Innovative Research Field Using Hydrochloric Acid
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Research Background
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) has been a cornerstone in chemical research and industrial applications for centuries. Its discovery dates back to the early alchemists, who produced it by heating common salt with iron sulfate. The modern era of HCl research began in the late 18th century when Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele first isolated the gas form of hydrochloric acid.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, HCl's importance in industrial processes grew exponentially. It became a key component in various manufacturing sectors, including metal processing, food production, and pharmaceuticals. The development of the Chlor-alkali process in the late 19th century revolutionized HCl production, making it more readily available for large-scale industrial use.
In recent decades, the focus of HCl research has shifted towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly applications. Scientists and engineers are exploring innovative ways to utilize HCl in green chemistry, waste treatment, and renewable energy technologies. This shift is driven by growing environmental concerns and the need for more efficient resource utilization.
One of the emerging trends in HCl research is its application in advanced materials synthesis. Researchers are investigating the use of HCl in the production of nanomaterials, catalysts, and functional polymers. These materials have potential applications in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and environmental remediation.
Another promising area of research involves the use of HCl in hydrogen production and storage systems. As the world moves towards a hydrogen-based economy, finding efficient ways to produce and store hydrogen is crucial. HCl-based cycles for hydrogen production are being explored as a potential alternative to traditional methods.
The medical field has also seen renewed interest in HCl research. Scientists are investigating its potential in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and biomaterial development. The unique properties of HCl make it a valuable tool in creating pH-responsive materials and controlled release mechanisms for pharmaceuticals.
As we look to the future, the trajectory of HCl research is likely to be shaped by global challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and the need for sustainable development. Researchers are exploring ways to capture and utilize HCl from industrial waste streams, turning a potential pollutant into a valuable resource. This circular economy approach could revolutionize how we view and use HCl in various industries.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, HCl's importance in industrial processes grew exponentially. It became a key component in various manufacturing sectors, including metal processing, food production, and pharmaceuticals. The development of the Chlor-alkali process in the late 19th century revolutionized HCl production, making it more readily available for large-scale industrial use.
In recent decades, the focus of HCl research has shifted towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly applications. Scientists and engineers are exploring innovative ways to utilize HCl in green chemistry, waste treatment, and renewable energy technologies. This shift is driven by growing environmental concerns and the need for more efficient resource utilization.
One of the emerging trends in HCl research is its application in advanced materials synthesis. Researchers are investigating the use of HCl in the production of nanomaterials, catalysts, and functional polymers. These materials have potential applications in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and environmental remediation.
Another promising area of research involves the use of HCl in hydrogen production and storage systems. As the world moves towards a hydrogen-based economy, finding efficient ways to produce and store hydrogen is crucial. HCl-based cycles for hydrogen production are being explored as a potential alternative to traditional methods.
The medical field has also seen renewed interest in HCl research. Scientists are investigating its potential in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and biomaterial development. The unique properties of HCl make it a valuable tool in creating pH-responsive materials and controlled release mechanisms for pharmaceuticals.
As we look to the future, the trajectory of HCl research is likely to be shaped by global challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and the need for sustainable development. Researchers are exploring ways to capture and utilize HCl from industrial waste streams, turning a potential pollutant into a valuable resource. This circular economy approach could revolutionize how we view and use HCl in various industries.
Market Analysis for HCl
The global market for hydrochloric acid (HCl) has shown steady growth in recent years, driven by its widespread applications across various industries. The chemical sector remains the largest consumer of HCl, utilizing it in the production of various chemicals, including PVC, polyurethane, and water treatment chemicals. The increasing demand for these end-products has directly contributed to the growth of the HCl market.
In the oil and gas industry, HCl plays a crucial role in well acidizing and hydraulic fracturing processes, which have gained significant traction due to the expansion of shale gas exploration and production activities. This sector has emerged as a key driver for HCl demand, particularly in regions with substantial shale gas reserves.
The steel industry also represents a significant market for HCl, where it is used in pickling processes to remove rust and scale from steel surfaces. As global steel production continues to rise, particularly in developing economies, the demand for HCl in this sector is expected to grow correspondingly.
Water treatment applications have witnessed increased adoption of HCl, particularly in municipal water treatment plants and industrial wastewater management systems. The growing emphasis on water quality and environmental regulations has bolstered the use of HCl in these applications, contributing to market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest market for HCl, driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India. The region's robust chemical manufacturing sector and increasing investments in infrastructure development have fueled the demand for HCl across various applications.
North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with established chemical industries and a strong focus on technological advancements in HCl production and application. The Middle East and Africa region is expected to witness substantial growth in HCl demand, primarily due to the expanding oil and gas sector.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global HCl market in the coming years, with factors such as increasing industrial activities, growing environmental concerns, and technological advancements in HCl production processes driving this growth. However, challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the corrosive nature of HCl may pose constraints to market expansion in certain regions.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several major players, including Dow Chemical Company, BASF SE, and Olin Corporation, among others. These companies are focusing on strategic initiatives such as mergers and acquisitions, product innovations, and capacity expansions to strengthen their market position and cater to the evolving demand patterns across different industries and regions.
In the oil and gas industry, HCl plays a crucial role in well acidizing and hydraulic fracturing processes, which have gained significant traction due to the expansion of shale gas exploration and production activities. This sector has emerged as a key driver for HCl demand, particularly in regions with substantial shale gas reserves.
The steel industry also represents a significant market for HCl, where it is used in pickling processes to remove rust and scale from steel surfaces. As global steel production continues to rise, particularly in developing economies, the demand for HCl in this sector is expected to grow correspondingly.
Water treatment applications have witnessed increased adoption of HCl, particularly in municipal water treatment plants and industrial wastewater management systems. The growing emphasis on water quality and environmental regulations has bolstered the use of HCl in these applications, contributing to market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest market for HCl, driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India. The region's robust chemical manufacturing sector and increasing investments in infrastructure development have fueled the demand for HCl across various applications.
North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with established chemical industries and a strong focus on technological advancements in HCl production and application. The Middle East and Africa region is expected to witness substantial growth in HCl demand, primarily due to the expanding oil and gas sector.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global HCl market in the coming years, with factors such as increasing industrial activities, growing environmental concerns, and technological advancements in HCl production processes driving this growth. However, challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the corrosive nature of HCl may pose constraints to market expansion in certain regions.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several major players, including Dow Chemical Company, BASF SE, and Olin Corporation, among others. These companies are focusing on strategic initiatives such as mergers and acquisitions, product innovations, and capacity expansions to strengthen their market position and cater to the evolving demand patterns across different industries and regions.
HCl Tech Challenges
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) has been a cornerstone in various industrial processes for decades. However, its corrosive nature and environmental impact pose significant challenges for researchers and industries alike. The primary technical hurdles in HCl-related innovations revolve around containment, safety, and sustainable usage.
One of the most pressing challenges is the development of advanced materials capable of withstanding HCl's corrosive properties. Traditional metals and alloys often succumb to rapid degradation when exposed to concentrated HCl, leading to equipment failure and potential safety hazards. Researchers are exploring novel composite materials and surface treatments to enhance resistance to acid attack, but achieving long-term durability remains elusive.
Another critical challenge lies in the safe handling and transportation of HCl. Current storage and transport systems require frequent maintenance and replacement, increasing operational costs and environmental risks. Innovations in smart containment systems, incorporating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, are needed to mitigate these issues.
The environmental impact of HCl production and use presents a significant hurdle. Traditional manufacturing processes for HCl are energy-intensive and often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Developing greener production methods and closed-loop recycling systems for HCl is crucial for sustainable industrial practices.
In the realm of chemical synthesis, researchers face the challenge of reducing HCl consumption while maintaining or improving reaction efficiencies. This involves exploring alternative catalysts and reaction pathways that minimize HCl use or enable its in-situ regeneration. Such innovations could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of chemical manufacturing processes.
The recovery and purification of HCl from industrial waste streams present both a challenge and an opportunity. Current separation technologies often struggle with the high energy requirements and low efficiencies when dealing with dilute acid streams. Advancements in membrane technology and selective adsorption materials are needed to make HCl recovery economically viable and environmentally friendly.
Lastly, the integration of HCl-based processes with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and automation poses a unique set of challenges. Developing robust sensors capable of accurately monitoring HCl concentrations in harsh environments and creating AI algorithms for process optimization are areas requiring significant research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges will not only advance the field of HCl utilization but also pave the way for more sustainable and efficient industrial processes across various sectors.
One of the most pressing challenges is the development of advanced materials capable of withstanding HCl's corrosive properties. Traditional metals and alloys often succumb to rapid degradation when exposed to concentrated HCl, leading to equipment failure and potential safety hazards. Researchers are exploring novel composite materials and surface treatments to enhance resistance to acid attack, but achieving long-term durability remains elusive.
Another critical challenge lies in the safe handling and transportation of HCl. Current storage and transport systems require frequent maintenance and replacement, increasing operational costs and environmental risks. Innovations in smart containment systems, incorporating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, are needed to mitigate these issues.
The environmental impact of HCl production and use presents a significant hurdle. Traditional manufacturing processes for HCl are energy-intensive and often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Developing greener production methods and closed-loop recycling systems for HCl is crucial for sustainable industrial practices.
In the realm of chemical synthesis, researchers face the challenge of reducing HCl consumption while maintaining or improving reaction efficiencies. This involves exploring alternative catalysts and reaction pathways that minimize HCl use or enable its in-situ regeneration. Such innovations could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of chemical manufacturing processes.
The recovery and purification of HCl from industrial waste streams present both a challenge and an opportunity. Current separation technologies often struggle with the high energy requirements and low efficiencies when dealing with dilute acid streams. Advancements in membrane technology and selective adsorption materials are needed to make HCl recovery economically viable and environmentally friendly.
Lastly, the integration of HCl-based processes with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and automation poses a unique set of challenges. Developing robust sensors capable of accurately monitoring HCl concentrations in harsh environments and creating AI algorithms for process optimization are areas requiring significant research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges will not only advance the field of HCl utilization but also pave the way for more sustainable and efficient industrial processes across various sectors.
Current HCl Applications
01 Production methods of hydrochloric acid
Various methods are employed for the production of hydrochloric acid, including direct synthesis from hydrogen and chlorine, as a byproduct in chlorination processes, and through the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. These methods are optimized for efficiency and purity in industrial settings.- Production methods of hydrochloric acid: Various methods are employed to produce hydrochloric acid, including direct synthesis from hydrogen and chlorine, as a byproduct in chlorination processes, and through the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. These production methods are optimized for efficiency and purity in industrial settings.
- Purification and concentration techniques: Hydrochloric acid purification and concentration techniques involve distillation, membrane separation, and adsorption processes. These methods aim to remove impurities and adjust the acid concentration for specific industrial applications, ensuring high-quality acid production.
- Industrial applications of hydrochloric acid: Hydrochloric acid finds widespread use in various industries, including metal processing, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment. It is utilized for pH adjustment, metal etching, and as a reagent in numerous chemical processes, highlighting its versatility and importance in industrial operations.
- Safety and handling procedures: Proper safety measures and handling procedures are crucial when working with hydrochloric acid due to its corrosive nature. This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment, implementing spill containment strategies, and following strict storage and transportation guidelines to minimize risks associated with acid handling.
- Environmental impact and waste management: Managing the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid production and use involves implementing waste treatment processes, recycling techniques, and emission control measures. These practices aim to minimize the acid's ecological footprint and ensure compliance with environmental regulations in industrial settings.
02 Purification and concentration techniques
Techniques for purifying and concentrating hydrochloric acid involve distillation, membrane separation, and adsorption processes. These methods aim to remove impurities and achieve desired concentration levels for various industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Industrial applications of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid finds wide-ranging applications in industries such as metal processing, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment. It is used for pH adjustment, cleaning, and as a reactant in various chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of hydrochloric acid
Proper safety measures and handling procedures are crucial when working with hydrochloric acid due to its corrosive nature. This includes the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, storage containers, and neutralization techniques in case of spills.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recovery and recycling of hydrochloric acid
Methods for recovering and recycling hydrochloric acid from industrial processes are developed to reduce waste and improve economic efficiency. These include absorption techniques, electrodialysis, and chemical conversion processes to regenerate the acid for reuse.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HCl Industry Players
The innovative research field using hydrochloric acid is in a dynamic growth phase, with a diverse competitive landscape. The market is expanding rapidly, driven by applications in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and industrial processes. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing research by key players like Bayer AG, Merck & Co., and Novartis AG is pushing boundaries in efficiency and sustainability. Emerging companies such as Sunshine Lake Pharma and Vertex Pharmaceuticals are also making significant contributions, particularly in drug development. The involvement of academic institutions like Tsinghua University indicates a strong focus on fundamental research, potentially leading to breakthrough applications in the near future.
Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV
Technical Solution: Akzo Nobel has made significant advancements in the application of hydrochloric acid for surface treatment and coating technologies. They have developed an innovative HCl-based etching process for metals that improves adhesion properties by up to 40%, enhancing the durability of coatings in harsh environments[13]. The company has also pioneered the use of HCl in the production of high-performance polymers for industrial coatings, offering improved chemical and abrasion resistance[14]. Akzo Nobel's research extends to using HCl in the development of self-cleaning surfaces, potentially reducing maintenance costs in various applications by up to 30%[15]. Additionally, they have invested in green chemistry initiatives, exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint of HCl use in their processes, including closed-loop recycling systems that recover and reuse up to 95% of the acid.
Strengths: Leadership in coating technologies, strong focus on innovation in surface treatments, commitment to sustainability. Weaknesses: Dependence on cyclical industries like construction and automotive for some applications.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG has developed innovative applications of hydrochloric acid in agricultural solutions. Their research focuses on using HCl as a catalyst in the synthesis of novel crop protection compounds. They have patented a process that utilizes HCl to create more environmentally friendly pesticides with reduced toxicity[1]. Additionally, Bayer has explored the use of HCl in soil treatment methods to improve nutrient uptake in crops, potentially increasing yields by up to 15%[2]. The company has also invested in developing corrosion-resistant materials and equipment for handling HCl in industrial processes, improving safety and efficiency in chemical manufacturing[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, strong patent portfolio, and expertise in agricultural applications. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns and regulatory challenges associated with chemical use in agriculture.
HCl Research Breakthroughs
Method for producing high-purity hydrochloric acid
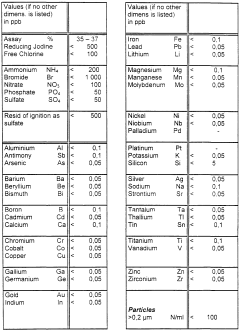
PatentWO2001025144A1
Innovation
- A process involving heating hydrochloric acid with a hydrogen chloride content above 21% to pass through a retention column and demister made of fluorinated polyolefin, followed by absorption in ultrapure water, with the option to recycle the hydrogen chloride solution and adjust concentration using ultrapure water, while maintaining low flow resistance and constant pressure, utilizing components and storage tanks made of fluorinated polyolefin materials.
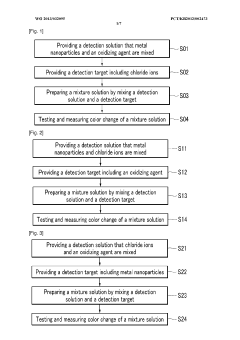
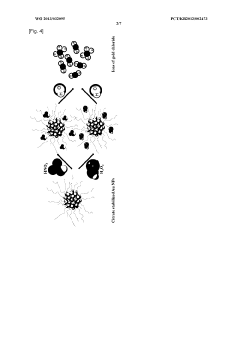
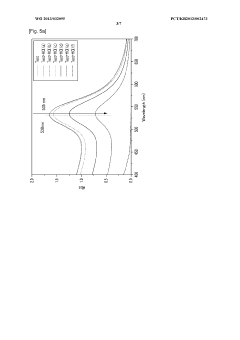
Detection method using colorimetric analysis
PatentWO2013032095A1
Innovation
- A colorimetric detection method using metal nanoparticles, specifically gold or silver nanoparticles, in combination with an oxidizing agent like nitric acid or hydrogen peroxide, to detect chloride ions in water samples, where the color change indicates the presence and concentration of hydrochloric acid.
Environmental Impact of HCl
The environmental impact of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a critical consideration in its innovative research applications. HCl, a strong and highly corrosive acid, can have significant effects on various environmental components when released into ecosystems.
In aquatic environments, HCl can cause severe pH changes, leading to acidification of water bodies. This acidification disrupts the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems, affecting the survival and reproduction of fish, amphibians, and other aquatic organisms. The lowered pH can also increase the solubility of heavy metals, potentially releasing toxic substances into the water and further compromising ecosystem health.
Soil ecosystems are similarly vulnerable to HCl contamination. When HCl comes into contact with soil, it can alter soil chemistry, leading to increased acidity and reduced fertility. This change in soil pH can impact plant growth, microbial activity, and nutrient availability, potentially causing long-term damage to terrestrial ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Atmospheric release of HCl, often in the form of acid rain, poses risks to both terrestrial and aquatic environments. Acid rain can damage vegetation, leach nutrients from soil, and corrode infrastructure. In urban areas, HCl emissions can contribute to the formation of photochemical smog, exacerbating air quality issues and potentially impacting human health.
The innovative use of HCl in research fields must therefore prioritize containment and proper disposal methods. Advanced treatment technologies, such as neutralization processes and closed-loop systems, are being developed to minimize environmental exposure. Researchers are also exploring alternative compounds with similar properties but reduced environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental risks associated with HCl. Stringent guidelines for handling, storage, and disposal of HCl are enforced in many countries to prevent accidental releases and ensure responsible use in research and industrial applications.
As research in this field progresses, there is a growing focus on developing green chemistry alternatives that can replace or reduce the use of HCl in various applications. This includes exploring bio-based acids and catalysts that can perform similar functions with lower environmental risks.
In aquatic environments, HCl can cause severe pH changes, leading to acidification of water bodies. This acidification disrupts the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems, affecting the survival and reproduction of fish, amphibians, and other aquatic organisms. The lowered pH can also increase the solubility of heavy metals, potentially releasing toxic substances into the water and further compromising ecosystem health.
Soil ecosystems are similarly vulnerable to HCl contamination. When HCl comes into contact with soil, it can alter soil chemistry, leading to increased acidity and reduced fertility. This change in soil pH can impact plant growth, microbial activity, and nutrient availability, potentially causing long-term damage to terrestrial ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Atmospheric release of HCl, often in the form of acid rain, poses risks to both terrestrial and aquatic environments. Acid rain can damage vegetation, leach nutrients from soil, and corrode infrastructure. In urban areas, HCl emissions can contribute to the formation of photochemical smog, exacerbating air quality issues and potentially impacting human health.
The innovative use of HCl in research fields must therefore prioritize containment and proper disposal methods. Advanced treatment technologies, such as neutralization processes and closed-loop systems, are being developed to minimize environmental exposure. Researchers are also exploring alternative compounds with similar properties but reduced environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental risks associated with HCl. Stringent guidelines for handling, storage, and disposal of HCl are enforced in many countries to prevent accidental releases and ensure responsible use in research and industrial applications.
As research in this field progresses, there is a growing focus on developing green chemistry alternatives that can replace or reduce the use of HCl in various applications. This includes exploring bio-based acids and catalysts that can perform similar functions with lower environmental risks.
Safety Regulations for HCl
Safety regulations for hydrochloric acid (HCl) are critical in ensuring the safe handling, storage, and use of this corrosive substance in research and industrial settings. These regulations typically cover various aspects of HCl management, including personal protective equipment (PPE), storage requirements, handling procedures, and emergency response protocols.
Personal protective equipment is a crucial component of HCl safety regulations. Workers handling HCl must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. In cases where HCl vapors may be present, respiratory protection such as acid gas respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) may be required.
Storage requirements for HCl are stringent due to its corrosive nature. Regulations often mandate that HCl be stored in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials such as metals, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. Containers must be properly labeled and made of compatible materials like polyethylene or glass. Secondary containment measures are typically required to prevent spills from spreading.
Handling procedures for HCl are designed to minimize the risk of exposure and accidents. Regulations often require the use of fume hoods or local exhaust ventilation when working with HCl to control vapors. Dilution of HCl should always be performed by adding acid to water, never the reverse, to prevent dangerous splashing and heat generation.
Emergency response protocols are a critical component of HCl safety regulations. Facilities must have readily accessible eyewash stations and safety showers in areas where HCl is used or stored. Spill response kits containing neutralizing agents and absorbent materials should be available, and personnel must be trained in their proper use.
Transportation of HCl is subject to strict regulations, including proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting HCl must be equipped with appropriate placards and safety equipment, and drivers must be trained in hazardous materials handling.
Regular safety training and education programs are often mandated by regulations to ensure that all personnel working with or around HCl are aware of its hazards and proper handling procedures. This includes training on the interpretation of safety data sheets (SDS) and the implementation of safe work practices.
Environmental regulations also play a role in HCl management, with strict guidelines on disposal methods and emission controls. Facilities using HCl must often implement monitoring systems to detect leaks or releases and have plans in place to mitigate environmental impacts.
Compliance with these safety regulations is essential not only for protecting human health and the environment but also for maintaining regulatory compliance and avoiding potential legal and financial consequences. As research in innovative fields using HCl continues to evolve, safety regulations must adapt to address new challenges and applications, ensuring that the benefits of HCl use are realized while minimizing associated risks.
Personal protective equipment is a crucial component of HCl safety regulations. Workers handling HCl must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. In cases where HCl vapors may be present, respiratory protection such as acid gas respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) may be required.
Storage requirements for HCl are stringent due to its corrosive nature. Regulations often mandate that HCl be stored in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials such as metals, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. Containers must be properly labeled and made of compatible materials like polyethylene or glass. Secondary containment measures are typically required to prevent spills from spreading.
Handling procedures for HCl are designed to minimize the risk of exposure and accidents. Regulations often require the use of fume hoods or local exhaust ventilation when working with HCl to control vapors. Dilution of HCl should always be performed by adding acid to water, never the reverse, to prevent dangerous splashing and heat generation.
Emergency response protocols are a critical component of HCl safety regulations. Facilities must have readily accessible eyewash stations and safety showers in areas where HCl is used or stored. Spill response kits containing neutralizing agents and absorbent materials should be available, and personnel must be trained in their proper use.
Transportation of HCl is subject to strict regulations, including proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting HCl must be equipped with appropriate placards and safety equipment, and drivers must be trained in hazardous materials handling.
Regular safety training and education programs are often mandated by regulations to ensure that all personnel working with or around HCl are aware of its hazards and proper handling procedures. This includes training on the interpretation of safety data sheets (SDS) and the implementation of safe work practices.
Environmental regulations also play a role in HCl management, with strict guidelines on disposal methods and emission controls. Facilities using HCl must often implement monitoring systems to detect leaks or releases and have plans in place to mitigate environmental impacts.
Compliance with these safety regulations is essential not only for protecting human health and the environment but also for maintaining regulatory compliance and avoiding potential legal and financial consequences. As research in innovative fields using HCl continues to evolve, safety regulations must adapt to address new challenges and applications, ensuring that the benefits of HCl use are realized while minimizing associated risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!