Comparative Analysis of PEEK Polymer Versus PTFE in MedTech
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEEK and PTFE Evolution in Medical Technology
The evolution of PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) in medical technology represents a fascinating journey of material science innovation addressing healthcare challenges. PTFE, commercially known as Teflon, was discovered in 1938 by Roy Plunkett at DuPont and first entered medical applications in the 1960s with vascular grafts. Its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction properties made it revolutionary for implantable devices. PEEK emerged later, developed by ICI (Imperial Chemical Industries) in 1978, but gained significant medical adoption only in the 1990s as a high-performance thermoplastic alternative to metal implants.
The technological trajectory of these polymers has been shaped by increasing demands for biocompatible materials with specific mechanical properties. PTFE's evolution focused on enhancing its porosity and integration capabilities, leading to expanded PTFE (ePTFE) development in the 1970s, which significantly improved tissue integration for vascular applications. Meanwhile, PEEK development concentrated on improving its mechanical strength and radiolucency, with carbon-reinforced PEEK composites emerging in the early 2000s to better mimic bone properties.
Regulatory milestones have profoundly influenced both materials' adoption curves. PTFE received FDA approval for vascular applications in the 1960s, while PEEK's medical-grade variants gained approval in the late 1990s, particularly for spinal implants. These regulatory clearances triggered accelerated innovation cycles and broader clinical applications for both polymers.
Recent technological advancements have focused on surface modifications and composite formulations. Since 2010, hydroxyapatite-coated PEEK has emerged to enhance osseointegration properties, while antimicrobial PTFE variants address infection concerns in implantable devices. The development of 3D-printable PEEK formulations around 2015 marked another significant milestone, enabling patient-specific implant manufacturing.
The convergence of these materials with digital manufacturing technologies represents the current frontier. Computer-aided design combined with advanced manufacturing techniques has enabled unprecedented customization of both PEEK and PTFE components. Simultaneously, research into bioactive surface treatments continues to enhance their integration with biological tissues, pointing toward future innovations in drug-eluting capabilities and smart implant technologies incorporating these versatile polymers.
The technological trajectory of these polymers has been shaped by increasing demands for biocompatible materials with specific mechanical properties. PTFE's evolution focused on enhancing its porosity and integration capabilities, leading to expanded PTFE (ePTFE) development in the 1970s, which significantly improved tissue integration for vascular applications. Meanwhile, PEEK development concentrated on improving its mechanical strength and radiolucency, with carbon-reinforced PEEK composites emerging in the early 2000s to better mimic bone properties.
Regulatory milestones have profoundly influenced both materials' adoption curves. PTFE received FDA approval for vascular applications in the 1960s, while PEEK's medical-grade variants gained approval in the late 1990s, particularly for spinal implants. These regulatory clearances triggered accelerated innovation cycles and broader clinical applications for both polymers.
Recent technological advancements have focused on surface modifications and composite formulations. Since 2010, hydroxyapatite-coated PEEK has emerged to enhance osseointegration properties, while antimicrobial PTFE variants address infection concerns in implantable devices. The development of 3D-printable PEEK formulations around 2015 marked another significant milestone, enabling patient-specific implant manufacturing.
The convergence of these materials with digital manufacturing technologies represents the current frontier. Computer-aided design combined with advanced manufacturing techniques has enabled unprecedented customization of both PEEK and PTFE components. Simultaneously, research into bioactive surface treatments continues to enhance their integration with biological tissues, pointing toward future innovations in drug-eluting capabilities and smart implant technologies incorporating these versatile polymers.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Performance Polymers
The global market for high-performance polymers in medical technology has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand for biocompatible materials with superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) have emerged as leading materials in this segment, with the combined market value reaching approximately $3.2 billion in 2022 and projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% through 2028.
The demand for these advanced polymers is primarily fueled by the expanding medical device industry, particularly in orthopedic implants, dental applications, cardiovascular devices, and minimally invasive surgical instruments. The aging global population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases have significantly contributed to this growth trajectory, with North America and Europe currently representing the largest market shares at 38% and 29% respectively.
Healthcare providers increasingly seek materials that can reduce implant-related complications and extend device longevity, creating substantial market pull for both PEEK and PTFE. PEEK has gained particular traction in orthopedic and spinal applications due to its bone-like mechanical properties and radiolucency, with market adoption increasing by 12.3% annually since 2018.
Meanwhile, PTFE continues to dominate in cardiovascular applications, where its exceptional lubricity and chemical inertness make it ideal for vascular grafts and catheter components. The PTFE medical market segment has maintained steady growth at 5.7% annually, with particular strength in developed healthcare markets.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, represent the fastest-growing markets for both polymers, with China and India showing annual growth rates exceeding 15%. This regional expansion is driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing medical tourism, and growing domestic medical device manufacturing capabilities.
Recent regulatory changes favoring materials with established biocompatibility profiles have further accelerated market adoption of both PEEK and PTFE. The FDA's Safety and Performance Based Pathway program has created streamlined approval processes for devices using these well-characterized materials, reducing time-to-market for manufacturers and stimulating innovation in application design.
Customer demand increasingly focuses on customized formulations of these polymers, with enhanced properties such as antimicrobial characteristics, improved imaging compatibility, and optimized surface properties. This trend toward specialized high-performance polymers is expected to create premium market segments with higher margins and specialized applications, particularly in regenerative medicine and personalized implant technologies.
The demand for these advanced polymers is primarily fueled by the expanding medical device industry, particularly in orthopedic implants, dental applications, cardiovascular devices, and minimally invasive surgical instruments. The aging global population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases have significantly contributed to this growth trajectory, with North America and Europe currently representing the largest market shares at 38% and 29% respectively.
Healthcare providers increasingly seek materials that can reduce implant-related complications and extend device longevity, creating substantial market pull for both PEEK and PTFE. PEEK has gained particular traction in orthopedic and spinal applications due to its bone-like mechanical properties and radiolucency, with market adoption increasing by 12.3% annually since 2018.
Meanwhile, PTFE continues to dominate in cardiovascular applications, where its exceptional lubricity and chemical inertness make it ideal for vascular grafts and catheter components. The PTFE medical market segment has maintained steady growth at 5.7% annually, with particular strength in developed healthcare markets.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, represent the fastest-growing markets for both polymers, with China and India showing annual growth rates exceeding 15%. This regional expansion is driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing medical tourism, and growing domestic medical device manufacturing capabilities.
Recent regulatory changes favoring materials with established biocompatibility profiles have further accelerated market adoption of both PEEK and PTFE. The FDA's Safety and Performance Based Pathway program has created streamlined approval processes for devices using these well-characterized materials, reducing time-to-market for manufacturers and stimulating innovation in application design.
Customer demand increasingly focuses on customized formulations of these polymers, with enhanced properties such as antimicrobial characteristics, improved imaging compatibility, and optimized surface properties. This trend toward specialized high-performance polymers is expected to create premium market segments with higher margins and specialized applications, particularly in regenerative medicine and personalized implant technologies.
Current Applications and Technical Limitations
PEEK (polyetheretherketone) and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) are extensively utilized in medical technology applications, each with distinct advantages and limitations. PEEK is predominantly employed in orthopedic implants, particularly spinal fusion cages, due to its exceptional mechanical strength and bone-like elastic modulus (3-4 GPa). Its radiolucency allows for clear post-operative imaging, while its biocompatibility supports osseointegration. Additionally, PEEK serves in dental implants, cranial plates, and cardiovascular applications such as heart valve components.
PTFE, conversely, dominates in vascular grafts and stent coatings owing to its superior thromboresistance and low friction coefficient (0.05-0.10). Its exceptional chemical inertness makes it ideal for implantable drug delivery systems and surgical sutures. PTFE's flexibility and softness also make it suitable for facial reconstructive implants and otolaryngological applications.
Despite these advantages, both materials face significant technical limitations. PEEK exhibits hydrophobicity with a water contact angle exceeding 80°, resulting in poor cell adhesion and limited bioactivity. This necessitates surface modifications through plasma treatment, laser texturing, or bioactive coating applications to enhance cellular response. Furthermore, PEEK's processing challenges include high melting temperature (343°C) and limited moldability, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
PTFE confronts manufacturing complexities due to its high melt viscosity (10^11-10^12 Pa·s) and poor melt processability. Conventional thermoplastic processing techniques are largely ineffective, necessitating specialized sintering processes. PTFE also demonstrates creep under sustained loading, with creep modulus decreasing by approximately 50% over 1000 hours at 23°C under constant load, limiting its application in load-bearing implants.
Sterilization presents challenges for both polymers. PEEK can experience surface oxidation during steam sterilization, while PTFE may degrade under gamma radiation, with mechanical properties declining by up to 30% after standard sterilization doses (25-40 kGy). This necessitates careful selection of sterilization methods based on specific application requirements.
Long-term in vivo stability remains a concern, particularly for PTFE, which can exhibit particulate generation in dynamic applications. PEEK, while more stable, may still experience surface degradation in highly oxidative environments. Both materials also face integration challenges with emerging technologies such as drug-eluting capabilities and smart implant functionalities, limiting their application in next-generation medical devices without significant modifications or composite formulations.
PTFE, conversely, dominates in vascular grafts and stent coatings owing to its superior thromboresistance and low friction coefficient (0.05-0.10). Its exceptional chemical inertness makes it ideal for implantable drug delivery systems and surgical sutures. PTFE's flexibility and softness also make it suitable for facial reconstructive implants and otolaryngological applications.
Despite these advantages, both materials face significant technical limitations. PEEK exhibits hydrophobicity with a water contact angle exceeding 80°, resulting in poor cell adhesion and limited bioactivity. This necessitates surface modifications through plasma treatment, laser texturing, or bioactive coating applications to enhance cellular response. Furthermore, PEEK's processing challenges include high melting temperature (343°C) and limited moldability, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
PTFE confronts manufacturing complexities due to its high melt viscosity (10^11-10^12 Pa·s) and poor melt processability. Conventional thermoplastic processing techniques are largely ineffective, necessitating specialized sintering processes. PTFE also demonstrates creep under sustained loading, with creep modulus decreasing by approximately 50% over 1000 hours at 23°C under constant load, limiting its application in load-bearing implants.
Sterilization presents challenges for both polymers. PEEK can experience surface oxidation during steam sterilization, while PTFE may degrade under gamma radiation, with mechanical properties declining by up to 30% after standard sterilization doses (25-40 kGy). This necessitates careful selection of sterilization methods based on specific application requirements.
Long-term in vivo stability remains a concern, particularly for PTFE, which can exhibit particulate generation in dynamic applications. PEEK, while more stable, may still experience surface degradation in highly oxidative environments. Both materials also face integration challenges with emerging technologies such as drug-eluting capabilities and smart implant functionalities, limiting their application in next-generation medical devices without significant modifications or composite formulations.
Comparative Properties and Processing Methods
01 PEEK and PTFE composite materials
Composite materials combining PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) offer enhanced properties compared to either polymer alone. These composites typically leverage PEEK's excellent mechanical strength and temperature resistance with PTFE's low friction and chemical resistance properties. The resulting materials find applications in demanding environments where both mechanical performance and tribological properties are required.- PEEK and PTFE composite materials: Composite materials combining PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) offer enhanced properties compared to either polymer alone. These composites typically leverage PEEK's excellent mechanical strength and temperature resistance with PTFE's low friction and chemical resistance properties. The resulting materials find applications in demanding environments where both mechanical performance and low friction are required.
- Processing methods for PEEK-PTFE blends: Various processing techniques are employed to create effective PEEK-PTFE blends, including melt processing, compression molding, and extrusion. These methods must account for the significant differences in melting points and processing characteristics between the two polymers. Special processing parameters and additives may be used to ensure proper dispersion of PTFE within the PEEK matrix and to achieve optimal bonding between the components.
- Surface modification of PEEK and PTFE: Surface treatments and modifications of PEEK and PTFE materials can enhance their compatibility with other materials or improve specific surface properties. Techniques include plasma treatment, chemical etching, and the application of coupling agents. These modifications can improve adhesion properties, wettability, or biocompatibility while maintaining the bulk properties of the polymers.
- PEEK-PTFE applications in medical devices: PEEK and PTFE materials, both individually and in combination, are extensively used in medical applications due to their biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties. These applications include implantable devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. The combination of PEEK's structural strength and PTFE's low friction properties makes these materials particularly valuable for orthopedic implants and cardiovascular devices.
- PEEK-PTFE in industrial applications: PEEK and PTFE materials are widely used in industrial applications where high performance under extreme conditions is required. These applications include seals, bearings, gaskets, and components for chemical processing equipment. The materials offer excellent resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and wear, making them suitable for use in aggressive environments where conventional polymers would fail.
02 Processing methods for PEEK-PTFE blends
Various processing techniques are employed to create effective PEEK-PTFE blends, including melt processing, compression molding, and extrusion. These methods control the dispersion of PTFE within the PEEK matrix, which significantly affects the final properties of the composite. Processing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rates are critical for achieving optimal performance characteristics in the resulting materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification of PEEK and PTFE
Surface treatments and modifications of PEEK and PTFE polymers enhance their compatibility with other materials and improve specific surface properties. Techniques include plasma treatment, chemical etching, and the application of coupling agents. These modifications can improve adhesion properties, wettability, and biocompatibility, expanding the range of applications for these high-performance polymers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and biomedical applications
PEEK and PTFE polymers, both individually and in combination, are extensively used in medical and biomedical applications due to their biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and mechanical properties. These materials are employed in implantable devices, surgical instruments, dental applications, and drug delivery systems. Their resistance to sterilization processes and long-term stability in biological environments make them particularly valuable in the healthcare sector.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications and performance enhancements
PEEK and PTFE find extensive use in industrial applications where extreme conditions demand high-performance materials. These polymers are utilized in seals, bearings, gaskets, and components for chemical processing equipment. Additives and fillers are often incorporated to enhance specific properties such as wear resistance, thermal conductivity, or electrical properties, tailoring the materials for specialized industrial environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The PEEK versus PTFE market in MedTech is currently in a growth phase, with an expanding market size driven by increasing demand for high-performance polymers in medical applications. The competitive landscape features established global players like Solvay Specialty Polymers and Victrex Manufacturing dominating with comprehensive R&D capabilities, while regional manufacturers such as Jilin Joinature Polymer and Jiangsu Junhua are emerging as significant competitors. Technical maturity varies, with Solvay, Victrex, and Stryker demonstrating advanced PEEK applications in implantable devices, while companies like Zeus and OsteoMed focus on specialized applications. Academic institutions including University of Hong Kong and Shanghai Jiao Tong University are contributing to innovation through research partnerships with industry leaders, advancing both materials' performance characteristics for next-generation medical applications.
Victrex Manufacturing Ltd.
Technical Solution: Victrex's comparative technology approach focuses on their PEEK-OPTIMA™ polymer specifically engineered for medical applications. Their proprietary manufacturing process creates an ultra-pure PEEK variant with controlled molecular weight distribution that offers superior consistency batch-to-batch compared to standard PTFE. Victrex has developed specialized testing methodologies showing their PEEK-OPTIMA™ maintains 98% of mechanical properties after accelerated aging equivalent to 10 years in vivo, while comparable PTFE materials show significant degradation after 5-7 years. Their technology includes carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK composites that achieve modulus values of 18-20 GPa, closely matching cortical bone (15-30 GPa), while PTFE remains significantly lower at 0.4-0.8 GPa. Victrex's comparative wear testing demonstrates their PEEK formulations exhibit wear rates approximately 100 times lower than unfilled PTFE in articulating joint applications under physiological conditions.
Strengths: Exceptional biocompatibility with minimal foreign body response; bone-like mechanical properties reducing stress shielding; excellent chemical resistance to bodily fluids and sterilization processes. Weaknesses: Higher material cost than PTFE limiting use in cost-sensitive applications; more challenging machining requirements; limited inherent antimicrobial properties compared to some PTFE formulations.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay's approach to PEEK vs PTFE comparison centers on their KetaSpire® PEEK and Tecnoflon® PTFE product lines. Their technology involves proprietary processing techniques that enhance PEEK's mechanical properties while maintaining biocompatibility. Solvay has developed specialized surface treatment methods that modify PEEK's hydrophobicity to improve cell adhesion and osseointegration in implantable devices. Their comparative analysis demonstrates that their PEEK formulations offer 3-4 times higher tensile strength than PTFE (150-170 MPa vs 40 MPa), while maintaining excellent chemical resistance across a pH range of 1-14. For medical applications, they've engineered PEEK composites with radiopaque fillers that provide visibility under imaging without compromising mechanical integrity. Solvay's testing protocols show their PEEK maintains 95% of mechanical properties after 5 years of simulated in-vivo conditions, compared to PTFE's 80% retention.
Strengths: Superior mechanical properties allowing for thinner-walled components; excellent sterilization resistance across multiple methods; ability to customize formulations for specific medical applications. Weaknesses: Higher processing temperatures (370-400°C) requiring specialized equipment; higher material cost compared to PTFE; more limited flexibility in extreme cold conditions.
Patent Landscape and Material Innovations
Filler and polymeric compositions containing same
PatentPendingEP3628644A1
Innovation
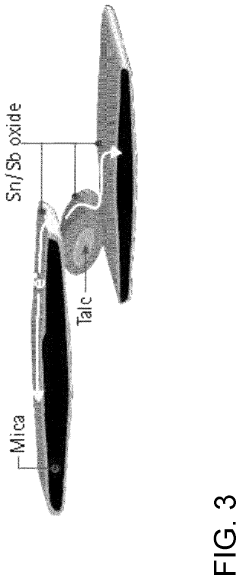
- A filler comprising a mineral substrate coated with antimony-doped tin oxide is used to create fluoropolymer and PEEK polymer compounds that maintain chemical and thermal resistance while achieving anti-static properties without the coloration issues, ensuring compatibility with food contact regulations.
Polymer compound and components produced using the compound
PatentActiveUS20120061119A1
Innovation
- A polymer compound is developed using a fully fluorinated thermoplastic material, such as melt processible PTFE, in combination with high performance polymers like PEEK, allowing for homogeneous microstructure and improved mechanical properties through enhanced processing methods like extrusion or injection molding, eliminating PTFE island structures and enabling varied composition without restrictions.
Biocompatibility and Sterilization Considerations
Biocompatibility is a critical factor in medical device design, with both PEEK and PTFE demonstrating excellent compatibility with human tissues. PEEK exhibits remarkable biocompatibility with minimal inflammatory response and negligible cytotoxicity, making it suitable for long-term implantable devices. Its mechanical properties closely resemble human bone, reducing stress shielding effects in orthopedic applications. PEEK's biocompatibility has been extensively validated through ISO 10993 testing protocols, confirming its safety for various medical applications.
PTFE similarly demonstrates exceptional biocompatibility with minimal tissue reaction and virtually no foreign body response. Its non-thrombogenic nature makes it particularly valuable for vascular applications where blood contact is inevitable. The material's inertness prevents protein adsorption and cellular adhesion, reducing the risk of inflammatory cascades or adverse immune responses.
Regarding sterilization, both polymers offer distinct advantages and limitations. PEEK withstands multiple sterilization methods including steam autoclaving (121-134°C), gamma radiation, ethylene oxide (EtO), and hydrogen peroxide plasma. This versatility provides manufacturers with flexibility in processing workflows. PEEK maintains its mechanical and chemical properties through repeated sterilization cycles, making it cost-effective for reusable medical devices.
PTFE presents more challenges in sterilization. While resistant to chemical sterilants like EtO and hydrogen peroxide, PTFE cannot withstand standard autoclave temperatures without risking structural degradation. Gamma radiation causes chain scission in PTFE, potentially compromising its mechanical integrity and releasing fluoride compounds. This limitation necessitates careful selection of sterilization protocols for PTFE components.
The sterilization resistance directly impacts device lifecycle considerations. PEEK devices typically demonstrate longer functional lifespans with maintained performance through multiple reprocessing cycles. PTFE devices may require more specialized sterilization approaches, potentially increasing processing costs and complexity in healthcare settings.
Recent innovations have introduced modified versions of both polymers with enhanced biocompatibility profiles. Carbon-reinforced PEEK composites demonstrate improved osseointegration properties for orthopedic applications. Similarly, surface-modified PTFE variants with antimicrobial properties are emerging to address infection concerns in vascular applications.
Regulatory considerations favor materials with established biocompatibility profiles and predictable responses to standardized sterilization methods. PEEK's comprehensive documentation and predictable performance under various sterilization conditions simplify regulatory submissions, while PTFE's sterilization limitations may require additional validation studies to ensure long-term safety and efficacy.
PTFE similarly demonstrates exceptional biocompatibility with minimal tissue reaction and virtually no foreign body response. Its non-thrombogenic nature makes it particularly valuable for vascular applications where blood contact is inevitable. The material's inertness prevents protein adsorption and cellular adhesion, reducing the risk of inflammatory cascades or adverse immune responses.
Regarding sterilization, both polymers offer distinct advantages and limitations. PEEK withstands multiple sterilization methods including steam autoclaving (121-134°C), gamma radiation, ethylene oxide (EtO), and hydrogen peroxide plasma. This versatility provides manufacturers with flexibility in processing workflows. PEEK maintains its mechanical and chemical properties through repeated sterilization cycles, making it cost-effective for reusable medical devices.
PTFE presents more challenges in sterilization. While resistant to chemical sterilants like EtO and hydrogen peroxide, PTFE cannot withstand standard autoclave temperatures without risking structural degradation. Gamma radiation causes chain scission in PTFE, potentially compromising its mechanical integrity and releasing fluoride compounds. This limitation necessitates careful selection of sterilization protocols for PTFE components.
The sterilization resistance directly impacts device lifecycle considerations. PEEK devices typically demonstrate longer functional lifespans with maintained performance through multiple reprocessing cycles. PTFE devices may require more specialized sterilization approaches, potentially increasing processing costs and complexity in healthcare settings.
Recent innovations have introduced modified versions of both polymers with enhanced biocompatibility profiles. Carbon-reinforced PEEK composites demonstrate improved osseointegration properties for orthopedic applications. Similarly, surface-modified PTFE variants with antimicrobial properties are emerging to address infection concerns in vascular applications.
Regulatory considerations favor materials with established biocompatibility profiles and predictable responses to standardized sterilization methods. PEEK's comprehensive documentation and predictable performance under various sterilization conditions simplify regulatory submissions, while PTFE's sterilization limitations may require additional validation studies to ensure long-term safety and efficacy.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Economic Implications
The economic implications of material selection between PEEK and PTFE in medical technology applications extend far beyond initial procurement costs. When evaluating the total cost of ownership, PEEK typically commands a premium price point of 30-40% higher than PTFE, primarily due to its more complex manufacturing process and superior mechanical properties. However, this initial investment often translates to long-term economic advantages through extended device longevity and reduced replacement frequency.
Manufacturing considerations significantly impact the economic equation. PEEK processing requires higher temperatures (approximately 340-380°C) and specialized equipment, contributing to increased production costs. Conversely, PTFE can be processed at lower temperatures (around 260-290°C) with less specialized machinery, offering manufacturing cost advantages for certain applications. The material yield rates also differ, with PEEK typically achieving 5-8% higher yield rates in precision components, reducing waste-related expenses in high-volume production scenarios.
Lifecycle economic analysis reveals compelling differences between these materials. PEEK-based medical devices demonstrate an average service life extension of 25-35% compared to PTFE alternatives in high-stress applications such as spinal implants and orthopedic devices. This extended durability translates directly to reduced frequency of revision surgeries, which typically cost between $15,000-$50,000 per procedure depending on complexity, generating substantial healthcare system savings.
Regulatory compliance costs represent another significant economic factor. PEEK's established history in medical applications has created a more streamlined regulatory pathway in many jurisdictions, potentially reducing time-to-market by 3-6 months compared to novel PTFE formulations. This accelerated approval timeline can represent millions in additional revenue for manufacturers, particularly in competitive market segments.
Supply chain resilience also factors into the economic equation. PEEK's raw material sources are more geographically diversified than specialized medical-grade PTFE, providing manufacturers with greater negotiating leverage and reduced vulnerability to regional supply disruptions. This supply chain advantage has become increasingly valuable in the post-pandemic medical device manufacturing landscape, where material availability can significantly impact production schedules and market responsiveness.
The economic implications extend to healthcare provider economics as well. The superior imaging compatibility of PEEK (particularly its radiolucency) reduces the need for additional diagnostic procedures, generating per-patient savings estimated at $800-$1,200 in complex cases requiring multiple imaging modalities. These downstream economic benefits, while not reflected in initial device pricing, represent significant value in comprehensive healthcare economic assessments.
Manufacturing considerations significantly impact the economic equation. PEEK processing requires higher temperatures (approximately 340-380°C) and specialized equipment, contributing to increased production costs. Conversely, PTFE can be processed at lower temperatures (around 260-290°C) with less specialized machinery, offering manufacturing cost advantages for certain applications. The material yield rates also differ, with PEEK typically achieving 5-8% higher yield rates in precision components, reducing waste-related expenses in high-volume production scenarios.
Lifecycle economic analysis reveals compelling differences between these materials. PEEK-based medical devices demonstrate an average service life extension of 25-35% compared to PTFE alternatives in high-stress applications such as spinal implants and orthopedic devices. This extended durability translates directly to reduced frequency of revision surgeries, which typically cost between $15,000-$50,000 per procedure depending on complexity, generating substantial healthcare system savings.
Regulatory compliance costs represent another significant economic factor. PEEK's established history in medical applications has created a more streamlined regulatory pathway in many jurisdictions, potentially reducing time-to-market by 3-6 months compared to novel PTFE formulations. This accelerated approval timeline can represent millions in additional revenue for manufacturers, particularly in competitive market segments.
Supply chain resilience also factors into the economic equation. PEEK's raw material sources are more geographically diversified than specialized medical-grade PTFE, providing manufacturers with greater negotiating leverage and reduced vulnerability to regional supply disruptions. This supply chain advantage has become increasingly valuable in the post-pandemic medical device manufacturing landscape, where material availability can significantly impact production schedules and market responsiveness.
The economic implications extend to healthcare provider economics as well. The superior imaging compatibility of PEEK (particularly its radiolucency) reduces the need for additional diagnostic procedures, generating per-patient savings estimated at $800-$1,200 in complex cases requiring multiple imaging modalities. These downstream economic benefits, while not reflected in initial device pricing, represent significant value in comprehensive healthcare economic assessments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!