How To Reduce Tungsten’s Environmental Impact?
Tungsten Sustainability Goals
Tungsten, a critical metal with unique properties, has long been essential in various industries. However, its extraction and processing have raised significant environmental concerns. To address these issues, the tungsten industry has set ambitious sustainability goals aimed at reducing its environmental impact while maintaining its crucial role in technological advancement.
One of the primary objectives is to minimize the ecological footprint of tungsten mining operations. This involves implementing more efficient extraction techniques that reduce waste generation and land disturbance. Advanced mining technologies, such as precision drilling and selective mining methods, are being developed to target ore bodies more accurately, thereby reducing the amount of overburden removed and minimizing habitat disruption.
Water management is another critical focus area. The industry aims to significantly reduce water consumption in mining and processing operations through innovative recycling systems and closed-loop water circuits. Additionally, there are efforts to improve wastewater treatment processes to ensure that any water released back into the environment meets or exceeds regulatory standards.
Energy efficiency and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions form a crucial part of the sustainability goals. The sector is investing in renewable energy sources to power mining and processing facilities, with some companies setting targets to achieve carbon neutrality in their operations within the next few decades. This includes the electrification of mining equipment and the optimization of processing plants to reduce energy consumption.
Circular economy principles are being integrated into tungsten production and use. The industry is working towards increasing the recycling rates of tungsten-containing products, aiming to reduce the demand for primary raw materials. This involves developing more efficient recycling technologies and establishing better collection systems for end-of-life products containing tungsten.
Biodiversity conservation is also a key sustainability goal. Mining companies are implementing comprehensive land rehabilitation programs to restore ecosystems post-mining. These efforts often go beyond regulatory requirements, with companies committing to leaving a positive biodiversity legacy in the areas where they operate.
The tungsten industry is also focusing on improving the sustainability of its supply chain. This includes ensuring responsible sourcing practices, promoting transparency, and working with suppliers to reduce the environmental impact throughout the value chain. Certification schemes and traceability systems are being developed to verify the sustainability credentials of tungsten products.
Research and development play a crucial role in achieving these sustainability goals. The industry is investing in innovative technologies to improve resource efficiency, reduce emissions, and develop more environmentally friendly tungsten products. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional processing methods that use fewer chemicals and generate less waste.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Tungsten
The global market for eco-friendly tungsten solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stricter regulations. As industries become more aware of the environmental impact of traditional tungsten mining and processing methods, there is a growing demand for sustainable alternatives that minimize ecological damage and reduce carbon footprints.
The automotive sector, one of the largest consumers of tungsten, has been at the forefront of this shift towards eco-friendly tungsten. With the rise of electric vehicles and the push for more fuel-efficient combustion engines, manufacturers are seeking tungsten components that are produced using environmentally responsible methods. This trend is expected to continue as automotive companies strive to meet increasingly stringent emissions standards and sustainability goals.
In the electronics industry, there is a rising demand for eco-friendly tungsten in the production of semiconductors, circuit boards, and other components. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, electronics manufacturers are under pressure to adopt greener supply chains, including the sourcing of sustainably produced tungsten for their products.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also showing increased interest in eco-friendly tungsten solutions. These industries require high-performance materials that can withstand extreme conditions, and tungsten remains a critical component in many applications. However, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of these materials throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
Mining companies and tungsten producers are responding to this market demand by investing in cleaner extraction and processing technologies. This includes developing more efficient recycling methods for tungsten scrap, implementing closed-loop water systems in processing plants, and exploring alternative energy sources for powering mining operations.
The construction industry is another sector where the demand for eco-friendly tungsten is on the rise. As green building practices gain traction worldwide, there is an increasing need for sustainable materials in construction projects. Tungsten's durability and strength make it an attractive option for various applications, and construction companies are seeking suppliers who can provide tungsten products with a lower environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the medical industry is showing interest in eco-friendly tungsten for use in medical devices and equipment. As healthcare facilities strive to reduce their environmental impact, there is a growing preference for medical supplies and instruments made from sustainably sourced materials, including tungsten components.
Overall, the market demand for eco-friendly tungsten is expected to continue its upward trajectory as industries across the board prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility. This trend presents significant opportunities for companies that can innovate and provide tungsten products and solutions that meet both performance requirements and environmental standards.
Environmental Challenges in Tungsten Production
Tungsten production poses significant environmental challenges due to its extraction, processing, and disposal methods. The mining of tungsten ore, primarily wolframite and scheelite, often involves open-pit mining, which leads to extensive land disturbance, deforestation, and habitat destruction. This process can result in soil erosion, altered landscapes, and disrupted ecosystems, affecting local biodiversity and wildlife populations.
The extraction and processing of tungsten ore generate substantial amounts of waste rock and tailings. These byproducts can contain harmful substances such as heavy metals, arsenic, and other toxic elements. When improperly managed, these materials can leach into soil and water systems, causing long-term contamination of groundwater and surface water resources. This pollution not only affects aquatic ecosystems but also poses risks to human health in surrounding communities.
Air pollution is another significant concern in tungsten production. The smelting and refining processes release various pollutants into the atmosphere, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air quality degradation, potentially leading to respiratory issues for workers and nearby residents. Furthermore, the high energy requirements of tungsten processing contribute to increased greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change concerns.
Water usage and contamination present additional environmental challenges. Tungsten production requires large volumes of water for ore processing and cooling systems. In water-scarce regions, this can lead to competition with local communities and ecosystems for limited water resources. Moreover, the discharge of process water, if not properly treated, can introduce pollutants into local water bodies, affecting aquatic life and downstream water users.
The disposal of waste from tungsten production, particularly tailings and slag, presents long-term environmental risks. These materials can contain residual heavy metals and other toxic substances that may persist in the environment for decades. Proper containment and management of these wastes are crucial to prevent environmental contamination and protect public health.
Addressing these environmental challenges requires a multifaceted approach. This includes implementing more sustainable mining practices, improving ore processing efficiency to reduce waste generation, adopting cleaner production technologies, and enhancing waste management strategies. Additionally, stricter environmental regulations, comprehensive site rehabilitation plans, and ongoing monitoring of environmental impacts are essential for mitigating the negative effects of tungsten production on the environment.
Current Green Tungsten Technologies
01 Environmental impact assessment of tungsten mining
Tungsten mining operations can have significant environmental impacts. This includes potential soil and water contamination, habitat disruption, and air pollution from mining activities. Environmental impact assessments are crucial to identify and mitigate these effects, ensuring sustainable extraction practices and minimizing ecological damage.- Environmental impact assessment of tungsten mining: Tungsten mining operations can have significant environmental impacts. This includes potential soil and water contamination, habitat disruption, and air pollution from mining activities. Environmental impact assessments are crucial to identify and mitigate these effects, ensuring sustainable mining practices and minimizing ecological damage.
- Recycling and waste management of tungsten products: Proper recycling and waste management of tungsten-containing products are essential to reduce environmental impact. This involves developing efficient recycling processes, implementing waste reduction strategies, and promoting the circular economy for tungsten materials. Effective management can help conserve resources and minimize the need for new mining operations.
- Energy efficiency in tungsten processing: Improving energy efficiency in tungsten processing can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. This includes optimizing production processes, implementing energy-saving technologies, and exploring alternative energy sources for tungsten refining and manufacturing. Enhanced energy efficiency can lead to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and overall environmental impact.
- Water management in tungsten production: Effective water management is crucial in tungsten production to minimize environmental impact. This involves implementing water conservation measures, treating and recycling process water, and preventing contamination of local water sources. Proper water management can help reduce the industry's water footprint and protect aquatic ecosystems.
- Sustainable alternatives and substitutes for tungsten: Research into sustainable alternatives and substitutes for tungsten can help reduce its environmental impact. This includes exploring new materials with similar properties but lower environmental footprints, developing more eco-friendly tungsten alloys, and investigating ways to reduce tungsten consumption in various applications without compromising performance.
02 Recycling and waste management of tungsten products
Proper recycling and waste management of tungsten-containing products are essential to reduce environmental impact. This involves developing efficient recycling processes, implementing waste reduction strategies, and promoting the circular economy for tungsten materials. Effective management can significantly decrease the need for new mining operations and reduce associated environmental risks.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy efficiency in tungsten processing
Improving energy efficiency in tungsten processing and manufacturing can help reduce the overall environmental footprint. This includes optimizing production processes, implementing energy-saving technologies, and exploring alternative energy sources for tungsten-related industries. Enhanced energy efficiency contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions and resource consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Water management in tungsten production
Effective water management is crucial in tungsten production to minimize environmental impact. This involves implementing water conservation measures, treating and recycling process water, and preventing contamination of local water sources. Proper water management helps protect aquatic ecosystems and ensures sustainable use of water resources in tungsten-related industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable alternatives and substitutes for tungsten
Research into sustainable alternatives and substitutes for tungsten can help reduce its environmental impact. This includes exploring new materials with similar properties but lower environmental footprints, developing composite materials that require less tungsten, and investigating ways to reduce tungsten consumption in various applications while maintaining performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Tungsten Industry
The tungsten industry is in a mature stage, with a global market size of around $3.5 billion. The environmental impact reduction of tungsten is becoming increasingly critical as sustainability concerns grow. Companies like Xiamen Tungsten Co., Ltd. and Chongyi Zhangyuan Tungsten Co., Ltd. are at the forefront of developing eco-friendly extraction and processing techniques. Research institutions such as Central South University and Jiangxi University of Science & Technology are contributing to technological advancements. The industry is seeing a shift towards recycling and circular economy approaches, with companies like Kyocera Corp. and OSRAM SYLVANIA, Inc. investing in recycling technologies. Overall, the technology maturity for reducing tungsten's environmental impact is moderate, with significant room for innovation and improvement.
Chongyi Zhangyuan Tungsten Co., Ltd.
Xiamen Tungsten Co., Ltd.
Innovations in Eco-Friendly Tungsten Extraction
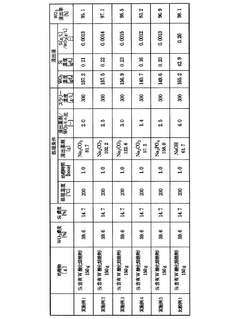
- The interaction of metals such as lead, tin, and antimony with tungsten in the presence of water and oxygen suppresses tungsten leachability by forming low-solubility tungstate precipitates, with lead oxide or sodium tungstate solutions effectively precipitating lead contaminants, reducing tungsten solubility and leachability.
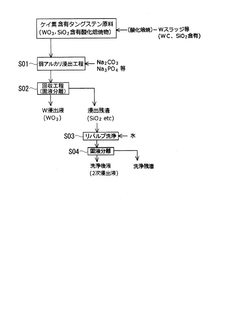
- A tungsten recovery method using weak alkali leaching with sodium carbonate or sodium phosphate to selectively leach tungsten while suppressing silicon leaching, reducing the number of processing steps and avoiding the use of hazardous chemicals like hydrogen fluoride, thereby simplifying equipment and reducing environmental impact.
Regulatory Framework for Tungsten Mining
The regulatory framework for tungsten mining plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of this industry. Governments worldwide have implemented various laws and regulations to ensure responsible mining practices and minimize ecological damage. These regulations typically cover areas such as land use, water management, waste disposal, and environmental restoration.
In many countries, mining companies are required to obtain environmental permits before commencing operations. These permits often mandate comprehensive environmental impact assessments, which evaluate potential risks to ecosystems, water resources, and local communities. Regulatory bodies also set strict standards for air and water quality, limiting the release of pollutants and heavy metals associated with tungsten mining.
Waste management is a key focus of tungsten mining regulations. Companies are often required to implement proper tailings management systems, including the construction of secure storage facilities and the treatment of mine water before discharge. Some jurisdictions have introduced regulations promoting the recycling of tungsten from mine waste and scrap, reducing the need for new extraction.
Land reclamation and rehabilitation requirements are another important aspect of the regulatory framework. Mining companies are typically obligated to restore mined areas to a state that supports local ecosystems and land use practices. This may involve re-contouring the landscape, replanting native vegetation, and monitoring long-term environmental recovery.
Worker safety and health regulations also contribute to reducing environmental impact by preventing accidents and spills that could harm surrounding ecosystems. These regulations often mandate the use of protective equipment, regular safety training, and the implementation of emergency response plans.
International agreements and guidelines, such as the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas, have influenced national regulations on tungsten mining. These frameworks promote responsible sourcing practices and encourage transparency in the mineral supply chain, indirectly supporting more environmentally conscious mining operations.
Enforcement mechanisms are critical to the effectiveness of these regulations. Many countries have established specialized environmental agencies or mining regulators with the authority to conduct inspections, impose fines, and revoke licenses for non-compliance. Some jurisdictions have also introduced financial assurance requirements, ensuring that funds are available for environmental remediation in case of company bankruptcy or abandonment of mining sites.
Life Cycle Assessment of Tungsten Products
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of tungsten products is a crucial approach to understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of this valuable metal. The assessment typically covers the entire lifecycle of tungsten products, from extraction and processing to use and disposal. This comprehensive analysis helps identify key areas where environmental improvements can be made.
The extraction phase of tungsten often involves open-pit or underground mining, which can lead to significant land disturbance and habitat destruction. The mining process also requires substantial energy inputs and may result in the release of harmful substances into the environment. Processing raw tungsten ore into usable forms involves energy-intensive steps such as crushing, grinding, and chemical treatments, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and potential water pollution.
During the manufacturing stage, tungsten products undergo various forming and shaping processes, often requiring high temperatures and specialized equipment. These processes contribute to energy consumption and may generate hazardous waste materials. The use phase of tungsten products generally has a lower environmental impact compared to other stages, as tungsten's durability and longevity reduce the need for frequent replacements.
End-of-life management of tungsten products presents both challenges and opportunities. While tungsten is highly recyclable, the collection and sorting of tungsten-containing products can be complex. Improper disposal may lead to the loss of this valuable resource and potential environmental contamination. However, effective recycling programs can significantly reduce the need for primary tungsten extraction, thereby lowering overall environmental impact.
LCA studies have shown that the production of primary tungsten has a higher environmental footprint compared to recycled tungsten. This highlights the importance of developing efficient recycling technologies and implementing circular economy principles in the tungsten industry. Additionally, LCA results can guide the development of more sustainable mining and processing techniques, such as using renewable energy sources or implementing closed-loop water systems.
By conducting thorough life cycle assessments, stakeholders in the tungsten industry can identify hotspots of environmental impact and prioritize areas for improvement. This approach enables the development of targeted strategies to reduce tungsten's environmental footprint across its entire lifecycle, from responsible mining practices to enhanced recycling efforts and more sustainable product design.