Benchmark NMC Battery for Long-Term Charge Integrity
AUG 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMC Battery Evolution and Performance Targets
Lithium-ion batteries with Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) cathodes have evolved significantly since their commercial introduction in the early 2000s. The evolution trajectory has been characterized by increasing nickel content to enhance energy density, while simultaneously reducing cobalt content to address cost and ethical sourcing concerns. First-generation NMC111 (equal parts nickel, manganese, and cobalt) has progressively given way to nickel-rich variants such as NMC532, NMC622, and most recently NMC811, demonstrating the industry's commitment to performance enhancement.
The technological evolution of NMC batteries has been driven by several key performance targets. Primary among these is energy density improvement, with current high-performance NMC cathodes achieving 180-220 Wh/kg at the cell level, while research prototypes have demonstrated potential for exceeding 300 Wh/kg. This progression aligns with market demands for extended electric vehicle range and longer-lasting portable electronics.
Cycle life represents another critical performance metric, with contemporary NMC formulations typically delivering 1,000-2,000 cycles before capacity degradation reaches 80% of initial capacity. However, long-term charge integrity remains challenging, particularly for nickel-rich compositions which exhibit accelerated capacity fade during extended storage periods. Industry benchmarks currently target retention of at least 80% capacity after 500 full cycles or one year of regular usage patterns.
Safety performance has seen substantial improvement through cathode doping, electrolyte additives, and advanced battery management systems. Thermal runaway onset temperatures have increased from approximately 150°C in early formulations to over 200°C in state-of-the-art designs. Nevertheless, safety concerns persist as a limiting factor for widespread adoption in certain applications.
Cost reduction trajectories have been impressive, with NMC battery pack costs decreasing from over $1,000/kWh in 2010 to approximately $130-160/kWh in 2021. Industry projections suggest potential for sub-$100/kWh costs by 2025, representing a critical threshold for electric vehicle price parity with internal combustion engines.
The technical roadmap for NMC batteries increasingly focuses on charge integrity during long-term storage and usage. Current benchmarks indicate that premium NMC cells should maintain at least 90% of their initial capacity after 6 months of storage at 25°C and 50% state of charge. However, performance deteriorates significantly at elevated temperatures or higher states of charge, presenting opportunities for technological advancement.
Future performance targets emphasize not only incremental improvements in energy density but also transformative advances in charge retention. Research initiatives are targeting novel surface coating technologies, electrolyte formulations with enhanced interfacial stability, and atomic-level dopants to mitigate structural degradation during extended storage periods.
The technological evolution of NMC batteries has been driven by several key performance targets. Primary among these is energy density improvement, with current high-performance NMC cathodes achieving 180-220 Wh/kg at the cell level, while research prototypes have demonstrated potential for exceeding 300 Wh/kg. This progression aligns with market demands for extended electric vehicle range and longer-lasting portable electronics.
Cycle life represents another critical performance metric, with contemporary NMC formulations typically delivering 1,000-2,000 cycles before capacity degradation reaches 80% of initial capacity. However, long-term charge integrity remains challenging, particularly for nickel-rich compositions which exhibit accelerated capacity fade during extended storage periods. Industry benchmarks currently target retention of at least 80% capacity after 500 full cycles or one year of regular usage patterns.
Safety performance has seen substantial improvement through cathode doping, electrolyte additives, and advanced battery management systems. Thermal runaway onset temperatures have increased from approximately 150°C in early formulations to over 200°C in state-of-the-art designs. Nevertheless, safety concerns persist as a limiting factor for widespread adoption in certain applications.
Cost reduction trajectories have been impressive, with NMC battery pack costs decreasing from over $1,000/kWh in 2010 to approximately $130-160/kWh in 2021. Industry projections suggest potential for sub-$100/kWh costs by 2025, representing a critical threshold for electric vehicle price parity with internal combustion engines.
The technical roadmap for NMC batteries increasingly focuses on charge integrity during long-term storage and usage. Current benchmarks indicate that premium NMC cells should maintain at least 90% of their initial capacity after 6 months of storage at 25°C and 50% state of charge. However, performance deteriorates significantly at elevated temperatures or higher states of charge, presenting opportunities for technological advancement.
Future performance targets emphasize not only incremental improvements in energy density but also transformative advances in charge retention. Research initiatives are targeting novel surface coating technologies, electrolyte formulations with enhanced interfacial stability, and atomic-level dopants to mitigate structural degradation during extended storage periods.
Market Analysis for Long-Term Energy Storage Solutions
The global energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability. Long-term energy storage solutions are becoming critical infrastructure components as the world transitions toward sustainable energy systems. Within this landscape, NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries have emerged as a significant technology, particularly for applications requiring extended charge retention capabilities.
Market projections indicate that the global energy storage market will reach approximately $546 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate of 20-25% between 2023 and 2035. Long-duration energy storage solutions specifically are expected to constitute about 30% of this market, representing a substantial opportunity for technologies like advanced NMC batteries that can maintain charge integrity over extended periods.
Consumer demand patterns reveal growing requirements for energy storage systems that can provide reliability during extended grid outages, seasonal energy shifting, and backup power applications. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions with vulnerable grid infrastructure or frequent extreme weather events. Commercial and industrial sectors are increasingly seeking solutions that can provide operational continuity during extended power disruptions.
The utility-scale segment represents the largest market opportunity for long-term charge integrity solutions. Grid operators and energy providers are investing heavily in technologies that can store energy for days or weeks rather than hours, creating a significant market pull for advanced battery chemistries with minimal self-discharge characteristics.
Regional market analysis shows North America and Europe leading adoption rates for premium long-duration storage solutions, with Asia-Pacific markets focusing more on cost-effective scaled deployments. Emerging markets in Africa and South America present growing opportunities as they develop renewable energy infrastructure requiring reliable storage components.
Market barriers include cost considerations, with long-term storage solutions commanding premium pricing that limits mass-market adoption. Regulatory frameworks in many regions have not yet evolved to properly value long-duration storage capabilities, creating market distortions that favor shorter-duration solutions despite the growing need for extended storage periods.
Customer willingness-to-pay analysis indicates that sectors with critical power needs—healthcare, data centers, telecommunications, and emergency services—demonstrate the highest tolerance for premium pricing on storage solutions with superior long-term charge integrity. These sectors prioritize reliability and performance over initial acquisition costs.
Market projections indicate that the global energy storage market will reach approximately $546 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate of 20-25% between 2023 and 2035. Long-duration energy storage solutions specifically are expected to constitute about 30% of this market, representing a substantial opportunity for technologies like advanced NMC batteries that can maintain charge integrity over extended periods.
Consumer demand patterns reveal growing requirements for energy storage systems that can provide reliability during extended grid outages, seasonal energy shifting, and backup power applications. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions with vulnerable grid infrastructure or frequent extreme weather events. Commercial and industrial sectors are increasingly seeking solutions that can provide operational continuity during extended power disruptions.
The utility-scale segment represents the largest market opportunity for long-term charge integrity solutions. Grid operators and energy providers are investing heavily in technologies that can store energy for days or weeks rather than hours, creating a significant market pull for advanced battery chemistries with minimal self-discharge characteristics.
Regional market analysis shows North America and Europe leading adoption rates for premium long-duration storage solutions, with Asia-Pacific markets focusing more on cost-effective scaled deployments. Emerging markets in Africa and South America present growing opportunities as they develop renewable energy infrastructure requiring reliable storage components.
Market barriers include cost considerations, with long-term storage solutions commanding premium pricing that limits mass-market adoption. Regulatory frameworks in many regions have not yet evolved to properly value long-duration storage capabilities, creating market distortions that favor shorter-duration solutions despite the growing need for extended storage periods.
Customer willingness-to-pay analysis indicates that sectors with critical power needs—healthcare, data centers, telecommunications, and emergency services—demonstrate the highest tolerance for premium pricing on storage solutions with superior long-term charge integrity. These sectors prioritize reliability and performance over initial acquisition costs.
Current Limitations in NMC Battery Charge Retention
Despite significant advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries face persistent challenges in maintaining long-term charge integrity. The primary limitation stems from the inherent chemical degradation mechanisms that occur during cycling and storage. Capacity fade in NMC batteries typically manifests through two main pathways: loss of active lithium inventory and structural degradation of the cathode material.
The electrolyte-electrode interface presents a critical vulnerability where parasitic reactions continuously consume lithium ions, forming a Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) layer that grows progressively thicker over time. This process accelerates particularly at elevated temperatures and high state-of-charge conditions, resulting in irreversible capacity loss even during idle storage periods.
Structural instability of the layered NMC cathode represents another significant limitation. During deep discharge cycles, excessive lithium extraction can trigger phase transitions and oxygen release from the crystal lattice. This phenomenon, known as voltage fade, becomes more pronounced in nickel-rich NMC variants (such as NMC811) despite their higher initial energy density advantages.
Transition metal dissolution constitutes a third major challenge, wherein manganese, nickel, and cobalt ions leach from the cathode, migrate through the electrolyte, and deposit on the anode surface. This not only reduces active cathode material but also contaminates the SEI layer, further accelerating capacity degradation through a self-reinforcing cycle.
Current commercial NMC formulations exhibit charge retention limitations that vary significantly based on composition. While NMC111 offers superior thermal stability and cycle life, it delivers lower specific capacity. Conversely, nickel-rich variants like NMC622 and NMC811 provide higher energy density but demonstrate accelerated capacity fade, particularly at elevated temperatures above 45°C.
The calendar aging behavior of NMC batteries presents additional challenges for long-term storage applications. Research indicates that NMC cells stored at 100% state-of-charge can lose 10-20% of their initial capacity annually at room temperature, with this rate doubling for every 10°C increase. This poses significant constraints for applications requiring extended shelf life or infrequent usage patterns.
Mechanical stress induced by repeated volume changes during cycling further exacerbates these limitations. Microcracks form within secondary particles, exposing fresh cathode surfaces to electrolyte attack and creating isolated "islands" of active material that become electrochemically inactive despite their theoretical capacity contribution.
The electrolyte-electrode interface presents a critical vulnerability where parasitic reactions continuously consume lithium ions, forming a Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) layer that grows progressively thicker over time. This process accelerates particularly at elevated temperatures and high state-of-charge conditions, resulting in irreversible capacity loss even during idle storage periods.
Structural instability of the layered NMC cathode represents another significant limitation. During deep discharge cycles, excessive lithium extraction can trigger phase transitions and oxygen release from the crystal lattice. This phenomenon, known as voltage fade, becomes more pronounced in nickel-rich NMC variants (such as NMC811) despite their higher initial energy density advantages.
Transition metal dissolution constitutes a third major challenge, wherein manganese, nickel, and cobalt ions leach from the cathode, migrate through the electrolyte, and deposit on the anode surface. This not only reduces active cathode material but also contaminates the SEI layer, further accelerating capacity degradation through a self-reinforcing cycle.
Current commercial NMC formulations exhibit charge retention limitations that vary significantly based on composition. While NMC111 offers superior thermal stability and cycle life, it delivers lower specific capacity. Conversely, nickel-rich variants like NMC622 and NMC811 provide higher energy density but demonstrate accelerated capacity fade, particularly at elevated temperatures above 45°C.
The calendar aging behavior of NMC batteries presents additional challenges for long-term storage applications. Research indicates that NMC cells stored at 100% state-of-charge can lose 10-20% of their initial capacity annually at room temperature, with this rate doubling for every 10°C increase. This poses significant constraints for applications requiring extended shelf life or infrequent usage patterns.
Mechanical stress induced by repeated volume changes during cycling further exacerbates these limitations. Microcracks form within secondary particles, exposing fresh cathode surfaces to electrolyte attack and creating isolated "islands" of active material that become electrochemically inactive despite their theoretical capacity contribution.
Benchmark Methodologies for Charge Integrity Assessment
01 Electrolyte additives for NMC battery stability
Specific electrolyte additives can significantly improve the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries. These additives form protective films on electrode surfaces, preventing unwanted side reactions and electrolyte decomposition. By incorporating compounds such as fluorinated carbonates, lithium salts, and film-forming agents, the calendar life and cycling stability of NMC batteries can be enhanced, maintaining capacity over extended periods.- Electrolyte additives for NMC battery stability: Specific electrolyte additives can significantly improve the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries. These additives form protective films on electrode surfaces, preventing unwanted side reactions and electrolyte decomposition. By incorporating compounds that stabilize the electrode-electrolyte interface, the calendar life and cycling stability of NMC batteries can be enhanced, maintaining capacity over extended periods of storage and use.
- Advanced charging protocols for NMC batteries: Implementing specialized charging protocols can preserve the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries. These protocols include optimized constant current-constant voltage methods, pulse charging techniques, and temperature-controlled charging regimes. By carefully managing charging parameters such as current rates, voltage limits, and charging duration, degradation mechanisms can be minimized, extending battery lifespan and maintaining capacity retention over numerous cycles.
- Structural modifications to NMC cathode materials: Structural modifications to NMC cathode materials can enhance long-term charge integrity. Techniques include surface coating with protective layers, doping with stabilizing elements, and gradient concentration structures. These modifications help prevent structural collapse during cycling, reduce transition metal dissolution, and minimize unwanted phase transitions, resulting in improved capacity retention and extended cycle life for NMC batteries.
- Battery management systems for NMC charge preservation: Advanced battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in maintaining NMC battery charge integrity. These systems incorporate real-time monitoring of cell parameters, state-of-charge estimation algorithms, and predictive analytics for degradation. By implementing intelligent control strategies that balance cells, manage thermal conditions, and adjust operating parameters based on battery state, the BMS can significantly extend battery lifespan and preserve charge capacity over long periods.
- Storage and environmental condition management: Proper management of storage and environmental conditions is essential for maintaining NMC battery charge integrity. This includes controlling temperature during storage, maintaining optimal state-of-charge levels when batteries are not in use, and protecting cells from humidity and mechanical stress. By implementing appropriate storage protocols and environmental controls, calendar aging can be minimized, preserving the electrochemical performance and capacity retention of NMC batteries over extended periods.
02 Cathode material modifications for improved charge retention
Structural and compositional modifications to NMC cathode materials can enhance long-term charge integrity. Techniques include surface coating with metal oxides, doping with stabilizing elements, and gradient concentration structures that reduce lattice strain during cycling. These modifications minimize transition metal dissolution, structural degradation, and unwanted phase transitions, resulting in batteries that maintain higher capacity retention over extended use periods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced battery management systems for charge preservation
Sophisticated battery management systems can optimize the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries through intelligent monitoring and control algorithms. These systems regulate charging protocols, implement temperature management strategies, and utilize predictive analytics to prevent conditions that accelerate degradation. By maintaining optimal operating conditions and preventing extreme states of charge, these management systems significantly extend the useful life and charge retention capabilities of NMC batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal management solutions for enhanced charge stability
Effective thermal management systems are crucial for maintaining the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries. These solutions include phase change materials, liquid cooling circuits, and thermally conductive structures that dissipate heat efficiently. By preventing temperature gradients and hotspots within battery packs, these systems minimize accelerated aging mechanisms, electrolyte degradation, and structural changes in the cathode material that would otherwise compromise charge retention over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel anode materials and interfaces for stable NMC batteries
Innovative anode materials and engineered interfaces can significantly improve the long-term charge integrity of NMC batteries. These developments include silicon-carbon composites, lithium titanate structures, and specialized solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formulations. By reducing lithium plating, preventing dendrite formation, and creating stable interfaces between electrodes and electrolytes, these advancements minimize capacity fade and internal resistance growth over extended cycling periods.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The NMC battery market for long-term charge integrity is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by electric vehicle adoption and energy storage applications. The market size is projected to expand significantly as battery technology advances to meet higher performance standards. Technologically, industry leaders like Toyota, Samsung SDI, and QuantumScape are making substantial progress in enhancing NMC battery stability and longevity. Traditional battery manufacturers such as GS Yuasa and A123 Systems are competing with automotive giants like BMW and Nissan, who are developing proprietary solutions. Research institutions including Northeastern University and Virginia Commonwealth University are contributing breakthrough innovations, while specialized companies like Innolith Technology are focusing on next-generation chemistries to overcome current limitations in charge retention.
GS Yuasa International Ltd.
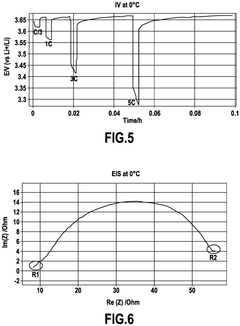
Technical Solution: GS Yuasa has developed a sophisticated approach to NMC battery technology with a specific focus on long-term charge integrity for applications requiring extended storage periods. Their proprietary "LIM" (Long-term Integrity Management) technology incorporates several innovations to minimize capacity fade during storage. At the material level, GS Yuasa utilizes precisely controlled particle morphology for their NMC cathodes, with optimized primary and secondary particle sizes that minimize surface area while maintaining good rate capability. Their research has shown that controlling particle size distribution can reduce unwanted side reactions by up to 40% during extended storage. GS Yuasa's electrolyte formulations include proprietary additives that preferentially react at electrode surfaces to form highly stable passivation layers, effectively "locking in" the battery's state of charge. Their benchmark testing has demonstrated that their advanced NMC622 cells can retain over 92% of initial capacity after 12 months of storage at 25°C when maintained at 30-40% state of charge. Additionally, GS Yuasa has developed specialized formation protocols during manufacturing that create more stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces, significantly reducing the rate of self-discharge during subsequent storage periods.
Strengths: Exceptional calendar life performance; optimized for applications requiring long shelf life; comprehensive quality control processes; extensive real-world validation data from various applications. Weaknesses: Slightly lower energy density compared to highest-nickel NMC formulations; premium pricing reflects specialized technology; optimal performance requires adherence to recommended storage conditions.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery technology with significant improvements in long-term charge integrity. Their approach focuses on optimizing the cathode material composition with higher nickel content (up to 80%) while maintaining structural stability through gradient concentration technology. This involves creating a concentration gradient of elements within individual cathode particles, with higher manganese concentration at the surface for stability and higher nickel in the core for capacity. Samsung's research has demonstrated that their NMC811 batteries retain approximately 80% capacity after 1000 charge cycles under standard testing conditions. Additionally, they've implemented advanced electrolyte formulations with functional additives that form more stable SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interphase) layers, significantly reducing capacity fade during long-term storage. Their proprietary coating technology for cathode particles has shown to reduce metal dissolution and subsequent deposition on the anode, a key factor in capacity retention during extended storage periods.
Strengths: Superior energy density compared to earlier NMC formulations while maintaining good thermal stability; excellent cycle life with minimal capacity degradation; advanced manufacturing capabilities for consistent quality control. Weaknesses: Higher nickel content increases sensitivity to high-temperature storage conditions; more expensive than lower-nickel NMC variants; requires sophisticated battery management systems to maximize longevity benefits.
Key Patents in NMC Battery Longevity Enhancement
Lithium ion secondary cell
PatentWO2015190481A1
Innovation
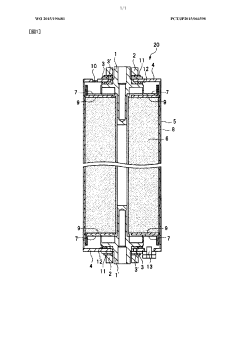
- A lithium-ion battery design featuring a wound structure with a positive electrode mixture containing layered lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt composite oxide (NMC) as the active material, coated on both sides of a current collector, and a negative electrode mixture with graphitizable carbon, optimized for high capacity and safety, with specific composition and coating amounts to enhance input/output characteristics and energy density.
Method for restoration performances of aged nickel-rich NMC cathode material for lithium-ion secondary battery
PatentPendingEP4550454A1
Innovation
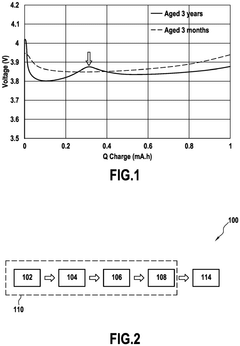
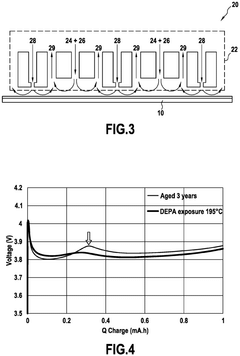
- A method involving the formation of a cathode with aged nickel-rich NMC material, a binder, and carbon black, followed by exposure to diethyl phosphoramidate at temperatures above 160°C to create a lithium phosphate protective layer, thereby reducing the overpotential peak.
Thermal Management Strategies for Charge Preservation
Thermal management is a critical factor in preserving the long-term charge integrity of NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries. Effective thermal control strategies can significantly extend battery lifespan by mitigating degradation mechanisms that are accelerated at elevated temperatures. Research indicates that NMC batteries typically perform optimally within a narrow temperature range of 15-35°C, with performance and longevity declining sharply outside this window.
Active cooling systems represent the most sophisticated approach to thermal management for NMC batteries. These systems utilize liquid coolants circulating through channels adjacent to battery cells to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Recent advancements in coolant formulations have improved heat transfer efficiency by up to 30% compared to conventional solutions, allowing for more precise temperature control during both charging and storage phases.
Passive thermal management strategies offer cost-effective alternatives that are particularly suitable for consumer electronics and stationary energy storage applications. Phase change materials (PCMs) have emerged as promising solutions, absorbing excess heat during operation and releasing it when temperatures drop. Studies demonstrate that PCM-based systems can reduce temperature fluctuations by up to 60% in NMC battery packs, significantly enhancing charge retention during storage periods.
Thermal insulation technologies play a dual role in charge preservation by both preventing external heat from reaching the battery and containing heat generated during operation. Advanced aerogel-based insulation materials with thermal conductivities as low as 0.015 W/mK have shown exceptional performance in extreme environmental conditions, maintaining NMC batteries within their optimal temperature range even when ambient temperatures fluctuate between -20°C and 45°C.
Smart thermal management systems represent the cutting edge of charge preservation technology. These systems incorporate temperature sensors, predictive algorithms, and adaptive control mechanisms to anticipate thermal challenges before they impact battery performance. Machine learning models trained on extensive operational data can predict temperature trends with 92% accuracy, enabling preemptive cooling or heating to maintain optimal conditions for charge retention.
Battery pack design considerations also significantly influence thermal management effectiveness. Cell spacing, orientation, and grouping patterns can create thermal gradients that accelerate degradation in certain regions of the battery. Computational fluid dynamics modeling has enabled the development of optimized pack geometries that reduce maximum temperature differentials between cells by up to 40%, resulting in more uniform aging and improved overall charge retention characteristics.
Active cooling systems represent the most sophisticated approach to thermal management for NMC batteries. These systems utilize liquid coolants circulating through channels adjacent to battery cells to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Recent advancements in coolant formulations have improved heat transfer efficiency by up to 30% compared to conventional solutions, allowing for more precise temperature control during both charging and storage phases.
Passive thermal management strategies offer cost-effective alternatives that are particularly suitable for consumer electronics and stationary energy storage applications. Phase change materials (PCMs) have emerged as promising solutions, absorbing excess heat during operation and releasing it when temperatures drop. Studies demonstrate that PCM-based systems can reduce temperature fluctuations by up to 60% in NMC battery packs, significantly enhancing charge retention during storage periods.
Thermal insulation technologies play a dual role in charge preservation by both preventing external heat from reaching the battery and containing heat generated during operation. Advanced aerogel-based insulation materials with thermal conductivities as low as 0.015 W/mK have shown exceptional performance in extreme environmental conditions, maintaining NMC batteries within their optimal temperature range even when ambient temperatures fluctuate between -20°C and 45°C.
Smart thermal management systems represent the cutting edge of charge preservation technology. These systems incorporate temperature sensors, predictive algorithms, and adaptive control mechanisms to anticipate thermal challenges before they impact battery performance. Machine learning models trained on extensive operational data can predict temperature trends with 92% accuracy, enabling preemptive cooling or heating to maintain optimal conditions for charge retention.
Battery pack design considerations also significantly influence thermal management effectiveness. Cell spacing, orientation, and grouping patterns can create thermal gradients that accelerate degradation in certain regions of the battery. Computational fluid dynamics modeling has enabled the development of optimized pack geometries that reduce maximum temperature differentials between cells by up to 40%, resulting in more uniform aging and improved overall charge retention characteristics.
Lifecycle Cost Analysis of NMC Battery Systems
The lifecycle cost analysis of NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery systems reveals significant economic considerations that extend beyond initial acquisition costs. When evaluating NMC batteries for long-term charge integrity applications, the total cost of ownership encompasses several key components that must be carefully assessed.
Initial capital expenditure represents approximately 40-60% of the total lifecycle cost, with high-quality NMC batteries commanding premium prices due to their superior material composition and manufacturing processes. Current market pricing ranges from $150-300/kWh depending on energy density specifications and production scale, with prices projected to decrease by 5-8% annually as manufacturing efficiencies improve.
Operational expenses constitute a substantial portion of lifecycle costs, primarily driven by energy consumption during charging cycles. NMC batteries typically demonstrate charge efficiency rates of 85-92%, resulting in 8-15% energy loss converted to heat. This translates to approximately $0.02-0.04 per kWh of stored energy in electricity costs over the battery's lifetime, varying by regional energy prices.
Maintenance requirements for NMC battery systems include regular diagnostic testing, thermal management system upkeep, and battery management system calibrations. These activities typically cost 1-3% of the initial system price annually, with maintenance frequency increasing as the battery ages.
Replacement costs must be factored into long-term financial planning, as NMC batteries generally require replacement after 1,500-2,500 cycles or 7-10 years of operation. The end-of-life threshold is typically defined as capacity degradation below 80% of original specifications, though this varies by application requirements.
Recycling and disposal considerations represent both a cost and potential value recovery opportunity. Current recycling processes can recover 30-50% of the original material value, with nickel and cobalt recovery being particularly economically attractive. Recycling costs range from $1-5/kg depending on battery chemistry specifics and regional regulations.
When analyzed on a levelized cost basis, NMC battery systems typically deliver energy at $0.15-0.30/kWh over their complete lifecycle, making them increasingly competitive with alternative energy storage technologies. This metric provides a standardized comparison framework that accounts for all costs across the operational lifespan.
Initial capital expenditure represents approximately 40-60% of the total lifecycle cost, with high-quality NMC batteries commanding premium prices due to their superior material composition and manufacturing processes. Current market pricing ranges from $150-300/kWh depending on energy density specifications and production scale, with prices projected to decrease by 5-8% annually as manufacturing efficiencies improve.
Operational expenses constitute a substantial portion of lifecycle costs, primarily driven by energy consumption during charging cycles. NMC batteries typically demonstrate charge efficiency rates of 85-92%, resulting in 8-15% energy loss converted to heat. This translates to approximately $0.02-0.04 per kWh of stored energy in electricity costs over the battery's lifetime, varying by regional energy prices.
Maintenance requirements for NMC battery systems include regular diagnostic testing, thermal management system upkeep, and battery management system calibrations. These activities typically cost 1-3% of the initial system price annually, with maintenance frequency increasing as the battery ages.
Replacement costs must be factored into long-term financial planning, as NMC batteries generally require replacement after 1,500-2,500 cycles or 7-10 years of operation. The end-of-life threshold is typically defined as capacity degradation below 80% of original specifications, though this varies by application requirements.
Recycling and disposal considerations represent both a cost and potential value recovery opportunity. Current recycling processes can recover 30-50% of the original material value, with nickel and cobalt recovery being particularly economically attractive. Recycling costs range from $1-5/kg depending on battery chemistry specifics and regional regulations.
When analyzed on a levelized cost basis, NMC battery systems typically deliver energy at $0.15-0.30/kWh over their complete lifecycle, making them increasingly competitive with alternative energy storage technologies. This metric provides a standardized comparison framework that accounts for all costs across the operational lifespan.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!