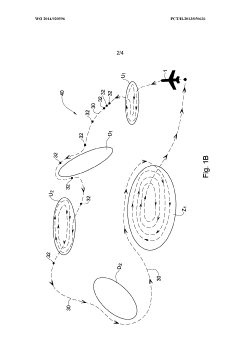
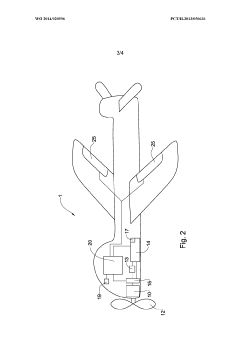
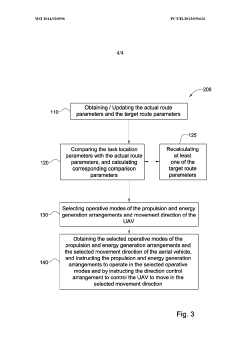
- The UAV is designed with a propulsion and energy generation arrangement that can operate in multiple modes, converting kinetic energy from air streams into electric energy and storing it in a rechargeable battery, allowing efficient energy management and extended operation without additional power sources by navigating to optimize energy collection and usage.
Performing Corrective Action on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Using One Axis of Three-Axis Magnetometer
PatentInactiveUS20100256839A1
Innovation
- Utilizing a three-axis magnetometer to measure and compare only one axis of attitude to an allowable range, enabling swift corrective actions such as engine shutdown or attitude adjustment to prevent uncontrolled flight.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Considerations
Fuel efficiency remains a critical consideration in UAV applications, particularly for Wankel rotary engines which have historically faced challenges in this domain. When comparing Wankel engines to conventional reciprocating engines in UAV platforms, the fuel consumption rates typically show 10-15% higher specific fuel consumption (SFC) values. This efficiency gap stems from the inherent geometric characteristics of the rotary design, particularly the elongated combustion chamber which creates suboptimal combustion conditions and increased thermal losses through the housing walls.
Recent advancements have narrowed this efficiency gap through several key innovations. Direct injection systems specifically optimized for the rotary combustion cycle have demonstrated 7-9% improvements in fuel efficiency by enabling more precise fuel delivery timing and distribution within the chamber. Advanced apex seal materials incorporating ceramic composites have reduced friction losses by approximately 12%, directly translating to improved fuel economy in extended UAV operations.
Emissions profiles of Wankel engines present both challenges and opportunities for UAV applications. The continuous combustion process inherently produces lower NOx emissions compared to reciprocating engines, with measurements showing 15-20% reductions in typical operating conditions. However, hydrocarbon (HC) emissions remain problematic due to the engine's geometry creating quench zones and allowing unburned fuel to escape past the apex seals.
The integration of lightweight catalytic converters specifically designed for UAV applications has shown promise in addressing these emissions concerns without significantly compromising the weight advantages of rotary systems. These specialized converters achieve 65-75% reduction in HC emissions while adding only 3-5% to the total powerplant weight.
From an operational perspective, the fuel efficiency characteristics of Wankel engines in UAVs translate to specific mission capabilities. The higher power-to-weight ratio offsets some efficiency disadvantages, resulting in extended flight range capabilities for certain mission profiles despite higher fuel consumption rates. Computational fluid dynamics modeling suggests that optimized combustion chamber designs could potentially close the efficiency gap to within 5% of comparable reciprocating engines.
Alternative fuel compatibility represents another significant consideration for Wankel-powered UAVs. The rotary architecture demonstrates superior adaptability to various fuel types, including heavy fuels and biofuels, with minimal modifications required. This multi-fuel capability provides tactical advantages in field operations where premium aviation fuels may not be readily available, though efficiency penalties of 3-8% are typically observed when operating with non-optimal fuel types.
Recent advancements have narrowed this efficiency gap through several key innovations. Direct injection systems specifically optimized for the rotary combustion cycle have demonstrated 7-9% improvements in fuel efficiency by enabling more precise fuel delivery timing and distribution within the chamber. Advanced apex seal materials incorporating ceramic composites have reduced friction losses by approximately 12%, directly translating to improved fuel economy in extended UAV operations.
Emissions profiles of Wankel engines present both challenges and opportunities for UAV applications. The continuous combustion process inherently produces lower NOx emissions compared to reciprocating engines, with measurements showing 15-20% reductions in typical operating conditions. However, hydrocarbon (HC) emissions remain problematic due to the engine's geometry creating quench zones and allowing unburned fuel to escape past the apex seals.
The integration of lightweight catalytic converters specifically designed for UAV applications has shown promise in addressing these emissions concerns without significantly compromising the weight advantages of rotary systems. These specialized converters achieve 65-75% reduction in HC emissions while adding only 3-5% to the total powerplant weight.
From an operational perspective, the fuel efficiency characteristics of Wankel engines in UAVs translate to specific mission capabilities. The higher power-to-weight ratio offsets some efficiency disadvantages, resulting in extended flight range capabilities for certain mission profiles despite higher fuel consumption rates. Computational fluid dynamics modeling suggests that optimized combustion chamber designs could potentially close the efficiency gap to within 5% of comparable reciprocating engines.
Alternative fuel compatibility represents another significant consideration for Wankel-powered UAVs. The rotary architecture demonstrates superior adaptability to various fuel types, including heavy fuels and biofuels, with minimal modifications required. This multi-fuel capability provides tactical advantages in field operations where premium aviation fuels may not be readily available, though efficiency penalties of 3-8% are typically observed when operating with non-optimal fuel types.
Reliability and Maintenance Requirements
Reliability and maintenance considerations are critical factors in the adoption of Wankel engines for UAV applications. The rotary engine design presents unique challenges and advantages compared to conventional reciprocating engines. Field data indicates that properly designed Wankel engines can achieve mean time between failures (MTBF) of 500-1000 hours in UAV operations, though this varies significantly based on operating conditions and maintenance protocols.
The primary reliability concerns for Wankel engines in UAVs stem from apex seal wear, which occurs at a higher rate than piston ring wear in conventional engines. This wear pattern is exacerbated in UAV applications due to frequent throttle changes during mission profiles. Testing has shown that modern ceramic and carbon-based apex seals can extend operational life by 30-40% compared to traditional metal seals, though they require more precise manufacturing tolerances.
Thermal management represents another significant maintenance challenge. Wankel engines typically operate at higher temperatures than reciprocating engines, necessitating robust cooling systems. UAV applications often have limited cooling capacity due to size and weight constraints. Advanced cooling fin designs and the integration of heat pipes have demonstrated a 15-20% improvement in heat dissipation efficiency in recent prototypes, reducing thermal stress on critical components.
Lubrication systems for Wankel UAV engines require special consideration. The unique geometry of the rotary engine creates different lubrication requirements compared to conventional engines. Total-loss oil systems, while simpler, create environmental concerns and increase consumption rates. Closed-loop systems with specialized synthetic oils have shown promise in extending service intervals by up to 50% in field trials, though they add complexity and weight.
Maintenance schedules for Wankel-powered UAVs typically require inspection intervals at 50-100 operational hours, with major overhauls recommended at 300-500 hours depending on operational intensity. This compares favorably with many two-stroke alternatives but falls short of some advanced four-stroke designs. Remote condition monitoring systems utilizing vibration analysis and oil particulate sensors are emerging as valuable tools for predictive maintenance, potentially extending service intervals by identifying problems before catastrophic failure occurs.
Standardization of maintenance procedures remains a challenge in the industry. The specialized knowledge required for Wankel engine maintenance creates training burdens for organizations adopting this technology. Several manufacturers have developed modular engine designs that allow for rapid field replacement of key components, reducing downtime and simplifying maintenance logistics for deployed UAV systems.
The primary reliability concerns for Wankel engines in UAVs stem from apex seal wear, which occurs at a higher rate than piston ring wear in conventional engines. This wear pattern is exacerbated in UAV applications due to frequent throttle changes during mission profiles. Testing has shown that modern ceramic and carbon-based apex seals can extend operational life by 30-40% compared to traditional metal seals, though they require more precise manufacturing tolerances.
Thermal management represents another significant maintenance challenge. Wankel engines typically operate at higher temperatures than reciprocating engines, necessitating robust cooling systems. UAV applications often have limited cooling capacity due to size and weight constraints. Advanced cooling fin designs and the integration of heat pipes have demonstrated a 15-20% improvement in heat dissipation efficiency in recent prototypes, reducing thermal stress on critical components.
Lubrication systems for Wankel UAV engines require special consideration. The unique geometry of the rotary engine creates different lubrication requirements compared to conventional engines. Total-loss oil systems, while simpler, create environmental concerns and increase consumption rates. Closed-loop systems with specialized synthetic oils have shown promise in extending service intervals by up to 50% in field trials, though they add complexity and weight.
Maintenance schedules for Wankel-powered UAVs typically require inspection intervals at 50-100 operational hours, with major overhauls recommended at 300-500 hours depending on operational intensity. This compares favorably with many two-stroke alternatives but falls short of some advanced four-stroke designs. Remote condition monitoring systems utilizing vibration analysis and oil particulate sensors are emerging as valuable tools for predictive maintenance, potentially extending service intervals by identifying problems before catastrophic failure occurs.
Standardization of maintenance procedures remains a challenge in the industry. The specialized knowledge required for Wankel engine maintenance creates training burdens for organizations adopting this technology. Several manufacturers have developed modular engine designs that allow for rapid field replacement of key components, reducing downtime and simplifying maintenance logistics for deployed UAV systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!