Ethyl Acetate in Printing: Modern Developments
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Printing Evolution
The evolution of ethyl acetate in printing has been marked by significant advancements and innovations over the past few decades. Initially used primarily as a solvent in traditional printing processes, ethyl acetate has undergone a transformation in its applications and formulations to meet the changing demands of the printing industry.
In the early stages of its use in printing, ethyl acetate was valued for its fast-drying properties and ability to dissolve a wide range of inks and coatings. This made it particularly useful in flexographic and gravure printing, where quick-drying solvents were essential for high-speed production. As environmental concerns grew, the industry began to focus on developing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations, leading to the creation of ethyl acetate-based inks with reduced solvent content.
The advent of digital printing technologies in the late 20th century initially reduced the reliance on solvent-based inks. However, ethyl acetate found new applications in this domain, particularly in the development of specialty inks for digital textile printing and UV-curable formulations. These innovations allowed for improved print quality and durability on a wider range of substrates.
Recent years have seen a resurgence in the use of ethyl acetate, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and bio-based materials. Manufacturers have developed bio-ethyl acetate, produced from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based solvents. This shift aligns with the printing industry's increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles.
The evolution of ethyl acetate in printing has also been characterized by improvements in its purity and quality. Advanced distillation and purification techniques have resulted in higher-grade ethyl acetate, which is crucial for achieving consistent print quality and reducing equipment maintenance issues. These high-purity grades have enabled the development of specialized inks for demanding applications, such as food packaging printing, where strict regulations on solvent residues apply.
In the realm of 3D printing, ethyl acetate has found novel applications as a smoothing agent for ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) prints. Its controlled evaporation rate and compatibility with ABS polymers make it an effective tool for post-processing, allowing for the creation of smoother, more professional-looking 3D printed objects.
The ongoing evolution of ethyl acetate in printing continues to be driven by technological advancements, environmental considerations, and changing market demands. As the industry moves towards more sustainable and efficient printing processes, ethyl acetate remains a key component, adapting and evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities in the printing landscape.
In the early stages of its use in printing, ethyl acetate was valued for its fast-drying properties and ability to dissolve a wide range of inks and coatings. This made it particularly useful in flexographic and gravure printing, where quick-drying solvents were essential for high-speed production. As environmental concerns grew, the industry began to focus on developing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations, leading to the creation of ethyl acetate-based inks with reduced solvent content.
The advent of digital printing technologies in the late 20th century initially reduced the reliance on solvent-based inks. However, ethyl acetate found new applications in this domain, particularly in the development of specialty inks for digital textile printing and UV-curable formulations. These innovations allowed for improved print quality and durability on a wider range of substrates.
Recent years have seen a resurgence in the use of ethyl acetate, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and bio-based materials. Manufacturers have developed bio-ethyl acetate, produced from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based solvents. This shift aligns with the printing industry's increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles.
The evolution of ethyl acetate in printing has also been characterized by improvements in its purity and quality. Advanced distillation and purification techniques have resulted in higher-grade ethyl acetate, which is crucial for achieving consistent print quality and reducing equipment maintenance issues. These high-purity grades have enabled the development of specialized inks for demanding applications, such as food packaging printing, where strict regulations on solvent residues apply.
In the realm of 3D printing, ethyl acetate has found novel applications as a smoothing agent for ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) prints. Its controlled evaporation rate and compatibility with ABS polymers make it an effective tool for post-processing, allowing for the creation of smoother, more professional-looking 3D printed objects.
The ongoing evolution of ethyl acetate in printing continues to be driven by technological advancements, environmental considerations, and changing market demands. As the industry moves towards more sustainable and efficient printing processes, ethyl acetate remains a key component, adapting and evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities in the printing landscape.
Printing Market Demand Analysis
The printing industry has witnessed a significant surge in demand for ethyl acetate in recent years, driven by its versatile applications and superior performance characteristics. As a key solvent in printing inks, ethyl acetate has become indispensable in various printing processes, including flexography, gravure, and digital printing. The global printing market, valued at approximately $800 billion in 2020, is projected to grow at a steady rate of 2-3% annually, with ethyl acetate playing a crucial role in this expansion.
The increasing demand for ethyl acetate in printing can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the rise of e-commerce and online retail has led to a boom in packaging and labeling requirements, driving the need for high-quality printing inks. Ethyl acetate's fast-drying properties and excellent solvent power make it ideal for these applications, ensuring quick turnaround times and vibrant print quality.
Furthermore, the shift towards environmentally friendly printing solutions has bolstered the adoption of ethyl acetate. As a relatively low-toxicity solvent with minimal environmental impact, it aligns well with the industry's sustainability goals. This has led to its increased use in water-based and UV-curable inks, which are gaining traction in the market due to their reduced VOC emissions and improved safety profiles.
The packaging industry, a major consumer of printing inks, has seen substantial growth, particularly in the food and beverage sector. Ethyl acetate's low odor and non-toxicity make it suitable for food-safe packaging applications, driving its demand in this segment. The flexible packaging market, which heavily relies on ethyl acetate-based inks, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4-5% through 2025, further boosting the demand for this solvent.
In the digital printing sector, which is experiencing rapid growth due to advancements in technology and increasing customization requirements, ethyl acetate is finding new applications. Its compatibility with a wide range of substrates and its ability to produce high-resolution prints make it valuable in digital ink formulations, especially for large-format printing and textile applications.
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is emerging as the largest market for ethyl acetate in printing applications. The region's booming manufacturing sector, coupled with increasing urbanization and rising disposable incomes, is driving the demand for packaged goods and printed materials. This trend is expected to continue, with the region projected to account for over 40% of the global ethyl acetate consumption in printing by 2025.
The increasing demand for ethyl acetate in printing can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the rise of e-commerce and online retail has led to a boom in packaging and labeling requirements, driving the need for high-quality printing inks. Ethyl acetate's fast-drying properties and excellent solvent power make it ideal for these applications, ensuring quick turnaround times and vibrant print quality.
Furthermore, the shift towards environmentally friendly printing solutions has bolstered the adoption of ethyl acetate. As a relatively low-toxicity solvent with minimal environmental impact, it aligns well with the industry's sustainability goals. This has led to its increased use in water-based and UV-curable inks, which are gaining traction in the market due to their reduced VOC emissions and improved safety profiles.
The packaging industry, a major consumer of printing inks, has seen substantial growth, particularly in the food and beverage sector. Ethyl acetate's low odor and non-toxicity make it suitable for food-safe packaging applications, driving its demand in this segment. The flexible packaging market, which heavily relies on ethyl acetate-based inks, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4-5% through 2025, further boosting the demand for this solvent.
In the digital printing sector, which is experiencing rapid growth due to advancements in technology and increasing customization requirements, ethyl acetate is finding new applications. Its compatibility with a wide range of substrates and its ability to produce high-resolution prints make it valuable in digital ink formulations, especially for large-format printing and textile applications.
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is emerging as the largest market for ethyl acetate in printing applications. The region's booming manufacturing sector, coupled with increasing urbanization and rising disposable incomes, is driving the demand for packaged goods and printed materials. This trend is expected to continue, with the region projected to account for over 40% of the global ethyl acetate consumption in printing by 2025.
Ethyl Acetate Challenges in Printing
The printing industry faces several challenges in the use of ethyl acetate, a widely employed solvent in various printing processes. One of the primary concerns is the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with ethyl acetate. As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, printers are under pressure to reduce their VOC emissions, which can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers.
Another significant challenge is the flammability of ethyl acetate. Its low flash point makes it highly flammable, requiring strict safety measures in storage, handling, and use. This necessitates specialized equipment and training for workers, increasing operational costs and complexity for printing businesses.
The rapid evaporation rate of ethyl acetate, while beneficial for quick drying in some applications, can also present difficulties in maintaining consistent print quality. Fluctuations in temperature and humidity can affect the evaporation rate, leading to variations in ink viscosity and drying time. This can result in inconsistent color reproduction and potential print defects, particularly in high-precision printing processes.
Ethyl acetate's strong solvent properties, while advantageous for dissolving many inks and coatings, can also pose challenges. It may cause excessive softening or swelling of certain substrates, particularly some plastics and rubber compounds. This can lead to substrate distortion or degradation, limiting the range of materials that can be effectively printed using ethyl acetate-based inks.
The cost and availability of ethyl acetate can also be a concern for the printing industry. As a petroleum-derived product, its price can be subject to fluctuations in the global oil market. Additionally, competition for ethyl acetate from other industries, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, can impact its availability and pricing for printing applications.
Health and safety concerns associated with ethyl acetate exposure present ongoing challenges. While it is considered less toxic than some other solvents, prolonged exposure can still cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Ensuring proper ventilation and personal protective equipment use adds to the operational complexities and costs for printing facilities.
Lastly, the printing industry faces challenges in finding suitable alternatives to ethyl acetate that offer similar performance characteristics without the associated environmental and safety concerns. While water-based and UV-curable inks have gained traction in some applications, they may not always match the versatility and performance of ethyl acetate-based systems across all printing processes and substrates.
Another significant challenge is the flammability of ethyl acetate. Its low flash point makes it highly flammable, requiring strict safety measures in storage, handling, and use. This necessitates specialized equipment and training for workers, increasing operational costs and complexity for printing businesses.
The rapid evaporation rate of ethyl acetate, while beneficial for quick drying in some applications, can also present difficulties in maintaining consistent print quality. Fluctuations in temperature and humidity can affect the evaporation rate, leading to variations in ink viscosity and drying time. This can result in inconsistent color reproduction and potential print defects, particularly in high-precision printing processes.
Ethyl acetate's strong solvent properties, while advantageous for dissolving many inks and coatings, can also pose challenges. It may cause excessive softening or swelling of certain substrates, particularly some plastics and rubber compounds. This can lead to substrate distortion or degradation, limiting the range of materials that can be effectively printed using ethyl acetate-based inks.
The cost and availability of ethyl acetate can also be a concern for the printing industry. As a petroleum-derived product, its price can be subject to fluctuations in the global oil market. Additionally, competition for ethyl acetate from other industries, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, can impact its availability and pricing for printing applications.
Health and safety concerns associated with ethyl acetate exposure present ongoing challenges. While it is considered less toxic than some other solvents, prolonged exposure can still cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Ensuring proper ventilation and personal protective equipment use adds to the operational complexities and costs for printing facilities.
Lastly, the printing industry faces challenges in finding suitable alternatives to ethyl acetate that offer similar performance characteristics without the associated environmental and safety concerns. While water-based and UV-curable inks have gained traction in some applications, they may not always match the versatility and performance of ethyl acetate-based systems across all printing processes and substrates.
Current Ethyl Acetate Printing Solutions
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include distillation techniques, reactive distillation, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and efficiency. The processes aim to optimize the production of high-purity ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods are employed for the production and purification of ethyl acetate, including distillation, extraction, and reactive distillation processes. These techniques aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate while reducing energy consumption and production costs.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in industrial processes: Ethyl acetate finds widespread use in industrial processes, such as solvent extraction, coating formulations, and as a reaction medium. It is particularly valuable in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials due to its favorable properties and versatility.
- Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science: Ethyl acetate plays a significant role in polymer and material science, particularly in the development of coatings, adhesives, and specialty materials. It is used as a solvent, plasticizer, and in the synthesis of various polymeric compounds, contributing to the creation of advanced materials with specific properties.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: The use and handling of ethyl acetate require careful consideration of environmental and safety aspects. This includes developing improved methods for its recovery and recycling, implementing proper storage and handling procedures, and addressing potential health and environmental impacts associated with its production and use.
- Novel synthesis routes and catalysts for ethyl acetate production: Research focuses on developing novel synthesis routes and catalysts for ethyl acetate production. These innovations aim to enhance reaction efficiency, selectivity, and sustainability, potentially leading to more economical and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
02 Ethyl acetate as a solvent in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent in various chemical processes and applications. Its properties make it suitable for use in extraction, purification, and as a reaction medium. The patents describe specific applications in areas such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, polymer processing, and organic synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate
Methods for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial processes are presented. These techniques aim to improve the economic efficiency and environmental sustainability of processes using ethyl acetate. The recovery methods include adsorption, membrane separation, and specialized distillation processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ethyl acetate in formulations and compositions
Ethyl acetate is used as an ingredient in various formulations and compositions. These include adhesives, coatings, inks, and personal care products. The patents describe specific formulations and the role of ethyl acetate in enhancing product performance or manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel synthesis routes for ethyl acetate
New and improved methods for synthesizing ethyl acetate are described. These include alternative feedstocks, novel catalytic systems, and innovative reaction conditions. The aim is to develop more efficient, cost-effective, or environmentally friendly production routes for ethyl acetate.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Ethyl Acetate Printing Players
The modern developments of Ethyl Acetate in Printing are characterized by a competitive landscape in a mature industry with steady market growth. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with established players like BASF Corp., DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and Kuraray Co., Ltd. leading the field. These companies have leveraged their extensive R&D capabilities to enhance the performance and sustainability of ethyl acetate-based printing solutions. The market is seeing increased demand for eco-friendly formulations, driving innovation in bio-based alternatives. Emerging players such as Nantong Baichuan New Material Co., Ltd. are also contributing to advancements in the field, particularly in specialized applications and regional markets.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative ethyl acetate-based solutions for the printing industry, focusing on sustainability and performance. Their EcoEthyl™ range incorporates bio-based ethyl acetate derived from renewable resources, reducing the carbon footprint of printing processes[1]. This technology offers improved solvent properties, faster drying times, and enhanced print quality. BASF's ethyl acetate formulations also feature reduced VOC emissions, meeting stringent environmental regulations[2]. The company has introduced advanced ethyl acetate recovery systems, allowing printers to recycle and reuse the solvent, significantly reducing waste and operational costs[3].
Strengths: Sustainable bio-based solutions, improved print quality, reduced environmental impact. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial costs, may require equipment modifications for optimal use.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has made significant strides in ethyl acetate applications for the printing industry through its Cyrel® FAST thermal plate technology. This innovative system utilizes ethyl acetate as a key component in the plate development process, eliminating the need for traditional solvents and reducing processing time by up to 300%[4]. The company has also developed ethyl acetate-based cleaning solutions for flexographic printing, which offer superior ink removal capabilities while being more environmentally friendly than conventional cleaners[5]. DuPont's research has led to the creation of ethyl acetate-infused inks that provide enhanced adhesion and durability on a wide range of substrates, particularly in packaging applications[6].
Strengths: Rapid plate processing, environmentally friendly solutions, versatile applications. Weaknesses: Specialized equipment requirements, potential learning curve for adoption.
Ethyl Acetate Printing Innovations
Use of ethylene vinyl acetals as binder in printing inks
PatentWO2022063743A1
Innovation
- Ethylene vinyl acetals with a high ethylene content (25-60 mol%) are used as binders, providing improved adhesion, compatibility, and oxygen barrier properties, eliminating the need for adhesion promoters and enhancing safety and environmental impact.
Aluminium acetoacetate compounds, the production and use thereof as printing ink additives
PatentWO1999016739A1
Innovation
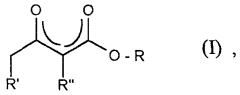
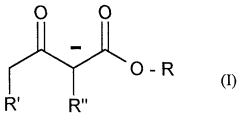
- Development of aluminum alkyl acetoacetate compounds with specific ligands, such as aluminum tris(methylacetoacetate) and aluminum tris(ethylacetoacetate), which are synthesized using ligand exchange reactions with aluminum alcoholates and glycol ether compounds as solvents, allowing for higher solubility and stability, and used in concentrations that prevent crystallization and hydrolysis.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Acetate Printing
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate in printing has become a significant concern as the industry strives for more sustainable practices. Ethyl acetate, widely used as a solvent in printing inks and coatings, presents both advantages and challenges from an environmental perspective.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ethyl acetate is its relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents used in printing. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment for extended periods, reducing long-term ecological risks. Additionally, ethyl acetate has a lower ozone depletion potential than many alternative solvents, contributing to the protection of the Earth's ozone layer.
However, the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with ethyl acetate usage remain a significant environmental concern. These emissions can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health. To address this issue, many printing facilities have implemented advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and carbon adsorption systems, to capture and treat VOC emissions effectively.
Water pollution is another environmental aspect to consider. While ethyl acetate is not highly soluble in water, improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies. This necessitates careful handling and waste management practices in printing facilities to minimize the risk of water pollution.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent developments in bio-based ethyl acetate production, using renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offer a more sustainable alternative with a reduced carbon footprint.
In response to environmental concerns, the printing industry has been exploring alternatives to ethyl acetate-based inks and coatings. Water-based and UV-curable formulations have gained traction, offering reduced VOC emissions and improved environmental performance. However, these alternatives often come with trade-offs in terms of print quality, drying time, or substrate compatibility, which must be carefully evaluated.
The lifecycle assessment of ethyl acetate in printing reveals opportunities for improvement in resource efficiency and waste reduction. Closed-loop solvent recovery systems have been implemented in many printing facilities, allowing for the recapture and reuse of ethyl acetate. This not only reduces environmental impact but also offers economic benefits through reduced solvent consumption.
As regulatory pressures increase and consumer demand for eco-friendly products grows, the printing industry continues to innovate in its use of ethyl acetate and other solvents. Ongoing research focuses on developing low-VOC formulations, improving emission control technologies, and exploring bio-based alternatives to further mitigate the environmental impact of printing processes.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ethyl acetate is its relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents used in printing. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment for extended periods, reducing long-term ecological risks. Additionally, ethyl acetate has a lower ozone depletion potential than many alternative solvents, contributing to the protection of the Earth's ozone layer.
However, the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with ethyl acetate usage remain a significant environmental concern. These emissions can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health. To address this issue, many printing facilities have implemented advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and carbon adsorption systems, to capture and treat VOC emissions effectively.
Water pollution is another environmental aspect to consider. While ethyl acetate is not highly soluble in water, improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies. This necessitates careful handling and waste management practices in printing facilities to minimize the risk of water pollution.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent developments in bio-based ethyl acetate production, using renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offer a more sustainable alternative with a reduced carbon footprint.
In response to environmental concerns, the printing industry has been exploring alternatives to ethyl acetate-based inks and coatings. Water-based and UV-curable formulations have gained traction, offering reduced VOC emissions and improved environmental performance. However, these alternatives often come with trade-offs in terms of print quality, drying time, or substrate compatibility, which must be carefully evaluated.
The lifecycle assessment of ethyl acetate in printing reveals opportunities for improvement in resource efficiency and waste reduction. Closed-loop solvent recovery systems have been implemented in many printing facilities, allowing for the recapture and reuse of ethyl acetate. This not only reduces environmental impact but also offers economic benefits through reduced solvent consumption.
As regulatory pressures increase and consumer demand for eco-friendly products grows, the printing industry continues to innovate in its use of ethyl acetate and other solvents. Ongoing research focuses on developing low-VOC formulations, improving emission control technologies, and exploring bio-based alternatives to further mitigate the environmental impact of printing processes.
Regulatory Framework for Ethyl Acetate Use
The regulatory framework for ethyl acetate use in the printing industry has evolved significantly in recent years, reflecting growing concerns about environmental and health impacts. At the international level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Labour Organization (ILO) have established guidelines for occupational exposure limits to ethyl acetate. These guidelines serve as a reference point for many national regulatory bodies.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for ethyl acetate at 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends a lower exposure limit of 400 ppm as a 10-hour time-weighted average. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to ethyl acetate vapors.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to ethyl acetate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register substances and provide safety information. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified ethyl acetate as a substance that may cause drowsiness or dizziness, necessitating appropriate labeling and safety measures.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have also established their own regulatory frameworks for ethyl acetate use. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has set emission standards for volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including ethyl acetate, in various industries. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established workplace exposure limits for ethyl acetate, aligning with international standards.
The printing industry has responded to these regulations by implementing various control measures. These include improved ventilation systems, personal protective equipment, and the use of enclosed printing systems to minimize worker exposure. Many companies have also invested in research and development to find alternative, less volatile solvents or water-based inks to reduce reliance on ethyl acetate.
Environmental regulations have also played a significant role in shaping the use of ethyl acetate in printing. Many countries have implemented strict VOC emission limits, encouraging the industry to adopt low-VOC or VOC-free printing technologies. This has led to innovations in ink formulations and printing processes that aim to maintain print quality while reducing environmental impact.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in the printing industry, regulatory bodies are likely to continue tightening restrictions on ethyl acetate use. This ongoing regulatory evolution is driving the development of new technologies and practices in the printing industry, balancing the need for high-quality printing with environmental and health considerations.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for ethyl acetate at 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends a lower exposure limit of 400 ppm as a 10-hour time-weighted average. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to ethyl acetate vapors.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to ethyl acetate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register substances and provide safety information. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified ethyl acetate as a substance that may cause drowsiness or dizziness, necessitating appropriate labeling and safety measures.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have also established their own regulatory frameworks for ethyl acetate use. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has set emission standards for volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including ethyl acetate, in various industries. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established workplace exposure limits for ethyl acetate, aligning with international standards.
The printing industry has responded to these regulations by implementing various control measures. These include improved ventilation systems, personal protective equipment, and the use of enclosed printing systems to minimize worker exposure. Many companies have also invested in research and development to find alternative, less volatile solvents or water-based inks to reduce reliance on ethyl acetate.
Environmental regulations have also played a significant role in shaping the use of ethyl acetate in printing. Many countries have implemented strict VOC emission limits, encouraging the industry to adopt low-VOC or VOC-free printing technologies. This has led to innovations in ink formulations and printing processes that aim to maintain print quality while reducing environmental impact.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in the printing industry, regulatory bodies are likely to continue tightening restrictions on ethyl acetate use. This ongoing regulatory evolution is driving the development of new technologies and practices in the printing industry, balancing the need for high-quality printing with environmental and health considerations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!