Discovering the Multifunctional Role of Ethyl Acetate
JUN 30, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, has gained significant attention in various industries due to its multifunctional properties. This colorless liquid, characterized by its fruity odor, is widely recognized for its role as a solvent and plays a crucial part in numerous applications across different sectors.
The compound's unique chemical structure, consisting of an ethyl group connected to an acetate group, contributes to its diverse range of uses. Its low toxicity, high solvency power, and relatively low boiling point make it an attractive option for many industrial processes. Ethyl acetate is primarily produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, a process that has been refined over the years to improve efficiency and yield.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as an important intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an excellent solvent for paints, coatings, and adhesives. The pharmaceutical sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of drugs and as an extraction solvent in the purification of antibiotics.
The food industry also benefits from ethyl acetate's properties. It is naturally present in many fruits and is used as a flavoring agent to enhance the taste and aroma of various food products. Additionally, it plays a role in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, offering a less harmful alternative to traditional methods.
In recent years, the electronics industry has found new applications for ethyl acetate. Its use in the production of flexible printed circuits and as a cleaning agent for electronic components has expanded its market presence. The compound's low toxicity and quick evaporation rate make it suitable for these sensitive applications.
Environmental considerations have also influenced the use of ethyl acetate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its impact on air quality is a concern. However, compared to many other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively environmentally friendly due to its biodegradability and lower toxicity. This has led to increased interest in its use as a green solvent in various applications.
The global market for ethyl acetate continues to grow, driven by increasing demand from end-use industries and ongoing research into new applications. As industries seek more sustainable and efficient processes, the multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate positions it as a valuable compound in the evolving landscape of chemical applications.
The compound's unique chemical structure, consisting of an ethyl group connected to an acetate group, contributes to its diverse range of uses. Its low toxicity, high solvency power, and relatively low boiling point make it an attractive option for many industrial processes. Ethyl acetate is primarily produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, a process that has been refined over the years to improve efficiency and yield.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as an important intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an excellent solvent for paints, coatings, and adhesives. The pharmaceutical sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of drugs and as an extraction solvent in the purification of antibiotics.
The food industry also benefits from ethyl acetate's properties. It is naturally present in many fruits and is used as a flavoring agent to enhance the taste and aroma of various food products. Additionally, it plays a role in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, offering a less harmful alternative to traditional methods.
In recent years, the electronics industry has found new applications for ethyl acetate. Its use in the production of flexible printed circuits and as a cleaning agent for electronic components has expanded its market presence. The compound's low toxicity and quick evaporation rate make it suitable for these sensitive applications.
Environmental considerations have also influenced the use of ethyl acetate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its impact on air quality is a concern. However, compared to many other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively environmentally friendly due to its biodegradability and lower toxicity. This has led to increased interest in its use as a green solvent in various applications.
The global market for ethyl acetate continues to grow, driven by increasing demand from end-use industries and ongoing research into new applications. As industries seek more sustainable and efficient processes, the multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate positions it as a valuable compound in the evolving landscape of chemical applications.
Market Analysis
The market for ethyl acetate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key solvent and intermediate in chemical processes, ethyl acetate's demand is closely tied to the performance of end-use sectors such as paints and coatings, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverages.
In the paints and coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an essential solvent due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The global paints and coatings market has been expanding, particularly in emerging economies, fueling the demand for ethyl acetate. The construction and automotive sectors are major contributors to this growth, as they require high-quality coatings for both aesthetic and protective purposes.
The adhesives industry is another significant consumer of ethyl acetate. With the rise of e-commerce and packaging innovations, the demand for adhesives in the packaging sector has surged, consequently boosting ethyl acetate consumption. Additionally, the growing trend of lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles in the automotive industry has increased the use of adhesives, further driving the ethyl acetate market.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The global pharmaceutical industry's continuous growth, coupled with increasing research and development activities, has positively impacted the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The food and beverage industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier and more diverse food options, the demand for natural and artificial flavors has increased, benefiting the ethyl acetate market.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and economic growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets and steady demand from established industries.
The market is also influenced by environmental regulations and sustainability concerns. As a result, there is a growing interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, which presents new opportunities for market players and aligns with the global push towards greener alternatives.
In conclusion, the multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate ensures its continued relevance across various industries. The market is expected to maintain its growth trajectory, supported by expanding end-use applications and emerging economies. However, manufacturers and stakeholders must remain adaptable to evolving regulatory landscapes and sustainability requirements to capitalize on future opportunities in the ethyl acetate market.
In the paints and coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an essential solvent due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The global paints and coatings market has been expanding, particularly in emerging economies, fueling the demand for ethyl acetate. The construction and automotive sectors are major contributors to this growth, as they require high-quality coatings for both aesthetic and protective purposes.
The adhesives industry is another significant consumer of ethyl acetate. With the rise of e-commerce and packaging innovations, the demand for adhesives in the packaging sector has surged, consequently boosting ethyl acetate consumption. Additionally, the growing trend of lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles in the automotive industry has increased the use of adhesives, further driving the ethyl acetate market.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The global pharmaceutical industry's continuous growth, coupled with increasing research and development activities, has positively impacted the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The food and beverage industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier and more diverse food options, the demand for natural and artificial flavors has increased, benefiting the ethyl acetate market.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and economic growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets and steady demand from established industries.
The market is also influenced by environmental regulations and sustainability concerns. As a result, there is a growing interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, which presents new opportunities for market players and aligns with the global push towards greener alternatives.
In conclusion, the multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate ensures its continued relevance across various industries. The market is expected to maintain its growth trajectory, supported by expanding end-use applications and emerging economies. However, manufacturers and stakeholders must remain adaptable to evolving regulatory landscapes and sustainability requirements to capitalize on future opportunities in the ethyl acetate market.
Technical Challenges
Despite the widespread use of ethyl acetate in various industries, several technical challenges persist in fully harnessing its multifunctional potential. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of production processes to enhance yield and purity while minimizing environmental impact. Current manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful catalysts, necessitating the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives.
Another significant challenge lies in the purification and separation of ethyl acetate from reaction mixtures. The compound's volatility and tendency to form azeotropes with water and other solvents complicate traditional distillation techniques. This necessitates the exploration of advanced separation technologies, such as membrane-based processes or novel extractive distillation methods, to achieve higher purity levels efficiently.
The stability of ethyl acetate under various conditions poses another technical hurdle. In certain applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries, the compound may undergo hydrolysis or degradation, affecting product quality and shelf life. Developing stabilization techniques or identifying suitable protective measures to maintain the integrity of ethyl acetate in diverse environments remains an ongoing challenge.
Furthermore, the toxicity and flammability of ethyl acetate present safety concerns in handling and storage. While its relatively low toxicity compared to other organic solvents is advantageous, prolonged exposure can still lead to health issues. Implementing robust safety protocols and developing safer formulations or delivery systems for ethyl acetate-based products is crucial for expanding its applications in consumer goods and industrial processes.
The multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate also presents challenges in tailoring its properties for specific applications. Fine-tuning its solvent characteristics, reactivity, and compatibility with various substrates often requires extensive research and development efforts. This includes exploring chemical modifications or developing novel formulations to enhance its performance in targeted applications without compromising its desirable properties.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate usage, particularly in food and pharmaceutical applications, poses challenges for manufacturers and researchers. Navigating the complex regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance with evolving standards across different regions demands continuous adaptation and investment in quality control measures. Addressing these technical challenges will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of ethyl acetate and expanding its role across diverse industries.
Another significant challenge lies in the purification and separation of ethyl acetate from reaction mixtures. The compound's volatility and tendency to form azeotropes with water and other solvents complicate traditional distillation techniques. This necessitates the exploration of advanced separation technologies, such as membrane-based processes or novel extractive distillation methods, to achieve higher purity levels efficiently.
The stability of ethyl acetate under various conditions poses another technical hurdle. In certain applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries, the compound may undergo hydrolysis or degradation, affecting product quality and shelf life. Developing stabilization techniques or identifying suitable protective measures to maintain the integrity of ethyl acetate in diverse environments remains an ongoing challenge.
Furthermore, the toxicity and flammability of ethyl acetate present safety concerns in handling and storage. While its relatively low toxicity compared to other organic solvents is advantageous, prolonged exposure can still lead to health issues. Implementing robust safety protocols and developing safer formulations or delivery systems for ethyl acetate-based products is crucial for expanding its applications in consumer goods and industrial processes.
The multifunctional nature of ethyl acetate also presents challenges in tailoring its properties for specific applications. Fine-tuning its solvent characteristics, reactivity, and compatibility with various substrates often requires extensive research and development efforts. This includes exploring chemical modifications or developing novel formulations to enhance its performance in targeted applications without compromising its desirable properties.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate usage, particularly in food and pharmaceutical applications, poses challenges for manufacturers and researchers. Navigating the complex regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance with evolving standards across different regions demands continuous adaptation and investment in quality control measures. Addressing these technical challenges will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of ethyl acetate and expanding its role across diverse industries.
Current Applications
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The production methods aim to optimize the reaction conditions and separation processes to obtain high-quality ethyl acetate efficiently.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The production methods aim to optimize the synthesis of ethyl acetate from ethanol and acetic acid or other precursors.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in industrial processes: Ethyl acetate finds diverse applications in industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, coatings, and adhesives. The compound is also utilized in extraction processes, as a reaction medium, and in the production of other chemicals.
- Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science: Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer and material science applications. It is used in the preparation of various polymers, as a solvent for resins, and in the development of composite materials. The compound's properties make it suitable for use in coating formulations and as a processing aid in material production.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: The use and handling of ethyl acetate involve environmental and safety considerations. This includes methods for reducing emissions, safe storage and transportation practices, and techniques for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate in industrial processes to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety.
- Novel synthesis routes and derivatives of ethyl acetate: Research into novel synthesis routes and derivatives of ethyl acetate is ongoing. This includes the development of new catalysts, alternative feedstocks, and the exploration of ethyl acetate-based compounds with enhanced properties for specific applications. These innovations aim to improve production efficiency and expand the utility of ethyl acetate and its derivatives.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in industrial processes
Ethyl acetate finds diverse applications in industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, coatings, and adhesives. The compound is also employed in extraction processes, as a reaction medium, and in the production of other chemicals. Its versatility makes it a valuable component in many manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science
Ethyl acetate plays a significant role in polymer and material science. It is used in the synthesis and processing of various polymers, as well as in the development of advanced materials. The compound's properties make it suitable for use in coating formulations, adhesive systems, and as a processing aid in the production of specialized materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
The use of ethyl acetate in industrial processes requires careful consideration of environmental and safety aspects. Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly production methods, reducing emissions, and improving handling and storage practices. Safety measures for working with ethyl acetate, including proper ventilation and personal protective equipment, are also emphasized.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel synthesis routes and catalysts for ethyl acetate production
Ongoing research explores novel synthesis routes and catalysts to enhance the production of ethyl acetate. These innovations aim to improve reaction efficiency, increase yield, and reduce energy consumption. New catalytic systems and process designs are being developed to address the limitations of traditional production methods and meet the growing demand for ethyl acetate in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Players
The market for ethyl acetate is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to exceed $4 billion by 2027. The industry is characterized by established players and steady growth, driven by diverse applications in coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Technological advancements focus on improving production efficiency and developing bio-based alternatives. Key players like Eastman Chemical Co., Celanese International Corp., and BASF Corp. dominate the market with their extensive product portfolios and global presence. Emerging companies from Asia, such as Nantong Acetic Acid Chemical Co., Ltd. and Jiangsu Hengli Chemical Fiber Co., Ltd., are increasingly competing with traditional Western manufacturers, leveraging cost advantages and expanding production capacities.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical Co. has developed advanced processes for the production and application of ethyl acetate. Their technology focuses on improving the efficiency and sustainability of ethyl acetate production through innovative catalytic processes. They have implemented a novel reactive distillation technique that combines esterification and purification steps, resulting in higher yields and reduced energy consumption[1]. Additionally, Eastman has explored the use of bio-based feedstocks to produce green ethyl acetate, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable chemicals[2]. Their research also extends to developing specialized formulations of ethyl acetate for high-performance coatings and adhesives, leveraging its excellent solvency properties[3].
Strengths: Advanced production technology, focus on sustainability, diverse application development. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs for bio-based ethyl acetate, market competition from established petrochemical routes.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has invested in cutting-edge technology for ethyl acetate production and application. Their VAntage® platform integrates advanced process control and proprietary catalyst systems to optimize ethyl acetate synthesis[4]. This technology allows for flexible feedstock utilization, including both petrochemical and bio-based sources. Celanese has also developed specialized grades of ethyl acetate for high-purity applications in electronics and pharmaceuticals[5]. Their research extends to exploring the use of ethyl acetate as a green solvent in various industrial processes, including the production of biodegradable plastics and as an extraction medium in food processing[6].
Strengths: Versatile production technology, high-purity product offerings, focus on green chemistry applications. Weaknesses: Potential vulnerability to raw material price fluctuations, competition in commodity markets.
Key Innovations
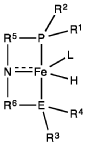
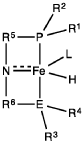
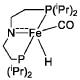
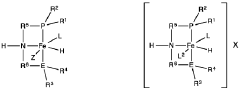
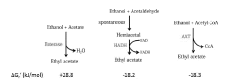
Homogeneous iron catalysts for the conversion of ethanol to ethyl acetate and hydrogen
PatentWO2019027965A1
Innovation
- A process utilizing a homogeneous iron catalyst with a tridentate pincer ligand for dehydrogenative coupling of ethanol at moderate temperatures, producing ethyl acetate efficiently and selectively, with iron loadings as low as 0.001 mol%, allowing for continuous operation and easy separation of ethyl acetate from the catalyst.
Alcohol acetyl transferases for ethyl acetate production
PatentWO2018100097A1
Innovation
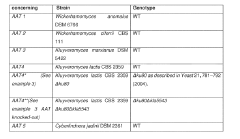
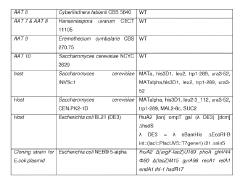
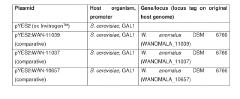
- Identification and utilization of novel polypeptides with alcohol acetyl transferase activity, specifically those with an alpha-beta hydrolase fold and a serine-histidine or serine-aspartic acid-histidine triad, for microbial production of ethyl acetate from ethanol and acetyl coenzyme A, using recombinant expression vectors in suitable host cells like E. coli and yeast species.
Environmental Impact
Ethyl acetate, a widely used organic solvent and chemical intermediate, has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The production, use, and disposal of ethyl acetate can impact various environmental compartments, including air, water, and soil.
In terms of air pollution, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). When released into the atmosphere, it can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity. These air quality issues can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. However, compared to many other solvents, ethyl acetate has a relatively low ozone depletion potential and global warming potential.
Water contamination is another environmental concern associated with ethyl acetate. Although it is not highly soluble in water, accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to the presence of ethyl acetate in surface and groundwater. This can potentially affect aquatic ecosystems and drinking water sources. Fortunately, ethyl acetate is biodegradable in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, which limits its long-term persistence in aquatic environments.
Soil contamination by ethyl acetate is generally less problematic due to its high volatility. Most of the compound released into soil will evaporate quickly. However, in cases of large spills or continuous release, it may temporarily affect soil microorganisms and plant life in the immediate vicinity.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate extends beyond its direct use. The production process, typically involving the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, requires energy and resources. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to more sustainable production methods, including the use of biocatalysts and renewable feedstocks.
Waste management and disposal of ethyl acetate-containing products also present environmental challenges. Proper handling and disposal protocols are essential to minimize environmental contamination. Recycling and recovery techniques have been developed to reduce waste and improve the overall environmental footprint of ethyl acetate use in industrial applications.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on finding more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional solvents like ethyl acetate. This has led to the development of bio-based solvents and green chemistry approaches that aim to reduce the environmental impact while maintaining the functionality required in various applications.
In terms of air pollution, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). When released into the atmosphere, it can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity. These air quality issues can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. However, compared to many other solvents, ethyl acetate has a relatively low ozone depletion potential and global warming potential.
Water contamination is another environmental concern associated with ethyl acetate. Although it is not highly soluble in water, accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to the presence of ethyl acetate in surface and groundwater. This can potentially affect aquatic ecosystems and drinking water sources. Fortunately, ethyl acetate is biodegradable in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, which limits its long-term persistence in aquatic environments.
Soil contamination by ethyl acetate is generally less problematic due to its high volatility. Most of the compound released into soil will evaporate quickly. However, in cases of large spills or continuous release, it may temporarily affect soil microorganisms and plant life in the immediate vicinity.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate extends beyond its direct use. The production process, typically involving the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, requires energy and resources. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to more sustainable production methods, including the use of biocatalysts and renewable feedstocks.
Waste management and disposal of ethyl acetate-containing products also present environmental challenges. Proper handling and disposal protocols are essential to minimize environmental contamination. Recycling and recovery techniques have been developed to reduce waste and improve the overall environmental footprint of ethyl acetate use in industrial applications.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on finding more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional solvents like ethyl acetate. This has led to the development of bio-based solvents and green chemistry approaches that aim to reduce the environmental impact while maintaining the functionality required in various applications.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in its multifunctional applications across various industries. As a widely used solvent and chemical intermediate, ethyl acetate is subject to diverse regulations that govern its production, handling, transportation, and use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA Inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ethyl acetate in the workplace, setting standards for air quality and worker safety.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of ethyl acetate in food-related applications. It is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance when used as a synthetic flavoring agent and adjuvant. However, its use in food packaging materials is subject to specific limitations and requirements outlined in FDA regulations.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Manufacturers and importers are required to register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation also applies, ensuring proper hazard communication for ethyl acetate.
Globally, the transportation of ethyl acetate is regulated by international agreements such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe handling and shipping of the substance across borders.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of ethyl acetate is governed by Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations. These guidelines ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products that may utilize ethyl acetate in their production processes.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the management of ethyl acetate. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards that affect the use of ethyl acetate in industrial processes and consumer products. These regulations aim to reduce air pollution and protect public health.
As the applications of ethyl acetate continue to expand, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new uses and potential risks. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires ongoing compliance efforts from industries utilizing ethyl acetate, ensuring its safe and responsible use across its multifunctional applications.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA Inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ethyl acetate in the workplace, setting standards for air quality and worker safety.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of ethyl acetate in food-related applications. It is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance when used as a synthetic flavoring agent and adjuvant. However, its use in food packaging materials is subject to specific limitations and requirements outlined in FDA regulations.
In the European Union, ethyl acetate falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Manufacturers and importers are required to register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation also applies, ensuring proper hazard communication for ethyl acetate.
Globally, the transportation of ethyl acetate is regulated by international agreements such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe handling and shipping of the substance across borders.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of ethyl acetate is governed by Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations. These guidelines ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products that may utilize ethyl acetate in their production processes.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the management of ethyl acetate. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards that affect the use of ethyl acetate in industrial processes and consumer products. These regulations aim to reduce air pollution and protect public health.
As the applications of ethyl acetate continue to expand, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new uses and potential risks. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires ongoing compliance efforts from industries utilizing ethyl acetate, ensuring its safe and responsible use across its multifunctional applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!