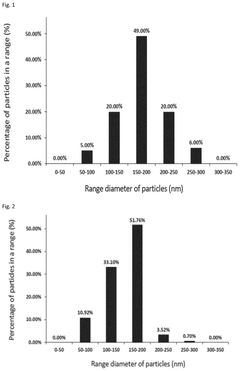
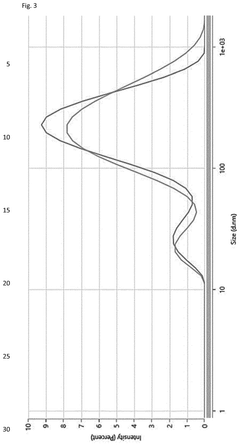
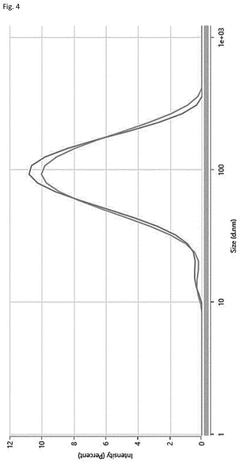
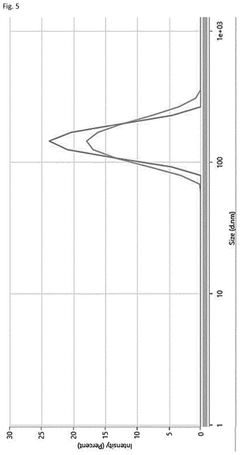
Scalable aseptic fill/finish solutions for LNP mRNA drug products with reduced cross-contamination risk
SEP 2, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LNP mRNA Fill/Finish Technology Evolution and Objectives
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems for mRNA therapeutics have evolved significantly since their inception, transforming from experimental constructs to critical components of life-saving vaccines and therapies. The fill/finish process, representing the final manufacturing step where drug products are filled into containers and sealed, has undergone parallel evolution to meet the unique requirements of these complex biologics.
The earliest LNP mRNA fill/finish operations utilized adapted small-scale equipment from traditional pharmaceutical manufacturing, with limited throughput and significant manual intervention. These initial processes, while functional for clinical trials, presented substantial challenges for commercial-scale production, particularly regarding sterility assurance and batch consistency.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed unprecedented acceleration in LNP mRNA manufacturing technology development. Within months, manufacturers scaled from laboratory production to millions of doses, necessitating rapid innovation in fill/finish technologies. This period saw the emergence of specialized aseptic filling systems designed specifically for temperature-sensitive LNP formulations.
Current technological objectives focus on developing scalable aseptic fill/finish solutions that can maintain product integrity while minimizing cross-contamination risks. The temperature sensitivity of mRNA constructs (typically requiring -70°C to -20°C storage) presents unique challenges for conventional filling equipment, driving innovation toward cryogenic-compatible systems with minimal product exposure to ambient conditions.
A key evolutionary trend is the movement toward closed systems and single-use technologies that reduce contamination vectors and simplify cleaning validation. Isolator technology has advanced to accommodate the specific requirements of LNP mRNA products, with improved transfer systems and more effective decontamination cycles.
The industry is now targeting fill/finish solutions that can seamlessly scale from clinical to commercial production volumes without significant process modifications. This "scale-out" rather than "scale-up" approach aims to maintain consistent product quality attributes across production volumes.
Automation represents another critical objective, with manufacturers seeking to minimize human interventions through advanced robotics and machine vision systems. These technologies not only reduce contamination risks but also improve batch-to-batch consistency and enable real-time process verification.
Looking forward, the industry aims to develop integrated continuous manufacturing systems where LNP formulation connects directly to fill/finish operations, eliminating intermediate hold steps and reducing opportunities for contamination. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing multi-product facilities with rapid changeover capabilities to maximize manufacturing flexibility while maintaining stringent segregation between products.
The earliest LNP mRNA fill/finish operations utilized adapted small-scale equipment from traditional pharmaceutical manufacturing, with limited throughput and significant manual intervention. These initial processes, while functional for clinical trials, presented substantial challenges for commercial-scale production, particularly regarding sterility assurance and batch consistency.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed unprecedented acceleration in LNP mRNA manufacturing technology development. Within months, manufacturers scaled from laboratory production to millions of doses, necessitating rapid innovation in fill/finish technologies. This period saw the emergence of specialized aseptic filling systems designed specifically for temperature-sensitive LNP formulations.
Current technological objectives focus on developing scalable aseptic fill/finish solutions that can maintain product integrity while minimizing cross-contamination risks. The temperature sensitivity of mRNA constructs (typically requiring -70°C to -20°C storage) presents unique challenges for conventional filling equipment, driving innovation toward cryogenic-compatible systems with minimal product exposure to ambient conditions.
A key evolutionary trend is the movement toward closed systems and single-use technologies that reduce contamination vectors and simplify cleaning validation. Isolator technology has advanced to accommodate the specific requirements of LNP mRNA products, with improved transfer systems and more effective decontamination cycles.
The industry is now targeting fill/finish solutions that can seamlessly scale from clinical to commercial production volumes without significant process modifications. This "scale-out" rather than "scale-up" approach aims to maintain consistent product quality attributes across production volumes.
Automation represents another critical objective, with manufacturers seeking to minimize human interventions through advanced robotics and machine vision systems. These technologies not only reduce contamination risks but also improve batch-to-batch consistency and enable real-time process verification.
Looking forward, the industry aims to develop integrated continuous manufacturing systems where LNP formulation connects directly to fill/finish operations, eliminating intermediate hold steps and reducing opportunities for contamination. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing multi-product facilities with rapid changeover capabilities to maximize manufacturing flexibility while maintaining stringent segregation between products.
Market Demand Analysis for Aseptic LNP mRNA Processing
The global mRNA therapeutics market has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. This market is projected to reach $37 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 28.4% from 2023 to 2030. The demand for scalable aseptic fill/finish solutions specifically for LNP mRNA drug products is being driven by several key factors in the pharmaceutical industry.
Biopharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in mRNA technology beyond vaccines, expanding into therapeutic areas such as oncology, rare genetic disorders, and autoimmune diseases. This diversification has created substantial demand for manufacturing solutions that can accommodate various batch sizes while maintaining stringent quality standards. The clinical pipeline for mRNA therapeutics has grown by over 50% since 2020, with more than 180 candidates currently in development globally.
Regulatory agencies worldwide have heightened their focus on cross-contamination risks in multi-product facilities. The FDA and EMA have recently updated their guidelines for aseptic processing, emphasizing the need for advanced containment strategies when handling different mRNA products. This regulatory landscape has created urgent market demand for innovative fill/finish solutions that can demonstrably reduce cross-contamination risks.
Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) represent a significant market segment, with 65% of biopharmaceutical companies outsourcing at least some portion of their mRNA drug manufacturing. These CDMOs require flexible, scalable systems that can accommodate multiple clients and products while ensuring product integrity and preventing cross-contamination.
The cost implications of product contamination events are substantial, with recalls potentially costing pharmaceutical companies between $10 million and $30 million per incident, not including reputational damage. This economic reality has intensified interest in advanced aseptic processing technologies that minimize contamination risks while maintaining production efficiency.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America currently holds the largest market share (approximately 42%) for LNP mRNA processing equipment, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (22%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate over the next five years as countries like China, South Korea, and Singapore invest heavily in biopharmaceutical manufacturing infrastructure.
End-user surveys indicate that pharmaceutical manufacturers prioritize three key features in aseptic fill/finish solutions: scalability across clinical and commercial manufacturing, validated cross-contamination prevention mechanisms, and integration capabilities with existing manufacturing systems. These market requirements are shaping technology development in the sector.
Biopharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in mRNA technology beyond vaccines, expanding into therapeutic areas such as oncology, rare genetic disorders, and autoimmune diseases. This diversification has created substantial demand for manufacturing solutions that can accommodate various batch sizes while maintaining stringent quality standards. The clinical pipeline for mRNA therapeutics has grown by over 50% since 2020, with more than 180 candidates currently in development globally.
Regulatory agencies worldwide have heightened their focus on cross-contamination risks in multi-product facilities. The FDA and EMA have recently updated their guidelines for aseptic processing, emphasizing the need for advanced containment strategies when handling different mRNA products. This regulatory landscape has created urgent market demand for innovative fill/finish solutions that can demonstrably reduce cross-contamination risks.
Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) represent a significant market segment, with 65% of biopharmaceutical companies outsourcing at least some portion of their mRNA drug manufacturing. These CDMOs require flexible, scalable systems that can accommodate multiple clients and products while ensuring product integrity and preventing cross-contamination.
The cost implications of product contamination events are substantial, with recalls potentially costing pharmaceutical companies between $10 million and $30 million per incident, not including reputational damage. This economic reality has intensified interest in advanced aseptic processing technologies that minimize contamination risks while maintaining production efficiency.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America currently holds the largest market share (approximately 42%) for LNP mRNA processing equipment, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (22%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate over the next five years as countries like China, South Korea, and Singapore invest heavily in biopharmaceutical manufacturing infrastructure.
End-user surveys indicate that pharmaceutical manufacturers prioritize three key features in aseptic fill/finish solutions: scalability across clinical and commercial manufacturing, validated cross-contamination prevention mechanisms, and integration capabilities with existing manufacturing systems. These market requirements are shaping technology development in the sector.
Current Challenges in Scalable Aseptic Fill/Finish Systems
The aseptic fill/finish process for LNP mRNA drug products faces significant challenges in scaling operations while maintaining sterility and preventing cross-contamination. Traditional fill/finish systems were designed for conventional pharmaceuticals and struggle to accommodate the unique properties of lipid nanoparticle formulations containing mRNA, which are highly sensitive to environmental conditions and contamination.
One primary challenge is the maintenance of aseptic conditions throughout the entire manufacturing process. As batch sizes increase, the risk of contamination grows exponentially, particularly during transitions between process steps. The complex nature of LNP formulations requires specialized handling that conventional systems cannot adequately provide at scale.
Cross-contamination between different mRNA products represents another critical concern. Unlike small molecule drugs, mRNA therapeutics carry genetic information that could trigger unintended biological responses if cross-contamination occurs. Current systems lack robust isolation mechanisms to prevent product carryover between batches, especially when manufacturing facilities produce multiple mRNA products.
Temperature control presents a substantial hurdle in scaled operations. LNP mRNA formulations require precise temperature maintenance throughout the fill/finish process to preserve stability and efficacy. Existing large-scale systems struggle to maintain the necessary temperature uniformity across larger volumes, leading to potential product degradation and quality inconsistencies.
The viscosity and particle characteristics of LNP formulations create additional complications for conventional filling equipment. Standard pumping and dispensing systems may cause shear stress that damages the nanoparticle structure, affecting drug efficacy. This becomes increasingly problematic as throughput requirements increase with scale.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) requirements for advanced therapeutics are stringent and evolving, with regulatory bodies demanding higher standards for cross-contamination prevention in multi-product facilities. Many existing systems were not designed with these enhanced requirements in mind.
Automation integration challenges also emerge at scale. While automation can reduce human intervention and contamination risk, interfacing robotic systems with aseptic processing equipment requires sophisticated engineering solutions that many current platforms lack. The industry faces a significant gap in validated automated solutions specifically designed for LNP mRNA products.
Equipment cleaning and changeover between products represents a substantial bottleneck. Traditional clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) systems may not completely eliminate nucleic acid residues, creating persistent cross-contamination risks that become more significant as production scales increase.
One primary challenge is the maintenance of aseptic conditions throughout the entire manufacturing process. As batch sizes increase, the risk of contamination grows exponentially, particularly during transitions between process steps. The complex nature of LNP formulations requires specialized handling that conventional systems cannot adequately provide at scale.
Cross-contamination between different mRNA products represents another critical concern. Unlike small molecule drugs, mRNA therapeutics carry genetic information that could trigger unintended biological responses if cross-contamination occurs. Current systems lack robust isolation mechanisms to prevent product carryover between batches, especially when manufacturing facilities produce multiple mRNA products.
Temperature control presents a substantial hurdle in scaled operations. LNP mRNA formulations require precise temperature maintenance throughout the fill/finish process to preserve stability and efficacy. Existing large-scale systems struggle to maintain the necessary temperature uniformity across larger volumes, leading to potential product degradation and quality inconsistencies.
The viscosity and particle characteristics of LNP formulations create additional complications for conventional filling equipment. Standard pumping and dispensing systems may cause shear stress that damages the nanoparticle structure, affecting drug efficacy. This becomes increasingly problematic as throughput requirements increase with scale.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) requirements for advanced therapeutics are stringent and evolving, with regulatory bodies demanding higher standards for cross-contamination prevention in multi-product facilities. Many existing systems were not designed with these enhanced requirements in mind.
Automation integration challenges also emerge at scale. While automation can reduce human intervention and contamination risk, interfacing robotic systems with aseptic processing equipment requires sophisticated engineering solutions that many current platforms lack. The industry faces a significant gap in validated automated solutions specifically designed for LNP mRNA products.
Equipment cleaning and changeover between products represents a substantial bottleneck. Traditional clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) systems may not completely eliminate nucleic acid residues, creating persistent cross-contamination risks that become more significant as production scales increase.
Current Contamination Control Strategies for LNP mRNA Products
01 Closed system aseptic fill/finish technologies
Closed system technologies for aseptic fill/finish operations minimize the risk of cross-contamination during the manufacturing of LNP mRNA drug products. These systems maintain sterility by eliminating direct exposure to the environment and human operators. Advanced isolator technology and closed transfer systems ensure product integrity throughout the filling process, reducing the risk of particulate contamination and microbial ingress that could compromise the sensitive mRNA formulations.- Closed system technologies for aseptic fill/finish: Closed system technologies are essential for aseptic fill/finish operations of LNP mRNA drug products to minimize cross-contamination risks. These systems maintain sterility throughout the manufacturing process by eliminating open handling of products. Advanced closed systems incorporate single-use components, automated transfer mechanisms, and sealed connections that prevent exposure to the environment. This approach significantly reduces the risk of cross-contamination between different mRNA products and batches.
- Dedicated equipment and facility design: Implementing dedicated equipment and specialized facility designs for LNP mRNA drug manufacturing helps mitigate cross-contamination risks. This includes segregated production areas, unidirectional material and personnel flow, and dedicated equipment for specific product lines. Proper facility layout with appropriate airlocks, pressure cascades, and HVAC systems creates controlled environments that minimize particle transfer between areas. These design considerations are crucial for maintaining product integrity during aseptic fill/finish operations.
- Advanced cleaning and decontamination protocols: Specialized cleaning and decontamination protocols are critical for preventing cross-contamination in LNP mRNA drug manufacturing. These include validated cleaning procedures with specific detergents effective against nucleic acids, enzymatic cleaners that degrade residual RNA, and advanced surface decontamination methods. Implementing robust cleaning validation studies ensures complete removal of product residues between manufacturing campaigns, which is essential for maintaining product purity and preventing cross-contamination.
- Single-use technologies and disposable systems: Single-use technologies and disposable systems offer significant advantages for aseptic fill/finish of LNP mRNA products by eliminating the need for cleaning validation between batches. These systems include pre-sterilized bags, tubing, connectors, filters, and filling needles that are disposed of after use. The implementation of comprehensive single-use strategies reduces cross-contamination risks, simplifies changeover procedures, and increases manufacturing flexibility while maintaining product quality and sterility.
- Process monitoring and contamination detection systems: Advanced process monitoring and contamination detection systems are essential for ensuring the integrity of aseptic fill/finish operations for LNP mRNA products. These include real-time monitoring technologies, nucleic acid-specific detection methods, and automated inspection systems that can identify potential contamination events. Implementation of comprehensive environmental monitoring programs, rapid microbial detection methods, and advanced analytics helps maintain process control and provides early warning of potential cross-contamination risks.
02 Single-use disposable components for LNP processing
Single-use disposable components and systems are increasingly utilized in LNP mRNA manufacturing to eliminate cross-contamination risks between batches. These disposable systems include pre-sterilized tubing, connectors, filters, and filling needles that are discarded after each production run. This approach eliminates the need for cleaning validation between different products and minimizes the risk of residual product carryover, which is particularly important for potent mRNA therapeutics where even trace contamination could affect safety and efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automated cleaning and decontamination protocols
Specialized automated cleaning and decontamination protocols have been developed specifically for LNP mRNA manufacturing equipment to address cross-contamination concerns. These protocols include validated cleaning procedures with specific detergents that effectively remove lipid residues without degrading equipment surfaces. Automated clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) systems ensure consistent and thorough decontamination between production runs, while real-time monitoring systems verify cleaning effectiveness to prevent product carryover.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dedicated manufacturing suites and equipment trains
Dedicated manufacturing suites and equipment trains designed exclusively for specific LNP mRNA products provide physical segregation to prevent cross-contamination. These purpose-built facilities feature unidirectional material and personnel flow, pressure cascades between rooms, and dedicated HVAC systems to maintain appropriate air classification. The dedicated approach eliminates shared equipment risks and allows for optimized process parameters specific to individual mRNA formulations, enhancing both safety and manufacturing efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced monitoring and containment technologies
Advanced monitoring and containment technologies are implemented to detect and prevent cross-contamination during LNP mRNA fill/finish operations. These include real-time particle monitoring systems, rapid microbial detection methods, and advanced air sampling techniques that can identify contamination events before they affect product quality. Specialized containment technologies such as restricted access barrier systems (RABS) and negative pressure isolators provide additional protection against environmental contaminants while handling the sensitive mRNA formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Aseptic Fill/Finish Technology
The mRNA LNP fill/finish technology market is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for scalable aseptic solutions with minimal cross-contamination risk. The market is expanding rapidly due to COVID-19 vaccine production experience, with an estimated value exceeding $2 billion annually. Leading players include established pharmaceutical companies (ModernaTX, BioNTech) who pioneered commercial mRNA vaccines, alongside specialized equipment manufacturers (West Pharmaceutical Services, Syntegon Technology) developing dedicated fill/finish systems. Academic institutions (University of Pennsylvania, MIT) continue advancing fundamental technologies while contract manufacturers are emerging to address capacity constraints. The technology remains in active development with innovations focusing on closed systems, single-use components, and automated solutions to enhance sterility assurance and reduce contamination risks.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed an automated, closed-system aseptic fill/finish platform specifically designed for LNP mRNA products. Their solution incorporates single-use components and isolator technology to maintain sterility throughout the manufacturing process. The system features in-line monitoring with real-time release testing capabilities and automated cleaning validation protocols between batches. Moderna's platform can process multiple mRNA products on the same line with minimal changeover time, utilizing disposable fluid paths to eliminate cross-contamination risks. Their system incorporates robotic handling for vial preparation, filling, and capping operations, with integrated vision systems for 100% inspection of filled units. The platform is designed with scalability in mind, capable of producing from clinical to commercial quantities (10,000-500,000 doses per batch) while maintaining consistent quality attributes.
Strengths: Industry-leading automation reduces human intervention and contamination risk; proven commercial-scale implementation during COVID-19 vaccine production; integrated quality control systems. Weaknesses: Proprietary system with high capital investment requirements; limited flexibility for very small batch sizes; requires specialized technical expertise for operation and maintenance.
West Pharmaceutical Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: West Pharmaceutical Services has developed specialized containment solutions specifically designed for aseptic fill/finish of LNP mRNA products. Their NovaPure® platform incorporates high-quality components engineered to minimize particulate contamination and ensure container closure integrity critical for sensitive mRNA formulations. The company's Crystal Zenith® cyclic olefin polymer containers provide an alternative to glass vials, offering enhanced break resistance and reduced interaction with LNP formulations. West's FluroTec® and B2-coating technologies create effective barriers between drug products and elastomeric closures, minimizing leachables and extractables that could compromise mRNA stability. Their ready-to-use (RTU) component systems eliminate the need for on-site washing and sterilization, reducing contamination risks in the fill/finish process. West has also developed specialized analytical services for container closure integrity testing specific to the requirements of temperature-sensitive mRNA products.
Strengths: Extensive expertise in container closure systems specifically designed for sensitive biologics; established supply chain with global manufacturing capabilities; comprehensive regulatory documentation support. Weaknesses: Focused primarily on components rather than complete fill/finish systems; requires integration with third-party filling equipment; higher component costs compared to standard packaging solutions.
Critical Technologies for Cross-Contamination Risk Reduction
Fluidic mixer unit device for nanoparticle production
PatentWO2024211518A1
Innovation
- A device with a microplate featuring an array of fluidic mixing units, each with multiple inlet channels converging into a mixing channel, allowing for simultaneous production and evaluation of lipid nanoparticles, compatible with pipetting robots, and enabling high-throughput screening of different lipid solutions and geometries.
METHOD FOR LAGRE-SCALE PRODUCTION OF LARGE-SIZE LNPs
PatentPendingUS20250041238A1
Innovation
- A scalable, GMP-compliant method involving tangential flow filtration (TFF) at low shear rates and controlled pH conditions, combined with a low percentage of PEGylated lipid, to produce LNPs with an average diameter of at least 140 nm, ensuring high encapsulation efficiency and stability.
Regulatory Requirements for LNP mRNA Drug Manufacturing
The regulatory landscape for LNP mRNA drug manufacturing is complex and stringent, reflecting the novel nature of these therapeutics and their critical importance in modern medicine. Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA, have established comprehensive frameworks that manufacturers must navigate to ensure product safety, efficacy, and quality.
For aseptic fill/finish operations specifically, regulations focus heavily on contamination control strategies. 21 CFR Part 211 (FDA) and Annex 1 of EU GMP guidelines outline requirements for sterile manufacturing environments, with particular emphasis on environmental monitoring, personnel qualification, and validation of aseptic processes. These regulations mandate robust risk assessment methodologies such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify potential cross-contamination vectors.
The FDA's guidance on "Sterile Drug Products Produced by Aseptic Processing" provides specific requirements for facility design, including appropriate air classification, pressure differentials, and material/personnel flow that minimize contamination risks during LNP mRNA fill/finish operations. Similarly, ICH Q7 guidelines establish expectations for Good Manufacturing Practices that apply throughout the production process.
For scalable solutions, regulatory bodies require demonstration of process consistency across different production scales. This includes validation of cleaning procedures between batches to prevent cross-contamination, particularly critical for multi-product facilities handling different mRNA constructs. The FDA's guidance on "Process Validation: General Principles and Practices" outlines the expectations for establishing scientific evidence that a process is capable of consistently delivering quality products.
Equipment qualification requirements present another regulatory consideration, with 21 CFR Part 11 governing computerized systems used in automated fill/finish operations. Validation of these systems must demonstrate that they can maintain product integrity while scaling production volumes.
Regulatory submissions for LNP mRNA products must include detailed descriptions of the fill/finish process, including justification for the selected container closure system and its compatibility with the LNP formulation. The Common Technical Document (CTD) format requires comprehensive data on process validation, including media fills that simulate the aseptic process under worst-case conditions.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of cross-contamination controls, with agencies expecting implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) principles that build quality into manufacturing processes rather than testing it retrospectively. Advanced technologies like closed systems and single-use components are increasingly recognized in regulatory frameworks as effective strategies for minimizing contamination risks in scalable operations.
For aseptic fill/finish operations specifically, regulations focus heavily on contamination control strategies. 21 CFR Part 211 (FDA) and Annex 1 of EU GMP guidelines outline requirements for sterile manufacturing environments, with particular emphasis on environmental monitoring, personnel qualification, and validation of aseptic processes. These regulations mandate robust risk assessment methodologies such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify potential cross-contamination vectors.
The FDA's guidance on "Sterile Drug Products Produced by Aseptic Processing" provides specific requirements for facility design, including appropriate air classification, pressure differentials, and material/personnel flow that minimize contamination risks during LNP mRNA fill/finish operations. Similarly, ICH Q7 guidelines establish expectations for Good Manufacturing Practices that apply throughout the production process.
For scalable solutions, regulatory bodies require demonstration of process consistency across different production scales. This includes validation of cleaning procedures between batches to prevent cross-contamination, particularly critical for multi-product facilities handling different mRNA constructs. The FDA's guidance on "Process Validation: General Principles and Practices" outlines the expectations for establishing scientific evidence that a process is capable of consistently delivering quality products.
Equipment qualification requirements present another regulatory consideration, with 21 CFR Part 11 governing computerized systems used in automated fill/finish operations. Validation of these systems must demonstrate that they can maintain product integrity while scaling production volumes.
Regulatory submissions for LNP mRNA products must include detailed descriptions of the fill/finish process, including justification for the selected container closure system and its compatibility with the LNP formulation. The Common Technical Document (CTD) format requires comprehensive data on process validation, including media fills that simulate the aseptic process under worst-case conditions.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of cross-contamination controls, with agencies expecting implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) principles that build quality into manufacturing processes rather than testing it retrospectively. Advanced technologies like closed systems and single-use components are increasingly recognized in regulatory frameworks as effective strategies for minimizing contamination risks in scalable operations.
Single-Use Technology Applications in Fill/Finish Operations
Single-use technologies have emerged as a transformative solution in the fill/finish operations for LNP mRNA drug products, offering significant advantages in addressing cross-contamination risks while enabling scalable aseptic processing. These disposable systems eliminate the need for complex cleaning validation and sterilization procedures between batches, substantially reducing the risk of product carryover and cross-contamination.
The implementation of single-use fluid paths in fill/finish operations provides a closed system approach that maintains sterility throughout the entire process. Pre-sterilized, ready-to-use components such as bags, tubing, connectors, and filters create an uninterrupted sterile boundary from formulation to final container closure, minimizing exposure to environmental contaminants and human intervention.
For LNP mRNA products specifically, single-use technology offers unique benefits due to the sensitive nature of these biologics. The reduced product contact with stainless steel surfaces minimizes potential adsorption issues and particle generation that could compromise product integrity. Additionally, the elimination of cleaning agents removes concerns about residual detergents or cleaning chemicals that might interact with the delicate lipid nanoparticle structures.
From a scalability perspective, single-use systems provide remarkable flexibility in production capacity. Manufacturers can rapidly switch between different batch sizes by simply exchanging the disposable components rather than reconfiguring and revalidating fixed equipment. This adaptability is particularly valuable for mRNA therapeutics, where production demands may fluctuate significantly based on clinical trial progression or emergency response requirements.
Recent advancements in single-use filling technologies include robotic fill systems with disposable fluid paths, automated disconnection mechanisms to maintain sterility, and integrated in-line monitoring capabilities. These innovations enable real-time process verification while maintaining the benefits of disposable components. Furthermore, suppliers have developed specialized single-use assemblies optimized for the temperature-sensitive handling requirements of LNP mRNA formulations.
Despite these advantages, implementation challenges remain, including concerns about extractables and leachables from polymer materials, potential supply chain vulnerabilities, and environmental sustainability considerations. Manufacturers must conduct comprehensive compatibility studies between single-use materials and their specific LNP mRNA formulations to ensure product stability throughout the fill/finish process.
The regulatory landscape increasingly acknowledges the contamination control benefits of single-use systems, with guidance documents specifically addressing their implementation in aseptic processing. This regulatory support, combined with the technical advantages, positions single-use technology as a cornerstone strategy for developing scalable, contamination-controlled fill/finish operations for the growing pipeline of LNP mRNA therapeutics.
The implementation of single-use fluid paths in fill/finish operations provides a closed system approach that maintains sterility throughout the entire process. Pre-sterilized, ready-to-use components such as bags, tubing, connectors, and filters create an uninterrupted sterile boundary from formulation to final container closure, minimizing exposure to environmental contaminants and human intervention.
For LNP mRNA products specifically, single-use technology offers unique benefits due to the sensitive nature of these biologics. The reduced product contact with stainless steel surfaces minimizes potential adsorption issues and particle generation that could compromise product integrity. Additionally, the elimination of cleaning agents removes concerns about residual detergents or cleaning chemicals that might interact with the delicate lipid nanoparticle structures.
From a scalability perspective, single-use systems provide remarkable flexibility in production capacity. Manufacturers can rapidly switch between different batch sizes by simply exchanging the disposable components rather than reconfiguring and revalidating fixed equipment. This adaptability is particularly valuable for mRNA therapeutics, where production demands may fluctuate significantly based on clinical trial progression or emergency response requirements.
Recent advancements in single-use filling technologies include robotic fill systems with disposable fluid paths, automated disconnection mechanisms to maintain sterility, and integrated in-line monitoring capabilities. These innovations enable real-time process verification while maintaining the benefits of disposable components. Furthermore, suppliers have developed specialized single-use assemblies optimized for the temperature-sensitive handling requirements of LNP mRNA formulations.
Despite these advantages, implementation challenges remain, including concerns about extractables and leachables from polymer materials, potential supply chain vulnerabilities, and environmental sustainability considerations. Manufacturers must conduct comprehensive compatibility studies between single-use materials and their specific LNP mRNA formulations to ensure product stability throughout the fill/finish process.
The regulatory landscape increasingly acknowledges the contamination control benefits of single-use systems, with guidance documents specifically addressing their implementation in aseptic processing. This regulatory support, combined with the technical advantages, positions single-use technology as a cornerstone strategy for developing scalable, contamination-controlled fill/finish operations for the growing pipeline of LNP mRNA therapeutics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!