Quantifying Precision in HPLC: Statistical Methods
SEP 19, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HPLC Precision Quantification Background and Objectives
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s, becoming an indispensable analytical technique in pharmaceutical, environmental, food safety, and clinical laboratories. The quantification of precision in HPLC represents a critical aspect of analytical method validation and quality control processes. This technical domain has witnessed substantial advancements over the past decades, transitioning from basic repeatability assessments to sophisticated statistical methodologies that ensure reliable and reproducible results.
The evolution of precision quantification in HPLC has been driven by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements, particularly in pharmaceutical analysis where the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines have established comprehensive frameworks for analytical method validation. Concurrently, technological innovations in instrumentation, column technology, and data processing capabilities have enabled more precise measurements and expanded the statistical tools available for precision assessment.
Current trends in HPLC precision quantification include the integration of advanced statistical approaches such as Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), nested variance component analysis, and robust statistical methods that can handle outliers without compromising data integrity. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on measurement uncertainty estimation, which provides a more comprehensive understanding of result reliability compared to traditional precision metrics.
The primary technical objectives of this investigation into HPLC precision quantification methods include developing a systematic framework for selecting appropriate statistical approaches based on specific analytical contexts. This framework must account for various factors including the nature of the analyte, matrix complexity, concentration range, and intended application of the analytical method.
Furthermore, this research aims to evaluate the comparative performance of traditional and emerging statistical methodologies for precision assessment, with particular focus on their applicability across different HPLC platforms and analytical challenges. The investigation will also explore the integration of machine learning algorithms for automated detection of systematic errors and drift patterns that may impact precision measurements over time.
Another critical objective involves establishing standardized protocols for precision data collection and analysis that can be readily implemented in routine laboratory operations while maintaining compliance with evolving regulatory standards. This includes optimizing experimental designs for precision studies to maximize statistical power while minimizing resource utilization.
Ultimately, this technical exploration seeks to bridge the gap between theoretical statistical concepts and practical laboratory applications, providing analytical scientists with robust tools to quantify, interpret, and improve HPLC method precision in an increasingly complex analytical landscape.
The evolution of precision quantification in HPLC has been driven by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements, particularly in pharmaceutical analysis where the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines have established comprehensive frameworks for analytical method validation. Concurrently, technological innovations in instrumentation, column technology, and data processing capabilities have enabled more precise measurements and expanded the statistical tools available for precision assessment.
Current trends in HPLC precision quantification include the integration of advanced statistical approaches such as Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), nested variance component analysis, and robust statistical methods that can handle outliers without compromising data integrity. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on measurement uncertainty estimation, which provides a more comprehensive understanding of result reliability compared to traditional precision metrics.
The primary technical objectives of this investigation into HPLC precision quantification methods include developing a systematic framework for selecting appropriate statistical approaches based on specific analytical contexts. This framework must account for various factors including the nature of the analyte, matrix complexity, concentration range, and intended application of the analytical method.
Furthermore, this research aims to evaluate the comparative performance of traditional and emerging statistical methodologies for precision assessment, with particular focus on their applicability across different HPLC platforms and analytical challenges. The investigation will also explore the integration of machine learning algorithms for automated detection of systematic errors and drift patterns that may impact precision measurements over time.
Another critical objective involves establishing standardized protocols for precision data collection and analysis that can be readily implemented in routine laboratory operations while maintaining compliance with evolving regulatory standards. This includes optimizing experimental designs for precision studies to maximize statistical power while minimizing resource utilization.
Ultimately, this technical exploration seeks to bridge the gap between theoretical statistical concepts and practical laboratory applications, providing analytical scientists with robust tools to quantify, interpret, and improve HPLC method precision in an increasingly complex analytical landscape.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Precision HPLC Methods
The global market for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) continues to expand significantly, driven by increasing demands for precision analytics across multiple industries. Current market valuations place the HPLC market at approximately 4.5 billion USD, with projections indicating growth to reach 6.7 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.3%.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the primary drivers of demand for high-precision HPLC methods, collectively accounting for over 60% of market utilization. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements and the critical need for accurate quantification in drug development and quality control processes. The FDA and EMA's increasingly rigorous standards for analytical method validation have directly influenced market growth for advanced statistical approaches in HPLC precision quantification.
Clinical diagnostics represents the fastest-growing application segment, with 12.4% annual growth, as healthcare providers increasingly rely on precise chromatographic methods for disease biomarker detection and therapeutic drug monitoring. The ability to detect compounds at nanogram or even picogram levels with statistical confidence has become essential in modern diagnostic protocols.
Environmental monitoring agencies and food safety laboratories have also emerged as significant market segments, collectively representing 17% of current demand. These sectors require statistical validation of trace contaminant analysis, particularly for emerging pollutants and food adulterants where regulatory thresholds continue to decrease, necessitating greater analytical precision.
Regional analysis reveals North America maintains market leadership with 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth trajectory at 11.2% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing, contract research organizations, and strengthening regulatory frameworks in China and India.
Market research indicates that 73% of laboratory managers consider statistical method validation capabilities as "very important" or "critical" when selecting HPLC systems and software. This represents a significant shift from five years ago when only 48% placed similar emphasis on statistical capabilities.
Software solutions for statistical analysis of HPLC data represent a particularly dynamic market segment, growing at 14.2% annually. End-users increasingly demand integrated platforms that combine chromatographic control with comprehensive statistical tools for method validation, uncertainty estimation, and compliance reporting.
The market demonstrates clear willingness to invest in solutions that enhance precision quantification, with 67% of survey respondents indicating plans to upgrade their statistical analysis capabilities for HPLC within the next two years. This trend is particularly pronounced among contract research organizations and pharmaceutical quality control laboratories where demonstrable precision directly impacts competitive advantage.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the primary drivers of demand for high-precision HPLC methods, collectively accounting for over 60% of market utilization. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements and the critical need for accurate quantification in drug development and quality control processes. The FDA and EMA's increasingly rigorous standards for analytical method validation have directly influenced market growth for advanced statistical approaches in HPLC precision quantification.
Clinical diagnostics represents the fastest-growing application segment, with 12.4% annual growth, as healthcare providers increasingly rely on precise chromatographic methods for disease biomarker detection and therapeutic drug monitoring. The ability to detect compounds at nanogram or even picogram levels with statistical confidence has become essential in modern diagnostic protocols.
Environmental monitoring agencies and food safety laboratories have also emerged as significant market segments, collectively representing 17% of current demand. These sectors require statistical validation of trace contaminant analysis, particularly for emerging pollutants and food adulterants where regulatory thresholds continue to decrease, necessitating greater analytical precision.
Regional analysis reveals North America maintains market leadership with 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth trajectory at 11.2% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing, contract research organizations, and strengthening regulatory frameworks in China and India.
Market research indicates that 73% of laboratory managers consider statistical method validation capabilities as "very important" or "critical" when selecting HPLC systems and software. This represents a significant shift from five years ago when only 48% placed similar emphasis on statistical capabilities.
Software solutions for statistical analysis of HPLC data represent a particularly dynamic market segment, growing at 14.2% annually. End-users increasingly demand integrated platforms that combine chromatographic control with comprehensive statistical tools for method validation, uncertainty estimation, and compliance reporting.
The market demonstrates clear willingness to invest in solutions that enhance precision quantification, with 67% of survey respondents indicating plans to upgrade their statistical analysis capabilities for HPLC within the next two years. This trend is particularly pronounced among contract research organizations and pharmaceutical quality control laboratories where demonstrable precision directly impacts competitive advantage.
Current Statistical Approaches and Technical Challenges
The field of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) has seen significant advancements in statistical approaches for precision quantification. Currently, the most widely adopted statistical methods include System Suitability Testing (SST), which employs parameters such as retention time variability, peak area reproducibility, and resolution factors to ensure consistent chromatographic performance. These metrics typically require relative standard deviation (RSD) values below predefined thresholds, commonly 1-2% for quantitative analyses.
Method validation protocols have evolved to incorporate robust statistical frameworks, with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines serving as the international standard. These protocols mandate evaluation of precision at three distinct levels: repeatability (intra-assay), intermediate precision (inter-day), and reproducibility (inter-laboratory). Statistical tools such as ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) have become essential for distinguishing between different sources of variability in multi-factor experimental designs.
Control charting methodologies, borrowed from industrial quality control, have gained prominence in HPLC laboratories. Shewhart charts, CUSUM (Cumulative Sum) charts, and EWMA (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average) charts enable continuous monitoring of system performance and early detection of analytical drift. These approaches facilitate distinction between random variations and systematic errors, enhancing overall method reliability.
Despite these advances, significant technical challenges persist in HPLC precision quantification. Matrix effects remain particularly problematic, as complex biological or environmental samples can introduce unpredictable interferences that compromise statistical validity. Current statistical models often struggle to account for these non-linear and sample-specific variations, leading to potential underestimation of measurement uncertainty.
The handling of outliers presents another substantial challenge. While statistical tests such as Grubbs' and Dixon's Q-test are commonly employed, the decision to exclude data points remains somewhat subjective. This introduces potential bias, especially in regulated environments where data integrity is paramount. More sophisticated approaches like robust statistical methods that downweight rather than exclude outliers are gaining traction but remain underutilized.
Measurement uncertainty estimation represents perhaps the most significant technical hurdle. The GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement) approach, while comprehensive, proves cumbersome for routine HPLC analyses. Simplified approaches based on method validation data often fail to capture all relevant uncertainty components, particularly those related to sample preparation and instrument calibration. The development of practical yet thorough uncertainty budgets remains an active area of research.
Emerging technologies like automated liquid handlers and robotic sample preparation systems introduce new variables into statistical models, requiring adaptation of traditional approaches. While these technologies promise improved precision, their integration into existing statistical frameworks presents significant challenges for method validation and quality control procedures.
Method validation protocols have evolved to incorporate robust statistical frameworks, with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines serving as the international standard. These protocols mandate evaluation of precision at three distinct levels: repeatability (intra-assay), intermediate precision (inter-day), and reproducibility (inter-laboratory). Statistical tools such as ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) have become essential for distinguishing between different sources of variability in multi-factor experimental designs.
Control charting methodologies, borrowed from industrial quality control, have gained prominence in HPLC laboratories. Shewhart charts, CUSUM (Cumulative Sum) charts, and EWMA (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average) charts enable continuous monitoring of system performance and early detection of analytical drift. These approaches facilitate distinction between random variations and systematic errors, enhancing overall method reliability.
Despite these advances, significant technical challenges persist in HPLC precision quantification. Matrix effects remain particularly problematic, as complex biological or environmental samples can introduce unpredictable interferences that compromise statistical validity. Current statistical models often struggle to account for these non-linear and sample-specific variations, leading to potential underestimation of measurement uncertainty.
The handling of outliers presents another substantial challenge. While statistical tests such as Grubbs' and Dixon's Q-test are commonly employed, the decision to exclude data points remains somewhat subjective. This introduces potential bias, especially in regulated environments where data integrity is paramount. More sophisticated approaches like robust statistical methods that downweight rather than exclude outliers are gaining traction but remain underutilized.
Measurement uncertainty estimation represents perhaps the most significant technical hurdle. The GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement) approach, while comprehensive, proves cumbersome for routine HPLC analyses. Simplified approaches based on method validation data often fail to capture all relevant uncertainty components, particularly those related to sample preparation and instrument calibration. The development of practical yet thorough uncertainty budgets remains an active area of research.
Emerging technologies like automated liquid handlers and robotic sample preparation systems introduce new variables into statistical models, requiring adaptation of traditional approaches. While these technologies promise improved precision, their integration into existing statistical frameworks presents significant challenges for method validation and quality control procedures.
Contemporary Statistical Solutions for HPLC Precision Assessment
01 Statistical methods for HPLC method validation
Various statistical approaches are used to validate HPLC methods, focusing on precision parameters such as repeatability, intermediate precision, and reproducibility. These methods include analysis of variance (ANOVA), standard deviation calculations, and relative standard deviation assessments to establish method reliability. Statistical validation ensures that HPLC methods consistently produce accurate and reliable results across different operational conditions.- Statistical analysis methods for HPLC precision evaluation: Various statistical methods can be applied to evaluate the precision of HPLC analyses. These methods include calculation of standard deviation, relative standard deviation (RSD), and coefficient of variation to quantify the dispersion of analytical results. Statistical tools such as ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) can be used to assess variability between different runs, instruments, or operators. These statistical approaches help in establishing the reliability and reproducibility of HPLC methods.
- System suitability testing for HPLC precision: System suitability testing is crucial for ensuring HPLC precision. This involves evaluating key parameters such as retention time reproducibility, peak resolution, tailing factor, and theoretical plate count. Statistical methods are applied to these parameters to establish acceptance criteria and control limits. Regular system suitability tests help in identifying instrument-related issues that might affect precision before sample analysis begins.
- Method validation approaches for HPLC precision: Method validation for HPLC precision involves systematic evaluation of repeatability, intermediate precision, and reproducibility. Statistical approaches include analyzing multiple sample preparations under various conditions to determine method robustness. Precision is typically assessed at different concentration levels across the analytical range. These validation procedures often follow regulatory guidelines that specify statistical criteria for acceptable precision in pharmaceutical and other analytical applications.
- Automated data processing for precision improvement: Advanced software solutions can significantly improve HPLC precision through automated data processing. These systems apply statistical algorithms for peak integration, baseline correction, and outlier detection. Machine learning approaches can be used to identify patterns in chromatographic data that might affect precision. Automated systems can also perform real-time statistical analysis to monitor system performance and alert analysts to potential precision issues.
- Quality control charts and trending for HPLC precision monitoring: Statistical quality control charts, such as Shewhart charts, CUSUM (Cumulative Sum) charts, and moving range charts, are valuable tools for monitoring HPLC precision over time. These charts help distinguish between random variations and systematic trends that might indicate deteriorating precision. Statistical trending analysis of system suitability parameters and quality control sample results allows for proactive maintenance and method adjustments before precision falls outside acceptable limits.
02 Data processing algorithms for HPLC precision enhancement
Advanced data processing algorithms are employed to enhance HPLC precision by reducing noise, improving peak detection, and optimizing signal processing. These computational methods include baseline correction algorithms, peak integration techniques, and signal filtering approaches that minimize variability in chromatographic data. Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques are increasingly being applied to improve data interpretation and precision in complex HPLC analyses.Expand Specific Solutions03 System calibration and quality control for HPLC precision
Systematic approaches to HPLC calibration and quality control involve statistical monitoring of system suitability parameters, instrument performance verification, and regular calibration procedures. These methods include the use of control charts, trend analysis, and statistical process control to maintain consistent system performance. Calibration models incorporate statistical techniques to ensure linearity, accuracy, and precision across the analytical range.Expand Specific Solutions04 Experimental design for optimizing HPLC precision
Statistical experimental design methodologies are applied to optimize HPLC precision by systematically evaluating factors affecting method performance. These approaches include Design of Experiments (DoE), factorial designs, and response surface methodology to identify critical parameters and their interactions. Statistical optimization techniques help establish robust operating conditions that minimize variability and maximize precision in HPLC analyses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Uncertainty estimation and error analysis in HPLC measurements
Statistical methods for uncertainty estimation and error analysis in HPLC provide quantitative assessments of measurement reliability. These techniques include propagation of error calculations, confidence interval determinations, and statistical hypothesis testing to evaluate method precision. Comprehensive error analysis incorporates contributions from sample preparation, instrument variability, and environmental factors to establish overall measurement uncertainty in HPLC results.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations and Vendors in HPLC Statistical Analysis
The HPLC precision quantification market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for statistical methods to enhance analytical reliability in pharmaceutical and chemical analysis. The global HPLC market is projected to reach approximately $5.5 billion by 2025, with precision analytics representing a significant segment. Technologically, the field is maturing with advanced statistical approaches being integrated into standard protocols. Leading players include pharmaceutical companies like Janssen Pharmaceutica and Merck Patent GmbH, who are developing proprietary statistical methods, while instrumentation specialists such as Hitachi High-Tech America and Agilent Technologies provide hardware solutions with built-in statistical capabilities. Academic institutions like The Regents of the University of California contribute fundamental research, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established corporations and innovative research entities.
Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.
Technical Solution: Hitachi High-Tech has developed advanced statistical methods for HPLC precision quantification through their ChromasterUltra Rs system. Their approach incorporates robust algorithm-based peak integration that minimizes manual intervention and reduces subjective interpretation errors. The system employs automated System Suitability Testing (SST) with comprehensive statistical analysis including relative standard deviation (RSD), signal-to-noise ratio calculations, and tailing factor assessments. Their method includes variance component analysis to distinguish between instrument, method, and operator contributions to measurement uncertainty. Hitachi's statistical package also features outlier detection algorithms based on Grubbs and Dixon tests, with automated flagging of statistically significant deviations. For method validation, they've implemented ICH-compliant statistical protocols that automatically calculate linearity, accuracy, precision, and detection limits with confidence interval reporting[1].
Strengths: Superior automation of statistical calculations reduces human error and increases throughput. Integration with laboratory information management systems enables comprehensive data trending and analysis. Weaknesses: Proprietary statistical algorithms may create vendor lock-in and require specialized training for optimal utilization. Higher initial investment compared to more basic HPLC systems.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck has pioneered a comprehensive statistical framework for HPLC precision quantification called "SmartAnalytics" that combines traditional statistical methods with machine learning approaches. Their system implements advanced variance component analysis (ANOVA) to isolate and quantify different sources of variability in chromatographic measurements. Merck's approach incorporates Monte Carlo simulation techniques to establish measurement uncertainty budgets, allowing for more accurate estimation of confidence intervals in complex sample matrices. The company has developed specialized algorithms for handling non-normal distributions commonly encountered in trace analysis, employing robust statistical estimators that are less sensitive to outliers. Their method validation protocols include automated calculation of detection capability parameters (CCα and CCβ) according to Commission Decision 2002/657/EC for regulated analyses. Merck's system also features predictive maintenance capabilities based on statistical process control of system suitability parameters, identifying trends before they impact analytical precision[2][3].
Strengths: Comprehensive statistical package that addresses both routine and complex analytical scenarios. Integration with reference materials and standards provides traceability to international measurement systems. Weaknesses: Complex statistical approaches require significant user training and understanding. System may be overengineered for simpler analytical applications.
Critical Statistical Models and Algorithms for HPLC Precision
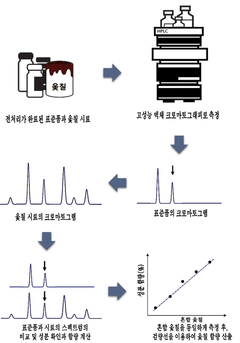
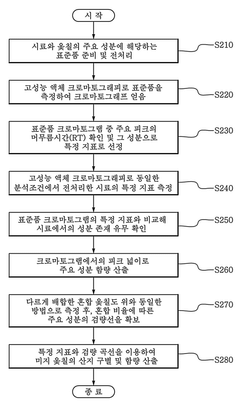
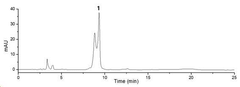
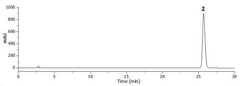
Method of identification and quantitative analysis of lacquers from different regions using high performance liquid chromatography
PatentActiveKR1020220022238A
Innovation
- A method using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to select a specific indicator (standard product) for each lacquer origin, measuring the main peak retention time, and generating calibration curves to determine the content of lacquer samples, enabling quick and accurate identification and quantification of lacquer origins.
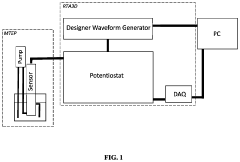
System for the Simultaneous Monitoring of Constituents of an Electroplating Bath
PatentPendingUS20240133074A1
Innovation
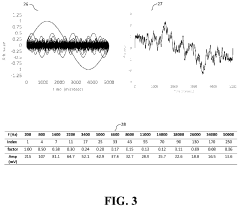
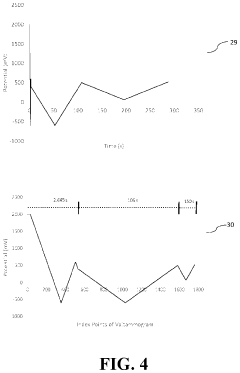
- The development of novel second-order, consolidated voltammetric waveforms combined with chemometric analysis and data compression techniques allows for the simultaneous measurement and analysis of all electroplating bath constituents without pretreatment, using a multi-frequency, variable amplitude waveform to generate a diagnostic voltammetric output that captures the synergistic interactions and maintains process control within the electroplating process.
Regulatory Compliance and Validation Requirements
Regulatory compliance represents a critical dimension in HPLC precision quantification, with laboratories facing increasingly stringent requirements from multiple oversight bodies. The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 establishes comprehensive guidelines for electronic records and signatures, mandating specific validation protocols for HPLC systems used in pharmaceutical analysis. These regulations require demonstrable precision metrics through statistical validation methods that confirm system suitability and analytical reliability.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q2(R1), provide the foundational framework for analytical method validation in HPLC applications. These guidelines explicitly require precision assessment through repeatability, intermediate precision, and reproducibility studies, with statistical evaluation serving as the quantitative backbone for compliance documentation. Organizations must implement robust statistical approaches that align with these guidelines to maintain regulatory approval.
USP <1225> and EP 2.2.46 chapters outline specific statistical parameters for chromatographic method validation, including relative standard deviation (RSD) limits that vary by analyte concentration. These pharmacopeial standards establish acceptance criteria that directly influence the statistical methodologies employed in precision quantification. Laboratories must design their statistical approaches to meet or exceed these predefined thresholds.
ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation requirements add another layer of compliance considerations, focusing on measurement uncertainty estimation through statistical analysis. This standard necessitates comprehensive uncertainty budgets that incorporate precision components quantified through statistical methods. The statistical approaches must be scientifically defensible and appropriate for the intended analytical purpose.
Regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize risk-based approaches to validation, requiring statistical methods that can identify and quantify potential sources of variability. Quality by Design (QbD) principles, endorsed by regulatory agencies, promote the use of statistical design of experiments (DoE) to establish method robustness and define the acceptable operating range for HPLC methods.
Validation documentation must include statistical justification for precision claims, with regulatory inspections frequently focusing on the appropriateness of statistical methods employed. The trend toward continuous process verification has elevated the importance of ongoing statistical monitoring of precision metrics rather than relying solely on initial validation studies. This shift requires implementation of statistical process control techniques to maintain demonstrable compliance throughout the analytical method lifecycle.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q2(R1), provide the foundational framework for analytical method validation in HPLC applications. These guidelines explicitly require precision assessment through repeatability, intermediate precision, and reproducibility studies, with statistical evaluation serving as the quantitative backbone for compliance documentation. Organizations must implement robust statistical approaches that align with these guidelines to maintain regulatory approval.
USP <1225> and EP 2.2.46 chapters outline specific statistical parameters for chromatographic method validation, including relative standard deviation (RSD) limits that vary by analyte concentration. These pharmacopeial standards establish acceptance criteria that directly influence the statistical methodologies employed in precision quantification. Laboratories must design their statistical approaches to meet or exceed these predefined thresholds.
ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation requirements add another layer of compliance considerations, focusing on measurement uncertainty estimation through statistical analysis. This standard necessitates comprehensive uncertainty budgets that incorporate precision components quantified through statistical methods. The statistical approaches must be scientifically defensible and appropriate for the intended analytical purpose.
Regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize risk-based approaches to validation, requiring statistical methods that can identify and quantify potential sources of variability. Quality by Design (QbD) principles, endorsed by regulatory agencies, promote the use of statistical design of experiments (DoE) to establish method robustness and define the acceptable operating range for HPLC methods.
Validation documentation must include statistical justification for precision claims, with regulatory inspections frequently focusing on the appropriateness of statistical methods employed. The trend toward continuous process verification has elevated the importance of ongoing statistical monitoring of precision metrics rather than relying solely on initial validation studies. This shift requires implementation of statistical process control techniques to maintain demonstrable compliance throughout the analytical method lifecycle.
Data Management and Integration Strategies
Effective data management and integration strategies are paramount in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) statistical analysis workflows. Modern HPLC systems generate vast quantities of chromatographic data that require sophisticated management approaches to ensure data integrity, accessibility, and analytical value. Laboratory information management systems (LIMS) specifically designed for chromatography data have emerged as essential tools, offering centralized repositories for raw data, processed results, and associated metadata while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements such as 21 CFR Part 11.
Data integration across multiple analytical platforms represents a significant challenge in quantitative HPLC analysis. Organizations increasingly implement middleware solutions that facilitate seamless data transfer between chromatography data systems (CDS), electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These integration frameworks eliminate manual data transcription errors and create unified data environments where precision metrics can be consistently applied and monitored across the analytical lifecycle.
Cloud-based data management solutions have revolutionized collaborative HPLC method development and validation. These platforms enable geographically dispersed teams to simultaneously access, analyze, and contribute to method development while maintaining version control and audit trails. The implementation of standardized data formats, such as Analytical Information Markup Language (AnIML) and Allotrope Data Format (ADF), further enhances interoperability between different vendor systems and analytical techniques.
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly deployed for automated data preprocessing, peak detection, and integration in HPLC workflows. These computational approaches significantly reduce analyst-to-analyst variability in peak integration decisions, a historically significant source of imprecision in quantitative analysis. Advanced pattern recognition algorithms can identify subtle chromatographic anomalies that might compromise precision, enabling proactive method adjustments before quality metrics are compromised.
Real-time data visualization dashboards provide immediate feedback on precision metrics across multiple analyses. These interactive tools allow analysts to monitor system suitability parameters, control chart trends, and precision metrics without waiting for end-of-batch processing. Such immediate visibility into analytical performance enables rapid intervention when precision begins to drift outside acceptable parameters, preserving data quality and reducing costly reanalysis.
Data lifecycle management strategies have become essential components of HPLC precision initiatives. Implementing policies for data retention, archiving, and retrieval ensures that historical precision data remains accessible for retrospective trend analysis and method comparison studies. Structured approaches to metadata capture—including sample preparation details, instrument conditions, and environmental factors—provide crucial context for interpreting precision metrics and troubleshooting variability sources.
Data integration across multiple analytical platforms represents a significant challenge in quantitative HPLC analysis. Organizations increasingly implement middleware solutions that facilitate seamless data transfer between chromatography data systems (CDS), electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These integration frameworks eliminate manual data transcription errors and create unified data environments where precision metrics can be consistently applied and monitored across the analytical lifecycle.
Cloud-based data management solutions have revolutionized collaborative HPLC method development and validation. These platforms enable geographically dispersed teams to simultaneously access, analyze, and contribute to method development while maintaining version control and audit trails. The implementation of standardized data formats, such as Analytical Information Markup Language (AnIML) and Allotrope Data Format (ADF), further enhances interoperability between different vendor systems and analytical techniques.
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly deployed for automated data preprocessing, peak detection, and integration in HPLC workflows. These computational approaches significantly reduce analyst-to-analyst variability in peak integration decisions, a historically significant source of imprecision in quantitative analysis. Advanced pattern recognition algorithms can identify subtle chromatographic anomalies that might compromise precision, enabling proactive method adjustments before quality metrics are compromised.
Real-time data visualization dashboards provide immediate feedback on precision metrics across multiple analyses. These interactive tools allow analysts to monitor system suitability parameters, control chart trends, and precision metrics without waiting for end-of-batch processing. Such immediate visibility into analytical performance enables rapid intervention when precision begins to drift outside acceptable parameters, preserving data quality and reducing costly reanalysis.
Data lifecycle management strategies have become essential components of HPLC precision initiatives. Implementing policies for data retention, archiving, and retrieval ensures that historical precision data remains accessible for retrospective trend analysis and method comparison studies. Structured approaches to metadata capture—including sample preparation details, instrument conditions, and environmental factors—provide crucial context for interpreting precision metrics and troubleshooting variability sources.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!