NMR Data Enhancement Through Standardized Calibration Methods
SEP 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Technology Evolution and Enhancement Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, transforming from a physics curiosity to an indispensable analytical tool across multiple scientific disciplines. The journey began with the pioneering work of Felix Bloch and Edward Purcell, who independently discovered the NMR phenomenon in 1946, earning them the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1952. This fundamental discovery laid the groundwork for what would become one of the most powerful non-destructive analytical techniques in modern science.
The 1960s marked a pivotal advancement with the introduction of Fourier Transform NMR (FT-NMR) by Richard Ernst, dramatically improving sensitivity and enabling the analysis of complex biological molecules. This innovation catalyzed the expansion of NMR applications beyond physics into chemistry, biochemistry, and medicine. The subsequent decades witnessed continuous refinement in magnet technology, with superconducting magnets enabling higher field strengths and consequently enhanced spectral resolution.
By the 1980s and 1990s, multidimensional NMR techniques emerged, revolutionizing structural biology by allowing scientists to determine three-dimensional protein structures in solution. Concurrently, the development of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) extended NMR principles to medical diagnostics, becoming an essential clinical tool worldwide. These advancements collectively demonstrate the remarkable versatility and adaptability of NMR technology across scientific domains.
Despite these achievements, NMR data quality remains heavily dependent on proper calibration procedures, which have historically lacked standardization across laboratories and equipment manufacturers. This inconsistency creates significant challenges in data reproducibility, inter-laboratory comparisons, and the establishment of reliable spectral databases. The variability in calibration methods affects everything from basic chemical shift references to complex pulse sequence optimizations.
The primary objective of standardized calibration methods for NMR data enhancement is to establish universal protocols that ensure consistent, high-quality spectral data regardless of the instrument or laboratory. This standardization aims to address several critical needs: improving reproducibility across different NMR systems, enhancing spectral resolution and sensitivity, reducing artifacts and baseline distortions, and enabling more reliable quantitative analyses.
Furthermore, standardized calibration would facilitate the creation of comprehensive spectral databases with enhanced reliability, supporting advanced applications in metabolomics, pharmaceutical research, and materials science. The ultimate goal is to transform NMR from a technique requiring significant expertise for optimal results to a more accessible and dependable analytical method with predictable outcomes across diverse research environments.
The 1960s marked a pivotal advancement with the introduction of Fourier Transform NMR (FT-NMR) by Richard Ernst, dramatically improving sensitivity and enabling the analysis of complex biological molecules. This innovation catalyzed the expansion of NMR applications beyond physics into chemistry, biochemistry, and medicine. The subsequent decades witnessed continuous refinement in magnet technology, with superconducting magnets enabling higher field strengths and consequently enhanced spectral resolution.
By the 1980s and 1990s, multidimensional NMR techniques emerged, revolutionizing structural biology by allowing scientists to determine three-dimensional protein structures in solution. Concurrently, the development of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) extended NMR principles to medical diagnostics, becoming an essential clinical tool worldwide. These advancements collectively demonstrate the remarkable versatility and adaptability of NMR technology across scientific domains.
Despite these achievements, NMR data quality remains heavily dependent on proper calibration procedures, which have historically lacked standardization across laboratories and equipment manufacturers. This inconsistency creates significant challenges in data reproducibility, inter-laboratory comparisons, and the establishment of reliable spectral databases. The variability in calibration methods affects everything from basic chemical shift references to complex pulse sequence optimizations.
The primary objective of standardized calibration methods for NMR data enhancement is to establish universal protocols that ensure consistent, high-quality spectral data regardless of the instrument or laboratory. This standardization aims to address several critical needs: improving reproducibility across different NMR systems, enhancing spectral resolution and sensitivity, reducing artifacts and baseline distortions, and enabling more reliable quantitative analyses.
Furthermore, standardized calibration would facilitate the creation of comprehensive spectral databases with enhanced reliability, supporting advanced applications in metabolomics, pharmaceutical research, and materials science. The ultimate goal is to transform NMR from a technique requiring significant expertise for optimal results to a more accessible and dependable analytical method with predictable outcomes across diverse research environments.
Market Analysis for Advanced NMR Calibration Solutions
The global market for advanced Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) calibration solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for precise analytical techniques across various industries. The market size for NMR technologies was valued at approximately 860 million USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 1.2 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 6.8%.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the largest consumers of NMR calibration solutions, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. These industries rely heavily on NMR spectroscopy for drug discovery, development, and quality control processes. The need for standardized calibration methods has become particularly acute as regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical products continue to tighten globally.
Academic and research institutions constitute the second-largest market segment at 30%, where NMR is extensively used for structural analysis of complex molecules and materials. The remaining market share is distributed among chemical manufacturing (15%), food and beverage testing (7%), and environmental monitoring (3%) sectors.
Regionally, North America dominates the market with approximately 40% share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate due to expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and increasing R&D investments.
Key market drivers include the growing complexity of molecular structures requiring analysis, rising quality control standards across industries, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with NMR data processing. The trend toward miniaturization and automation of NMR systems is also creating demand for more sophisticated calibration solutions.
Customer pain points in the current market include inconsistent calibration standards between different NMR systems, time-consuming manual calibration processes, and difficulties in comparing data across different laboratories or instruments. End-users are increasingly seeking automated calibration solutions that can reduce human error and improve reproducibility of results.
Market surveys indicate that customers are willing to pay premium prices for calibration solutions that offer demonstrable improvements in data quality, reproducibility, and analysis speed. The return on investment for advanced calibration methods is typically realized through reduced experimental failures, faster analytical workflows, and more reliable research outcomes.
Emerging market opportunities include cloud-based calibration services, subscription models for calibration standard materials, and integrated software solutions that combine calibration with advanced data analysis capabilities. The development of industry-specific calibration standards represents another growth avenue, particularly for specialized applications in metabolomics, proteomics, and materials science.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the largest consumers of NMR calibration solutions, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. These industries rely heavily on NMR spectroscopy for drug discovery, development, and quality control processes. The need for standardized calibration methods has become particularly acute as regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical products continue to tighten globally.
Academic and research institutions constitute the second-largest market segment at 30%, where NMR is extensively used for structural analysis of complex molecules and materials. The remaining market share is distributed among chemical manufacturing (15%), food and beverage testing (7%), and environmental monitoring (3%) sectors.
Regionally, North America dominates the market with approximately 40% share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate due to expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and increasing R&D investments.
Key market drivers include the growing complexity of molecular structures requiring analysis, rising quality control standards across industries, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with NMR data processing. The trend toward miniaturization and automation of NMR systems is also creating demand for more sophisticated calibration solutions.
Customer pain points in the current market include inconsistent calibration standards between different NMR systems, time-consuming manual calibration processes, and difficulties in comparing data across different laboratories or instruments. End-users are increasingly seeking automated calibration solutions that can reduce human error and improve reproducibility of results.
Market surveys indicate that customers are willing to pay premium prices for calibration solutions that offer demonstrable improvements in data quality, reproducibility, and analysis speed. The return on investment for advanced calibration methods is typically realized through reduced experimental failures, faster analytical workflows, and more reliable research outcomes.
Emerging market opportunities include cloud-based calibration services, subscription models for calibration standard materials, and integrated software solutions that combine calibration with advanced data analysis capabilities. The development of industry-specific calibration standards represents another growth avenue, particularly for specialized applications in metabolomics, proteomics, and materials science.
Current Limitations in NMR Data Standardization
Despite significant advancements in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the field continues to face substantial challenges in data standardization that impede optimal utilization of this powerful analytical technique. Current NMR data processing workflows suffer from inconsistent calibration methodologies across different laboratories and research institutions, resulting in difficulties when comparing or integrating datasets from multiple sources. This lack of standardization creates significant barriers to reproducibility, a cornerstone principle in scientific research.
One of the primary limitations is the absence of universally accepted reference standards for chemical shift calibration. While tetramethylsilane (TMS) is commonly used for organic samples, its application varies in concentration and implementation protocols. For biological samples, the reference compounds differ even more widely, with 4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-sulfonic acid (DSS), trimethylsilylpropanoic acid (TSP), and others being used without consistent guidelines.
Instrument-specific variations present another significant challenge. Different NMR spectrometer manufacturers implement proprietary data formats and processing algorithms, creating compatibility issues when transferring data between systems. These variations extend to hardware components such as probe designs and gradient systems, which introduce systematic differences in spectral quality and resolution that are difficult to normalize without standardized calibration protocols.
Environmental factors further complicate standardization efforts. Temperature fluctuations, even minor ones, can cause significant chemical shift variations in NMR spectra. Current practices for temperature calibration lack precision across different laboratories, with deviations of ±1°C being common. Such variations dramatically affect the reproducibility of measurements for temperature-sensitive samples, particularly in biomolecular NMR studies.
Sample preparation inconsistencies represent another critical limitation. Variations in solvent purity, concentration methods, pH adjustment procedures, and buffer compositions directly impact spectral quality and chemical shift values. The absence of standardized protocols for these preparatory steps introduces significant variability in the resulting data, complicating multi-center research efforts and meta-analyses.
Data processing workflows exhibit considerable heterogeneity across the NMR community. Phase correction, baseline adjustment, and integration methods vary widely between software packages and individual researchers. These processing differences can introduce artificial variations in the final spectral data that are difficult to distinguish from genuine sample differences, undermining the reliability of comparative analyses.
The lack of comprehensive metadata standards further exacerbates these issues. Current NMR data files often contain insufficient experimental details, making it challenging to reproduce experiments or properly account for methodological differences when comparing results. This metadata deficiency becomes particularly problematic when attempting to apply machine learning or other advanced analytical approaches to NMR datasets from diverse sources.
One of the primary limitations is the absence of universally accepted reference standards for chemical shift calibration. While tetramethylsilane (TMS) is commonly used for organic samples, its application varies in concentration and implementation protocols. For biological samples, the reference compounds differ even more widely, with 4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-sulfonic acid (DSS), trimethylsilylpropanoic acid (TSP), and others being used without consistent guidelines.
Instrument-specific variations present another significant challenge. Different NMR spectrometer manufacturers implement proprietary data formats and processing algorithms, creating compatibility issues when transferring data between systems. These variations extend to hardware components such as probe designs and gradient systems, which introduce systematic differences in spectral quality and resolution that are difficult to normalize without standardized calibration protocols.
Environmental factors further complicate standardization efforts. Temperature fluctuations, even minor ones, can cause significant chemical shift variations in NMR spectra. Current practices for temperature calibration lack precision across different laboratories, with deviations of ±1°C being common. Such variations dramatically affect the reproducibility of measurements for temperature-sensitive samples, particularly in biomolecular NMR studies.
Sample preparation inconsistencies represent another critical limitation. Variations in solvent purity, concentration methods, pH adjustment procedures, and buffer compositions directly impact spectral quality and chemical shift values. The absence of standardized protocols for these preparatory steps introduces significant variability in the resulting data, complicating multi-center research efforts and meta-analyses.
Data processing workflows exhibit considerable heterogeneity across the NMR community. Phase correction, baseline adjustment, and integration methods vary widely between software packages and individual researchers. These processing differences can introduce artificial variations in the final spectral data that are difficult to distinguish from genuine sample differences, undermining the reliability of comparative analyses.
The lack of comprehensive metadata standards further exacerbates these issues. Current NMR data files often contain insufficient experimental details, making it challenging to reproduce experiments or properly account for methodological differences when comparing results. This metadata deficiency becomes particularly problematic when attempting to apply machine learning or other advanced analytical approaches to NMR datasets from diverse sources.
Contemporary NMR Data Calibration Methodologies
01 Signal processing techniques for NMR data enhancement
Various signal processing algorithms and methods can be applied to enhance NMR data quality. These techniques include noise reduction filters, baseline correction algorithms, and advanced mathematical transformations that improve signal-to-noise ratio. By applying these digital processing techniques to raw NMR data, researchers can extract clearer spectral information and enhance the resolution of NMR signals, leading to more accurate analysis and interpretation of molecular structures.- Signal processing techniques for NMR data enhancement: Various signal processing algorithms and methods can be applied to enhance NMR data quality. These techniques include noise reduction filters, baseline correction algorithms, and advanced mathematical transformations that improve signal-to-noise ratio. By applying these digital processing techniques to raw NMR data, researchers can extract clearer spectral information and enhance the resolution of NMR signals, leading to more accurate analysis and interpretation of molecular structures.
- Hardware improvements for NMR signal enhancement: Advancements in NMR hardware design contribute significantly to data enhancement. These improvements include more sensitive detection coils, optimized magnet configurations, and enhanced probe designs that minimize interference. Hardware innovations focus on increasing magnetic field homogeneity and stability, resulting in sharper peaks and better spectral resolution. These physical enhancements to NMR equipment allow for detection of weaker signals and acquisition of higher quality data.
- Pulse sequence optimization for enhanced NMR data: Specialized pulse sequences can be designed to enhance specific aspects of NMR data. These optimized sequences can suppress unwanted signals, enhance particular molecular interactions, or improve resolution in complex samples. By carefully timing and shaping the radiofrequency pulses applied during NMR experiments, researchers can selectively highlight information of interest while minimizing interference from other signals, resulting in cleaner and more informative spectra.
- Machine learning and AI applications in NMR data enhancement: Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being applied to enhance NMR data quality and interpretation. These computational approaches can identify patterns in noisy data, automatically correct artifacts, and extract meaningful information from complex spectra. Neural networks and other AI techniques can be trained to recognize spectral features that might be missed by conventional analysis methods, enabling more comprehensive and accurate interpretation of NMR results.
- Multi-dimensional NMR techniques for enhanced spectral resolution: Multi-dimensional NMR methods provide enhanced resolution by spreading spectral information across multiple frequency dimensions. These techniques correlate different types of nuclear interactions, allowing researchers to separate overlapping signals and resolve complex molecular structures. By acquiring data in two, three, or more dimensions, these methods can untangle complicated spectra and provide detailed structural information that would be impossible to obtain from conventional one-dimensional experiments.
02 Hardware improvements for NMR signal enhancement
Advancements in NMR hardware design contribute significantly to data enhancement. These include improved magnet designs, more sensitive RF coils, and optimized probe configurations. Hardware innovations focus on increasing magnetic field homogeneity, enhancing detection sensitivity, and reducing electronic noise. These physical improvements to NMR instrumentation result in higher quality raw data acquisition, which forms the foundation for subsequent data processing and analysis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pulse sequence optimization for enhanced NMR data
Specialized pulse sequences can be designed to enhance specific aspects of NMR data. These sequences manipulate nuclear spins in ways that highlight particular molecular features, suppress unwanted signals, or enhance sensitivity for specific applications. Advanced pulse sequence techniques include multi-dimensional experiments, selective excitation methods, and coherence pathway selection. By tailoring the pulse sequence to the specific analytical needs, researchers can significantly improve the quality and information content of NMR data.Expand Specific Solutions04 Machine learning and AI approaches for NMR data enhancement
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being applied to enhance NMR data quality and interpretation. These computational approaches can identify patterns in noisy data, reconstruct incomplete spectra, and automatically correct artifacts. Neural networks and other AI techniques can be trained to distinguish between signal and noise, enabling enhanced spectral resolution and more accurate peak identification. These methods are particularly valuable for complex samples or when working with limited or low-quality data.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sample preparation and experimental condition optimization
Improvements in sample preparation techniques and experimental conditions can significantly enhance NMR data quality. This includes methods for reducing sample impurities, optimizing solvent selection, controlling temperature stability, and enhancing molecular alignment in specific applications. Proper shimming procedures and calibration techniques also contribute to better spectral quality. By optimizing these pre-acquisition factors, researchers can obtain cleaner, more informative NMR data that requires less post-processing enhancement.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in NMR Technology Development
NMR data enhancement through standardized calibration methods is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing applications in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and industrial testing. The global market size for NMR technologies is estimated at $1.5-2 billion, growing at 5-7% annually. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players like Siemens Healthineers, Roche Diagnostics, and United Imaging Healthcare focus on high-end clinical applications, while specialized firms such as Aspect Imaging and Niumag Analytical develop compact systems. Academic institutions including Emory University and Xiamen University contribute significant research advancements. The industry is witnessing a trend toward more standardized calibration protocols to improve data reliability and cross-platform compatibility.
Siemens Healthineers AG
Technical Solution: Siemens Healthineers has developed a sophisticated NMR data enhancement framework centered on their syngo.MR software platform. Their approach implements multi-parameter standardized calibration that accounts for both hardware variations and sample conditions. The technology incorporates reference phantoms with precisely known chemical compositions to establish calibration baselines across different magnetic field strengths and gradient systems. Siemens' solution features automated protocols that apply standardized corrections for temperature fluctuations, magnetic field inhomogeneities, and electronic noise[2]. Their system employs advanced signal processing algorithms including wavelet-based denoising and statistical parameter mapping to enhance spectral quality while maintaining quantitative accuracy. The platform also includes cloud-based calibration reference databases that enable cross-site standardization and facilitate multi-center research studies requiring consistent NMR data quality.
Strengths: Exceptional integration with clinical workflows; robust performance across different magnetic field strengths; comprehensive quality control metrics. Weaknesses: Primarily optimized for clinical rather than research applications; higher initial investment; proprietary calibration standards may limit interoperability with other systems.
Wuhan Zhongke-Niujin Magnetic Resonance Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wuhan Zhongke-Niujin has developed a comprehensive NMR data enhancement system focused on standardized calibration methods particularly suited for benchtop and portable NMR applications. Their technology incorporates reference standard compounds specifically designed for low-field NMR systems, enabling precise calibration across different magnetic field strengths. The company's approach includes automated protocols for temperature compensation, magnetic field drift correction, and electronic noise reduction that maintain data quality in variable environmental conditions. Their solution features proprietary algorithms for spectral deconvolution and peak integration that work in conjunction with their calibration standards to ensure quantitative accuracy even in challenging field conditions[4]. The system implements machine learning techniques to recognize patterns in calibration spectra and automatically adjust acquisition parameters to maintain consistency. Additionally, their platform includes cloud-based calibration reference databases that enable cross-instrument standardization and facilitate collaborative research requiring consistent NMR data quality.
Strengths: Exceptional performance in portable and benchtop NMR applications; robust operation in variable environmental conditions; cost-effective implementation compared to high-field alternatives. Weaknesses: Limited application in ultra-high field research settings; smaller reference compound library compared to major competitors; less extensive integration with laboratory information management systems.
Critical Patents in NMR Signal Processing
Method of performing error-correction of NMR data.
PatentActiveMX2014009202A
Innovation
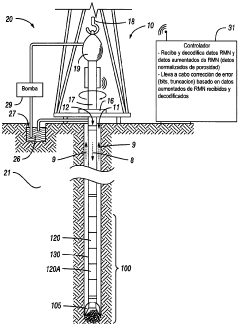
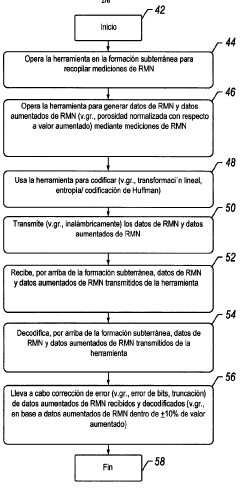
- A method and system for generating and encoding NMR data in underground formations, followed by error correction using augmented NMR data and decoding above ground, employing techniques like linear transformation and entropy encoding, along with bit and truncation error correction mechanisms.
System and method for nuclear magnetic resonance calibration
PatentPendingUS20250251476A1
Innovation
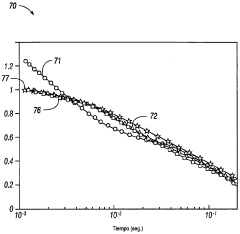
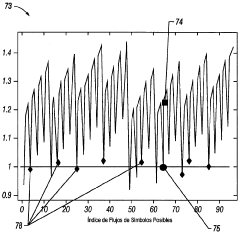
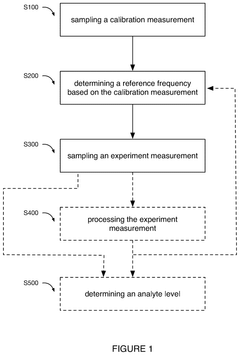
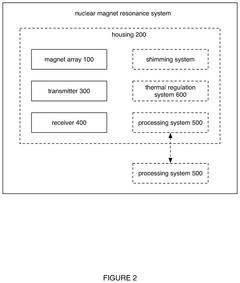
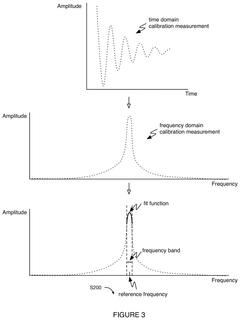
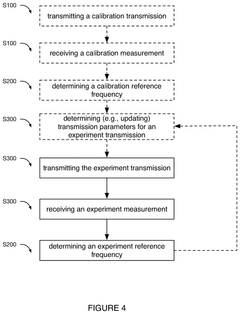
- A software-based calibration method is employed to adjust transmission parameters and correct for frequency drift, utilizing a magnet array, transmitter, and receiver to sample calibration and experiment measurements, with a focus on reducing delay and improving accuracy by using small tip angles and thermal regulation.
Regulatory Standards for NMR Data in Scientific Research
The regulatory landscape for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in scientific research has evolved significantly over the past decades, reflecting the growing importance of standardization in analytical chemistry. Currently, several international bodies govern the standards for NMR data acquisition, processing, and reporting, including the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
These regulatory frameworks typically address key aspects of NMR data management, including calibration protocols, reference standards, and data reporting formats. For instance, IUPAC has established guidelines for chemical shift referencing, recommending the use of tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the primary reference standard for 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. This standardization ensures comparability of results across different laboratories and instruments.
The pharmaceutical industry faces particularly stringent requirements under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have implemented specific guidelines for NMR data in drug development and quality control processes, emphasizing the need for validated calibration methods and comprehensive documentation of experimental parameters.
Recent regulatory developments have focused on data integrity and traceability. The FDA's guidance on data integrity requires complete audit trails for NMR data, including raw data preservation and documentation of all processing steps. Similarly, the EMA's guidelines emphasize the importance of maintaining the original spectral data alongside processed results to ensure reproducibility and facilitate regulatory review.
Academic journals have also established their own standards for NMR data reporting. Publications like the Journal of Magnetic Resonance and the Journal of Biomolecular NMR require authors to provide detailed experimental conditions, including spectrometer frequency, temperature, solvent, and reference standards used. These requirements help ensure that published results can be independently verified and reproduced.
The emergence of digital repositories for NMR data, such as the Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank (BMRB) and the Metabolomics Workbench, has further driven standardization efforts. These repositories typically enforce specific data formats and metadata requirements, promoting the FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) for scientific data management.
Despite these advances, significant gaps remain in global regulatory harmonization for NMR data. Different regions and industries often follow varying standards, creating challenges for international collaboration and data exchange. Efforts are underway through organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) to develop more unified approaches to NMR data standardization across different regulatory jurisdictions.
These regulatory frameworks typically address key aspects of NMR data management, including calibration protocols, reference standards, and data reporting formats. For instance, IUPAC has established guidelines for chemical shift referencing, recommending the use of tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the primary reference standard for 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. This standardization ensures comparability of results across different laboratories and instruments.
The pharmaceutical industry faces particularly stringent requirements under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have implemented specific guidelines for NMR data in drug development and quality control processes, emphasizing the need for validated calibration methods and comprehensive documentation of experimental parameters.
Recent regulatory developments have focused on data integrity and traceability. The FDA's guidance on data integrity requires complete audit trails for NMR data, including raw data preservation and documentation of all processing steps. Similarly, the EMA's guidelines emphasize the importance of maintaining the original spectral data alongside processed results to ensure reproducibility and facilitate regulatory review.
Academic journals have also established their own standards for NMR data reporting. Publications like the Journal of Magnetic Resonance and the Journal of Biomolecular NMR require authors to provide detailed experimental conditions, including spectrometer frequency, temperature, solvent, and reference standards used. These requirements help ensure that published results can be independently verified and reproduced.
The emergence of digital repositories for NMR data, such as the Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank (BMRB) and the Metabolomics Workbench, has further driven standardization efforts. These repositories typically enforce specific data formats and metadata requirements, promoting the FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) for scientific data management.
Despite these advances, significant gaps remain in global regulatory harmonization for NMR data. Different regions and industries often follow varying standards, creating challenges for international collaboration and data exchange. Efforts are underway through organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) to develop more unified approaches to NMR data standardization across different regulatory jurisdictions.
Cross-Industry Applications of Standardized NMR Data
Standardized NMR data has demonstrated remarkable versatility across multiple industries, extending far beyond its traditional applications in chemistry and pharmaceutical research. In the food and beverage industry, standardized NMR calibration methods have revolutionized quality control processes, enabling precise authentication of premium products such as olive oils, wines, and honey. These methods can detect adulterations and verify geographical origins with unprecedented accuracy, protecting both consumers and legitimate producers from fraudulent practices.
The petroleum and energy sectors have embraced standardized NMR data for optimizing extraction processes and characterizing complex hydrocarbon mixtures. By implementing uniform calibration protocols, companies can now compare data across different operational sites and equipment manufacturers, leading to more efficient resource utilization and reduced environmental impact. This standardization has been particularly valuable for multinational corporations managing diverse global operations.
In environmental monitoring, standardized NMR techniques have emerged as powerful tools for analyzing soil compositions, water contaminants, and atmospheric pollutants. Regulatory agencies and research institutions can now share and compare results meaningfully, creating comprehensive environmental datasets that inform policy decisions and remediation efforts. The ability to detect minute concentrations of pollutants with calibrated precision has significantly enhanced environmental protection capabilities.
The medical diagnostics field represents perhaps the most promising cross-industry application of standardized NMR data. Metabolomic profiling using calibrated NMR spectroscopy has enabled early detection of various diseases through non-invasive methods. Hospitals and clinical laboratories adopting these standardized protocols can exchange patient data securely while maintaining consistent diagnostic quality, regardless of the equipment manufacturer or geographical location.
Materials science and manufacturing industries have leveraged standardized NMR calibration to improve quality control in polymer production, composite materials, and nanomaterials. This has facilitated international collaboration in developing advanced materials with precisely controlled properties. The semiconductor industry, in particular, has benefited from enhanced purity verification of silicon and other critical materials through standardized NMR methods.
Agricultural applications have expanded significantly, with standardized NMR data supporting soil health assessment, fertilizer optimization, and crop quality evaluation. Farmers and agricultural scientists can now make data-driven decisions based on reliable, comparable measurements across different growing regions and seasons, contributing to more sustainable farming practices and improved food security globally.
The petroleum and energy sectors have embraced standardized NMR data for optimizing extraction processes and characterizing complex hydrocarbon mixtures. By implementing uniform calibration protocols, companies can now compare data across different operational sites and equipment manufacturers, leading to more efficient resource utilization and reduced environmental impact. This standardization has been particularly valuable for multinational corporations managing diverse global operations.
In environmental monitoring, standardized NMR techniques have emerged as powerful tools for analyzing soil compositions, water contaminants, and atmospheric pollutants. Regulatory agencies and research institutions can now share and compare results meaningfully, creating comprehensive environmental datasets that inform policy decisions and remediation efforts. The ability to detect minute concentrations of pollutants with calibrated precision has significantly enhanced environmental protection capabilities.
The medical diagnostics field represents perhaps the most promising cross-industry application of standardized NMR data. Metabolomic profiling using calibrated NMR spectroscopy has enabled early detection of various diseases through non-invasive methods. Hospitals and clinical laboratories adopting these standardized protocols can exchange patient data securely while maintaining consistent diagnostic quality, regardless of the equipment manufacturer or geographical location.
Materials science and manufacturing industries have leveraged standardized NMR calibration to improve quality control in polymer production, composite materials, and nanomaterials. This has facilitated international collaboration in developing advanced materials with precisely controlled properties. The semiconductor industry, in particular, has benefited from enhanced purity verification of silicon and other critical materials through standardized NMR methods.
Agricultural applications have expanded significantly, with standardized NMR data supporting soil health assessment, fertilizer optimization, and crop quality evaluation. Farmers and agricultural scientists can now make data-driven decisions based on reliable, comparable measurements across different growing regions and seasons, contributing to more sustainable farming practices and improved food security globally.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!