Measure NMC Battery's Lifecycle Accuracy Using Modern Techniques
AUG 27, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMC Battery Lifecycle Measurement Background and Objectives
Lithium-ion batteries with nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC) cathodes have emerged as a dominant technology in the energy storage landscape, powering everything from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and grid-scale storage systems. The accurate measurement and prediction of NMC battery lifecycle performance represent critical challenges that have significant implications for product reliability, warranty management, and overall system economics.
The evolution of NMC battery technology has progressed through several generations, from early NMC111 (equal parts nickel, manganese, and cobalt) to more recent high-nickel formulations like NMC811, each offering improved energy density but presenting unique degradation mechanisms. This technological progression has necessitated increasingly sophisticated measurement techniques to accurately characterize battery performance throughout its operational life.
Traditional lifecycle assessment methods relied heavily on simplified cycling protocols and basic capacity measurements, which often failed to capture the complex degradation behaviors that occur under real-world operating conditions. These limitations have led to significant discrepancies between laboratory-predicted lifetimes and actual field performance, creating challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike.
The primary objective of modern NMC battery lifecycle measurement is to develop methodologies that can accurately predict battery degradation across diverse usage patterns and environmental conditions. This includes quantifying capacity fade, power capability decline, and internal resistance growth with high precision and reproducibility. Furthermore, these measurements must be applicable across different cell formats, from small consumer cells to large-format automotive and grid storage systems.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more sophisticated approaches to lifecycle assessment, including advanced electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, differential voltage analysis, and machine learning-based predictive models. These techniques aim to provide deeper insights into degradation mechanisms at the molecular and structural levels, allowing for more accurate lifetime predictions.
The integration of in-situ and operando measurement techniques represents a significant frontier in this field, enabling real-time monitoring of battery health parameters without disrupting normal operation. These approaches, coupled with big data analytics and artificial intelligence, are creating new possibilities for predictive maintenance and adaptive battery management strategies.
As global deployment of NMC batteries continues to accelerate, particularly in electric mobility and renewable energy integration, the economic and environmental importance of accurate lifecycle measurement grows correspondingly. Improved measurement accuracy directly translates to optimized battery utilization, reduced warranty costs, and more effective end-of-life management strategies, ultimately supporting broader sustainability goals in the transition to clean energy systems.
The evolution of NMC battery technology has progressed through several generations, from early NMC111 (equal parts nickel, manganese, and cobalt) to more recent high-nickel formulations like NMC811, each offering improved energy density but presenting unique degradation mechanisms. This technological progression has necessitated increasingly sophisticated measurement techniques to accurately characterize battery performance throughout its operational life.
Traditional lifecycle assessment methods relied heavily on simplified cycling protocols and basic capacity measurements, which often failed to capture the complex degradation behaviors that occur under real-world operating conditions. These limitations have led to significant discrepancies between laboratory-predicted lifetimes and actual field performance, creating challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike.
The primary objective of modern NMC battery lifecycle measurement is to develop methodologies that can accurately predict battery degradation across diverse usage patterns and environmental conditions. This includes quantifying capacity fade, power capability decline, and internal resistance growth with high precision and reproducibility. Furthermore, these measurements must be applicable across different cell formats, from small consumer cells to large-format automotive and grid storage systems.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more sophisticated approaches to lifecycle assessment, including advanced electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, differential voltage analysis, and machine learning-based predictive models. These techniques aim to provide deeper insights into degradation mechanisms at the molecular and structural levels, allowing for more accurate lifetime predictions.
The integration of in-situ and operando measurement techniques represents a significant frontier in this field, enabling real-time monitoring of battery health parameters without disrupting normal operation. These approaches, coupled with big data analytics and artificial intelligence, are creating new possibilities for predictive maintenance and adaptive battery management strategies.
As global deployment of NMC batteries continues to accelerate, particularly in electric mobility and renewable energy integration, the economic and environmental importance of accurate lifecycle measurement grows correspondingly. Improved measurement accuracy directly translates to optimized battery utilization, reduced warranty costs, and more effective end-of-life management strategies, ultimately supporting broader sustainability goals in the transition to clean energy systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Accurate Battery Lifecycle Testing
The global market for accurate battery lifecycle testing solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage systems, and portable electronics. The NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery market specifically is projected to reach $45 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 12.3% from 2021. This growth trajectory underscores the critical importance of precise lifecycle measurement technologies.
Consumer electronics manufacturers represent a substantial market segment, demanding increasingly accurate battery lifecycle testing to meet consumer expectations for longer-lasting devices. According to industry surveys, 78% of smartphone users cite battery life as a top three purchasing consideration, creating downstream pressure on manufacturers to optimize battery performance and accurately predict lifecycle.
The electric vehicle sector presents perhaps the most robust demand driver for advanced NMC battery lifecycle testing. With global EV sales surpassing 10 million units in 2022 and projected to reach 30 million by 2030, automotive manufacturers require precise battery performance data to provide warranty guarantees and meet regulatory requirements. Battery lifecycle accuracy directly impacts vehicle range estimates, a critical competitive differentiator in the EV market.
Grid-scale energy storage represents another expanding market segment, with installed capacity growing at 27% annually. Utility companies and grid operators require highly accurate battery lifecycle predictions to optimize investment planning and operational efficiency. The financial implications of battery replacement schedules measured in gigawatt-hours make precision testing technologies particularly valuable in this sector.
Market research indicates a growing preference for testing solutions that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These advanced techniques can reduce testing time by up to 60% while improving prediction accuracy by 25-30% compared to traditional methods. This trend is reshaping competitive dynamics among testing equipment providers.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific dominating the market with 42% share, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (23%). China's aggressive push toward electrification has created particularly strong demand for advanced battery testing solutions, with domestic manufacturers rapidly scaling production capacity.
The regulatory landscape further amplifies market demand, with new standards from organizations like ISO and IEC establishing more stringent requirements for battery performance verification. These standards increasingly specify accuracy thresholds for lifecycle testing, creating compliance-driven demand for advanced measurement technologies.
Consumer electronics manufacturers represent a substantial market segment, demanding increasingly accurate battery lifecycle testing to meet consumer expectations for longer-lasting devices. According to industry surveys, 78% of smartphone users cite battery life as a top three purchasing consideration, creating downstream pressure on manufacturers to optimize battery performance and accurately predict lifecycle.
The electric vehicle sector presents perhaps the most robust demand driver for advanced NMC battery lifecycle testing. With global EV sales surpassing 10 million units in 2022 and projected to reach 30 million by 2030, automotive manufacturers require precise battery performance data to provide warranty guarantees and meet regulatory requirements. Battery lifecycle accuracy directly impacts vehicle range estimates, a critical competitive differentiator in the EV market.
Grid-scale energy storage represents another expanding market segment, with installed capacity growing at 27% annually. Utility companies and grid operators require highly accurate battery lifecycle predictions to optimize investment planning and operational efficiency. The financial implications of battery replacement schedules measured in gigawatt-hours make precision testing technologies particularly valuable in this sector.
Market research indicates a growing preference for testing solutions that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These advanced techniques can reduce testing time by up to 60% while improving prediction accuracy by 25-30% compared to traditional methods. This trend is reshaping competitive dynamics among testing equipment providers.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific dominating the market with 42% share, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (23%). China's aggressive push toward electrification has created particularly strong demand for advanced battery testing solutions, with domestic manufacturers rapidly scaling production capacity.
The regulatory landscape further amplifies market demand, with new standards from organizations like ISO and IEC establishing more stringent requirements for battery performance verification. These standards increasingly specify accuracy thresholds for lifecycle testing, creating compliance-driven demand for advanced measurement technologies.
Current Challenges in NMC Battery Lifecycle Assessment
Despite significant advancements in battery technology, the accurate assessment of NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery lifecycle remains a formidable challenge for researchers and industry professionals. Current methodologies face several critical limitations that impede precise predictions and reliable performance evaluations across the battery's operational lifespan.
One of the primary challenges is the inherent complexity of degradation mechanisms in NMC batteries. These mechanisms operate simultaneously and interact in ways that are difficult to isolate and quantify. Structural changes, electrolyte decomposition, solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer formation, and transition metal dissolution occur concurrently, creating a multifaceted degradation profile that conventional models struggle to capture accurately.
The variability in operating conditions presents another significant obstacle. NMC batteries experience widely different temperature profiles, charge-discharge rates, depth of discharge patterns, and mechanical stresses depending on their application environment. Current assessment techniques often fail to account for this real-world variability, leading to substantial discrepancies between laboratory predictions and actual field performance.
Accelerated aging tests, while necessary for timely evaluations, introduce methodological challenges. These tests typically subject batteries to extreme conditions to expedite degradation, but the correlation between accelerated aging and natural aging processes remains imperfectly understood. This translation gap compromises the reliability of lifecycle projections based on such accelerated testing protocols.
Data acquisition limitations further complicate accurate assessment. Non-invasive measurement techniques often lack the sensitivity to detect early-stage degradation indicators, while invasive techniques destroy the battery, preventing continuous monitoring of the same cell throughout its lifecycle. This creates a fundamental dilemma in obtaining comprehensive degradation data without altering the very object being studied.
The industry also faces challenges related to standardization. Different manufacturers employ varying testing protocols, reporting metrics, and performance criteria, making cross-comparison of lifecycle data problematic. This lack of standardization impedes collaborative research efforts and slows the development of universal assessment methodologies.
Computational modeling approaches, while promising, still struggle with the immense computational resources required to simulate all relevant physical and chemical processes at appropriate time scales. Current models often make simplifying assumptions that compromise their predictive accuracy, particularly for novel NMC chemistries or innovative cell designs.
Finally, there exists a significant gap between laboratory-scale testing and real-world battery pack behavior. Factors such as thermal management systems, battery management algorithms, and cell-to-cell variations within packs introduce additional complexities that are rarely captured in standard lifecycle assessment protocols.
One of the primary challenges is the inherent complexity of degradation mechanisms in NMC batteries. These mechanisms operate simultaneously and interact in ways that are difficult to isolate and quantify. Structural changes, electrolyte decomposition, solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer formation, and transition metal dissolution occur concurrently, creating a multifaceted degradation profile that conventional models struggle to capture accurately.
The variability in operating conditions presents another significant obstacle. NMC batteries experience widely different temperature profiles, charge-discharge rates, depth of discharge patterns, and mechanical stresses depending on their application environment. Current assessment techniques often fail to account for this real-world variability, leading to substantial discrepancies between laboratory predictions and actual field performance.
Accelerated aging tests, while necessary for timely evaluations, introduce methodological challenges. These tests typically subject batteries to extreme conditions to expedite degradation, but the correlation between accelerated aging and natural aging processes remains imperfectly understood. This translation gap compromises the reliability of lifecycle projections based on such accelerated testing protocols.
Data acquisition limitations further complicate accurate assessment. Non-invasive measurement techniques often lack the sensitivity to detect early-stage degradation indicators, while invasive techniques destroy the battery, preventing continuous monitoring of the same cell throughout its lifecycle. This creates a fundamental dilemma in obtaining comprehensive degradation data without altering the very object being studied.
The industry also faces challenges related to standardization. Different manufacturers employ varying testing protocols, reporting metrics, and performance criteria, making cross-comparison of lifecycle data problematic. This lack of standardization impedes collaborative research efforts and slows the development of universal assessment methodologies.
Computational modeling approaches, while promising, still struggle with the immense computational resources required to simulate all relevant physical and chemical processes at appropriate time scales. Current models often make simplifying assumptions that compromise their predictive accuracy, particularly for novel NMC chemistries or innovative cell designs.
Finally, there exists a significant gap between laboratory-scale testing and real-world battery pack behavior. Factors such as thermal management systems, battery management algorithms, and cell-to-cell variations within packs introduce additional complexities that are rarely captured in standard lifecycle assessment protocols.
Modern Techniques for NMC Battery Lifecycle Measurement
01 Battery lifecycle prediction models
Advanced prediction models are used to accurately estimate the lifecycle of NMC batteries. These models incorporate various parameters such as charge-discharge cycles, temperature variations, and usage patterns to predict battery degradation over time. Machine learning algorithms and statistical methods enhance the accuracy of these predictions, allowing for better battery management and replacement planning.- Battery lifecycle prediction and monitoring systems: Systems designed to predict and monitor the lifecycle of NMC batteries using advanced algorithms and real-time data collection. These systems can accurately estimate remaining useful life, state of health, and performance degradation over time. By continuously monitoring battery parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and impedance, these systems provide precise lifecycle predictions that help optimize battery usage and maintenance schedules.
- Machine learning approaches for battery lifecycle accuracy: Implementation of machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques to improve the accuracy of NMC battery lifecycle predictions. These approaches utilize historical battery performance data to train models that can identify patterns and correlations between various operational parameters and battery degradation. Machine learning algorithms can adapt to different battery chemistries and usage conditions, providing more accurate lifecycle estimations than traditional methods.
- Battery management systems with enhanced accuracy: Advanced battery management systems specifically designed to improve the accuracy of NMC battery lifecycle assessments. These systems incorporate sophisticated sensors and control mechanisms to precisely measure and regulate battery parameters. By maintaining optimal operating conditions and preventing harmful usage patterns, these management systems can significantly extend battery life while providing accurate remaining life estimations.
- Testing and validation methodologies for lifecycle accuracy: Specialized testing and validation methodologies developed to verify and improve the accuracy of NMC battery lifecycle predictions. These approaches include accelerated aging tests, cycle life testing under various conditions, and comparative analysis between predicted and actual degradation rates. By establishing standardized testing protocols, these methodologies enable more reliable comparisons between different battery technologies and prediction models.
- Data analytics frameworks for battery performance assessment: Comprehensive data analytics frameworks designed to process and analyze large volumes of battery performance data to improve lifecycle accuracy predictions. These frameworks integrate multiple data sources, including operational data, environmental conditions, and manufacturing information, to create holistic views of battery health and performance. Advanced statistical methods and visualization techniques help identify critical factors affecting battery lifecycle and enable more precise degradation modeling.
02 Real-time monitoring systems for NMC batteries
Real-time monitoring systems track the performance and health of NMC batteries throughout their lifecycle. These systems collect data on voltage, current, temperature, and other critical parameters to assess battery condition. By continuously monitoring these factors, the systems can detect early signs of degradation, predict remaining useful life, and improve the accuracy of lifecycle estimations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Data analytics for battery lifecycle assessment
Advanced data analytics techniques are applied to large datasets collected from NMC batteries to improve lifecycle accuracy assessments. These techniques include big data processing, pattern recognition, and trend analysis to identify factors affecting battery performance. By analyzing historical and operational data, more precise lifecycle predictions can be made, leading to optimized battery utilization and maintenance schedules.Expand Specific Solutions04 Improved testing methodologies for NMC batteries
Enhanced testing methodologies have been developed to accurately assess the lifecycle of NMC batteries. These include accelerated aging tests, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and capacity retention measurements under various conditions. Standardized testing protocols ensure consistent and reliable evaluation of battery performance, enabling more accurate predictions of battery lifespan and degradation patterns.Expand Specific Solutions05 Battery management systems for extending NMC lifecycle
Sophisticated battery management systems are designed to optimize the operation of NMC batteries and extend their useful life. These systems regulate charging and discharging processes, maintain optimal temperature conditions, and balance cell voltages. By implementing adaptive control strategies based on accurate lifecycle models, these management systems can significantly improve battery longevity and performance reliability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Battery Testing Technology
The NMC battery lifecycle accuracy measurement market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by electric vehicle and energy storage applications. The market size is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant value as battery technology becomes more critical for sustainable energy solutions. Technologically, major players like Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and BYD are leading innovation with advanced measurement techniques, while established automotive companies such as Toyota, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi are integrating these technologies into their product development cycles. Research institutions like KAIST and Keio University are contributing fundamental advancements, while specialized companies like Saft Groupe and FDK Corp are developing niche applications. The competitive landscape shows a blend of battery manufacturers, automotive OEMs, and technology providers collaborating to improve NMC battery lifecycle prediction accuracy.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed a comprehensive Battery Management System (BMS) specifically designed for NMC batteries that incorporates multiple modern techniques for lifecycle accuracy measurement. Their approach combines electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) with machine learning algorithms to create a dynamic aging model. The system continuously monitors impedance changes across multiple frequency ranges to detect subtle shifts in battery chemistry and structure. Samsung's proprietary algorithm integrates temperature-compensated voltage measurements with coulomb counting to achieve over 95% accuracy in state-of-health (SOH) estimation. Their technique also employs differential voltage analysis (DVA) to identify specific aging mechanisms, distinguishing between capacity loss due to lithium plating, SEI growth, and active material degradation. Samsung has implemented this technology in their latest generation of energy storage systems and EV battery packs, allowing for real-time health monitoring and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Strengths: Samsung's approach excels in accuracy by combining multiple measurement techniques, reducing dependency on any single method's limitations. Their machine learning models continuously improve with data collection, enhancing prediction accuracy over time. Weaknesses: The system requires significant computational resources for real-time analysis, potentially increasing BMS costs. The technology also depends on extensive calibration during manufacturing to establish baseline performance metrics.
BYD Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BYD has developed an integrated "Blade Battery Lifecycle Management" (BBLM) system specifically optimized for their NMC battery technology. This system employs a multi-layered approach to lifecycle measurement combining both invasive and non-invasive techniques. At the core of BYD's technology is a high-precision digital twin model that simulates electrochemical processes at the cell level, continuously calibrated through operational data. Their approach incorporates frequency domain analysis of current and voltage responses during normal charging/discharging cycles, eliminating the need for special test conditions. BYD's system features distributed fiber optic sensors embedded within battery modules to detect microscopic physical changes and temperature gradients with sub-millimeter spatial resolution. The BBLM technology also employs a novel "partial charging entropy measurement" technique that can identify changes in reaction kinetics indicative of aging processes. All measurement data feeds into BYD's proprietary AI algorithm that correlates multiple degradation indicators to predict remaining useful life with claimed accuracy exceeding 92% even after 1000+ cycles.
Strengths: BYD's digital twin approach allows for physics-based predictions that can adapt to different usage patterns and environmental conditions. Their fiber optic sensing provides unique insights into mechanical degradation not captured by electrical measurements alone. Weaknesses: The sophisticated sensor network increases manufacturing complexity and cost. The system requires significant computational resources for real-time digital twin simulation, potentially limiting implementation in lower-cost applications.
Critical Patents and Research in Battery Testing Accuracy
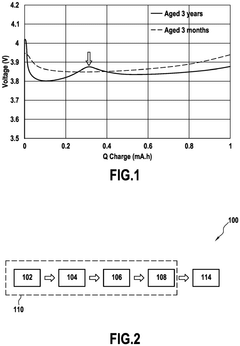
Active material for cathode of lithium-ion battery, cathode comprising said active material, and method for preparing said cathode
PatentWO2023170449A1
Innovation
- A cathode active material is developed by combining lithium manganese oxide (LMO) with lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC) in specific mole ratios, enhancing stability and cycle life, and incorporating a binder and conductive material for improved electron and ion transfer, with the mixture's mass ratio optimized for high energy density and long cycle life.
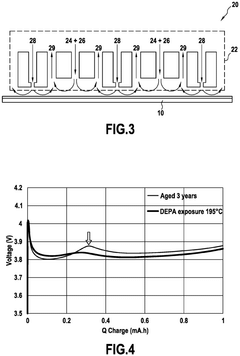
Method for restoration performances of aged nickel-rich NMC cathode material for lithium-ion secondary battery
PatentPendingEP4550454A1
Innovation
- A method involving the formation of a cathode with aged nickel-rich NMC material, a binder, and carbon black, followed by exposure to diethyl phosphoramidate at temperatures above 160°C to create a lithium phosphate protective layer, thereby reducing the overpotential peak.
Standardization Efforts in Battery Performance Metrics
The standardization of battery performance metrics has become increasingly critical as the energy storage industry expands and diversifies. For NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries specifically, the lack of universally accepted measurement protocols has led to inconsistent lifecycle accuracy assessments across research institutions and manufacturers.
Several international organizations are currently leading efforts to establish standardized testing procedures. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed IEC 62660 series standards specifically addressing performance and lifecycle testing methodologies for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. These standards provide detailed protocols for capacity measurement, internal resistance determination, and cycle life evaluation under various temperature conditions.
Similarly, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has introduced IEEE 1625 and IEEE 1725 standards that include specific provisions for lifecycle performance verification. While these standards were initially developed for portable computing and mobile device applications, their methodological approaches have been adapted for larger format NMC cells.
The Battery Performance and Cost (BatPaC) model developed by Argonne National Laboratory represents another significant standardization effort. This model incorporates standardized performance metrics that enable consistent comparison of different battery chemistries, including various NMC formulations (NMC 111, 532, 622, and 811).
In the European context, the Battery Directive is undergoing revision to include more stringent requirements for lifecycle performance reporting. The proposed Battery Passport initiative will require manufacturers to disclose standardized lifecycle data, creating market pressure for consistent measurement methodologies.
Industry consortia are also contributing to standardization efforts. The Global Battery Alliance has established a working group focused specifically on performance metrics standardization, with particular attention to cycle life measurement protocols for NMC batteries. Their framework proposes standardized testing conditions including discharge rates, depth of discharge parameters, and temperature profiles.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has published J2288 standards for life cycle testing of electric vehicle battery modules, which include specific provisions for NMC chemistry evaluation. These standards are increasingly being adopted by manufacturers seeking to provide comparable performance data.
Despite these advances, challenges remain in harmonizing standards across different applications and markets. The diversity of NMC formulations (varying nickel, manganese, and cobalt ratios) necessitates flexible yet consistent measurement frameworks that can accommodate chemical variations while maintaining comparability of results.
Several international organizations are currently leading efforts to establish standardized testing procedures. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed IEC 62660 series standards specifically addressing performance and lifecycle testing methodologies for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. These standards provide detailed protocols for capacity measurement, internal resistance determination, and cycle life evaluation under various temperature conditions.
Similarly, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has introduced IEEE 1625 and IEEE 1725 standards that include specific provisions for lifecycle performance verification. While these standards were initially developed for portable computing and mobile device applications, their methodological approaches have been adapted for larger format NMC cells.
The Battery Performance and Cost (BatPaC) model developed by Argonne National Laboratory represents another significant standardization effort. This model incorporates standardized performance metrics that enable consistent comparison of different battery chemistries, including various NMC formulations (NMC 111, 532, 622, and 811).
In the European context, the Battery Directive is undergoing revision to include more stringent requirements for lifecycle performance reporting. The proposed Battery Passport initiative will require manufacturers to disclose standardized lifecycle data, creating market pressure for consistent measurement methodologies.
Industry consortia are also contributing to standardization efforts. The Global Battery Alliance has established a working group focused specifically on performance metrics standardization, with particular attention to cycle life measurement protocols for NMC batteries. Their framework proposes standardized testing conditions including discharge rates, depth of discharge parameters, and temperature profiles.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has published J2288 standards for life cycle testing of electric vehicle battery modules, which include specific provisions for NMC chemistry evaluation. These standards are increasingly being adopted by manufacturers seeking to provide comparable performance data.
Despite these advances, challenges remain in harmonizing standards across different applications and markets. The diversity of NMC formulations (varying nickel, manganese, and cobalt ratios) necessitates flexible yet consistent measurement frameworks that can accommodate chemical variations while maintaining comparability of results.
Environmental Impact of Battery Lifecycle Testing Methods
The environmental implications of battery lifecycle testing methodologies have become increasingly significant as the global demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to surge. Modern techniques for measuring NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery lifecycle accuracy must be evaluated not only for their technical precision but also for their ecological footprint.
Traditional accelerated aging tests, while efficient for rapid data collection, often require energy-intensive climate chambers operating continuously for weeks or months. These chambers consume substantial electricity, contributing to indirect carbon emissions that can undermine the sustainability goals of battery development. Research indicates that a single comprehensive lifecycle test using conventional methods can consume between 200-500 kWh of electricity, equivalent to the monthly consumption of an average household.
Chemical waste generation presents another environmental concern. Electrolyte samples, electrode materials, and testing reagents used in destructive testing methods often contain toxic compounds including organic solvents, lithium salts, and heavy metals. Without proper disposal protocols, these substances risk contaminating soil and water systems. A recent industry analysis revealed that approximately 5-8 kg of hazardous waste may be generated per battery unit tested using conventional methods.
Water usage in cooling systems for thermal management during high-rate cycling tests represents a hidden environmental cost. Advanced testing facilities can consume thousands of gallons of water annually, particularly in regions where water-intensive cooling technologies are employed rather than closed-loop systems. This aspect is often overlooked in environmental assessments of battery testing infrastructure.
Emerging non-destructive testing techniques offer promising alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Methods such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and ultrasonic characterization enable multiple measurements on the same battery unit, significantly reducing material waste. Similarly, machine learning approaches that can predict lifecycle performance from limited test data help minimize the duration and intensity of physical testing, thereby reducing energy consumption by up to 60% compared to traditional methods.
The carbon footprint of data centers supporting computational battery models must also be considered. As testing methodologies increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and complex simulations, the energy demands of these computational resources grow correspondingly. However, when properly optimized, these digital approaches can ultimately reduce the overall environmental impact by minimizing physical testing requirements.
Standardization efforts are underway to develop environmentally responsible testing protocols. Organizations including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) are incorporating sustainability metrics into their battery testing standards, encouraging the adoption of greener methodologies throughout the industry.
Traditional accelerated aging tests, while efficient for rapid data collection, often require energy-intensive climate chambers operating continuously for weeks or months. These chambers consume substantial electricity, contributing to indirect carbon emissions that can undermine the sustainability goals of battery development. Research indicates that a single comprehensive lifecycle test using conventional methods can consume between 200-500 kWh of electricity, equivalent to the monthly consumption of an average household.
Chemical waste generation presents another environmental concern. Electrolyte samples, electrode materials, and testing reagents used in destructive testing methods often contain toxic compounds including organic solvents, lithium salts, and heavy metals. Without proper disposal protocols, these substances risk contaminating soil and water systems. A recent industry analysis revealed that approximately 5-8 kg of hazardous waste may be generated per battery unit tested using conventional methods.
Water usage in cooling systems for thermal management during high-rate cycling tests represents a hidden environmental cost. Advanced testing facilities can consume thousands of gallons of water annually, particularly in regions where water-intensive cooling technologies are employed rather than closed-loop systems. This aspect is often overlooked in environmental assessments of battery testing infrastructure.
Emerging non-destructive testing techniques offer promising alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Methods such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and ultrasonic characterization enable multiple measurements on the same battery unit, significantly reducing material waste. Similarly, machine learning approaches that can predict lifecycle performance from limited test data help minimize the duration and intensity of physical testing, thereby reducing energy consumption by up to 60% compared to traditional methods.
The carbon footprint of data centers supporting computational battery models must also be considered. As testing methodologies increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and complex simulations, the energy demands of these computational resources grow correspondingly. However, when properly optimized, these digital approaches can ultimately reduce the overall environmental impact by minimizing physical testing requirements.
Standardization efforts are underway to develop environmentally responsible testing protocols. Organizations including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) are incorporating sustainability metrics into their battery testing standards, encouraging the adoption of greener methodologies throughout the industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!