Evaluating Complex Mixtures via Advanced Multidetector NMR
SEP 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Advanced Multidetector NMR Technology Background and Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, transforming from a technique primarily used for structural determination of simple molecules to a sophisticated analytical method capable of evaluating complex mixtures. The development of multidetector NMR represents a pivotal advancement in this evolution, enabling simultaneous acquisition of multiple types of spectroscopic data and providing unprecedented insights into molecular structures and interactions.
Traditional NMR techniques have been limited by their ability to analyze complex mixtures effectively, often requiring separation procedures prior to analysis. The emergence of advanced multidetector NMR technology addresses this limitation by integrating multiple detection channels, allowing for the simultaneous acquisition of different nuclear signals and correlations between them. This technological progression has been driven by the increasing demand for more comprehensive analytical tools in fields such as pharmaceuticals, metabolomics, and materials science.
The current trajectory of multidetector NMR development is focused on enhancing sensitivity, resolution, and data processing capabilities. Recent innovations include the implementation of cryogenic probe technology, higher magnetic field strengths, and sophisticated pulse sequences that enable more selective excitation and detection. These advancements have collectively contributed to the improved analysis of complex mixtures without prior separation.
The primary objective of advanced multidetector NMR technology is to provide a comprehensive characterization of complex mixtures by simultaneously capturing multiple dimensions of molecular information. This includes not only structural elucidation but also quantitative analysis, conformational dynamics, and intermolecular interactions. By achieving these objectives, multidetector NMR aims to overcome the limitations of conventional analytical techniques when dealing with complex sample matrices.
Looking forward, the field is moving towards greater integration with other analytical technologies, such as mass spectrometry and chromatography, to create hybrid systems capable of even more detailed molecular characterization. Additionally, there is significant interest in miniaturization and automation to make these powerful analytical capabilities more accessible and user-friendly for routine applications in various industries.
The technical goals for advanced multidetector NMR include improving signal-to-noise ratios, reducing acquisition times, enhancing spectral resolution, and developing more sophisticated data analysis algorithms. These improvements are essential for expanding the application scope of NMR in analyzing increasingly complex mixtures encountered in modern scientific and industrial challenges.
As computational capabilities continue to advance, machine learning and artificial intelligence are being incorporated into NMR data processing workflows, enabling more efficient extraction of meaningful information from complex spectral datasets. This convergence of advanced hardware and intelligent software represents the next frontier in multidetector NMR technology development.
Traditional NMR techniques have been limited by their ability to analyze complex mixtures effectively, often requiring separation procedures prior to analysis. The emergence of advanced multidetector NMR technology addresses this limitation by integrating multiple detection channels, allowing for the simultaneous acquisition of different nuclear signals and correlations between them. This technological progression has been driven by the increasing demand for more comprehensive analytical tools in fields such as pharmaceuticals, metabolomics, and materials science.
The current trajectory of multidetector NMR development is focused on enhancing sensitivity, resolution, and data processing capabilities. Recent innovations include the implementation of cryogenic probe technology, higher magnetic field strengths, and sophisticated pulse sequences that enable more selective excitation and detection. These advancements have collectively contributed to the improved analysis of complex mixtures without prior separation.
The primary objective of advanced multidetector NMR technology is to provide a comprehensive characterization of complex mixtures by simultaneously capturing multiple dimensions of molecular information. This includes not only structural elucidation but also quantitative analysis, conformational dynamics, and intermolecular interactions. By achieving these objectives, multidetector NMR aims to overcome the limitations of conventional analytical techniques when dealing with complex sample matrices.
Looking forward, the field is moving towards greater integration with other analytical technologies, such as mass spectrometry and chromatography, to create hybrid systems capable of even more detailed molecular characterization. Additionally, there is significant interest in miniaturization and automation to make these powerful analytical capabilities more accessible and user-friendly for routine applications in various industries.
The technical goals for advanced multidetector NMR include improving signal-to-noise ratios, reducing acquisition times, enhancing spectral resolution, and developing more sophisticated data analysis algorithms. These improvements are essential for expanding the application scope of NMR in analyzing increasingly complex mixtures encountered in modern scientific and industrial challenges.
As computational capabilities continue to advance, machine learning and artificial intelligence are being incorporated into NMR data processing workflows, enabling more efficient extraction of meaningful information from complex spectral datasets. This convergence of advanced hardware and intelligent software represents the next frontier in multidetector NMR technology development.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Complex Mixture Analysis
The global market for complex mixture analysis technologies has been experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demands across multiple industries. The pharmaceutical sector represents the largest market segment, where advanced multidetector NMR techniques are critical for drug discovery, development, and quality control processes. Pharmaceutical companies require precise characterization of complex biological samples, metabolites, and drug formulations to ensure efficacy and safety of their products.
The food and beverage industry constitutes another significant market, with growing regulatory requirements for product authentication, quality control, and detection of adulterants. Advanced NMR technologies enable detailed compositional analysis of complex food matrices, detection of contaminants, and verification of product origins, addressing increasing consumer demands for transparency in food production.
Environmental monitoring represents a rapidly expanding application area, with governmental agencies and research institutions investing in sophisticated analytical technologies for comprehensive analysis of environmental samples. The ability of multidetector NMR to simultaneously identify and quantify multiple compounds in complex environmental matrices provides valuable data for pollution monitoring and remediation efforts.
The petrochemical industry has traditionally been a major user of NMR technologies, with ongoing demand for detailed characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures. Advanced multidetector approaches offer improved resolution and sensitivity for analyzing crude oil, refined products, and biofuels, supporting process optimization and quality control.
Market analysis indicates that the global analytical instrumentation market for complex mixture analysis is projected to grow significantly, with NMR technologies representing a premium segment due to their unparalleled capabilities for structural elucidation and quantitative analysis without sample destruction. The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by expanding pharmaceutical and chemical industries, increased research funding, and strengthening regulatory frameworks.
Customer requirements are evolving toward more integrated analytical solutions that combine hardware advancements with sophisticated software for data interpretation. End users increasingly demand systems capable of handling higher sample throughput, improved sensitivity for trace component detection, and enhanced data processing capabilities to extract meaningful information from complex spectral datasets.
The economic value proposition for advanced multidetector NMR systems centers on their ability to reduce analysis time, decrease sample requirements, and provide more comprehensive characterization compared to traditional analytical approaches. While initial investment costs remain high, the return on investment is justified through improved decision-making capabilities, reduced development timelines, and enhanced quality control processes across multiple industries.
The food and beverage industry constitutes another significant market, with growing regulatory requirements for product authentication, quality control, and detection of adulterants. Advanced NMR technologies enable detailed compositional analysis of complex food matrices, detection of contaminants, and verification of product origins, addressing increasing consumer demands for transparency in food production.
Environmental monitoring represents a rapidly expanding application area, with governmental agencies and research institutions investing in sophisticated analytical technologies for comprehensive analysis of environmental samples. The ability of multidetector NMR to simultaneously identify and quantify multiple compounds in complex environmental matrices provides valuable data for pollution monitoring and remediation efforts.
The petrochemical industry has traditionally been a major user of NMR technologies, with ongoing demand for detailed characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures. Advanced multidetector approaches offer improved resolution and sensitivity for analyzing crude oil, refined products, and biofuels, supporting process optimization and quality control.
Market analysis indicates that the global analytical instrumentation market for complex mixture analysis is projected to grow significantly, with NMR technologies representing a premium segment due to their unparalleled capabilities for structural elucidation and quantitative analysis without sample destruction. The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by expanding pharmaceutical and chemical industries, increased research funding, and strengthening regulatory frameworks.
Customer requirements are evolving toward more integrated analytical solutions that combine hardware advancements with sophisticated software for data interpretation. End users increasingly demand systems capable of handling higher sample throughput, improved sensitivity for trace component detection, and enhanced data processing capabilities to extract meaningful information from complex spectral datasets.
The economic value proposition for advanced multidetector NMR systems centers on their ability to reduce analysis time, decrease sample requirements, and provide more comprehensive characterization compared to traditional analytical approaches. While initial investment costs remain high, the return on investment is justified through improved decision-making capabilities, reduced development timelines, and enhanced quality control processes across multiple industries.
Current Capabilities and Technical Challenges in Multidetector NMR
Multidetector Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) technology has evolved significantly over the past decade, offering unprecedented capabilities for analyzing complex mixtures. Current systems can simultaneously detect multiple nuclei (1H, 13C, 15N, 31P) with high sensitivity and resolution, enabling comprehensive structural elucidation of complex molecular systems. Advanced pulse sequences and gradient techniques have substantially improved signal-to-noise ratios, allowing for detection of components at concentrations as low as micromolar levels in certain applications.
The integration of cryogenic probe technology has further enhanced sensitivity by reducing thermal noise, enabling up to 4-fold improvement in signal detection compared to conventional probes. Modern multidetector NMR systems also feature automated sample handling capabilities, supporting high-throughput screening of multiple samples with minimal human intervention. Data processing algorithms have evolved to handle multidimensional datasets, with capabilities for automated peak picking, assignment, and quantification.
Despite these advancements, significant technical challenges persist in multidetector NMR analysis of complex mixtures. Signal overlap remains a fundamental limitation, particularly when analyzing mixtures containing hundreds of components with similar chemical structures. This challenge is especially pronounced in biological samples like biofluids, plant extracts, and fermentation broths, where component concentration can span several orders of magnitude.
Sensitivity constraints continue to limit detection of trace components, particularly when analyzing nuclei with low natural abundance or low gyromagnetic ratios. While hyperpolarization techniques offer promising solutions, their implementation in routine analysis remains challenging due to cost and technical complexity. The quantitative accuracy of multidetector NMR also faces challenges from differential relaxation effects, which can lead to systematic errors in concentration measurements.
Data processing and interpretation represent another significant hurdle. The exponential increase in data complexity with additional detection dimensions necessitates sophisticated computational approaches. Current software solutions often struggle with fully automated analysis of complex multidetector datasets, requiring significant expert intervention for reliable results.
Hardware limitations also impact multidetector NMR capabilities. Maintaining uniform magnetic field homogeneity across different detection channels presents engineering challenges, while probe designs must balance sensitivity, resolution, and multi-nuclear detection capabilities. The high cost of advanced multidetector systems (often exceeding $1-2 million) restricts widespread adoption, particularly in smaller research institutions and industrial settings.
Standardization of protocols represents another challenge, with limited consensus on optimal acquisition parameters, calibration methods, and data processing workflows for complex mixture analysis. This hampers reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and instrument platforms.
The integration of cryogenic probe technology has further enhanced sensitivity by reducing thermal noise, enabling up to 4-fold improvement in signal detection compared to conventional probes. Modern multidetector NMR systems also feature automated sample handling capabilities, supporting high-throughput screening of multiple samples with minimal human intervention. Data processing algorithms have evolved to handle multidimensional datasets, with capabilities for automated peak picking, assignment, and quantification.
Despite these advancements, significant technical challenges persist in multidetector NMR analysis of complex mixtures. Signal overlap remains a fundamental limitation, particularly when analyzing mixtures containing hundreds of components with similar chemical structures. This challenge is especially pronounced in biological samples like biofluids, plant extracts, and fermentation broths, where component concentration can span several orders of magnitude.
Sensitivity constraints continue to limit detection of trace components, particularly when analyzing nuclei with low natural abundance or low gyromagnetic ratios. While hyperpolarization techniques offer promising solutions, their implementation in routine analysis remains challenging due to cost and technical complexity. The quantitative accuracy of multidetector NMR also faces challenges from differential relaxation effects, which can lead to systematic errors in concentration measurements.
Data processing and interpretation represent another significant hurdle. The exponential increase in data complexity with additional detection dimensions necessitates sophisticated computational approaches. Current software solutions often struggle with fully automated analysis of complex multidetector datasets, requiring significant expert intervention for reliable results.
Hardware limitations also impact multidetector NMR capabilities. Maintaining uniform magnetic field homogeneity across different detection channels presents engineering challenges, while probe designs must balance sensitivity, resolution, and multi-nuclear detection capabilities. The high cost of advanced multidetector systems (often exceeding $1-2 million) restricts widespread adoption, particularly in smaller research institutions and industrial settings.
Standardization of protocols represents another challenge, with limited consensus on optimal acquisition parameters, calibration methods, and data processing workflows for complex mixture analysis. This hampers reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and instrument platforms.
Current Methodologies for Complex Mixture Evaluation
01 Multi-dimensional NMR techniques for complex mixture analysis
Advanced multi-dimensional NMR spectroscopy techniques enable comprehensive analysis of complex mixtures by providing enhanced spectral resolution and structural information. These techniques separate overlapping signals across multiple dimensions, allowing for better identification and quantification of components in complex mixtures. The methods include 2D correlation spectroscopy (COSY), heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC), and total correlation spectroscopy (TOCSY) that reveal molecular connectivity and structural relationships between different nuclei.- Multi-dimensional NMR techniques for complex mixture analysis: Advanced multi-dimensional NMR spectroscopy techniques enable comprehensive analysis of complex mixtures by providing enhanced spectral resolution and structural information. These techniques separate overlapping signals across multiple dimensions, allowing for better identification and quantification of components in complex mixtures. Multi-dimensional approaches such as 2D and 3D NMR can reveal correlations between nuclei, helping to elucidate molecular structures and interactions within complex samples.
- Pulse sequence optimization for complex mixture analysis: Specialized pulse sequences are developed to enhance the detection and characterization of components in complex mixtures. These optimized sequences can suppress unwanted signals, enhance sensitivity for specific molecular features, and provide selective information about particular compound classes. Advanced pulse sequence design enables better discrimination between similar compounds and improves the overall quality of spectral data obtained from complex mixtures.
- Automated data processing and interpretation algorithms: Sophisticated computational methods are employed to process and interpret the large datasets generated by multidetector NMR analysis of complex mixtures. These algorithms can perform automated peak picking, spectral deconvolution, and component identification. Machine learning and statistical analysis techniques help extract meaningful patterns from complex NMR data, enabling more efficient characterization of mixture components and their relative concentrations.
- Hyphenated NMR techniques for enhanced mixture analysis: Combining NMR with other analytical techniques creates powerful hyphenated methods for complex mixture analysis. These approaches integrate the structural information from NMR with complementary data from techniques such as mass spectrometry, chromatography, or optical spectroscopy. Hyphenated techniques provide multidimensional analytical information, enabling more comprehensive characterization of complex mixtures than would be possible with NMR alone.
- Specialized hardware configurations for complex mixture analysis: Advanced hardware configurations enhance the capabilities of NMR systems for complex mixture analysis. These include multiple detector arrays, cryogenic probes, microcoil detectors, and specialized sample handling systems. Such hardware innovations improve sensitivity, resolution, and throughput, allowing for detection of trace components and better characterization of complex mixtures with heterogeneous compositions.
02 Pulse sequence optimization for complex mixture analysis
Specialized pulse sequences are developed to enhance the sensitivity and selectivity of NMR measurements for complex mixtures. These optimized sequences can suppress unwanted signals, enhance specific molecular interactions, and improve the detection of minor components in complex matrices. Advanced techniques include selective excitation methods, solvent suppression sequences, and diffusion-ordered spectroscopy (DOSY) that separate components based on their diffusion coefficients, providing a virtual chromatographic dimension to NMR analysis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automated data processing and pattern recognition for NMR spectra
Sophisticated computational methods are employed to process and interpret complex NMR spectral data from multidetector systems. These include automated peak picking, spectral deconvolution, and pattern recognition algorithms that can identify characteristic spectral signatures in complex mixtures. Machine learning and statistical analysis techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS) are applied to extract meaningful information from large datasets, enabling rapid identification and quantification of components in complex mixtures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hardware innovations for multidetector NMR systems
Advanced hardware configurations for multidetector NMR systems include multiple receiver coils, cryogenic probes, and parallel acquisition capabilities that significantly enhance sensitivity and throughput. These innovations enable simultaneous detection of multiple nuclei and faster acquisition of multidimensional spectra. Microcoil and microfluidic NMR technologies allow for analysis of volume-limited samples, while high-field magnets provide improved spectral resolution for complex mixture analysis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hyphenated NMR techniques for complex mixture characterization
Integration of NMR with complementary analytical techniques creates powerful hyphenated methods for comprehensive characterization of complex mixtures. These approaches combine the structural elucidation capabilities of NMR with separation techniques such as liquid chromatography (LC-NMR), gas chromatography (GC-NMR), or mass spectrometry (NMR-MS). Such hyphenated systems provide enhanced component identification and quantification in complex mixtures by leveraging the strengths of multiple analytical platforms simultaneously.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Advanced NMR
Advanced Multidetector NMR for complex mixture evaluation is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing applications in pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries. The technology is maturing rapidly, with key players demonstrating varying levels of sophistication. Bruker Switzerland AG and Thermo Finnigan Corp. lead commercial instrumentation development, while academic institutions like University of Padua and Rice University contribute fundamental research innovations. Pharmaceutical companies including Bristol Myers Squibb, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, and Momenta Pharmaceuticals are leveraging this technology for drug development and quality control. Bio-Rad Laboratories and Waters Technology are advancing complementary analytical technologies, creating a competitive ecosystem where industry-academia collaborations are driving technological refinement and expanding applications.
Thermo Finnigan Corp.
Technical Solution: Thermo Finnigan (now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific) has developed hybrid analytical platforms that combine NMR with their high-resolution mass spectrometry systems for comprehensive analysis of complex mixtures. Their technology focuses on hyphenated techniques such as LC-NMR-MS, where liquid chromatography separates mixture components before sequential or parallel analysis by both NMR and mass spectrometry. The company's Orbitrap technology, when combined with NMR data, provides complementary structural information that enhances identification confidence for unknown compounds in complex matrices. Thermo's data integration software allows researchers to correlate spectral information from multiple detection methods, creating a more complete analytical picture of complex samples such as natural products, metabolites, and pharmaceutical impurities.
Strengths: Exceptional mass spectrometry capabilities that complement NMR data; extensive experience with hyphenated techniques; strong presence in analytical laboratories worldwide. Weaknesses: Primary focus on mass spectrometry rather than NMR as core technology; requires significant expertise to effectively integrate data from multiple detection platforms.
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Technical Solution: Bio-Rad has developed specialized NMR-based metabolomics platforms that utilize multiple detection parameters to characterize complex biological mixtures. Their technology incorporates pulse sequence optimization for selective detection of specific compound classes within complex matrices, particularly useful for biofluid analysis. The company's automated sample handling systems are designed to maintain sample integrity throughout the analytical workflow, critical for accurate quantification in complex mixtures. Bio-Rad's statistical analysis software package is specifically designed for multivariate analysis of complex NMR datasets, enabling pattern recognition and biomarker discovery in metabolomic studies. Their approach combines targeted and untargeted analysis methods to provide both specific compound quantification and comprehensive profiling of complex biological samples.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in biological and clinical applications of NMR; strong bioinformatics capabilities for metabolomics data; integrated workflow solutions from sample preparation to data analysis. Weaknesses: More focused on specific application areas rather than fundamental NMR technology development; less emphasis on hardware innovation compared to dedicated NMR manufacturers.
Key Innovations in Multidetector NMR Signal Processing
NMR method for differentiating complex mixtures
PatentInactiveUS20070055456A1
Innovation
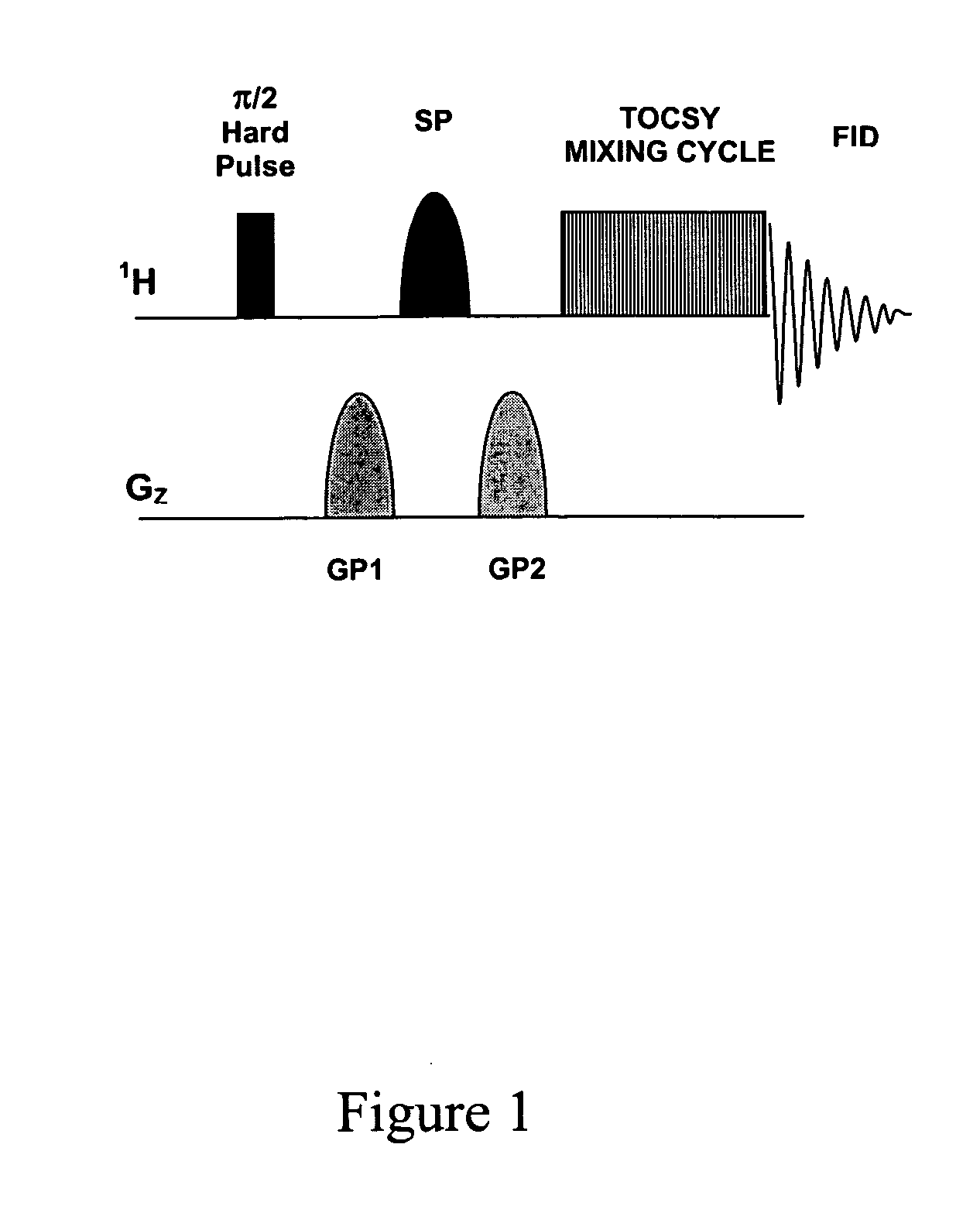
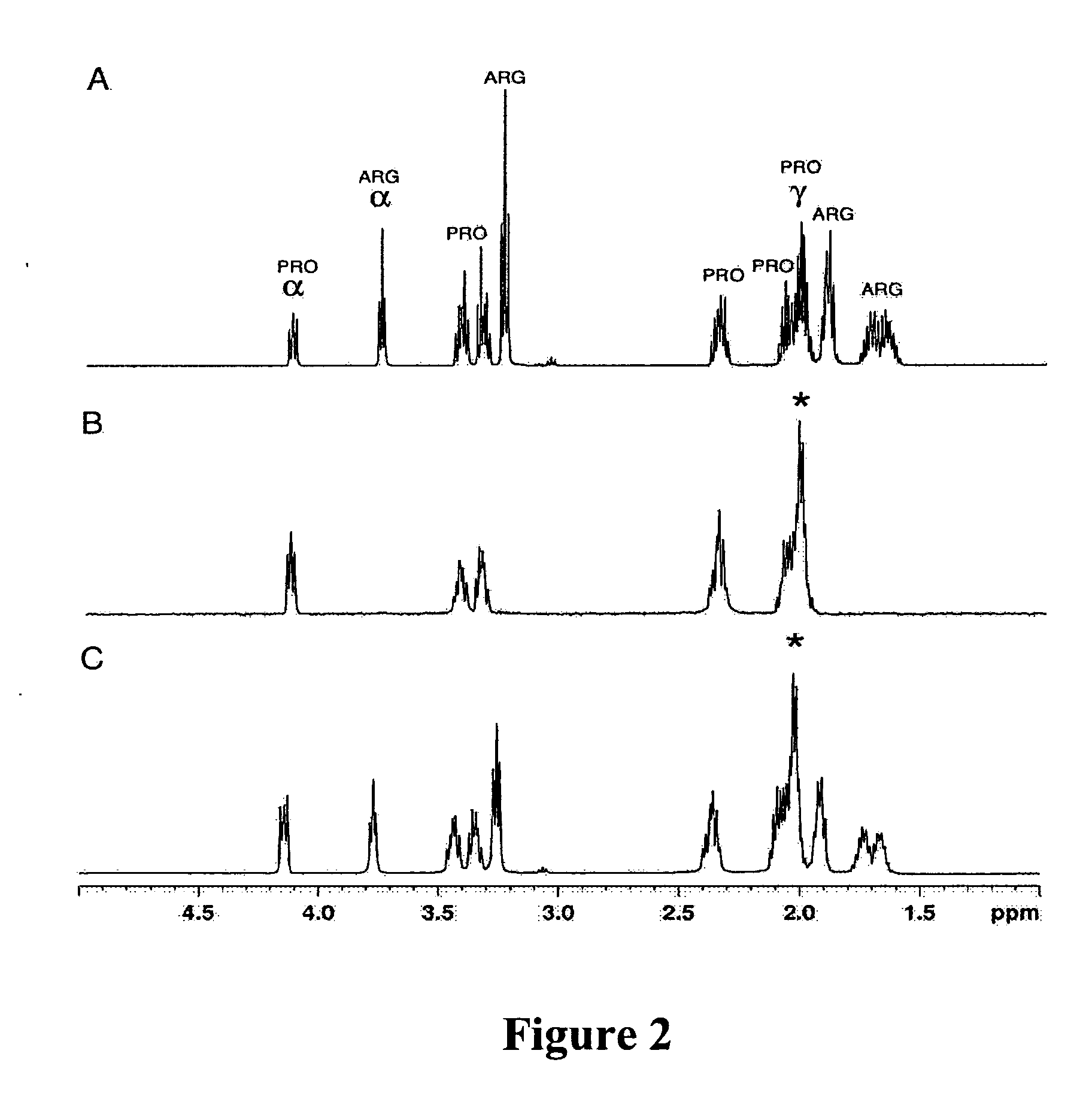
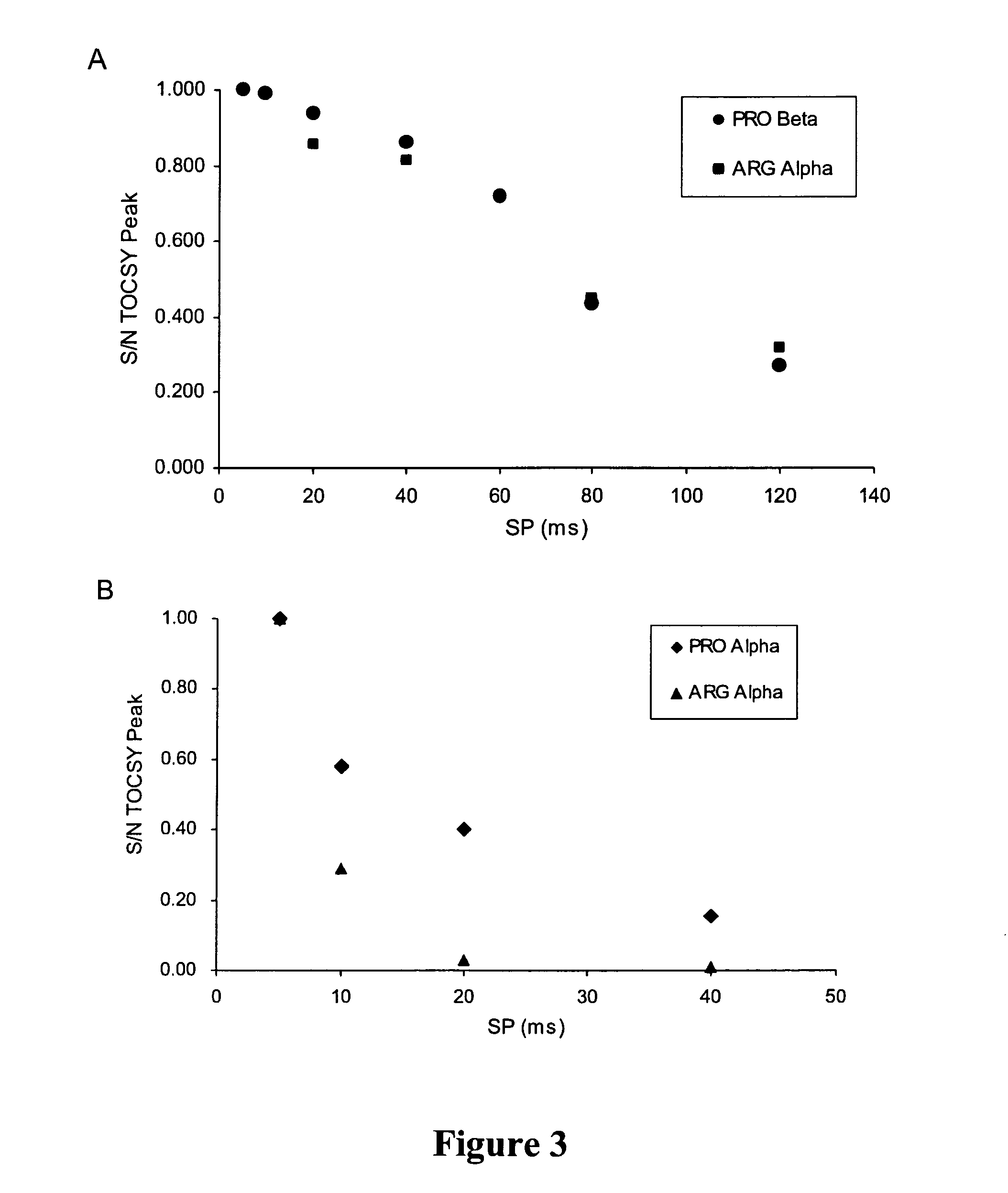
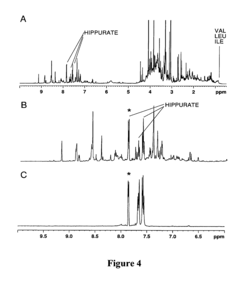
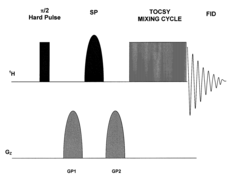
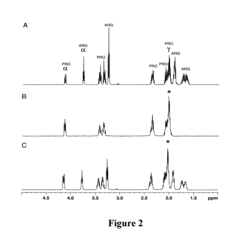
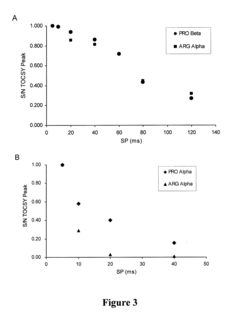
- The method employs selective total correlation spectroscopy (TOCSY) combined with multivariate statistical analysis, such as PCA, to differentiate and quantify chemical species by focusing on pre-selected components and using short excitation pulse durations to enhance sensitivity and selectivity, and applying the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient to assess peak purity.
NMR method for differentiating complex mixtures
PatentInactiveUS20110202285A1
Innovation
- The method employs selective total correlation spectroscopy (TOCSY) combined with multivariate statistical analysis to differentiate and quantify chemical species in complex mixtures by producing individual spectral peaks and using the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient to ensure peak purity, allowing for the detection of minor components and differentiation of similar samples.
Validation Protocols and Quality Assurance in NMR Analysis
The validation of NMR analytical methods for complex mixtures requires rigorous protocols to ensure data reliability and reproducibility. Establishing standardized validation procedures is essential for maintaining analytical integrity across different laboratories and experimental conditions. These protocols typically encompass several critical parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limits, and robustness.
Specificity validation in multidetector NMR analysis involves confirming that the analytical method can accurately distinguish the analyte of interest from other components in complex mixtures. This is particularly challenging when dealing with overlapping signals, requiring advanced pulse sequences and multidimensional techniques to achieve adequate resolution.
Linearity assessment evaluates the relationship between analyte concentration and detector response across a defined range. For complex mixtures, this often necessitates the preparation of multiple calibration standards that mimic the matrix composition of the actual samples. Statistical methods such as regression analysis are employed to verify linearity and determine appropriate concentration ranges.
Accuracy validation compares measured values against reference standards or certified reference materials. In multidetector NMR, this may involve spike recovery experiments where known quantities of target analytes are added to samples, followed by quantification to determine recovery percentages.
Precision testing examines the repeatability and reproducibility of the analytical method. This includes intra-day and inter-day variability assessments, as well as evaluations across different instruments and operators. For complex mixtures, precision is often evaluated at multiple concentration levels to account for matrix effects.
Detection and quantification limits must be established to determine the lowest concentrations at which analytes can be reliably detected and quantified. These parameters are particularly important when analyzing trace components in complex matrices.
Quality assurance systems for advanced multidetector NMR typically incorporate regular instrument performance verification using standard reference materials. This includes checks on chemical shift accuracy, resolution, sensitivity, and lineshape. Automated system suitability tests are increasingly being implemented to ensure consistent instrument performance before sample analysis.
Data integrity measures are also crucial components of NMR validation protocols. These include secure data storage systems, audit trails for data modifications, and electronic signatures for results approval. Modern NMR facilities often implement laboratory information management systems (LIMS) to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure traceability of analytical results.
Interlaboratory comparison studies provide an additional layer of validation by comparing results across different facilities using the same or similar methodologies. These studies help identify systematic errors and establish consensus values for complex mixture analysis.
Specificity validation in multidetector NMR analysis involves confirming that the analytical method can accurately distinguish the analyte of interest from other components in complex mixtures. This is particularly challenging when dealing with overlapping signals, requiring advanced pulse sequences and multidimensional techniques to achieve adequate resolution.
Linearity assessment evaluates the relationship between analyte concentration and detector response across a defined range. For complex mixtures, this often necessitates the preparation of multiple calibration standards that mimic the matrix composition of the actual samples. Statistical methods such as regression analysis are employed to verify linearity and determine appropriate concentration ranges.
Accuracy validation compares measured values against reference standards or certified reference materials. In multidetector NMR, this may involve spike recovery experiments where known quantities of target analytes are added to samples, followed by quantification to determine recovery percentages.
Precision testing examines the repeatability and reproducibility of the analytical method. This includes intra-day and inter-day variability assessments, as well as evaluations across different instruments and operators. For complex mixtures, precision is often evaluated at multiple concentration levels to account for matrix effects.
Detection and quantification limits must be established to determine the lowest concentrations at which analytes can be reliably detected and quantified. These parameters are particularly important when analyzing trace components in complex matrices.
Quality assurance systems for advanced multidetector NMR typically incorporate regular instrument performance verification using standard reference materials. This includes checks on chemical shift accuracy, resolution, sensitivity, and lineshape. Automated system suitability tests are increasingly being implemented to ensure consistent instrument performance before sample analysis.
Data integrity measures are also crucial components of NMR validation protocols. These include secure data storage systems, audit trails for data modifications, and electronic signatures for results approval. Modern NMR facilities often implement laboratory information management systems (LIMS) to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure traceability of analytical results.
Interlaboratory comparison studies provide an additional layer of validation by comparing results across different facilities using the same or similar methodologies. These studies help identify systematic errors and establish consensus values for complex mixture analysis.
Integration with Other Analytical Techniques
The integration of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) with complementary analytical techniques represents a significant advancement in the comprehensive characterization of complex mixtures. Mass Spectrometry (MS) stands as a natural partner for NMR analysis, offering exceptional sensitivity and molecular weight determination capabilities that complement NMR's structural elucidation strengths. When combined, these techniques provide a more complete molecular profile, with MS identifying components that may be below NMR detection limits and NMR clarifying structural isomers that MS cannot differentiate.
Chromatographic methods, particularly High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC), enhance multidetector NMR systems by providing separation prior to spectroscopic analysis. Hyphenated techniques such as LC-NMR and GC-NMR have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for real-time structural identification of separated components. These integrated systems are particularly valuable in metabolomics, natural product research, and pharmaceutical quality control where complex mixtures require both separation and detailed structural analysis.
Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy offer complementary vibrational information that, when correlated with NMR data, provides confirmation of functional groups and molecular interactions. Advanced data fusion algorithms now enable the correlation of spectral features across these different techniques, creating multi-dimensional analytical frameworks that significantly improve the accuracy of component identification in complex mixtures.
X-ray crystallography, while requiring crystalline samples, provides definitive three-dimensional structural information that can validate NMR-derived structures. The combination of solution-state NMR with solid-state structural data has proven particularly valuable for understanding how molecular conformation may differ between states, offering insights into bioavailability and formulation science for pharmaceutical compounds.
Computational methods have become essential in integrating these diverse analytical outputs. Machine learning algorithms and chemometric approaches now facilitate the correlation of data from multiple analytical platforms, extracting meaningful patterns and relationships that might otherwise remain obscured. These computational tools are increasingly capable of automated structural assignment when presented with complementary datasets from different analytical techniques.
The future of complex mixture analysis lies in fully integrated analytical platforms that combine multiple detection methods with automated data processing. Emerging miniaturized systems that incorporate NMR with other techniques promise to make comprehensive analysis more accessible and cost-effective. As these integrated approaches continue to evolve, they will enable more rapid and accurate characterization of complex mixtures across numerous scientific and industrial applications.
Chromatographic methods, particularly High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC), enhance multidetector NMR systems by providing separation prior to spectroscopic analysis. Hyphenated techniques such as LC-NMR and GC-NMR have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for real-time structural identification of separated components. These integrated systems are particularly valuable in metabolomics, natural product research, and pharmaceutical quality control where complex mixtures require both separation and detailed structural analysis.
Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy offer complementary vibrational information that, when correlated with NMR data, provides confirmation of functional groups and molecular interactions. Advanced data fusion algorithms now enable the correlation of spectral features across these different techniques, creating multi-dimensional analytical frameworks that significantly improve the accuracy of component identification in complex mixtures.
X-ray crystallography, while requiring crystalline samples, provides definitive three-dimensional structural information that can validate NMR-derived structures. The combination of solution-state NMR with solid-state structural data has proven particularly valuable for understanding how molecular conformation may differ between states, offering insights into bioavailability and formulation science for pharmaceutical compounds.
Computational methods have become essential in integrating these diverse analytical outputs. Machine learning algorithms and chemometric approaches now facilitate the correlation of data from multiple analytical platforms, extracting meaningful patterns and relationships that might otherwise remain obscured. These computational tools are increasingly capable of automated structural assignment when presented with complementary datasets from different analytical techniques.
The future of complex mixture analysis lies in fully integrated analytical platforms that combine multiple detection methods with automated data processing. Emerging miniaturized systems that incorporate NMR with other techniques promise to make comprehensive analysis more accessible and cost-effective. As these integrated approaches continue to evolve, they will enable more rapid and accurate characterization of complex mixtures across numerous scientific and industrial applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!