Regulatory And Certification Path For Room-Temperature Sodium-Sulfur Batteries
AUG 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Na-S Battery Regulatory Background and Objectives
Sodium-sulfur (Na-S) battery technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s by Ford Motor Company. Initially developed as high-temperature systems operating at 300-350°C, recent breakthroughs have enabled room-temperature operation, dramatically expanding potential applications from grid-scale storage to electric vehicles and portable electronics. This technological evolution represents a paradigm shift in energy storage, offering a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries with advantages in cost, resource availability, and energy density.
The regulatory landscape for room-temperature Na-S batteries remains largely underdeveloped compared to established battery technologies. Currently, these batteries fall under broader regulatory frameworks for energy storage systems, including IEC 62619 for industrial applications and UN 38.3 for transport safety. However, the unique chemistry of Na-S batteries, particularly their use of sulfur and potential for thermal events, necessitates specialized regulatory consideration that existing frameworks may not adequately address.
Global standardization bodies including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) have begun preliminary work on standards specific to sodium-based battery technologies. The IEC Technical Committee 21 has established working groups focused on sodium battery safety protocols, while UL is developing test methodologies for room-temperature sodium battery certification.
The primary technical objectives for regulatory development include establishing comprehensive safety standards addressing the specific failure modes of room-temperature Na-S batteries, developing accelerated testing protocols that accurately predict long-term performance and degradation, and creating transportation regulations that account for the unique properties of sodium and sulfur components.
Market acceptance objectives focus on achieving certification parity with lithium-ion technologies to enable fair market competition, developing internationally harmonized standards to facilitate global market access, and creating regulatory frameworks that acknowledge the sustainability benefits of Na-S technology while ensuring appropriate safety measures.
Research objectives include gathering extensive data on failure mechanisms specific to room-temperature Na-S chemistry, developing standardized testing methodologies that accurately assess safety across various use conditions, and establishing clear performance metrics that enable meaningful comparison with other battery technologies. These objectives must balance innovation enablement with rigorous safety assurance to support the technology's commercial viability.
The regulatory path forward requires collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and regulatory bodies to develop evidence-based standards that address the unique characteristics of room-temperature Na-S batteries while facilitating their market adoption and technological advancement.
The regulatory landscape for room-temperature Na-S batteries remains largely underdeveloped compared to established battery technologies. Currently, these batteries fall under broader regulatory frameworks for energy storage systems, including IEC 62619 for industrial applications and UN 38.3 for transport safety. However, the unique chemistry of Na-S batteries, particularly their use of sulfur and potential for thermal events, necessitates specialized regulatory consideration that existing frameworks may not adequately address.
Global standardization bodies including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) have begun preliminary work on standards specific to sodium-based battery technologies. The IEC Technical Committee 21 has established working groups focused on sodium battery safety protocols, while UL is developing test methodologies for room-temperature sodium battery certification.
The primary technical objectives for regulatory development include establishing comprehensive safety standards addressing the specific failure modes of room-temperature Na-S batteries, developing accelerated testing protocols that accurately predict long-term performance and degradation, and creating transportation regulations that account for the unique properties of sodium and sulfur components.
Market acceptance objectives focus on achieving certification parity with lithium-ion technologies to enable fair market competition, developing internationally harmonized standards to facilitate global market access, and creating regulatory frameworks that acknowledge the sustainability benefits of Na-S technology while ensuring appropriate safety measures.
Research objectives include gathering extensive data on failure mechanisms specific to room-temperature Na-S chemistry, developing standardized testing methodologies that accurately assess safety across various use conditions, and establishing clear performance metrics that enable meaningful comparison with other battery technologies. These objectives must balance innovation enablement with rigorous safety assurance to support the technology's commercial viability.
The regulatory path forward requires collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and regulatory bodies to develop evidence-based standards that address the unique characteristics of room-temperature Na-S batteries while facilitating their market adoption and technological advancement.
Market Analysis for Room-Temperature Na-S Batteries
The global market for room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT Na-S) batteries is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions. Current market valuations indicate that the energy storage sector is projected to reach $546 billion by 2035, with RT Na-S batteries positioned to capture a growing share due to their cost advantages and material abundance compared to lithium-ion alternatives.
Market segmentation reveals three primary application sectors for RT Na-S technology: grid-scale energy storage, renewable energy integration, and electric vehicle applications. Grid-scale storage represents the largest immediate opportunity, with utility companies seeking long-duration storage solutions that offer lower levelized cost of storage (LCOS) than current technologies. The renewable energy sector presents substantial growth potential as intermittent power sources like solar and wind require efficient storage solutions to ensure grid stability.
Consumer demand patterns indicate a shift toward more sustainable and ethically sourced battery technologies. RT Na-S batteries address these concerns by utilizing abundant materials without reliance on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel that face supply constraints and ethical sourcing challenges. This alignment with sustainability goals enhances market receptivity among environmentally conscious consumers and organizations with strong ESG commitments.
Regional market analysis shows varying adoption rates, with Asia-Pacific leading in manufacturing capacity development, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea. European markets demonstrate strong policy support through initiatives like the European Battery Alliance, while North American markets are increasingly investing in domestic supply chain development following recent legislative support for clean energy technologies.
Competitive pricing analysis reveals that RT Na-S batteries currently have higher upfront costs compared to mature lithium-ion technologies but offer potentially lower lifetime costs due to longer cycle life and reduced material costs. Industry projections suggest that with scaled production, RT Na-S batteries could achieve price parity with lithium-ion by 2028-2030, significantly accelerating market adoption.
Market barriers include limited manufacturing infrastructure, technical challenges related to dendrite formation and capacity fade, and customer hesitancy toward adopting relatively unproven technologies. However, these barriers are counterbalanced by strong market drivers including material cost advantages, supply chain security benefits, and alignment with circular economy principles through easier recyclability compared to current commercial alternatives.
Market segmentation reveals three primary application sectors for RT Na-S technology: grid-scale energy storage, renewable energy integration, and electric vehicle applications. Grid-scale storage represents the largest immediate opportunity, with utility companies seeking long-duration storage solutions that offer lower levelized cost of storage (LCOS) than current technologies. The renewable energy sector presents substantial growth potential as intermittent power sources like solar and wind require efficient storage solutions to ensure grid stability.
Consumer demand patterns indicate a shift toward more sustainable and ethically sourced battery technologies. RT Na-S batteries address these concerns by utilizing abundant materials without reliance on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel that face supply constraints and ethical sourcing challenges. This alignment with sustainability goals enhances market receptivity among environmentally conscious consumers and organizations with strong ESG commitments.
Regional market analysis shows varying adoption rates, with Asia-Pacific leading in manufacturing capacity development, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea. European markets demonstrate strong policy support through initiatives like the European Battery Alliance, while North American markets are increasingly investing in domestic supply chain development following recent legislative support for clean energy technologies.
Competitive pricing analysis reveals that RT Na-S batteries currently have higher upfront costs compared to mature lithium-ion technologies but offer potentially lower lifetime costs due to longer cycle life and reduced material costs. Industry projections suggest that with scaled production, RT Na-S batteries could achieve price parity with lithium-ion by 2028-2030, significantly accelerating market adoption.
Market barriers include limited manufacturing infrastructure, technical challenges related to dendrite formation and capacity fade, and customer hesitancy toward adopting relatively unproven technologies. However, these barriers are counterbalanced by strong market drivers including material cost advantages, supply chain security benefits, and alignment with circular economy principles through easier recyclability compared to current commercial alternatives.
Regulatory Landscape and Technical Barriers
The regulatory landscape for room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT-Na-S) batteries remains fragmented globally, with significant variations across regions. In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) has established preliminary guidelines for sodium-based battery technologies, but specific standards for RT-Na-S batteries are still under development. The Battery Safety Standards Committee of Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is working to adapt existing lithium-ion battery standards (UL 1642 and UL 2054) for sodium-based chemistries, recognizing their unique safety profiles and operational characteristics.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is guided by the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC) and its recent updates, which primarily focus on environmental impact and end-of-life management. However, these regulations were not designed with sodium-sulfur chemistry in mind, creating compliance challenges for manufacturers. The European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) has initiated working groups to develop specific standards for emerging battery technologies, including RT-Na-S systems.
Asia presents a varied regulatory environment, with Japan's industrial standards (JIS) having the most developed framework for sodium-sulfur batteries, largely due to NGK Insulators' early commercialization of high-temperature versions. China's rapid battery industry growth has prompted the development of new standards through the China Electrical Equipment Industrial Association, though these primarily address lithium technologies rather than sodium-based alternatives.
Technical barriers to certification include the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for RT-Na-S chemistry. Current tests for thermal runaway, electrical safety, and abuse conditions are calibrated for lithium-ion systems and may not accurately assess the different failure modes of sodium-sulfur batteries. The corrosive nature of polysulfides formed during operation presents unique safety challenges that existing standards do not adequately address.
Material compatibility testing represents another significant barrier, as the interaction between sodium, sulfur compounds, and various containment materials requires specialized evaluation protocols not covered by current standards. Additionally, long-term cycling stability assessment methods need adaptation to account for the different degradation mechanisms in RT-Na-S batteries compared to lithium-ion technologies.
Transportation regulations present further complications, with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and International Maritime Organization (IMO) lacking specific provisions for sodium-sulfur batteries. Currently, these batteries often fall under more restrictive "catch-all" dangerous goods classifications, significantly increasing shipping costs and logistical complexity for manufacturers and researchers.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is guided by the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC) and its recent updates, which primarily focus on environmental impact and end-of-life management. However, these regulations were not designed with sodium-sulfur chemistry in mind, creating compliance challenges for manufacturers. The European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) has initiated working groups to develop specific standards for emerging battery technologies, including RT-Na-S systems.
Asia presents a varied regulatory environment, with Japan's industrial standards (JIS) having the most developed framework for sodium-sulfur batteries, largely due to NGK Insulators' early commercialization of high-temperature versions. China's rapid battery industry growth has prompted the development of new standards through the China Electrical Equipment Industrial Association, though these primarily address lithium technologies rather than sodium-based alternatives.
Technical barriers to certification include the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for RT-Na-S chemistry. Current tests for thermal runaway, electrical safety, and abuse conditions are calibrated for lithium-ion systems and may not accurately assess the different failure modes of sodium-sulfur batteries. The corrosive nature of polysulfides formed during operation presents unique safety challenges that existing standards do not adequately address.
Material compatibility testing represents another significant barrier, as the interaction between sodium, sulfur compounds, and various containment materials requires specialized evaluation protocols not covered by current standards. Additionally, long-term cycling stability assessment methods need adaptation to account for the different degradation mechanisms in RT-Na-S batteries compared to lithium-ion technologies.
Transportation regulations present further complications, with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and International Maritime Organization (IMO) lacking specific provisions for sodium-sulfur batteries. Currently, these batteries often fall under more restrictive "catch-all" dangerous goods classifications, significantly increasing shipping costs and logistical complexity for manufacturers and researchers.
Current Certification Pathways and Requirements
01 Safety standards and certification requirements for room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries
Room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries must meet specific safety standards and certification requirements before commercial deployment. These include testing for thermal stability, electrical safety, and resistance to physical damage. Certification processes typically involve third-party testing laboratories that verify compliance with international standards such as IEC and UL specifications for energy storage systems. These regulations help ensure that the batteries can operate safely under various environmental conditions without risk of fire or explosion.- Safety standards and certification requirements: Room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries must meet specific safety standards and certification requirements before commercial deployment. These include testing for thermal stability, electrical safety, and containment of reactive materials. Certification processes typically involve third-party testing laboratories that verify compliance with international standards such as IEC and UL specifications. The regulatory framework addresses potential hazards associated with sodium and sulfur components operating at room temperature.
- Environmental compliance and disposal regulations: Regulations governing the environmental impact of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries focus on manufacturing processes, operational emissions, and end-of-life disposal. These batteries must comply with hazardous material handling protocols due to the reactive nature of sodium. Manufacturers must establish recycling programs and proper disposal methods that prevent environmental contamination. Documentation of compliance with environmental regulations is required for market approval in most jurisdictions.
- Transportation and storage regulations: Specific regulations govern the transportation and storage of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries to ensure safety during handling and distribution. These include requirements for specialized packaging, labeling with hazard information, and restrictions on shipping methods. Storage facilities must implement specific safety measures including temperature control, fire suppression systems, and containment protocols. Compliance with international dangerous goods regulations is mandatory for cross-border transportation.
- Performance testing and quality assurance standards: Room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries must undergo standardized performance testing to verify capacity, cycle life, efficiency, and safety under various operating conditions. Quality assurance standards specify manufacturing processes, material purity requirements, and consistency in production. Testing protocols include accelerated aging tests, thermal cycling, and electrical performance verification. Documentation of these test results is required for regulatory approval and market certification.
- Market-specific regulatory frameworks: Different regions have established specific regulatory frameworks for room-temperature sodium-sulfur battery certification. These include variations in safety requirements, environmental standards, and application-specific certifications for grid storage, electric vehicles, or consumer electronics. Manufacturers must navigate these regional differences to achieve market access, often requiring multiple certifications for global distribution. Some regions offer expedited approval processes for technologies that meet specific energy efficiency or sustainability criteria.
02 Environmental compliance and disposal regulations
Regulatory frameworks govern the environmental aspects of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries throughout their lifecycle. These include manufacturing standards to minimize toxic emissions, transportation regulations for battery components, and end-of-life disposal requirements. Unlike traditional high-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries, room-temperature versions may have different disposal considerations due to their material composition. Manufacturers must comply with regional waste management directives such as WEEE in Europe or equivalent regulations in other jurisdictions to ensure proper recycling and disposal of battery materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Performance validation and quality control standards
Room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries undergo rigorous performance validation and quality control testing to meet industry standards. These tests evaluate cycle life, energy density, power output, and operational stability across various temperature ranges. Quality control protocols include batch testing, accelerated aging tests, and statistical process control during manufacturing. Standardized testing methodologies ensure that performance claims are verifiable and comparable across different manufacturers, providing confidence to end-users and regulatory bodies about battery reliability and performance consistency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Grid integration and utility approval requirements
For grid-connected applications, room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries must meet additional regulatory requirements related to grid integration. These include compliance with grid codes, interconnection standards, and utility approval processes. The batteries must demonstrate compatibility with existing power systems, including response to grid signals, fault behavior, and power quality characteristics. Certification for grid-connected operation typically involves testing for electromagnetic compatibility, voltage and frequency ride-through capabilities, and communication protocols that enable integration with energy management systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Transportation and shipping regulations
Room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries are subject to specific transportation and shipping regulations due to their chemical composition. These regulations govern how batteries can be packaged, labeled, and transported across different modes of transport including air, sea, and land. UN transportation classifications, dangerous goods regulations, and state-specific requirements must be followed to ensure safe handling during transit. Manufacturers must provide safety data sheets and proper documentation, while carriers need specialized training for handling these energy storage systems to prevent accidents during transportation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Industry Stakeholders
Room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT-NaS) battery technology is currently in an early growth phase, with the market expected to expand significantly due to its potential cost advantages over lithium-ion batteries. The global regulatory landscape for RT-NaS batteries is still evolving, with certification paths being established as the technology matures. NGK Insulators leads commercial deployment with established high-temperature NaS technology, while companies like LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and Toyota are investing in RT-NaS research. Academic institutions including Cornell University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Drexel University are advancing fundamental research. Certification challenges include safety standards development, cycle life validation, and environmental compliance, with organizations like Battelle Memorial Institute supporting testing protocols. The technology is approaching commercial viability, with companies like 24M Technologies developing manufacturing processes to accelerate market entry.
NGK Insulators, Ltd.
Technical Solution: NGK Insulators是钠硫(NaS)电池技术的全球领导者,拥有超过30年的研发经验。该公司已开发出一套完整的室温钠硫电池认证路径,包括与日本经济产业省(METI)和国际电工委员会(IEC)合作制定的标准。NGK的认证策略分为三个关键阶段:首先进行材料安全性评估,确保电池材料符合国际化学品分类标准;其次进行电池单元测试,包括UL 1973和IEC 62619等标准下的热失控、短路和过充测试;最后进行系统级认证,遵循IEC 62933等大型储能系统标准。NGK还与美国保险商实验室(UL)建立了战略合作,简化其产品在北美市场的认证流程,并积极参与ISO/TC 203电能储存系统工作组,推动全球统一的钠硫电池标准制定。
优势:拥有成熟的高温钠硫电池商业化经验,可将认证经验迁移至室温技术;与多国监管机构建立了长期合作关系,能够影响标准制定。劣势:传统上专注于高温钠硫电池(300°C以上),向室温技术转型需要重新建立部分认证流程;认证过程耗时长,可能延缓产品上市时间。
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: 三星SDI开发了综合性的室温钠硫电池认证路径,核心是其"多层安全设计"(Multi-Layer Safety Design)技术方案。该方案采用专利的高稳定性聚合物电解质和纳米结构硫正极材料,显著降低了电池的热失控风险。三星SDI的认证策略基于"全生命周期安全评估"理念,从原材料采购到电池回收的每个环节都建立了严格的安全标准。公司遵循IEC 62660(电动汽车用锂离子电池)标准框架,同时开发了针对钠硫化学特性的补充测试方法,包括改进的针刺测试和热循环测试。三星SDI与韩国产业技术试验院(KTL)合作建立了专门的钠基电池测试实验室,并与美国UL和德国TÜV等国际认证机构共同开发适用于室温钠硫电池的测试标准。公司还积极参与国际电动汽车标准化工作组(EVS-GTR)的活动,推动将钠硫电池纳入全球电动汽车安全法规。
优势:拥有丰富的电池认证经验和全球认证资源网络;多层安全设计技术提高了通过安全认证的成功率。劣势:主要认证经验来自锂离子电池领域,需要调整以适应钠硫电池的特性;认证过程复杂且成本高,可能影响产品的市场竞争力。
Critical Safety Standards and Testing Protocols
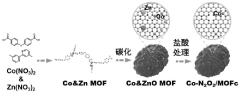
Room-temperature sodium-sulfur battery and preparation method thereof
PatentPendingCN118099560A
Innovation
- Metal-organic framework materials (MOF) are used as precursors to synthesize single-atom catalyst Co-N2O2/MOFc composites as sulfur storage materials, which can be used as cathodes of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries to improve polysulfide conversion efficiency and prevent shuttle and loss.
International Harmonization of Battery Standards
The global battery industry faces significant challenges in navigating diverse regulatory frameworks across different regions. For room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries to achieve widespread commercial adoption, international harmonization of battery standards is essential. Currently, major standards organizations including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) maintain separate certification requirements, creating market entry barriers and increasing compliance costs.
The IEC 62660 series, which primarily addresses lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, provides a potential framework that could be adapted for sodium-sulfur technology. Similarly, UL 1973 for stationary applications and UL 2580 for electric vehicles offer certification pathways that would need modification to accommodate the unique characteristics of room-temperature sodium-sulfur chemistry.
Recent progress in harmonization efforts includes the development of the Global Technical Regulation (GTR) for electric vehicle safety under the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), which could potentially incorporate sodium-based battery technologies. Additionally, the Battery Innovation Group (BIG) Map initiative aims to create a unified global approach to battery standards, though it currently focuses predominantly on lithium-ion technologies.
Key challenges in standards harmonization for room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries include the lack of specific safety protocols addressing their unique thermal characteristics and failure modes, which differ significantly from lithium-ion batteries. The absence of standardized testing methodologies for cycle life assessment and performance verification under various environmental conditions further complicates certification processes.
Industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies have established working groups focused on emerging battery technologies, including the IEC Technical Committee 21 and the SAE International Battery Standards Committee. These groups are actively developing frameworks that could incorporate sodium-sulfur technologies, though progress remains incremental.
For manufacturers pursuing commercialization of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries, a strategic approach involves engaging with standards development organizations early in the product development cycle. Participation in technical committees and contribution to standards development can help ensure that emerging frameworks adequately address the specific characteristics of sodium-sulfur chemistry, potentially accelerating the path to market acceptance and regulatory approval across multiple jurisdictions.
The IEC 62660 series, which primarily addresses lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, provides a potential framework that could be adapted for sodium-sulfur technology. Similarly, UL 1973 for stationary applications and UL 2580 for electric vehicles offer certification pathways that would need modification to accommodate the unique characteristics of room-temperature sodium-sulfur chemistry.
Recent progress in harmonization efforts includes the development of the Global Technical Regulation (GTR) for electric vehicle safety under the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), which could potentially incorporate sodium-based battery technologies. Additionally, the Battery Innovation Group (BIG) Map initiative aims to create a unified global approach to battery standards, though it currently focuses predominantly on lithium-ion technologies.
Key challenges in standards harmonization for room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries include the lack of specific safety protocols addressing their unique thermal characteristics and failure modes, which differ significantly from lithium-ion batteries. The absence of standardized testing methodologies for cycle life assessment and performance verification under various environmental conditions further complicates certification processes.
Industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies have established working groups focused on emerging battery technologies, including the IEC Technical Committee 21 and the SAE International Battery Standards Committee. These groups are actively developing frameworks that could incorporate sodium-sulfur technologies, though progress remains incremental.
For manufacturers pursuing commercialization of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries, a strategic approach involves engaging with standards development organizations early in the product development cycle. Participation in technical committees and contribution to standards development can help ensure that emerging frameworks adequately address the specific characteristics of sodium-sulfur chemistry, potentially accelerating the path to market acceptance and regulatory approval across multiple jurisdictions.
Environmental Impact Assessment Requirements
The environmental impact assessment for room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT Na-S) batteries requires comprehensive evaluation across multiple ecological dimensions. These batteries, while promising for sustainable energy storage, contain materials that necessitate careful environmental scrutiny throughout their lifecycle. Regulatory bodies worldwide increasingly demand detailed environmental impact assessments before certifying new battery technologies for commercial deployment.
Primary environmental concerns include the extraction and processing of raw materials, particularly sulfur and sodium compounds. While sodium is abundant and relatively low-impact to source, sulfur extraction methods vary in environmental footprint. Manufacturers must document sourcing practices and demonstrate compliance with regional mining and processing regulations, which differ significantly between jurisdictions like the EU, North America, and Asia.
Manufacturing processes for RT Na-S batteries must be assessed for emissions, waste generation, and resource consumption. Certification pathways typically require quantification of carbon footprint, water usage, and chemical releases during production. The EU Battery Directive and similar frameworks in other regions mandate specific thresholds for environmental impacts during manufacturing, with increasingly stringent standards being implemented as climate policies evolve.
End-of-life considerations represent a critical component of environmental assessment requirements. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, RT Na-S batteries contain different material compositions that may present unique recycling challenges and opportunities. Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate extended producer responsibility principles, requiring manufacturers to establish viable recycling pathways before certification approval.
Toxicity assessments form another mandatory element of environmental impact evaluation. While room-temperature sodium-sulfur chemistry generally presents lower toxicity concerns than some competing technologies, comprehensive leachate testing and material safety assessments remain necessary for certification. The potential formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under failure conditions requires specific safety protocols and environmental risk mitigation strategies to be documented.
Water impact analysis has become increasingly prominent in battery certification requirements, with authorities requiring quantification of water consumption throughout the lifecycle and potential impacts on local watersheds from manufacturing facilities. Similarly, land use impacts and biodiversity considerations must be addressed, particularly for large-scale production facilities.
Certification pathways typically require comparative lifecycle assessment against incumbent technologies, demonstrating the relative environmental advantages of RT Na-S batteries over conventional energy storage solutions. These assessments must follow standardized methodologies such as ISO 14040/14044 and incorporate sensitivity analyses to account for regional variations in energy mix and resource availability.
Primary environmental concerns include the extraction and processing of raw materials, particularly sulfur and sodium compounds. While sodium is abundant and relatively low-impact to source, sulfur extraction methods vary in environmental footprint. Manufacturers must document sourcing practices and demonstrate compliance with regional mining and processing regulations, which differ significantly between jurisdictions like the EU, North America, and Asia.
Manufacturing processes for RT Na-S batteries must be assessed for emissions, waste generation, and resource consumption. Certification pathways typically require quantification of carbon footprint, water usage, and chemical releases during production. The EU Battery Directive and similar frameworks in other regions mandate specific thresholds for environmental impacts during manufacturing, with increasingly stringent standards being implemented as climate policies evolve.
End-of-life considerations represent a critical component of environmental assessment requirements. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, RT Na-S batteries contain different material compositions that may present unique recycling challenges and opportunities. Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate extended producer responsibility principles, requiring manufacturers to establish viable recycling pathways before certification approval.
Toxicity assessments form another mandatory element of environmental impact evaluation. While room-temperature sodium-sulfur chemistry generally presents lower toxicity concerns than some competing technologies, comprehensive leachate testing and material safety assessments remain necessary for certification. The potential formation of hydrogen sulfide gas under failure conditions requires specific safety protocols and environmental risk mitigation strategies to be documented.
Water impact analysis has become increasingly prominent in battery certification requirements, with authorities requiring quantification of water consumption throughout the lifecycle and potential impacts on local watersheds from manufacturing facilities. Similarly, land use impacts and biodiversity considerations must be addressed, particularly for large-scale production facilities.
Certification pathways typically require comparative lifecycle assessment against incumbent technologies, demonstrating the relative environmental advantages of RT Na-S batteries over conventional energy storage solutions. These assessments must follow standardized methodologies such as ISO 14040/14044 and incorporate sensitivity analyses to account for regional variations in energy mix and resource availability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!