How to Reduce Hydrochloric Acid's Carbon Footprint?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Production Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) production has been a cornerstone of the chemical industry for decades, playing a crucial role in various applications ranging from steel pickling to food processing. However, the growing concern over climate change has brought the carbon footprint of HCl production into sharp focus. The primary objective of this technical research is to explore innovative methods and technologies to reduce the carbon emissions associated with HCl manufacturing processes.
The evolution of HCl production techniques has seen significant advancements since its initial large-scale production in the early 20th century. Initially, the Hargreaves process, which involved the reaction of salt, sulfuric acid, and air, was widely used. This was followed by the development of the chlor-alkali process, which remains a dominant method today. However, these traditional methods are energy-intensive and often rely on fossil fuels, contributing substantially to greenhouse gas emissions.
Recent technological trends in HCl production have been driven by the need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly processes. This includes the exploration of renewable energy sources to power production facilities, the development of more efficient catalysts to reduce energy requirements, and the implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste and emissions. Additionally, there is a growing interest in carbon capture and utilization technologies that could potentially transform CO2 emissions into valuable products.
The global market for HCl is expected to continue growing, driven by increasing demand from various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and water treatment. This growth, however, is accompanied by stricter environmental regulations and a shift towards sustainable production methods. As a result, the industry faces the challenge of meeting rising demand while simultaneously reducing its environmental impact.
To address these challenges, several key technological objectives have been identified. These include optimizing existing production processes to improve energy efficiency, developing new catalysts that can operate at lower temperatures, exploring alternative feedstocks that have a lower carbon footprint, and integrating renewable energy sources into the production chain. Additionally, there is a focus on improving waste heat recovery systems and implementing advanced process control technologies to minimize energy consumption and emissions.
The path towards reducing the carbon footprint of HCl production requires a multifaceted approach, combining incremental improvements in existing technologies with breakthrough innovations. This technical research aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of HCl production, identify the most promising avenues for carbon footprint reduction, and outline the potential technological roadmap for achieving sustainable HCl manufacturing in the coming decades.
The evolution of HCl production techniques has seen significant advancements since its initial large-scale production in the early 20th century. Initially, the Hargreaves process, which involved the reaction of salt, sulfuric acid, and air, was widely used. This was followed by the development of the chlor-alkali process, which remains a dominant method today. However, these traditional methods are energy-intensive and often rely on fossil fuels, contributing substantially to greenhouse gas emissions.
Recent technological trends in HCl production have been driven by the need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly processes. This includes the exploration of renewable energy sources to power production facilities, the development of more efficient catalysts to reduce energy requirements, and the implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste and emissions. Additionally, there is a growing interest in carbon capture and utilization technologies that could potentially transform CO2 emissions into valuable products.
The global market for HCl is expected to continue growing, driven by increasing demand from various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and water treatment. This growth, however, is accompanied by stricter environmental regulations and a shift towards sustainable production methods. As a result, the industry faces the challenge of meeting rising demand while simultaneously reducing its environmental impact.
To address these challenges, several key technological objectives have been identified. These include optimizing existing production processes to improve energy efficiency, developing new catalysts that can operate at lower temperatures, exploring alternative feedstocks that have a lower carbon footprint, and integrating renewable energy sources into the production chain. Additionally, there is a focus on improving waste heat recovery systems and implementing advanced process control technologies to minimize energy consumption and emissions.
The path towards reducing the carbon footprint of HCl production requires a multifaceted approach, combining incremental improvements in existing technologies with breakthrough innovations. This technical research aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of HCl production, identify the most promising avenues for carbon footprint reduction, and outline the potential technological roadmap for achieving sustainable HCl manufacturing in the coming decades.
Market Analysis for Low-Carbon HCl
The global market for low-carbon hydrochloric acid (HCl) is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainable industrial practices. As industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint, the demand for eco-friendly alternatives to traditional HCl production methods is rising rapidly.
The market size for low-carbon HCl is projected to expand substantially over the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to outpace that of conventional HCl. This growth is primarily fueled by stringent environmental policies in developed regions such as Europe and North America, where governments are implementing carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions reduction targets.
Key industries driving the demand for low-carbon HCl include chemical manufacturing, steel production, and water treatment. The chemical sector, in particular, is showing a strong shift towards sustainable practices, with many companies setting ambitious carbon neutrality goals. This transition is creating a robust market for low-carbon HCl as a critical raw material in various chemical processes.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the market for low-carbon HCl, thanks to its advanced regulatory framework and strong commitment to reducing industrial emissions. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific regions, especially in China and India, as these countries intensify their efforts to combat air pollution and meet international climate commitments.
The market is also seeing increased interest from end-users in the pharmaceutical and food industries, where the use of low-carbon HCl aligns with broader sustainability goals and enhances brand reputation. This diversification of end-user industries is expected to provide additional growth opportunities for low-carbon HCl producers.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as higher production costs compared to traditional HCl and the need for significant infrastructure investments. However, technological advancements and economies of scale are gradually reducing these cost differentials, making low-carbon HCl more competitive in the long term.
Several major chemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve low-carbon HCl production technologies. These efforts are focused on enhancing energy efficiency, utilizing renewable energy sources, and exploring innovative carbon capture and utilization methods in the production process.
The market is also witnessing the emergence of new business models, such as circular economy approaches, where HCl is produced as a by-product of other low-carbon industrial processes. This trend is expected to further drive the adoption of low-carbon HCl across various industries.
The market size for low-carbon HCl is projected to expand substantially over the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to outpace that of conventional HCl. This growth is primarily fueled by stringent environmental policies in developed regions such as Europe and North America, where governments are implementing carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions reduction targets.
Key industries driving the demand for low-carbon HCl include chemical manufacturing, steel production, and water treatment. The chemical sector, in particular, is showing a strong shift towards sustainable practices, with many companies setting ambitious carbon neutrality goals. This transition is creating a robust market for low-carbon HCl as a critical raw material in various chemical processes.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the market for low-carbon HCl, thanks to its advanced regulatory framework and strong commitment to reducing industrial emissions. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific regions, especially in China and India, as these countries intensify their efforts to combat air pollution and meet international climate commitments.
The market is also seeing increased interest from end-users in the pharmaceutical and food industries, where the use of low-carbon HCl aligns with broader sustainability goals and enhances brand reputation. This diversification of end-user industries is expected to provide additional growth opportunities for low-carbon HCl producers.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as higher production costs compared to traditional HCl and the need for significant infrastructure investments. However, technological advancements and economies of scale are gradually reducing these cost differentials, making low-carbon HCl more competitive in the long term.
Several major chemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve low-carbon HCl production technologies. These efforts are focused on enhancing energy efficiency, utilizing renewable energy sources, and exploring innovative carbon capture and utilization methods in the production process.
The market is also witnessing the emergence of new business models, such as circular economy approaches, where HCl is produced as a by-product of other low-carbon industrial processes. This trend is expected to further drive the adoption of low-carbon HCl across various industries.
Current Challenges in HCl Carbon Footprint Reduction
The reduction of hydrochloric acid's carbon footprint presents several significant challenges in the current industrial landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the energy-intensive nature of traditional HCl production methods. The Mannheim process and the direct synthesis method, which are widely used, require substantial thermal energy inputs, contributing to high carbon emissions.
Another challenge lies in the transportation and storage of hydrochloric acid. Due to its corrosive nature, specialized containers and handling procedures are necessary, often involving energy-intensive processes and materials with high embodied carbon. This aspect of the supply chain significantly adds to the overall carbon footprint of HCl.
The recycling and reuse of hydrochloric acid pose additional difficulties. While recycling can potentially reduce the carbon footprint, the processes involved in purifying and reconcentrating used HCl are often energy-intensive themselves. Balancing the environmental benefits of recycling against the carbon costs of these processes remains a complex issue.
Furthermore, the diverse applications of hydrochloric acid across various industries complicate efforts to implement standardized carbon reduction strategies. Each sector, from chemical manufacturing to food processing, has unique requirements and constraints, making it challenging to develop universal solutions.
The lack of cost-effective, low-carbon alternatives to traditional HCl production methods is another significant hurdle. While some innovative approaches are being explored, such as electrolysis-based production, these technologies are not yet economically viable or scalable for widespread industrial adoption.
Regulatory challenges also play a role in hindering carbon footprint reduction efforts. The absence of unified global standards for carbon accounting and emissions reduction in chemical production creates inconsistencies in how companies approach and report their environmental impact.
Additionally, the interconnected nature of industrial processes means that changes in HCl production or usage can have ripple effects throughout supply chains. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and address the carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid without considering broader systemic impacts.
Lastly, there is a significant knowledge gap in accurately measuring and tracking the full lifecycle carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid. This lack of comprehensive data hampers efforts to identify the most effective areas for carbon reduction and to quantify the impact of improvement initiatives.
Another challenge lies in the transportation and storage of hydrochloric acid. Due to its corrosive nature, specialized containers and handling procedures are necessary, often involving energy-intensive processes and materials with high embodied carbon. This aspect of the supply chain significantly adds to the overall carbon footprint of HCl.
The recycling and reuse of hydrochloric acid pose additional difficulties. While recycling can potentially reduce the carbon footprint, the processes involved in purifying and reconcentrating used HCl are often energy-intensive themselves. Balancing the environmental benefits of recycling against the carbon costs of these processes remains a complex issue.
Furthermore, the diverse applications of hydrochloric acid across various industries complicate efforts to implement standardized carbon reduction strategies. Each sector, from chemical manufacturing to food processing, has unique requirements and constraints, making it challenging to develop universal solutions.
The lack of cost-effective, low-carbon alternatives to traditional HCl production methods is another significant hurdle. While some innovative approaches are being explored, such as electrolysis-based production, these technologies are not yet economically viable or scalable for widespread industrial adoption.
Regulatory challenges also play a role in hindering carbon footprint reduction efforts. The absence of unified global standards for carbon accounting and emissions reduction in chemical production creates inconsistencies in how companies approach and report their environmental impact.
Additionally, the interconnected nature of industrial processes means that changes in HCl production or usage can have ripple effects throughout supply chains. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and address the carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid without considering broader systemic impacts.
Lastly, there is a significant knowledge gap in accurately measuring and tracking the full lifecycle carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid. This lack of comprehensive data hampers efforts to identify the most effective areas for carbon reduction and to quantify the impact of improvement initiatives.
Existing Carbon Reduction Strategies for HCl
01 Carbon footprint reduction in hydrochloric acid production
Various methods are employed to reduce the carbon footprint in hydrochloric acid production. These include optimizing production processes, utilizing renewable energy sources, and implementing energy-efficient technologies. Such approaches aim to minimize greenhouse gas emissions associated with the manufacturing of hydrochloric acid.- Carbon footprint reduction in hydrochloric acid production: Various methods are employed to reduce the carbon footprint in hydrochloric acid production. These include optimizing production processes, utilizing renewable energy sources, and implementing more efficient technologies. Such approaches aim to minimize greenhouse gas emissions associated with the manufacturing of hydrochloric acid.
- Life cycle assessment of hydrochloric acid: Life cycle assessment techniques are used to evaluate the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid throughout its entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. This comprehensive analysis helps identify areas where carbon emissions can be reduced and overall sustainability improved.
- Alternative production methods for hydrochloric acid: Research into alternative production methods for hydrochloric acid focuses on developing processes with lower carbon footprints. These may include using renewable feedstocks, implementing catalytic processes, or exploring novel chemical reactions that result in reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon capture and utilization in hydrochloric acid industry: Carbon capture and utilization technologies are being integrated into hydrochloric acid production facilities to reduce their carbon footprint. These systems capture CO2 emissions from the production process and either store them or convert them into useful products, thereby mitigating the environmental impact.
- Energy efficiency improvements in hydrochloric acid production: Efforts to improve energy efficiency in hydrochloric acid production aim to reduce the overall carbon footprint. This includes implementing advanced process control systems, heat recovery technologies, and more efficient equipment to minimize energy consumption and associated emissions.
02 Life cycle assessment of hydrochloric acid
Life cycle assessment techniques are used to evaluate the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid throughout its entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. This comprehensive analysis helps identify areas where carbon emissions can be reduced and informs sustainable production strategies.Expand Specific Solutions03 Carbon capture and utilization in hydrochloric acid plants
Carbon capture technologies are implemented in hydrochloric acid production facilities to reduce emissions. The captured carbon dioxide can be utilized in various applications or stored safely, contributing to a lower overall carbon footprint of the production process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Green chemistry approaches for hydrochloric acid synthesis
Innovative green chemistry techniques are developed to synthesize hydrochloric acid with reduced environmental impact. These methods focus on using renewable feedstocks, catalysts, and reaction conditions that minimize energy consumption and waste generation, thereby lowering the carbon footprint.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and circular economy in hydrochloric acid industry
Implementing recycling processes and circular economy principles in the hydrochloric acid industry helps reduce its carbon footprint. This includes recovering and reusing waste streams, implementing closed-loop systems, and finding alternative uses for by-products to minimize overall environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Low-Carbon HCl Industry
The competition landscape for reducing hydrochloric acid's carbon footprint is evolving rapidly, reflecting the growing emphasis on sustainable chemical production. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing demand driven by stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals. While the market size is expanding, it remains relatively niche compared to traditional chemical processes. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like DuPont de Nemours, Ebb Carbon, and Siemens leading innovation. These firms are developing electrochemical processes, carbon capture technologies, and energy-efficient production methods to address the challenge. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, indicating significant potential for further advancements and market growth in the coming years.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a novel membrane-based technology for hydrochloric acid (HCl) recovery and purification, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of HCl production. This process utilizes advanced polymer membranes that selectively separate HCl from waste streams, allowing for efficient recycling and reuse. The technology incorporates a multi-stage membrane system that achieves high purity HCl recovery while minimizing energy consumption. DuPont's approach also includes the integration of renewable energy sources to power the membrane separation process, further reducing the overall carbon emissions associated with HCl production[1][3].
Strengths: High efficiency in HCl recovery, reduced energy consumption, and integration of renewable energy. Weaknesses: Initial implementation costs may be high, and the technology may require specialized maintenance.
Ebb Carbon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ebb Carbon has pioneered an innovative electrochemical process to reduce the carbon footprint of hydrochloric acid production. Their technology leverages renewable electricity to split saltwater into hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, effectively capturing CO2 in the process. This method not only produces HCl with a significantly lower carbon footprint but also generates valuable by-products. The process utilizes a specially designed electrolyzer that optimizes energy efficiency and minimizes waste. Ebb Carbon's approach also incorporates advanced catalysts to enhance the reaction kinetics, resulting in higher yields and reduced energy requirements[2][5].
Strengths: Carbon-negative HCl production, utilization of renewable energy, and valuable by-product generation. Weaknesses: Scalability challenges and potential high costs for large-scale implementation.
Innovative Technologies for Green HCl Production
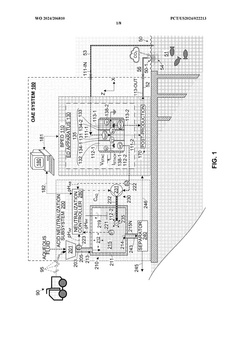
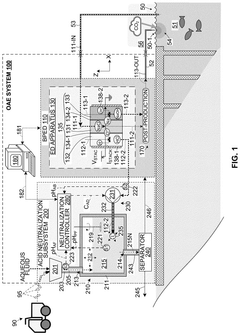
Ocean alkalinity enhancement system with controlled acid neutralization
PatentWO2024206810A1
Innovation
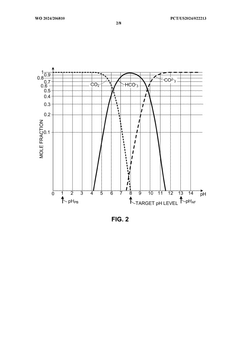
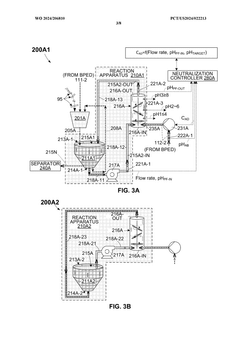
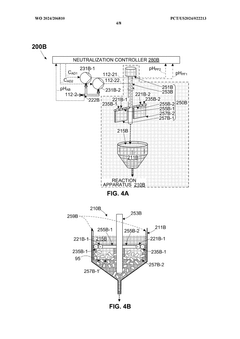
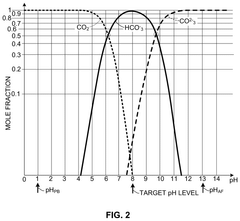
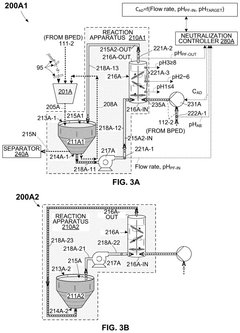
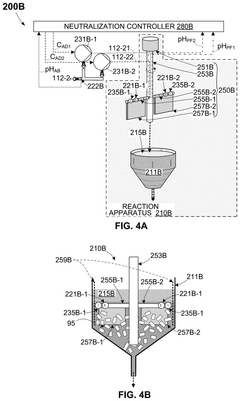
- An OAE system with a bipolar electrodialysis device and an acid neutralization subsystem that uses an aqueous alkaline fluid to neutralize hydrochloric acid, with a neutralization controller maintaining the process fluid at a target pH level above 8 to prevent CO2 release, thereby maximizing acid neutralization efficiency while minimizing carbon footprint.
OAE System With Controlled Acid Neutralization
PatentActiveUS20240327260A1
Innovation
- An acid neutralization subsystem that utilizes an aqueous alkaline fluid to neutralize hydrochloric acid, maintaining the process fluid at a predetermined pH level to prevent CO2 release, while minimizing costs and carbon footprint, using a bipolar electrodialysis device and a reaction apparatus with sensors and flow control to optimize the neutralization process.
Environmental Regulations Impact on HCl Industry
Environmental regulations have significantly impacted the hydrochloric acid (HCl) industry, driving substantial changes in production processes, waste management, and overall industry practices. These regulations aim to mitigate the environmental impact of HCl production and use, particularly focusing on reducing carbon emissions and improving sustainability.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented stricter emissions standards for industrial processes, including HCl production. These regulations often set limits on greenhouse gas emissions, particulate matter, and other pollutants associated with HCl manufacturing. As a result, HCl producers have been compelled to invest in cleaner technologies and more efficient production methods to comply with these standards.
One of the key areas affected by environmental regulations is the energy consumption in HCl production. Many jurisdictions have introduced carbon pricing mechanisms or cap-and-trade systems, which incentivize companies to reduce their carbon footprint. This has led to increased adoption of energy-efficient equipment and processes in HCl plants, as well as the exploration of alternative energy sources to power production facilities.
Waste management practices in the HCl industry have also been significantly influenced by environmental regulations. Stricter rules on the disposal of hazardous waste and byproducts have prompted companies to develop more sophisticated recycling and treatment processes. This has not only reduced the environmental impact but also improved resource efficiency in many cases.
The transportation of HCl has come under scrutiny due to environmental concerns. Regulations governing the safe transport of hazardous materials have become more stringent, leading to improvements in containment systems and transportation protocols. This has helped minimize the risk of accidental releases and their potential environmental consequences.
Environmental regulations have also spurred innovation in the HCl industry. Companies are increasingly investing in research and development to find more sustainable production methods and applications for HCl. This includes exploring bio-based feedstocks, developing closed-loop production systems, and investigating novel catalysts that can reduce energy requirements and emissions.
The impact of these regulations extends beyond direct production processes. Many countries now require companies to report their environmental performance and carbon emissions, increasing transparency and accountability in the industry. This has led to the adoption of more comprehensive environmental management systems and the integration of sustainability considerations into corporate strategies.
While compliance with environmental regulations has posed challenges for the HCl industry, it has also created opportunities for differentiation and competitive advantage. Companies that have successfully adapted to these regulations often find themselves better positioned in the market, as customers increasingly prioritize environmentally responsible suppliers.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented stricter emissions standards for industrial processes, including HCl production. These regulations often set limits on greenhouse gas emissions, particulate matter, and other pollutants associated with HCl manufacturing. As a result, HCl producers have been compelled to invest in cleaner technologies and more efficient production methods to comply with these standards.
One of the key areas affected by environmental regulations is the energy consumption in HCl production. Many jurisdictions have introduced carbon pricing mechanisms or cap-and-trade systems, which incentivize companies to reduce their carbon footprint. This has led to increased adoption of energy-efficient equipment and processes in HCl plants, as well as the exploration of alternative energy sources to power production facilities.
Waste management practices in the HCl industry have also been significantly influenced by environmental regulations. Stricter rules on the disposal of hazardous waste and byproducts have prompted companies to develop more sophisticated recycling and treatment processes. This has not only reduced the environmental impact but also improved resource efficiency in many cases.
The transportation of HCl has come under scrutiny due to environmental concerns. Regulations governing the safe transport of hazardous materials have become more stringent, leading to improvements in containment systems and transportation protocols. This has helped minimize the risk of accidental releases and their potential environmental consequences.
Environmental regulations have also spurred innovation in the HCl industry. Companies are increasingly investing in research and development to find more sustainable production methods and applications for HCl. This includes exploring bio-based feedstocks, developing closed-loop production systems, and investigating novel catalysts that can reduce energy requirements and emissions.
The impact of these regulations extends beyond direct production processes. Many countries now require companies to report their environmental performance and carbon emissions, increasing transparency and accountability in the industry. This has led to the adoption of more comprehensive environmental management systems and the integration of sustainability considerations into corporate strategies.
While compliance with environmental regulations has posed challenges for the HCl industry, it has also created opportunities for differentiation and competitive advantage. Companies that have successfully adapted to these regulations often find themselves better positioned in the market, as customers increasingly prioritize environmentally responsible suppliers.
Life Cycle Assessment of HCl Production
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of hydrochloric acid (HCl) production is a crucial step in understanding and reducing its carbon footprint. This comprehensive analysis examines the environmental impacts associated with HCl throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling.
The production of HCl typically involves two main methods: the chlor-alkali process and the direct synthesis method. The chlor-alkali process, which produces chlorine as a co-product of sodium hydroxide production, is the most common source of HCl. This process involves the electrolysis of sodium chloride brine, consuming significant amounts of electricity and contributing to the carbon footprint.
In contrast, the direct synthesis method involves the reaction of hydrogen and chlorine gases at high temperatures. While this method is less energy-intensive than the chlor-alkali process, it still requires substantial energy input for gas production and heating.
Raw material extraction, particularly for sodium chloride in the chlor-alkali process, contributes to the overall carbon footprint through mining and transportation activities. The production of hydrogen and chlorine gases for the direct synthesis method also involves energy-intensive processes, often relying on fossil fuels.
Transportation of raw materials and finished products is another significant contributor to the carbon footprint. HCl is typically transported in concentrated form to reduce shipping volume, but this requires specialized containers and handling procedures, potentially increasing the environmental impact.
The use phase of HCl generally has a lower carbon footprint compared to production and transportation. However, improper handling or accidental releases can lead to environmental damage and indirect carbon emissions through remediation efforts.
End-of-life considerations for HCl include neutralization and disposal, which may require additional chemicals and energy, contributing to the overall carbon footprint. Recycling and reuse opportunities are limited but can help reduce the environmental impact when feasible.
To reduce the carbon footprint of HCl production, several strategies can be implemented. These include improving energy efficiency in production processes, transitioning to renewable energy sources for electricity generation, optimizing transportation logistics, and exploring more sustainable raw material sources. Additionally, developing more efficient recycling and reuse methods can help minimize the overall environmental impact of HCl throughout its life cycle.
The production of HCl typically involves two main methods: the chlor-alkali process and the direct synthesis method. The chlor-alkali process, which produces chlorine as a co-product of sodium hydroxide production, is the most common source of HCl. This process involves the electrolysis of sodium chloride brine, consuming significant amounts of electricity and contributing to the carbon footprint.
In contrast, the direct synthesis method involves the reaction of hydrogen and chlorine gases at high temperatures. While this method is less energy-intensive than the chlor-alkali process, it still requires substantial energy input for gas production and heating.
Raw material extraction, particularly for sodium chloride in the chlor-alkali process, contributes to the overall carbon footprint through mining and transportation activities. The production of hydrogen and chlorine gases for the direct synthesis method also involves energy-intensive processes, often relying on fossil fuels.
Transportation of raw materials and finished products is another significant contributor to the carbon footprint. HCl is typically transported in concentrated form to reduce shipping volume, but this requires specialized containers and handling procedures, potentially increasing the environmental impact.
The use phase of HCl generally has a lower carbon footprint compared to production and transportation. However, improper handling or accidental releases can lead to environmental damage and indirect carbon emissions through remediation efforts.
End-of-life considerations for HCl include neutralization and disposal, which may require additional chemicals and energy, contributing to the overall carbon footprint. Recycling and reuse opportunities are limited but can help reduce the environmental impact when feasible.
To reduce the carbon footprint of HCl production, several strategies can be implemented. These include improving energy efficiency in production processes, transitioning to renewable energy sources for electricity generation, optimizing transportation logistics, and exploring more sustainable raw material sources. Additionally, developing more efficient recycling and reuse methods can help minimize the overall environmental impact of HCl throughout its life cycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!