The Role of Ethyl Acetate in Flavor and Fragrance Industries
JUN 27, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, plays a crucial role in the flavor and fragrance industries. This colorless liquid ester is characterized by its fruity odor and low toxicity, making it an ideal component in various applications. Its widespread use can be attributed to its unique properties, including high solubility, low boiling point, and pleasant aroma.
In the flavor industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key ingredient in creating and enhancing fruit flavors. It is particularly notable for its ability to impart a sweet, fruity essence reminiscent of pears and apples. This characteristic makes it an essential component in the formulation of artificial fruit flavors for a wide range of food and beverage products. Additionally, ethyl acetate contributes to the overall flavor profile of many fermented foods and beverages, such as wine and beer, where it occurs naturally as a byproduct of fermentation.
The fragrance industry also heavily relies on ethyl acetate for its aromatic properties. It is commonly used as a solvent and fixative in perfumes and colognes, helping to blend and stabilize other fragrance components. Its subtle, fruity scent adds depth and complexity to various perfume formulations, enhancing the overall olfactory experience. Moreover, ethyl acetate's ability to evaporate quickly makes it an excellent choice for top notes in perfumery, providing an initial burst of fragrance upon application.
From a production standpoint, ethyl acetate is synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, as well as the Tishchenko reaction of acetaldehyde. Its relatively simple and cost-effective production process contributes to its widespread availability and use in the industry. Furthermore, ethyl acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an environmentally friendly option compared to some other solvents used in flavor and fragrance applications.
The versatility of ethyl acetate extends beyond its direct use in flavors and fragrances. It also serves as an important solvent in the extraction and purification of various natural flavors and fragrances from plant materials. This application is particularly valuable in the production of essential oils and other natural aromatic compounds, further cementing its importance in the industry.
In the flavor industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key ingredient in creating and enhancing fruit flavors. It is particularly notable for its ability to impart a sweet, fruity essence reminiscent of pears and apples. This characteristic makes it an essential component in the formulation of artificial fruit flavors for a wide range of food and beverage products. Additionally, ethyl acetate contributes to the overall flavor profile of many fermented foods and beverages, such as wine and beer, where it occurs naturally as a byproduct of fermentation.
The fragrance industry also heavily relies on ethyl acetate for its aromatic properties. It is commonly used as a solvent and fixative in perfumes and colognes, helping to blend and stabilize other fragrance components. Its subtle, fruity scent adds depth and complexity to various perfume formulations, enhancing the overall olfactory experience. Moreover, ethyl acetate's ability to evaporate quickly makes it an excellent choice for top notes in perfumery, providing an initial burst of fragrance upon application.
From a production standpoint, ethyl acetate is synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, as well as the Tishchenko reaction of acetaldehyde. Its relatively simple and cost-effective production process contributes to its widespread availability and use in the industry. Furthermore, ethyl acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an environmentally friendly option compared to some other solvents used in flavor and fragrance applications.
The versatility of ethyl acetate extends beyond its direct use in flavors and fragrances. It also serves as an important solvent in the extraction and purification of various natural flavors and fragrances from plant materials. This application is particularly valuable in the production of essential oils and other natural aromatic compounds, further cementing its importance in the industry.
Market Analysis
The flavor and fragrance industries have witnessed significant growth in recent years, with ethyl acetate playing a crucial role in their expansion. The global market for ethyl acetate in these sectors is projected to experience steady growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and synthetic flavors and fragrances across various applications.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate is widely used as a flavoring agent, contributing to the characteristic taste and aroma of many products. Its fruity and sweet odor makes it particularly popular in confectionery, baked goods, and beverages. The rising consumer preference for natural and organic products has led to an increased demand for ethyl acetate derived from natural sources, such as fruits and vegetables.
The personal care and cosmetics sector also represents a significant market for ethyl acetate. Its use in perfumes, lotions, and other beauty products has grown due to its ability to enhance and stabilize fragrances. The global cosmetics market's expansion, particularly in emerging economies, has further boosted the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries. This growth is attributed to the region's rapidly expanding food and beverage sector, increasing disposable incomes, and changing consumer preferences. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by innovation in product formulations and a strong presence of major flavor and fragrance companies.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized producers. Key players are focusing on developing sustainable and bio-based ethyl acetate to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly ingredients. This trend is likely to shape the market landscape in the coming years, as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures increase.
Despite its widespread use, the ethyl acetate market faces challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly those of ethanol and acetic acid, can impact production costs and market dynamics. Additionally, stringent regulations regarding the use of synthetic chemicals in food and personal care products may influence market growth in certain regions.
Overall, the market for ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries is poised for growth, driven by diverse applications, evolving consumer preferences, and technological advancements. The industry's ability to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes and sustainability demands will be crucial in shaping its future trajectory.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate is widely used as a flavoring agent, contributing to the characteristic taste and aroma of many products. Its fruity and sweet odor makes it particularly popular in confectionery, baked goods, and beverages. The rising consumer preference for natural and organic products has led to an increased demand for ethyl acetate derived from natural sources, such as fruits and vegetables.
The personal care and cosmetics sector also represents a significant market for ethyl acetate. Its use in perfumes, lotions, and other beauty products has grown due to its ability to enhance and stabilize fragrances. The global cosmetics market's expansion, particularly in emerging economies, has further boosted the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries. This growth is attributed to the region's rapidly expanding food and beverage sector, increasing disposable incomes, and changing consumer preferences. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by innovation in product formulations and a strong presence of major flavor and fragrance companies.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized producers. Key players are focusing on developing sustainable and bio-based ethyl acetate to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly ingredients. This trend is likely to shape the market landscape in the coming years, as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures increase.
Despite its widespread use, the ethyl acetate market faces challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly those of ethanol and acetic acid, can impact production costs and market dynamics. Additionally, stringent regulations regarding the use of synthetic chemicals in food and personal care products may influence market growth in certain regions.
Overall, the market for ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries is poised for growth, driven by diverse applications, evolving consumer preferences, and technological advancements. The industry's ability to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes and sustainability demands will be crucial in shaping its future trajectory.
Technical Challenges
Despite the widespread use of ethyl acetate in flavor and fragrance industries, several technical challenges persist in its production, application, and environmental impact. One of the primary concerns is the optimization of production processes to enhance yield and purity while reducing costs. Current manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful catalysts, necessitating the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly production techniques.
The volatility of ethyl acetate presents another significant challenge, particularly in fragrance applications. Its high vapor pressure can lead to rapid evaporation, resulting in reduced longevity of scents and flavors. This necessitates the development of advanced encapsulation technologies or molecular modification strategies to improve the stability and controlled release of ethyl acetate-based fragrances.
Quality control and consistency in ethyl acetate production pose additional challenges. Variations in raw materials and production conditions can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, affecting its organoleptic properties and overall performance in flavor and fragrance formulations. Implementing robust quality management systems and developing more precise analytical methods for purity assessment are crucial to addressing this issue.
The potential for allergenic reactions and sensitivities to ethyl acetate in certain individuals presents a challenge for its widespread use in consumer products. This necessitates ongoing research into alternative compounds or modified versions of ethyl acetate that maintain its desirable properties while reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Environmental concerns surrounding the use of ethyl acetate also pose significant challenges. While it is considered less harmful than many other solvents, its production and disposal still have environmental implications. Developing biodegradable alternatives or implementing closed-loop recycling systems for ethyl acetate in industrial processes are areas that require further research and innovation.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle, as different regions have varying standards and restrictions on the use of ethyl acetate in food and cosmetic products. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and ensuring compliance across global markets requires ongoing vigilance and adaptability in product formulations and manufacturing processes.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl acetate into complex flavor and fragrance formulations presents technical challenges in maintaining stability, preventing unwanted interactions with other ingredients, and ensuring consistent performance across different product matrices. This necessitates advanced formulation techniques and extensive compatibility testing to optimize the use of ethyl acetate in diverse applications.
The volatility of ethyl acetate presents another significant challenge, particularly in fragrance applications. Its high vapor pressure can lead to rapid evaporation, resulting in reduced longevity of scents and flavors. This necessitates the development of advanced encapsulation technologies or molecular modification strategies to improve the stability and controlled release of ethyl acetate-based fragrances.
Quality control and consistency in ethyl acetate production pose additional challenges. Variations in raw materials and production conditions can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, affecting its organoleptic properties and overall performance in flavor and fragrance formulations. Implementing robust quality management systems and developing more precise analytical methods for purity assessment are crucial to addressing this issue.
The potential for allergenic reactions and sensitivities to ethyl acetate in certain individuals presents a challenge for its widespread use in consumer products. This necessitates ongoing research into alternative compounds or modified versions of ethyl acetate that maintain its desirable properties while reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Environmental concerns surrounding the use of ethyl acetate also pose significant challenges. While it is considered less harmful than many other solvents, its production and disposal still have environmental implications. Developing biodegradable alternatives or implementing closed-loop recycling systems for ethyl acetate in industrial processes are areas that require further research and innovation.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle, as different regions have varying standards and restrictions on the use of ethyl acetate in food and cosmetic products. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and ensuring compliance across global markets requires ongoing vigilance and adaptability in product formulations and manufacturing processes.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl acetate into complex flavor and fragrance formulations presents technical challenges in maintaining stability, preventing unwanted interactions with other ingredients, and ensuring consistent performance across different product matrices. This necessitates advanced formulation techniques and extensive compatibility testing to optimize the use of ethyl acetate in diverse applications.
Current Applications
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts. These processes aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in industrial processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse industrial applications, such as solvent extraction, coating formulations, and as a reaction medium. Its properties make it suitable for use in various manufacturing processes and chemical syntheses.
- Ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations: The use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations is explored, including its role as a solvent, excipient, or active ingredient carrier. Its application in these industries is based on its favorable properties and compatibility with various formulations.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling procedures.
- Novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate: Innovations in creating new derivatives or modified forms of ethyl acetate are presented. These developments aim to enhance its properties or create new compounds with improved characteristics for specific applications.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, such as solvent extraction, as a reaction medium, and in the production of other chemicals. Its properties make it suitable for various industrial applications, including pharmaceuticals and polymer synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in coating and adhesive formulations
Ethyl acetate is employed in the formulation of coatings, adhesives, and related products. Its solvent properties and compatibility with various resins make it valuable in these applications, contributing to improved product performance and characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate
Methods for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial processes are described. These techniques aim to improve process efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact by reusing the solvent in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Ethyl acetate as a green solvent alternative
Ethyl acetate is explored as an environmentally friendly solvent alternative in various processes. Its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability make it attractive for replacing more harmful solvents in industrial and consumer applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The ethyl acetate market in the flavor and fragrance industries is in a mature stage, with a stable global market size. The technology is well-established, with major players like Symrise, BASF, International Flavors & Fragrances, and Firmenich dominating the field. These companies have advanced research capabilities and extensive product portfolios, indicating high technological maturity. The market is characterized by ongoing innovation in application techniques and product formulations, with a focus on natural and sustainable sources. Emerging players like Wanhua Chemical and Nantong Baichuan are also contributing to the competitive landscape, particularly in the Asian market.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has leveraged its chemical expertise to optimize the production and application of ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries. They have developed high-purity ethyl acetate grades specifically tailored for these sensitive applications, ensuring consistent quality and performance[13]. BASF's research includes the development of novel catalysts for more efficient ethyl acetate synthesis, reducing energy consumption and improving yield[14]. The company has also explored the use of ethyl acetate as a green solvent in the extraction of natural flavors and fragrances, aligning with industry trends towards sustainability[15].
Strengths: High-purity product offerings, efficient production technologies, and expertise in green extraction methods. Weaknesses: Less specialized in flavor and fragrance applications compared to dedicated F&F companies.
International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc.
Technical Solution: IFF has pioneered the use of ethyl acetate in creating natural and nature-identical flavors. Their proprietary extraction processes utilize ethyl acetate's excellent solvent properties to isolate key flavor compounds from natural sources, resulting in highly concentrated and authentic flavor profiles[4]. The company has also developed novel ethyl acetate-based delivery systems for fragrances, enhancing their performance in various consumer products[5]. IFF's research extends to the sensory impact of ethyl acetate, mapping its contribution to overall flavor and fragrance perceptions across different concentrations and matrices[6].
Strengths: Expertise in natural flavor extraction, innovative delivery systems, and comprehensive sensory research. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges associated with natural and nature-identical flavor claims.
Key Innovations
Perfume mixtures containing Cyclopent-2-Enyl-ethyl acetate
PatentActiveEP2474301A1
Innovation
- A fragrance mixture comprising cyclopent-2-enyl-acetate ethyl ester combined with one or more floral odor notes from alcohols or aldehydes, and ketones, ethers, and esters, which effectively emphasizes or masks specific odor aspects, particularly fatty and technical notes, without dominating the overall sensory impression.
Fruity odorant
PatentActiveUS20110097291A1
Innovation
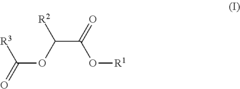
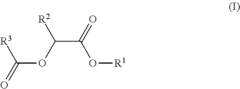
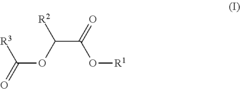
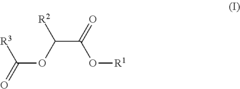
- Development of di-ester compounds of formula (I), specifically C8 or C10 compounds with specific alkyl and alkenyl groups, which can be used as perfuming ingredients to impart fruity-apricot or fruity-vinous notes without herbaceous characteristics, and their incorporation into perfuming compositions or articles.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the compound's widespread use and potential impacts on human health and the environment. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies ethyl acetate as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products, subject to good manufacturing practices. This designation allows for its use as a flavoring agent and solvent in various food applications.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has also evaluated ethyl acetate and approved its use in food products. However, the EU has established specific migration limits for ethyl acetate when used in food contact materials, ensuring that any potential transfer to food remains within safe levels. These regulations are outlined in Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
In the fragrance industry, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) plays a crucial role in self-regulation. IFRA has established standards for the safe use of fragrance materials, including ethyl acetate, which are widely adopted by the industry. These standards take into account potential skin sensitization, phototoxicity, and other safety concerns associated with fragrance ingredients.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of ethyl acetate in these industries. In many jurisdictions, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC), subject to emissions controls. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Clean Air Act, setting limits on its release into the atmosphere from industrial processes.
Occupational safety regulations further govern the handling and use of ethyl acetate in industrial settings. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for workers handling ethyl acetate, requiring appropriate safety measures and personal protective equipment.
Globally, the transportation and storage of ethyl acetate are subject to hazardous materials regulations. The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards, including those associated with ethyl acetate.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of chemicals used in flavor and fragrance production. This includes initiatives to promote green chemistry and reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes involving ethyl acetate and similar compounds.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has also evaluated ethyl acetate and approved its use in food products. However, the EU has established specific migration limits for ethyl acetate when used in food contact materials, ensuring that any potential transfer to food remains within safe levels. These regulations are outlined in Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
In the fragrance industry, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) plays a crucial role in self-regulation. IFRA has established standards for the safe use of fragrance materials, including ethyl acetate, which are widely adopted by the industry. These standards take into account potential skin sensitization, phototoxicity, and other safety concerns associated with fragrance ingredients.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of ethyl acetate in these industries. In many jurisdictions, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC), subject to emissions controls. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Clean Air Act, setting limits on its release into the atmosphere from industrial processes.
Occupational safety regulations further govern the handling and use of ethyl acetate in industrial settings. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for workers handling ethyl acetate, requiring appropriate safety measures and personal protective equipment.
Globally, the transportation and storage of ethyl acetate are subject to hazardous materials regulations. The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards, including those associated with ethyl acetate.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of chemicals used in flavor and fragrance production. This includes initiatives to promote green chemistry and reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes involving ethyl acetate and similar compounds.
Sustainability Aspects
The sustainability aspects of ethyl acetate in the flavor and fragrance industries are becoming increasingly important as companies strive to meet environmental goals and consumer demands for eco-friendly products. Ethyl acetate, a widely used solvent and fragrance ingredient, presents both challenges and opportunities in terms of sustainability.
One of the primary sustainability advantages of ethyl acetate is its potential for bio-based production. Traditionally derived from petrochemical sources, ethyl acetate can now be manufactured from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn. This shift towards bio-based production significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with its manufacture and aligns with circular economy principles.
However, the production of bio-based ethyl acetate raises concerns about land use and competition with food crops. Careful consideration must be given to sourcing practices to ensure that the production of this compound does not contribute to deforestation or food insecurity in developing regions.
In terms of environmental impact, ethyl acetate is generally considered less harmful than many other solvents used in the flavor and fragrance industries. It has low toxicity and is biodegradable, breaking down relatively quickly in the environment. This characteristic makes it a preferred choice for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
The volatile nature of ethyl acetate presents both sustainability challenges and opportunities. While its high volatility can lead to emissions during production and use, it also allows for efficient recovery and recycling processes. Advanced distillation and membrane separation technologies are being developed to capture and reuse ethyl acetate, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Energy consumption in the production and purification of ethyl acetate remains a significant sustainability concern. Efforts are underway to optimize production processes and implement energy-efficient technologies to reduce the overall energy footprint. This includes the exploration of alternative synthesis routes and the use of renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities.
As the flavor and fragrance industries continue to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles in the application of ethyl acetate. This includes developing formulations that minimize the use of solvents, exploring alternative extraction methods, and investigating natural sources of esters that could potentially replace synthetic ethyl acetate in certain applications.
One of the primary sustainability advantages of ethyl acetate is its potential for bio-based production. Traditionally derived from petrochemical sources, ethyl acetate can now be manufactured from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn. This shift towards bio-based production significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with its manufacture and aligns with circular economy principles.
However, the production of bio-based ethyl acetate raises concerns about land use and competition with food crops. Careful consideration must be given to sourcing practices to ensure that the production of this compound does not contribute to deforestation or food insecurity in developing regions.
In terms of environmental impact, ethyl acetate is generally considered less harmful than many other solvents used in the flavor and fragrance industries. It has low toxicity and is biodegradable, breaking down relatively quickly in the environment. This characteristic makes it a preferred choice for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
The volatile nature of ethyl acetate presents both sustainability challenges and opportunities. While its high volatility can lead to emissions during production and use, it also allows for efficient recovery and recycling processes. Advanced distillation and membrane separation technologies are being developed to capture and reuse ethyl acetate, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Energy consumption in the production and purification of ethyl acetate remains a significant sustainability concern. Efforts are underway to optimize production processes and implement energy-efficient technologies to reduce the overall energy footprint. This includes the exploration of alternative synthesis routes and the use of renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities.
As the flavor and fragrance industries continue to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles in the application of ethyl acetate. This includes developing formulations that minimize the use of solvents, exploring alternative extraction methods, and investigating natural sources of esters that could potentially replace synthetic ethyl acetate in certain applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!