Tungsten's Impact On Energy Storage Systems
Tungsten in ESS: Background and Objectives
Tungsten, a metal with remarkable properties, has emerged as a potential game-changer in the field of energy storage systems (ESS). The evolution of tungsten's role in ESS can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring its unique characteristics for enhancing battery performance. As global energy demands continue to rise and the need for efficient, sustainable storage solutions becomes more pressing, tungsten has garnered increased attention from scientists and engineers alike.
The primary objective of incorporating tungsten into ESS is to address several key challenges faced by conventional energy storage technologies. These include improving energy density, enhancing cycle life, and increasing overall system efficiency. Tungsten's high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and superior mechanical strength make it an ideal candidate for tackling these issues.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing tungsten-based materials for various components of energy storage systems. For instance, tungsten oxides have shown promise as electrode materials in lithium-ion batteries, offering higher capacity and improved stability compared to traditional graphite anodes. Additionally, tungsten carbide has been investigated for its potential in supercapacitors, demonstrating exceptional charge storage capabilities.
The technological trajectory of tungsten in ESS has been marked by significant milestones. Early research primarily centered on tungsten's use as a coating material to enhance the durability of battery components. As understanding of its properties deepened, scientists began exploring more intricate applications, such as tungsten-doped cathode materials and tungsten-based electrocatalysts for fuel cells.
Current trends in tungsten-related ESS research are focused on nanotechnology, with efforts to develop tungsten nanostructures that can dramatically improve the performance of energy storage devices. These nanostructures offer increased surface area and unique electronic properties, potentially revolutionizing the way energy is stored and delivered.
Looking ahead, the integration of tungsten into ESS is expected to play a crucial role in advancing renewable energy technologies. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, the demand for efficient and reliable storage solutions will continue to grow. Tungsten's impact on ESS is poised to contribute significantly to this global shift, potentially enabling the development of next-generation batteries and capacitors that can meet the increasing energy demands of the future.
Market Analysis for Tungsten-Enhanced ESS
The market for tungsten-enhanced energy storage systems (ESS) is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and durable energy storage solutions. Tungsten's unique properties, including its high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion, make it an attractive material for enhancing the performance of various energy storage technologies.
In the lithium-ion battery sector, tungsten-based coatings and additives are being explored to improve electrode stability and longevity. This application is particularly relevant in the electric vehicle (EV) market, where battery life and performance are critical factors. As the global EV market continues to expand, the demand for tungsten-enhanced batteries is expected to grow correspondingly.
The renewable energy sector is another key driver for tungsten-enhanced ESS. With the increasing integration of intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind into power grids, there is a growing need for reliable and efficient energy storage solutions. Tungsten-based materials are being investigated for use in flow batteries and other grid-scale storage technologies, offering potential improvements in cycle life and energy density.
Industrial and commercial applications represent another significant market segment for tungsten-enhanced ESS. These sectors require robust, long-lasting energy storage solutions for backup power, peak shaving, and load balancing. Tungsten's durability and high-temperature resistance make it well-suited for these demanding applications.
The aerospace and defense industries are also showing interest in tungsten-enhanced ESS, particularly for applications requiring high-performance energy storage in extreme conditions. Tungsten's ability to withstand high temperatures and radiation makes it valuable for space-based and military energy storage systems.
Geographically, the market for tungsten-enhanced ESS is most developed in regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities and strong research and development ecosystems. North America, Europe, and East Asia are currently leading in the adoption and development of these technologies. However, as the benefits of tungsten-enhanced ESS become more widely recognized, emerging markets in South America, Southeast Asia, and Africa are expected to see increased adoption.
Market analysts project substantial growth for the tungsten-enhanced ESS sector over the next decade. This growth is anticipated to be driven by advancements in material science, increasing energy storage demands, and the push for more sustainable and efficient energy solutions across various industries.
Current Challenges in Tungsten-Based Energy Storage
Tungsten-based energy storage systems face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary issues is the high cost associated with tungsten materials. As a rare metal, tungsten's extraction and processing are expensive, making it less economically viable for large-scale energy storage applications compared to more abundant alternatives.
Another challenge lies in the weight of tungsten-based systems. While tungsten's high density contributes to its excellent energy storage capacity, it also results in heavy storage units. This weight issue can limit the portability and applicability of tungsten-based energy storage in certain sectors, particularly in mobile or lightweight applications.
The manufacturing process of tungsten-based energy storage components presents additional hurdles. Tungsten's high melting point and hardness make it difficult to shape and process, requiring specialized equipment and techniques. This complexity in manufacturing contributes to increased production costs and potential scalability issues.
Durability and cycle life pose ongoing concerns for tungsten-based energy storage systems. While tungsten is known for its strength, repeated charge and discharge cycles can lead to structural changes and degradation over time. Researchers are working to improve the long-term stability of these systems to ensure consistent performance throughout their operational lifespan.
Environmental considerations also present challenges. Tungsten mining and processing can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat disruption and potential contamination of water sources. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in energy technologies, addressing these environmental concerns is crucial for the future of tungsten-based energy storage.
Thermal management is another critical issue in tungsten-based systems. The high energy density can lead to substantial heat generation during charge and discharge cycles. Effective cooling mechanisms are necessary to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance, adding complexity to system design and potentially increasing overall costs.
Integration with existing energy infrastructure presents additional challenges. Tungsten-based storage systems may require specialized charging equipment or power management systems, which can complicate their adoption in current energy grids and applications.
Lastly, there is a need for further research and development to fully understand and optimize the performance of tungsten in energy storage applications. While tungsten shows promise, more comprehensive studies are required to address its limitations and exploit its full potential in various energy storage scenarios.
Existing Tungsten ESS Solutions
01 Tungsten deposition methods
Various methods for depositing tungsten on substrates, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and atomic layer deposition (ALD). These techniques are used to create thin films of tungsten for applications in semiconductor manufacturing and other industries.- Tungsten deposition methods: Various methods for depositing tungsten on substrates, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and atomic layer deposition (ALD). These techniques are used to create thin films of tungsten for applications in semiconductor manufacturing and other industries.
- Tungsten-based alloys and composites: Development of tungsten-based alloys and composites with improved properties, such as enhanced strength, hardness, and thermal stability. These materials find applications in aerospace, defense, and high-temperature industrial processes.
- Tungsten in semiconductor devices: Utilization of tungsten in semiconductor devices, including its use as interconnects, gate electrodes, and diffusion barriers. Tungsten's low resistivity and high melting point make it suitable for various semiconductor applications.
- Tungsten processing and recycling: Methods for processing tungsten ores, refining tungsten, and recycling tungsten-containing materials. These processes aim to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and recover valuable tungsten from waste materials.
- Tungsten in lighting and electronic applications: Use of tungsten in lighting applications, such as filaments for incandescent bulbs, and in various electronic components. Tungsten's high melting point and good electrical conductivity make it suitable for these applications.
02 Tungsten etching processes
Techniques for selectively removing tungsten from surfaces, often used in semiconductor fabrication. These processes may involve chemical or plasma etching methods to create precise patterns or structures in tungsten layers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Tungsten alloys and composites
Development of tungsten-based alloys and composite materials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, hardness, or thermal conductivity. These materials find applications in various industries, including aerospace and electronics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Tungsten in electronic components
Use of tungsten in the manufacture of electronic components, such as interconnects, vias, and electrodes. Tungsten's properties make it suitable for high-performance and miniaturized electronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tungsten processing and recycling
Methods for processing raw tungsten ore, refining tungsten, and recycling tungsten-containing materials. These processes aim to improve efficiency in tungsten production and reduce environmental impact through recycling.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Tungsten ESS Industry
The impact of tungsten on energy storage systems is gaining attention in a rapidly evolving market. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions. The global market size for advanced energy storage systems is expanding, driven by renewable energy integration and grid stability needs. Technologically, tungsten-based energy storage is still in early stages of development, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Companies like Applied Materials, GS Yuasa International, and Toshiba are at the forefront, investing in R&D to leverage tungsten's unique properties. Academic institutions such as Central South University and Boston University are contributing to fundamental research, while industry players like Hitachi and Robert Bosch are exploring practical applications, indicating a competitive landscape spanning both research and commercial sectors.
GS Yuasa International Ltd.
Toshiba Corp.
Innovative Tungsten ESS Technologies
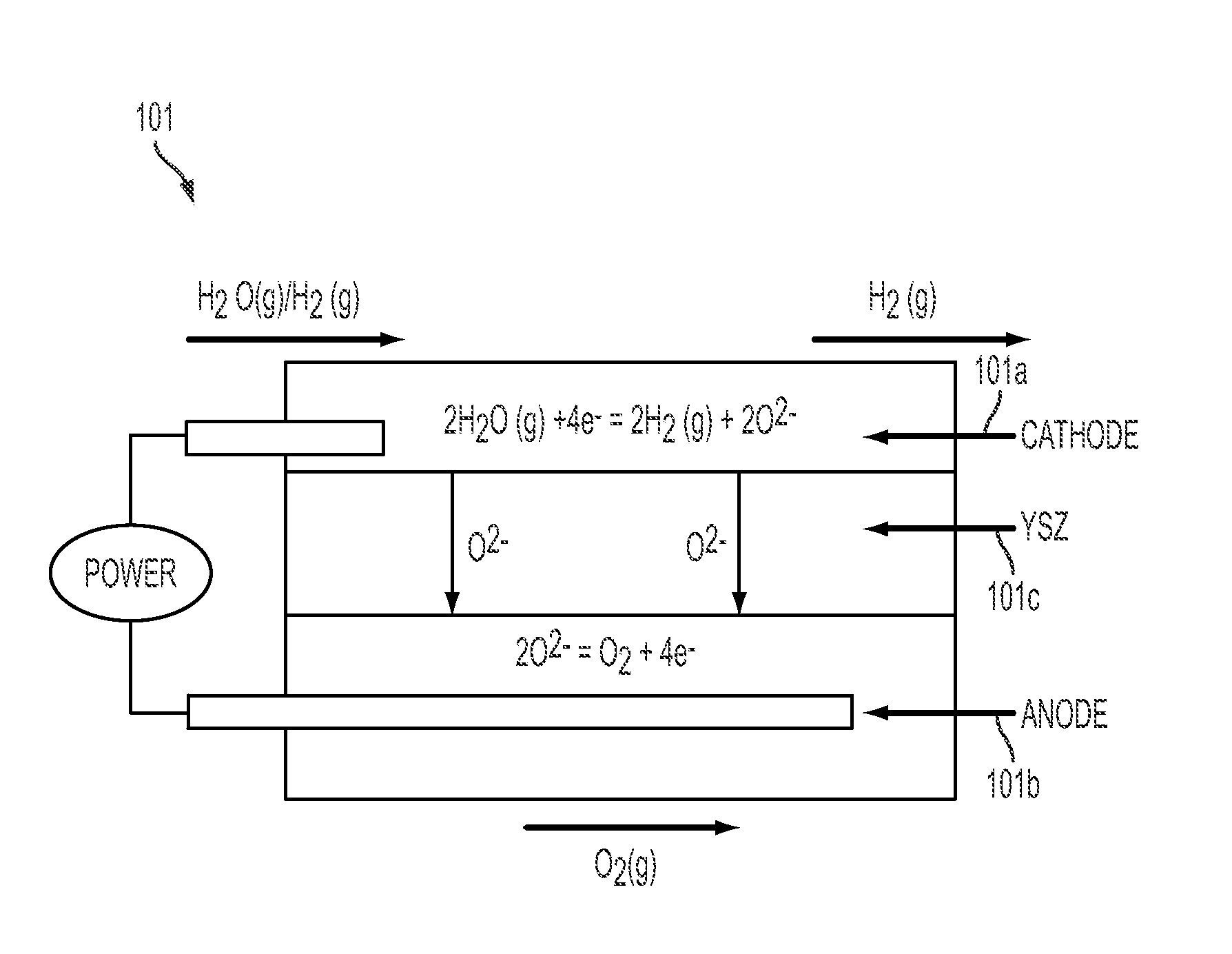
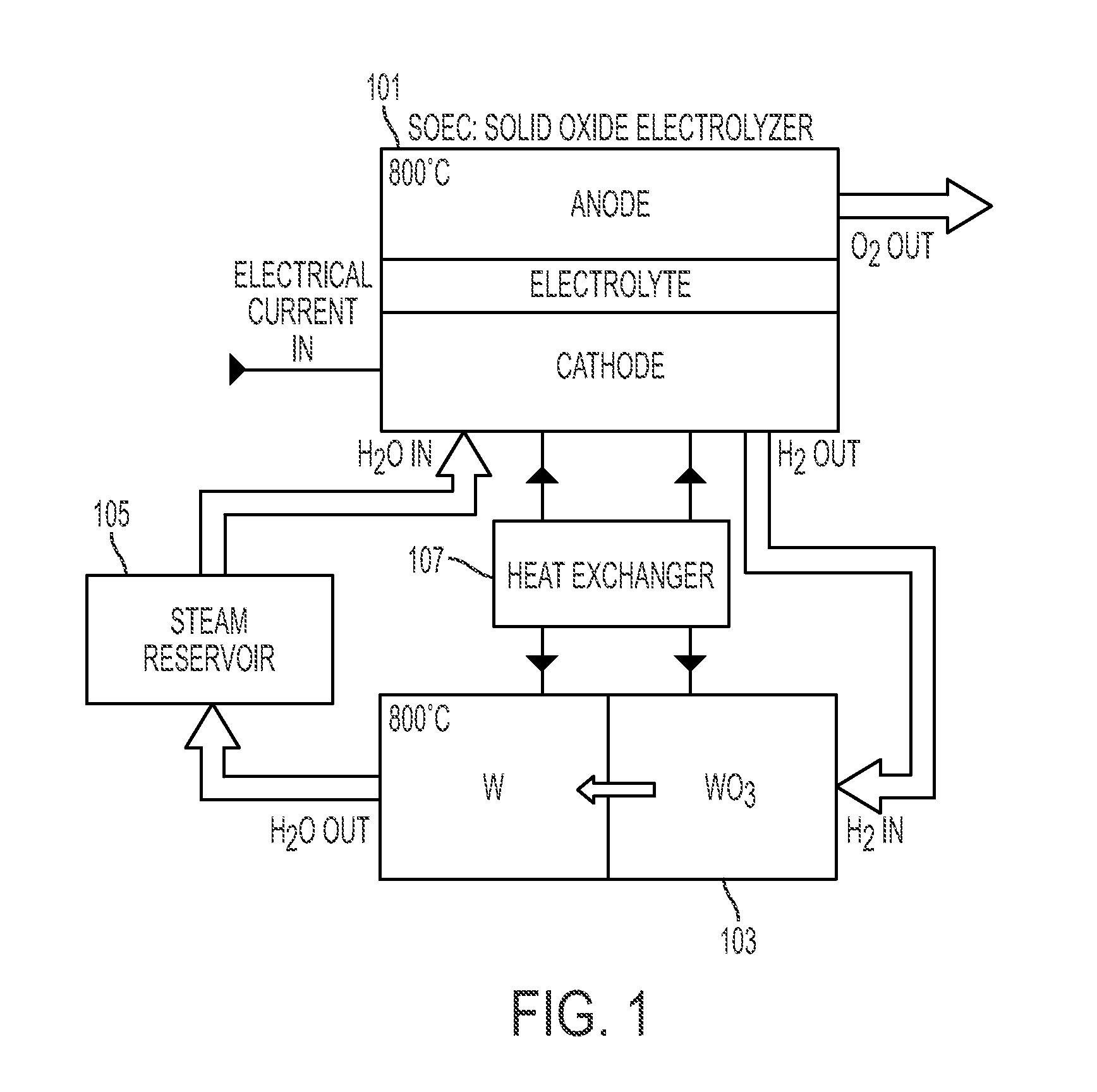
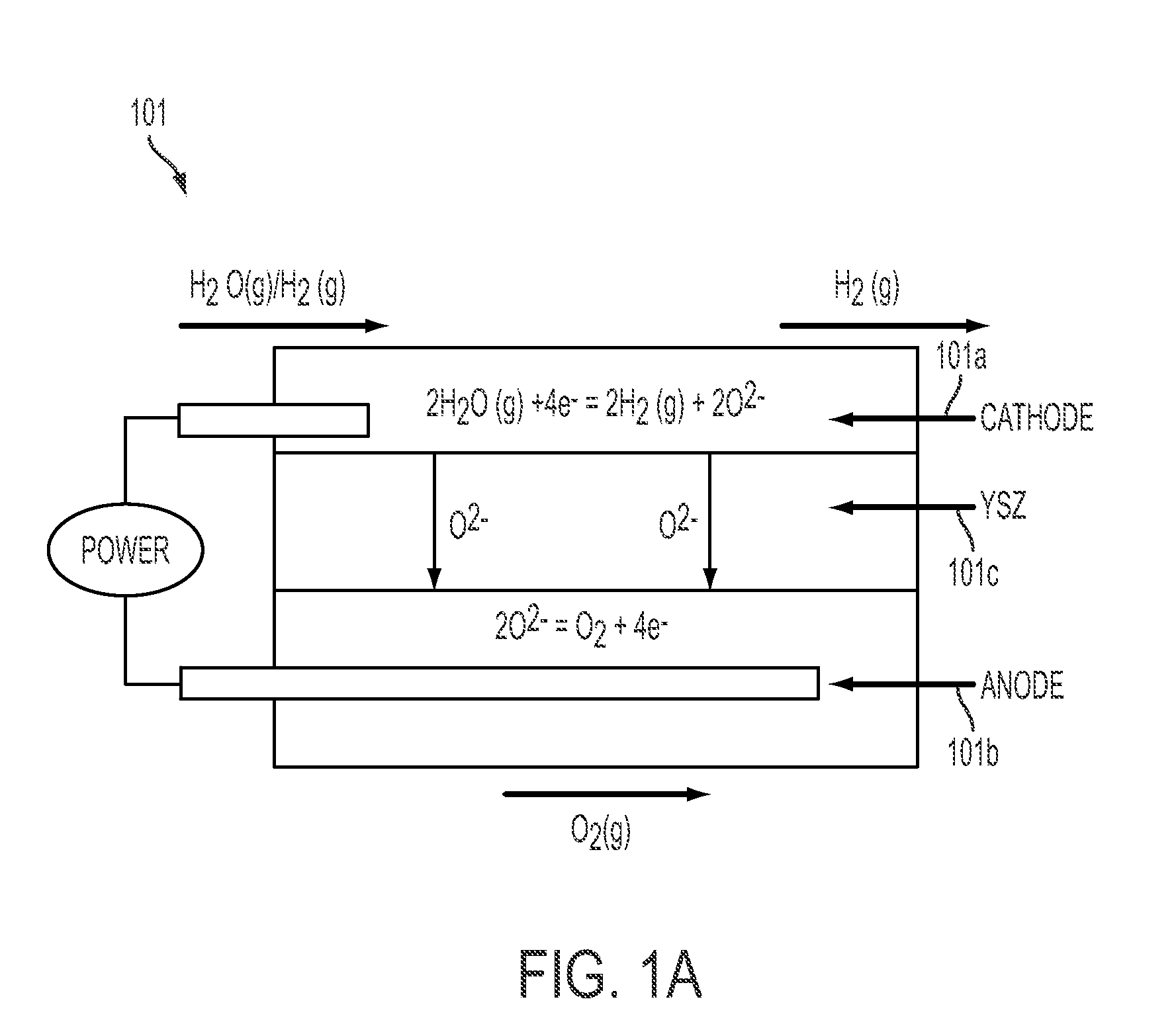
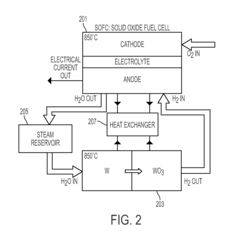
- A reversible solid oxide electrochemical cell (RSOEC) system using a porous cathode, anode, and electrolyte with a reactor containing tungsten or tungsten oxide, capable of electrolyzing water to store energy and converting back to electricity, operating between 600°C to 1000°C, with a heat exchanger for efficient energy transfer.
- The use of a positive electrode with a tungsten-containing active material and a negative electrode featuring carbon-coated solid graphite, where the graphite has a low void percentage and is coated with a carbonaceous material at a mass percentage of 12.0% or more, effectively suppresses the precipitation of tungsten on the graphite surface, thereby maintaining capacity.
Environmental Impact of Tungsten in ESS
The environmental impact of tungsten in Energy Storage Systems (ESS) is a critical consideration as the demand for energy storage solutions continues to grow. Tungsten, known for its high melting point and excellent electrical conductivity, plays a significant role in various components of ESS, particularly in electrodes and current collectors.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with tungsten in ESS is its extraction process. Tungsten mining can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The extraction often involves open-pit mining, which can result in large-scale landscape alterations and ecosystem disruptions. Additionally, the processing of tungsten ore requires substantial energy and water resources, contributing to increased carbon emissions and water stress in mining regions.
The production of tungsten-based components for ESS also raises environmental issues. The manufacturing process involves high-temperature treatments and chemical processes that can release harmful emissions if not properly controlled. These emissions may include particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, and greenhouse gases, potentially impacting air quality and contributing to climate change.
However, the use of tungsten in ESS also offers environmental benefits. Its durability and resistance to corrosion contribute to longer-lasting energy storage systems, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. This longevity can lead to a lower overall environmental footprint over the lifecycle of the ESS.
Recycling and end-of-life management of tungsten-containing ESS components present both challenges and opportunities. While tungsten is recyclable, the complex nature of ESS often makes the separation and recovery process difficult and energy-intensive. Improving recycling technologies and implementing effective collection systems are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of tungsten in ESS.
The potential for tungsten to leach into the environment from discarded or improperly managed ESS is another concern. Although tungsten is generally considered to have low toxicity, its accumulation in soil and water bodies could have long-term ecological effects that are not yet fully understood. This underscores the importance of proper disposal and recycling practices for ESS components containing tungsten.
In conclusion, while tungsten offers valuable properties for enhancing the performance of Energy Storage Systems, its environmental impact throughout the lifecycle of ESS must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of tungsten use with sustainable practices in mining, manufacturing, and recycling is essential for minimizing negative environmental consequences and maximizing the positive contributions of ESS to clean energy solutions.
Supply Chain Considerations for Tungsten ESS
The supply chain for tungsten-based energy storage systems (ESS) presents unique challenges and opportunities that significantly impact the development and deployment of these technologies. Tungsten, a rare metal with exceptional properties, is a critical component in various ESS applications, particularly in high-temperature and high-power density systems.
The global tungsten supply chain is characterized by geographical concentration, with China dominating both production and processing. This concentration poses potential risks in terms of supply stability and price volatility. As demand for tungsten in ESS applications grows, diversification of supply sources becomes increasingly important to mitigate these risks.
Extraction and processing of tungsten ore are complex and energy-intensive processes, which can impact the overall environmental footprint of tungsten-based ESS. Sustainable mining practices and efficient processing technologies are crucial for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring long-term viability of the supply chain.
Recycling and circular economy principles play a vital role in the tungsten ESS supply chain. Given the scarcity and value of tungsten, developing effective recycling processes for end-of-life ESS components can significantly reduce reliance on primary production and improve overall resource efficiency.
The manufacturing of tungsten components for ESS requires specialized equipment and expertise. Establishing robust manufacturing capabilities and fostering innovation in production techniques are essential for scaling up tungsten-based ESS technologies and reducing costs.
Quality control throughout the supply chain is critical, as the performance and reliability of ESS heavily depend on the purity and consistency of tungsten components. Implementing stringent quality standards and traceability measures ensures the integrity of the final products.
Logistics and transportation of tungsten materials and components present challenges due to their high density and potential regulatory restrictions. Optimizing transportation routes and modes can significantly impact the overall cost and environmental footprint of tungsten-based ESS.
Collaboration between ESS manufacturers, tungsten suppliers, and research institutions is crucial for addressing supply chain challenges and driving innovation. Such partnerships can lead to the development of new tungsten alloys or composites tailored for specific ESS applications, potentially improving performance and reducing material requirements.
As the demand for energy storage solutions grows, particularly in renewable energy integration and grid stabilization, the tungsten ESS supply chain must evolve to meet these needs. This evolution may involve developing new mining techniques, improving processing efficiencies, and exploring alternative materials that can complement or partially replace tungsten in certain applications.