How to Safeguard Processes Involving Hydrochloric Acid?
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Safety Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) has been a cornerstone in various industrial processes for decades, playing crucial roles in metal processing, oil well acidizing, and chemical manufacturing. As its applications have expanded, so too has the need for robust safety measures to protect workers and the environment. The evolution of HCl safety protocols mirrors the broader development of industrial safety standards, reflecting a growing understanding of chemical hazards and risk management.
The primary objective in safeguarding processes involving hydrochloric acid is to minimize the risk of exposure, spills, and chemical reactions that could lead to harmful outcomes. This encompasses a multifaceted approach, addressing not only the immediate handling of the acid but also the design of storage facilities, transport mechanisms, and emergency response procedures. The goal is to create a comprehensive safety ecosystem that anticipates and mitigates potential hazards at every stage of HCl use.
Historically, the approach to HCl safety has progressed from basic protective equipment to sophisticated engineering controls and automated systems. Early measures focused on personal protective equipment (PPE) such as acid-resistant gloves and face shields. However, as incidents occurred and knowledge accumulated, the industry recognized the need for more systemic solutions. This led to the development of closed-loop systems, advanced ventilation techniques, and specialized containment structures designed to handle HCl's corrosive properties.
Recent technological advancements have further refined safety protocols, introducing real-time monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and improved materials for containment and transport. These innovations aim to provide early warning of potential leaks or equipment failures, allowing for proactive intervention before incidents occur. Additionally, there's a growing emphasis on training and simulation, utilizing virtual reality and augmented reality technologies to prepare workers for handling HCl in various scenarios without exposure to actual risk.
The current landscape of HCl safety is characterized by a holistic approach that integrates engineering controls, administrative procedures, and cutting-edge technology. This includes the implementation of inherently safer design principles in process engineering, where the focus is on minimizing the presence of HCl where possible and designing systems that are inherently less prone to failure or release. Concurrently, there's an increased focus on sustainability, driving research into alternatives to HCl in certain applications and exploring methods to reduce its environmental impact when use is unavoidable.
Looking forward, the objectives for HCl safety continue to evolve. There's a push towards zero-incident operations, necessitating even more sophisticated prediction and prevention mechanisms. This includes the development of smart sensors capable of detecting minute changes in process conditions, AI-driven risk assessment tools, and advanced materials that offer superior resistance to HCl corrosion. Furthermore, there's a growing emphasis on integrating safety considerations into the earliest stages of process design, ensuring that HCl handling is as safe as technologically possible from conception to implementation.
The primary objective in safeguarding processes involving hydrochloric acid is to minimize the risk of exposure, spills, and chemical reactions that could lead to harmful outcomes. This encompasses a multifaceted approach, addressing not only the immediate handling of the acid but also the design of storage facilities, transport mechanisms, and emergency response procedures. The goal is to create a comprehensive safety ecosystem that anticipates and mitigates potential hazards at every stage of HCl use.
Historically, the approach to HCl safety has progressed from basic protective equipment to sophisticated engineering controls and automated systems. Early measures focused on personal protective equipment (PPE) such as acid-resistant gloves and face shields. However, as incidents occurred and knowledge accumulated, the industry recognized the need for more systemic solutions. This led to the development of closed-loop systems, advanced ventilation techniques, and specialized containment structures designed to handle HCl's corrosive properties.
Recent technological advancements have further refined safety protocols, introducing real-time monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and improved materials for containment and transport. These innovations aim to provide early warning of potential leaks or equipment failures, allowing for proactive intervention before incidents occur. Additionally, there's a growing emphasis on training and simulation, utilizing virtual reality and augmented reality technologies to prepare workers for handling HCl in various scenarios without exposure to actual risk.
The current landscape of HCl safety is characterized by a holistic approach that integrates engineering controls, administrative procedures, and cutting-edge technology. This includes the implementation of inherently safer design principles in process engineering, where the focus is on minimizing the presence of HCl where possible and designing systems that are inherently less prone to failure or release. Concurrently, there's an increased focus on sustainability, driving research into alternatives to HCl in certain applications and exploring methods to reduce its environmental impact when use is unavoidable.
Looking forward, the objectives for HCl safety continue to evolve. There's a push towards zero-incident operations, necessitating even more sophisticated prediction and prevention mechanisms. This includes the development of smart sensors capable of detecting minute changes in process conditions, AI-driven risk assessment tools, and advanced materials that offer superior resistance to HCl corrosion. Furthermore, there's a growing emphasis on integrating safety considerations into the earliest stages of process design, ensuring that HCl handling is as safe as technologically possible from conception to implementation.
Industrial Demand for HCl Safety Solutions
The industrial demand for hydrochloric acid (HCl) safety solutions has been steadily increasing due to the widespread use of this corrosive substance in various sectors. Chemical manufacturing, metal processing, oil and gas, and pharmaceutical industries are among the primary consumers of HCl, driving the need for robust safety measures. These industries require comprehensive safety solutions to protect workers, equipment, and the environment from the hazards associated with HCl handling and storage.
One of the key factors fueling the demand for HCl safety solutions is the stringent regulatory environment. Governments and international bodies have implemented strict guidelines and standards for the safe handling of hazardous chemicals, including HCl. This has compelled industries to invest in advanced safety technologies and equipment to ensure compliance and avoid hefty fines or operational shutdowns.
The market for HCl safety solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services. Personal protective equipment (PPE) specifically designed for HCl exposure, such as acid-resistant suits, gloves, and respiratory protection, forms a significant portion of the market. Containment systems, including specialized storage tanks, piping, and transfer equipment, are also in high demand to prevent leaks and spills.
Advanced monitoring and detection systems have gained traction in recent years. These include real-time HCl vapor detectors, automated alarm systems, and integrated safety management platforms that provide continuous monitoring and rapid response capabilities. The integration of IoT and AI technologies in these systems has further enhanced their effectiveness and appeal to industrial users.
Emergency response equipment and neutralization solutions are crucial components of HCl safety protocols. Industries are increasingly investing in emergency showers, eyewash stations, and spill containment kits specifically designed for acid-related incidents. Additionally, there is a growing demand for environmentally friendly neutralization agents that can quickly and safely neutralize HCl spills while minimizing ecological impact.
Training and education services form another vital segment of the HCl safety solutions market. Companies are recognizing the importance of comprehensive training programs for employees handling HCl, covering topics such as proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. This has led to an increased demand for specialized training providers and simulation-based learning tools.
The industrial demand for HCl safety solutions is expected to continue growing as industries expand and safety regulations become more stringent. Emerging markets in developing countries, where industrial growth is rapid, present significant opportunities for safety solution providers. Moreover, the ongoing focus on workplace safety and environmental protection is likely to drive innovation in HCl safety technologies, leading to more efficient and cost-effective solutions in the future.
One of the key factors fueling the demand for HCl safety solutions is the stringent regulatory environment. Governments and international bodies have implemented strict guidelines and standards for the safe handling of hazardous chemicals, including HCl. This has compelled industries to invest in advanced safety technologies and equipment to ensure compliance and avoid hefty fines or operational shutdowns.
The market for HCl safety solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services. Personal protective equipment (PPE) specifically designed for HCl exposure, such as acid-resistant suits, gloves, and respiratory protection, forms a significant portion of the market. Containment systems, including specialized storage tanks, piping, and transfer equipment, are also in high demand to prevent leaks and spills.
Advanced monitoring and detection systems have gained traction in recent years. These include real-time HCl vapor detectors, automated alarm systems, and integrated safety management platforms that provide continuous monitoring and rapid response capabilities. The integration of IoT and AI technologies in these systems has further enhanced their effectiveness and appeal to industrial users.
Emergency response equipment and neutralization solutions are crucial components of HCl safety protocols. Industries are increasingly investing in emergency showers, eyewash stations, and spill containment kits specifically designed for acid-related incidents. Additionally, there is a growing demand for environmentally friendly neutralization agents that can quickly and safely neutralize HCl spills while minimizing ecological impact.
Training and education services form another vital segment of the HCl safety solutions market. Companies are recognizing the importance of comprehensive training programs for employees handling HCl, covering topics such as proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. This has led to an increased demand for specialized training providers and simulation-based learning tools.
The industrial demand for HCl safety solutions is expected to continue growing as industries expand and safety regulations become more stringent. Emerging markets in developing countries, where industrial growth is rapid, present significant opportunities for safety solution providers. Moreover, the ongoing focus on workplace safety and environmental protection is likely to drive innovation in HCl safety technologies, leading to more efficient and cost-effective solutions in the future.
Current HCl Handling Challenges
The handling of hydrochloric acid (HCl) presents significant challenges in industrial processes due to its corrosive nature and potential health hazards. Current practices face several key issues that demand attention and innovative solutions.
One of the primary challenges is the corrosion of storage and transport equipment. HCl's highly acidic properties can rapidly degrade metal surfaces, leading to leaks, equipment failure, and potential environmental contamination. This necessitates the use of specialized materials such as high-grade stainless steel, fiber-reinforced plastics, or rubber-lined vessels, which significantly increase operational costs.
Worker safety remains a paramount concern in HCl handling. Exposure to HCl vapors can cause severe respiratory irritation, while skin contact can result in chemical burns. Current personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols, while effective, can be cumbersome and may impede worker mobility and comfort during extended periods of use.
Accurate monitoring and control of HCl concentrations pose another significant challenge. Maintaining precise acid strength is crucial for many industrial processes, yet traditional measurement techniques can be affected by the corrosive environment, leading to inaccurate readings and potential process inefficiencies.
The transportation of HCl, particularly in large quantities, presents logistical and safety challenges. Current regulations require specialized containers and handling procedures, which can increase transportation costs and complexity. Additionally, the risk of accidental spills during transit remains a concern, necessitating robust emergency response protocols.
Environmental considerations also play a crucial role in HCl handling challenges. Proper disposal and neutralization of waste acid streams are essential to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Current treatment methods can be energy-intensive and costly, prompting the need for more efficient and sustainable solutions.
The volatility of HCl presents challenges in maintaining workplace air quality. Existing ventilation systems must be carefully designed and maintained to effectively remove acid vapors, which can be particularly problematic in confined spaces or areas with poor air circulation.
Lastly, the storage of large volumes of HCl requires specialized containment systems and rigorous safety protocols. Current storage solutions must address the risk of pressure build-up due to hydrogen gas generation, particularly in warm environments or when contaminants are present. This necessitates the implementation of robust venting systems and regular integrity checks, adding to the complexity of HCl management.
One of the primary challenges is the corrosion of storage and transport equipment. HCl's highly acidic properties can rapidly degrade metal surfaces, leading to leaks, equipment failure, and potential environmental contamination. This necessitates the use of specialized materials such as high-grade stainless steel, fiber-reinforced plastics, or rubber-lined vessels, which significantly increase operational costs.
Worker safety remains a paramount concern in HCl handling. Exposure to HCl vapors can cause severe respiratory irritation, while skin contact can result in chemical burns. Current personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols, while effective, can be cumbersome and may impede worker mobility and comfort during extended periods of use.
Accurate monitoring and control of HCl concentrations pose another significant challenge. Maintaining precise acid strength is crucial for many industrial processes, yet traditional measurement techniques can be affected by the corrosive environment, leading to inaccurate readings and potential process inefficiencies.
The transportation of HCl, particularly in large quantities, presents logistical and safety challenges. Current regulations require specialized containers and handling procedures, which can increase transportation costs and complexity. Additionally, the risk of accidental spills during transit remains a concern, necessitating robust emergency response protocols.
Environmental considerations also play a crucial role in HCl handling challenges. Proper disposal and neutralization of waste acid streams are essential to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Current treatment methods can be energy-intensive and costly, prompting the need for more efficient and sustainable solutions.
The volatility of HCl presents challenges in maintaining workplace air quality. Existing ventilation systems must be carefully designed and maintained to effectively remove acid vapors, which can be particularly problematic in confined spaces or areas with poor air circulation.
Lastly, the storage of large volumes of HCl requires specialized containment systems and rigorous safety protocols. Current storage solutions must address the risk of pressure build-up due to hydrogen gas generation, particularly in warm environments or when contaminants are present. This necessitates the implementation of robust venting systems and regular integrity checks, adding to the complexity of HCl management.
Existing HCl Safeguarding Methods
01 Personal protective equipment for handling hydrochloric acid
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling hydrochloric acid. This includes acid-resistant gloves, goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in certain situations. Using appropriate PPE helps prevent skin contact, inhalation, and eye exposure to the corrosive acid.- Personal protective equipment for handling hydrochloric acid: Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling hydrochloric acid. This includes acid-resistant gloves, goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in certain situations. Using appropriate PPE helps prevent skin contact, inhalation, and eye exposure to the corrosive acid.
- Storage and containment systems for hydrochloric acid: Safe storage of hydrochloric acid requires specialized containment systems. These may include corrosion-resistant tanks, secondary containment measures, and proper ventilation. Implementing effective storage solutions helps prevent leaks, spills, and potential chemical reactions that could lead to safety hazards.
- Neutralization and disposal methods for hydrochloric acid: Proper neutralization and disposal of hydrochloric acid are essential for safety and environmental protection. This may involve using alkaline substances to neutralize the acid before disposal or implementing specialized waste treatment processes. Correct disposal methods help prevent environmental contamination and potential harm to living organisms.
- Emergency response and first aid for hydrochloric acid exposure: Developing and implementing emergency response protocols for hydrochloric acid exposure is crucial. This includes proper first aid measures such as immediate flushing with water for skin or eye contact, and seeking medical attention. Having readily available safety showers and eyewash stations in areas where hydrochloric acid is used can help mitigate the effects of accidental exposure.
- Monitoring and detection systems for hydrochloric acid: Implementing monitoring and detection systems can enhance safety when working with hydrochloric acid. This may include gas detectors, pH monitors, or other sensors that can alert personnel to the presence of acid vapors or leaks. Early detection allows for prompt response to potential hazards, reducing the risk of exposure and accidents.
02 Storage and containment systems for hydrochloric acid
Safe storage of hydrochloric acid requires specialized containment systems. These may include corrosion-resistant tanks, secondary containment measures, and proper ventilation. Implementing appropriate storage solutions helps prevent leaks, spills, and potential chemical reactions, ensuring the safety of workers and the environment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neutralization and disposal methods for hydrochloric acid
Proper neutralization and disposal of hydrochloric acid are essential for safety. This may involve using alkaline substances to neutralize the acid before disposal or implementing specialized waste treatment processes. Correct disposal methods help prevent environmental contamination and protect workers from exposure to hazardous materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Emergency response and first aid procedures
Establishing clear emergency response and first aid procedures is crucial for hydrochloric acid safety. This includes having readily available eyewash stations and safety showers, as well as training personnel on proper response techniques. Quick and appropriate action in case of exposure can significantly reduce the severity of injuries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and detection systems for hydrochloric acid
Implementing monitoring and detection systems helps ensure early identification of potential leaks or dangerous concentrations of hydrochloric acid. This may include gas detectors, pH monitors, and alarm systems. Early detection allows for prompt response and mitigation of potential hazards, enhancing overall safety in facilities handling hydrochloric acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HCl Safety Industry
The safeguarding of processes involving hydrochloric acid is a mature field with established safety protocols and technologies. The market for related safety equipment and solutions is substantial, driven by the widespread use of hydrochloric acid in various industries. Key players like Covestro Deutschland AG, Halliburton Energy Services, and Dow Global Technologies LLC are at the forefront of developing innovative safety solutions. These companies, along with others such as Fluid Energy Group Ltd. and EcoPhos SA, are continuously improving technologies for handling, storing, and neutralizing hydrochloric acid, focusing on enhancing worker safety and environmental protection. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical corporations and specialized safety equipment manufacturers, all striving to meet increasingly stringent safety regulations and industry standards.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has implemented a comprehensive safety strategy for processes involving hydrochloric acid, focusing on both prevention and mitigation. Their approach includes the use of advanced materials science to develop highly resistant polymers and coatings for HCl handling equipment[17]. They have also implemented state-of-the-art process control systems that incorporate machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent potential safety incidents[18]. Covestro's safety measures extend to the design of their facilities, incorporating features such as containment dikes, neutralization systems, and emergency shutdown mechanisms[19]. Additionally, they have developed innovative personal protective equipment specifically designed for HCl exposure, including smart PPE with integrated sensors for real-time monitoring of exposure levels[20].
Strengths: Strong focus on materials innovation, advanced process control systems, and smart PPE development. Comprehensive approach to facility design and safety infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potential high costs associated with implementing cutting-edge technologies and the need for continuous research and development to stay ahead in materials science.
Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: Halliburton has developed advanced safety protocols for handling hydrochloric acid in oil and gas operations. Their approach includes using corrosion-resistant materials, such as specialized alloys and coatings, for equipment that comes into contact with HCl[1]. They have also implemented automated acid injection systems with real-time monitoring capabilities to ensure precise control over acid concentration and flow rates[2]. Additionally, Halliburton has developed proprietary acid inhibitors and neutralizers to mitigate risks associated with accidental spills or leaks[3]. Their comprehensive safety program includes regular equipment inspections, employee training on proper handling procedures, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) specifically designed for HCl exposure[4].
Strengths: Extensive experience in handling HCl in challenging environments, advanced automation and monitoring systems, and proprietary chemical solutions for risk mitigation. Weaknesses: Potential high costs associated with specialized equipment and materials, and the need for continuous training and updating of safety protocols.
Innovative HCl Safety Technologies
Using Synthetic Acid Compositions as Alternatives to Conventional Acids in The Oil And Gas Industry
PatentActiveUS20230086463A1
Innovation
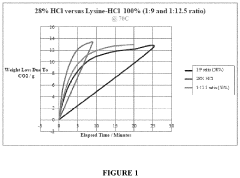
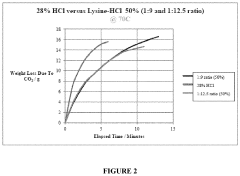
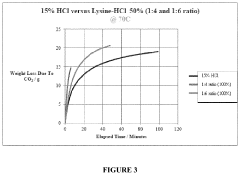
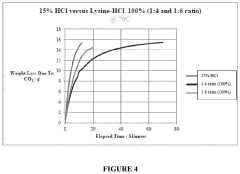
- An aqueous synthetic acid composition comprising lysine and hydrogen chloride in specific molar ratios, which provides low corrosion rates, biodegradability, controlled reaction rates, and thermal stability up to 220°C, reducing toxicity and environmental impact while maintaining the effectiveness of hydrochloric acid.
Synthetic acid and associated methods
PatentActiveAU2021200047A1
Innovation
- A synthetic acid, hydrogen glycine, is created by mixing glycine with hydrogen chloride gas, offering a safer, non-corrosive, and environmentally friendly alternative for various applications, including surface cleaning, well fracturing, and pH adjustment, with a pH level similar to hydrochloric acid but without fuming or significant corrosion.
Regulatory Framework for HCl Handling
The regulatory framework for handling hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a critical aspect of ensuring safety in processes involving this hazardous substance. Governments and international organizations have established comprehensive guidelines and regulations to minimize risks associated with HCl handling, storage, and transportation.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific standards for HCl exposure limits and safety protocols. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) for HCl is 5 parts per million (ppm) as a ceiling value, meaning this concentration should never be exceeded during any part of the workday. OSHA also mandates the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls to reduce worker exposure.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HCl under the Clean Air Act as a hazardous air pollutant. Facilities using or producing HCl must comply with emission standards and reporting requirements. The EPA also classifies HCl as a hazardous substance under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), which governs the cleanup of contaminated sites.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Under GHS, HCl is classified as a corrosive substance, requiring specific labeling and safety data sheets.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation applies to HCl production and use within the EU. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information to downstream users.
Transportation of HCl is regulated by various agencies, including the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code. These regulations specify requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during transport.
Industry-specific guidelines, such as those provided by the American Chemistry Council's Chlorine Institute, offer detailed best practices for HCl handling in chemical manufacturing and processing facilities. These guidelines often go beyond regulatory requirements, addressing specific scenarios and providing practical implementation strategies.
Compliance with these regulations requires ongoing training, documentation, and periodic audits. Companies must stay informed about regulatory updates and adjust their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure worker safety.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific standards for HCl exposure limits and safety protocols. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) for HCl is 5 parts per million (ppm) as a ceiling value, meaning this concentration should never be exceeded during any part of the workday. OSHA also mandates the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls to reduce worker exposure.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HCl under the Clean Air Act as a hazardous air pollutant. Facilities using or producing HCl must comply with emission standards and reporting requirements. The EPA also classifies HCl as a hazardous substance under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), which governs the cleanup of contaminated sites.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Under GHS, HCl is classified as a corrosive substance, requiring specific labeling and safety data sheets.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation applies to HCl production and use within the EU. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information to downstream users.
Transportation of HCl is regulated by various agencies, including the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code. These regulations specify requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during transport.
Industry-specific guidelines, such as those provided by the American Chemistry Council's Chlorine Institute, offer detailed best practices for HCl handling in chemical manufacturing and processing facilities. These guidelines often go beyond regulatory requirements, addressing specific scenarios and providing practical implementation strategies.
Compliance with these regulations requires ongoing training, documentation, and periodic audits. Companies must stay informed about regulatory updates and adjust their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure worker safety.
Environmental Impact of HCl Processes
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) processes are widely used in various industries, but their environmental impact is a significant concern that requires careful consideration and management. The production, use, and disposal of HCl can have far-reaching consequences on air quality, water resources, soil composition, and ecosystems if not properly controlled.
Air pollution is one of the primary environmental concerns associated with HCl processes. When released into the atmosphere, HCl can form acid aerosols that contribute to acid rain formation. These acidic emissions can travel long distances, affecting areas far from the source and causing damage to vegetation, buildings, and aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, HCl emissions can react with other atmospheric compounds, potentially forming secondary pollutants that further degrade air quality.
Water contamination is another critical environmental issue related to HCl processes. Accidental spills or improper disposal of HCl-containing waste can lead to the acidification of water bodies, severely impacting aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance. The low pH levels caused by HCl contamination can dissolve toxic metals from sediments, making them bioavailable and potentially entering the food chain. This can have long-lasting effects on both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, as well as pose risks to human health through contaminated drinking water sources.
Soil degradation is also a significant concern in areas where HCl processes are prevalent. Acid deposition from air emissions or direct contact with HCl can alter soil chemistry, leading to increased soil acidity. This change in soil pH can affect nutrient availability, microbial activity, and plant growth, potentially resulting in reduced agricultural productivity and ecosystem disruption. Furthermore, acidified soils may leach toxic metals, contaminating groundwater and surrounding ecosystems.
The impact on biodiversity is a broader environmental concern associated with HCl processes. The cumulative effects of air, water, and soil pollution can lead to habitat degradation and loss of species diversity. Sensitive organisms may be particularly vulnerable to the direct and indirect effects of HCl contamination, potentially causing shifts in ecosystem composition and functioning.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries utilizing HCl processes must implement comprehensive environmental management strategies. These may include advanced emission control technologies, proper waste management and disposal protocols, and continuous monitoring of environmental parameters. Additionally, adopting cleaner production techniques, exploring alternative processes or chemicals, and investing in research for more environmentally friendly solutions can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of HCl-related activities.
Regulatory compliance and adherence to environmental standards play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact of HCl processes. Stringent regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and handling procedures help ensure that industries implement necessary safeguards. Furthermore, regular environmental impact assessments and audits can identify potential risks and areas for improvement, allowing for proactive measures to protect the environment.
Air pollution is one of the primary environmental concerns associated with HCl processes. When released into the atmosphere, HCl can form acid aerosols that contribute to acid rain formation. These acidic emissions can travel long distances, affecting areas far from the source and causing damage to vegetation, buildings, and aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, HCl emissions can react with other atmospheric compounds, potentially forming secondary pollutants that further degrade air quality.
Water contamination is another critical environmental issue related to HCl processes. Accidental spills or improper disposal of HCl-containing waste can lead to the acidification of water bodies, severely impacting aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance. The low pH levels caused by HCl contamination can dissolve toxic metals from sediments, making them bioavailable and potentially entering the food chain. This can have long-lasting effects on both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, as well as pose risks to human health through contaminated drinking water sources.
Soil degradation is also a significant concern in areas where HCl processes are prevalent. Acid deposition from air emissions or direct contact with HCl can alter soil chemistry, leading to increased soil acidity. This change in soil pH can affect nutrient availability, microbial activity, and plant growth, potentially resulting in reduced agricultural productivity and ecosystem disruption. Furthermore, acidified soils may leach toxic metals, contaminating groundwater and surrounding ecosystems.
The impact on biodiversity is a broader environmental concern associated with HCl processes. The cumulative effects of air, water, and soil pollution can lead to habitat degradation and loss of species diversity. Sensitive organisms may be particularly vulnerable to the direct and indirect effects of HCl contamination, potentially causing shifts in ecosystem composition and functioning.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries utilizing HCl processes must implement comprehensive environmental management strategies. These may include advanced emission control technologies, proper waste management and disposal protocols, and continuous monitoring of environmental parameters. Additionally, adopting cleaner production techniques, exploring alternative processes or chemicals, and investing in research for more environmentally friendly solutions can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of HCl-related activities.
Regulatory compliance and adherence to environmental standards play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact of HCl processes. Stringent regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and handling procedures help ensure that industries implement necessary safeguards. Furthermore, regular environmental impact assessments and audits can identify potential risks and areas for improvement, allowing for proactive measures to protect the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!