Resolving Anisotropic Separations in NMR Sample Analysis
SEP 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Anisotropic Separation Background and Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, becoming an indispensable analytical tool in chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. The phenomenon of anisotropic separation in NMR sample analysis represents one of the most challenging aspects of this technology, stemming from the directional dependence of molecular interactions within samples. This technical challenge has gained increasing attention as researchers push the boundaries of molecular structure determination and dynamic analysis.
The evolution of NMR technology has progressed from simple one-dimensional proton spectra to sophisticated multi-dimensional experiments capable of elucidating complex molecular structures. Throughout this development, the issue of anisotropic effects has persistently complicated accurate interpretation of spectral data, particularly in solid-state NMR and partially oriented samples such as liquid crystals, membrane proteins, and polymeric materials.
Recent technological advancements in magnet design, pulse sequence development, and computational methods have created new opportunities to address these challenges. High-field magnets exceeding 1 GHz for proton frequency, combined with advanced probe technologies, have improved spectral resolution significantly. However, anisotropic separations continue to present fundamental limitations to the analytical power of NMR spectroscopy.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate current methodologies for resolving anisotropic separations in NMR sample analysis and identify promising directions for innovation. We aim to develop improved techniques that can effectively separate and interpret anisotropic interactions, thereby enhancing the accuracy and applicability of NMR spectroscopy across diverse sample types.
Specifically, this research seeks to achieve several interconnected goals: first, to characterize the fundamental physical principles underlying anisotropic effects in various sample environments; second, to assess the effectiveness of existing methodological approaches including magic angle spinning (MAS), specialized pulse sequences, and tensor-based mathematical models; and third, to explore emerging technologies such as dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) and machine learning algorithms that may offer novel solutions to these longstanding challenges.
The technological trajectory suggests that resolving anisotropic separations will be critical for expanding NMR applications in materials science, structural biology, and pharmaceutical development. As researchers increasingly focus on complex heterogeneous systems and in-situ measurements, the ability to accurately account for and utilize anisotropic information will become a defining capability in advanced analytical chemistry.
The evolution of NMR technology has progressed from simple one-dimensional proton spectra to sophisticated multi-dimensional experiments capable of elucidating complex molecular structures. Throughout this development, the issue of anisotropic effects has persistently complicated accurate interpretation of spectral data, particularly in solid-state NMR and partially oriented samples such as liquid crystals, membrane proteins, and polymeric materials.
Recent technological advancements in magnet design, pulse sequence development, and computational methods have created new opportunities to address these challenges. High-field magnets exceeding 1 GHz for proton frequency, combined with advanced probe technologies, have improved spectral resolution significantly. However, anisotropic separations continue to present fundamental limitations to the analytical power of NMR spectroscopy.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate current methodologies for resolving anisotropic separations in NMR sample analysis and identify promising directions for innovation. We aim to develop improved techniques that can effectively separate and interpret anisotropic interactions, thereby enhancing the accuracy and applicability of NMR spectroscopy across diverse sample types.
Specifically, this research seeks to achieve several interconnected goals: first, to characterize the fundamental physical principles underlying anisotropic effects in various sample environments; second, to assess the effectiveness of existing methodological approaches including magic angle spinning (MAS), specialized pulse sequences, and tensor-based mathematical models; and third, to explore emerging technologies such as dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) and machine learning algorithms that may offer novel solutions to these longstanding challenges.
The technological trajectory suggests that resolving anisotropic separations will be critical for expanding NMR applications in materials science, structural biology, and pharmaceutical development. As researchers increasingly focus on complex heterogeneous systems and in-situ measurements, the ability to accurately account for and utilize anisotropic information will become a defining capability in advanced analytical chemistry.
Market Analysis for Advanced NMR Analytical Solutions
The global Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy market continues to expand significantly, with a current valuation exceeding $2.5 billion and projected growth rates of 4-5% annually through 2028. This growth is primarily driven by increasing demand for advanced analytical solutions across pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and academic research sectors, where precise molecular characterization is essential for drug development and scientific advancement.
The market for specialized NMR solutions addressing anisotropic separations represents a particularly dynamic segment. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly willing to invest in premium NMR technologies that can resolve complex molecular structures and interactions, with average expenditures for advanced NMR systems ranging from $500,000 to $2 million depending on field strength and capabilities.
Recent market surveys indicate that over 70% of pharmaceutical R&D facilities consider enhanced anisotropic resolution capabilities as "highly important" or "critical" for their analytical workflows. This demand is creating significant opportunities for technology providers who can deliver solutions that overcome traditional limitations in sample analysis, particularly for complex biomolecules and novel therapeutic compounds.
Geographically, North America continues to dominate the advanced NMR market with approximately 40% market share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging markets, particularly China and India, where investments in life science research infrastructure are expanding rapidly, with annual growth rates exceeding 8%.
The competitive landscape features established players like Bruker, JEOL, and Thermo Fisher Scientific controlling nearly 75% of the global NMR market. However, specialized solution providers focusing on anisotropic separation technologies are gaining traction, particularly those offering software and sample preparation innovations that enhance existing hardware capabilities.
Customer segmentation reveals distinct needs across different sectors. Pharmaceutical companies prioritize throughput and reproducibility, academic institutions value flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while contract research organizations emphasize integration with existing workflows and data management systems. This diversification of requirements is driving the development of more customized NMR solutions.
Market forecasts suggest that technologies specifically addressing anisotropic separation challenges could grow at 1.5-2 times the rate of the broader NMR market over the next five years. This acceleration is supported by increasing regulatory requirements for structural characterization of complex biologics and the growing importance of detailed molecular interaction studies in drug discovery programs.
The market for specialized NMR solutions addressing anisotropic separations represents a particularly dynamic segment. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly willing to invest in premium NMR technologies that can resolve complex molecular structures and interactions, with average expenditures for advanced NMR systems ranging from $500,000 to $2 million depending on field strength and capabilities.
Recent market surveys indicate that over 70% of pharmaceutical R&D facilities consider enhanced anisotropic resolution capabilities as "highly important" or "critical" for their analytical workflows. This demand is creating significant opportunities for technology providers who can deliver solutions that overcome traditional limitations in sample analysis, particularly for complex biomolecules and novel therapeutic compounds.
Geographically, North America continues to dominate the advanced NMR market with approximately 40% market share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging markets, particularly China and India, where investments in life science research infrastructure are expanding rapidly, with annual growth rates exceeding 8%.
The competitive landscape features established players like Bruker, JEOL, and Thermo Fisher Scientific controlling nearly 75% of the global NMR market. However, specialized solution providers focusing on anisotropic separation technologies are gaining traction, particularly those offering software and sample preparation innovations that enhance existing hardware capabilities.
Customer segmentation reveals distinct needs across different sectors. Pharmaceutical companies prioritize throughput and reproducibility, academic institutions value flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while contract research organizations emphasize integration with existing workflows and data management systems. This diversification of requirements is driving the development of more customized NMR solutions.
Market forecasts suggest that technologies specifically addressing anisotropic separation challenges could grow at 1.5-2 times the rate of the broader NMR market over the next five years. This acceleration is supported by increasing regulatory requirements for structural characterization of complex biologics and the growing importance of detailed molecular interaction studies in drug discovery programs.
Current Challenges in Anisotropic NMR Separations
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy faces significant challenges when dealing with anisotropic separations, particularly in complex sample analysis. The fundamental issue stems from molecular orientation dependencies that create anisotropic interactions, leading to spectral complications that conventional isotropic NMR methods struggle to resolve. These orientation-dependent effects manifest as line broadening, signal overlap, and reduced resolution, severely limiting analytical precision.
One major technical hurdle involves the alignment of molecules in magnetic fields, where anisotropic magnetic susceptibility causes differential alignment that varies with molecular structure. This creates inconsistent spectral patterns across similar compounds, making comparative analysis problematic. Current hardware configurations often lack the sensitivity required to detect subtle anisotropic effects, necessitating extended acquisition times that may introduce sample degradation artifacts.
Sample preparation presents another significant challenge, as traditional methods often fail to maintain consistent molecular orientation throughout the sample volume. This heterogeneity introduces variability in spectral data that complicates interpretation and reduces reproducibility. The development of specialized sample holders and preparation protocols has progressed slowly, with limited standardization across research facilities.
Data processing algorithms represent a critical bottleneck in anisotropic NMR analysis. Conventional processing methods designed for isotropic conditions fail to adequately separate overlapping signals resulting from anisotropic interactions. While advanced computational approaches like tensor-based decomposition show promise, they remain computationally intensive and require specialized expertise not widely available in analytical laboratories.
Temperature control during analysis presents particular difficulties, as anisotropic interactions demonstrate significant temperature dependence. Even minor temperature fluctuations can dramatically alter spectral characteristics, yet achieving uniform temperature distribution throughout samples remains technically challenging, especially for viscous or heterogeneous samples.
The integration of anisotropic NMR data with other analytical techniques presents interoperability challenges. Current data formats and processing workflows lack standardized methods for combining anisotropic NMR information with complementary techniques like mass spectrometry or X-ray crystallography, limiting holistic sample characterization.
Field homogeneity represents perhaps the most persistent technical limitation, as anisotropic separations require exceptionally uniform magnetic fields to achieve meaningful resolution. Current magnet technologies struggle to maintain the required homogeneity across the entire sample volume, particularly at higher field strengths where anisotropic effects become more pronounced.
One major technical hurdle involves the alignment of molecules in magnetic fields, where anisotropic magnetic susceptibility causes differential alignment that varies with molecular structure. This creates inconsistent spectral patterns across similar compounds, making comparative analysis problematic. Current hardware configurations often lack the sensitivity required to detect subtle anisotropic effects, necessitating extended acquisition times that may introduce sample degradation artifacts.
Sample preparation presents another significant challenge, as traditional methods often fail to maintain consistent molecular orientation throughout the sample volume. This heterogeneity introduces variability in spectral data that complicates interpretation and reduces reproducibility. The development of specialized sample holders and preparation protocols has progressed slowly, with limited standardization across research facilities.
Data processing algorithms represent a critical bottleneck in anisotropic NMR analysis. Conventional processing methods designed for isotropic conditions fail to adequately separate overlapping signals resulting from anisotropic interactions. While advanced computational approaches like tensor-based decomposition show promise, they remain computationally intensive and require specialized expertise not widely available in analytical laboratories.
Temperature control during analysis presents particular difficulties, as anisotropic interactions demonstrate significant temperature dependence. Even minor temperature fluctuations can dramatically alter spectral characteristics, yet achieving uniform temperature distribution throughout samples remains technically challenging, especially for viscous or heterogeneous samples.
The integration of anisotropic NMR data with other analytical techniques presents interoperability challenges. Current data formats and processing workflows lack standardized methods for combining anisotropic NMR information with complementary techniques like mass spectrometry or X-ray crystallography, limiting holistic sample characterization.
Field homogeneity represents perhaps the most persistent technical limitation, as anisotropic separations require exceptionally uniform magnetic fields to achieve meaningful resolution. Current magnet technologies struggle to maintain the required homogeneity across the entire sample volume, particularly at higher field strengths where anisotropic effects become more pronounced.
Current Methodologies for Anisotropic Separation Resolution
01 NMR techniques for anisotropic sample analysis
Various NMR techniques have been developed specifically for analyzing anisotropic samples. These techniques involve specialized pulse sequences and data processing methods that can detect and characterize anisotropic properties in materials. The methods allow for enhanced resolution and separation of signals based on anisotropic interactions, providing detailed structural information about complex samples.- NMR techniques for anisotropic sample analysis: Various NMR techniques have been developed specifically for analyzing anisotropic samples. These techniques involve specialized pulse sequences and data processing methods that can detect and characterize anisotropic properties in materials. The methods allow for enhanced resolution and separation of signals based on anisotropic interactions, providing detailed structural information that cannot be obtained from conventional isotropic NMR experiments.
- Hardware configurations for anisotropic NMR measurements: Specialized hardware configurations have been designed for NMR measurements of anisotropic samples. These include modified probe designs, gradient coil arrangements, and magnet systems that can generate controlled field gradients or maintain sample orientation. Such hardware enables the measurement of anisotropic properties by creating controlled conditions that enhance the detection of directional dependencies in molecular interactions.
- Analysis of geological samples using anisotropic NMR: Anisotropic NMR techniques are particularly valuable for analyzing geological samples such as rock cores and oil-bearing formations. These methods can determine directional permeability, fluid flow characteristics, and structural properties of porous media. By measuring the anisotropic diffusion of fluids within these samples, researchers can extract information about pore structure, connectivity, and fluid dynamics that is crucial for reservoir characterization and oil extraction optimization.
- Biological applications of anisotropic NMR separations: Anisotropic NMR separations have important applications in biological research, particularly for studying oriented biomolecules such as membrane proteins, fibrils, and liquid crystals. These techniques can resolve structural features based on orientation-dependent interactions, providing insights into molecular alignment, dynamics, and function. The methods are especially valuable for analyzing complex biological systems where conventional isotropic NMR would provide insufficient resolution or information.
- Advanced data processing for anisotropic NMR signals: Sophisticated data processing algorithms have been developed to extract meaningful information from anisotropic NMR signals. These include multidimensional analysis techniques, tensor-based processing methods, and computational approaches that can separate overlapping signals based on their anisotropic properties. Such advanced processing enables researchers to interpret complex spectral patterns and extract quantitative parameters related to molecular orientation, order, and dynamics in anisotropic samples.
02 Hardware configurations for anisotropic NMR measurements
Specialized hardware configurations have been designed to facilitate anisotropic NMR measurements. These include modified probe designs, gradient systems, and magnet arrangements that can generate controlled field gradients or maintain sample orientation. Such hardware innovations enable more precise measurements of anisotropic properties and improve the quality of data obtained from samples with directional dependencies.Expand Specific Solutions03 Analysis of geological samples using anisotropic NMR
Anisotropic NMR techniques are particularly valuable for analyzing geological samples such as rock cores and oil-bearing formations. These methods can characterize the directional permeability, porosity, and fluid flow properties in such samples. By measuring anisotropic diffusion and relaxation parameters, these techniques provide insights into the structural organization of porous media and help in reservoir characterization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biological and medical applications of anisotropic NMR
Anisotropic NMR separations are valuable in biological and medical applications, particularly for analyzing tissues with directional structures like muscle fibers, nerve tracts, and collagen. These techniques can detect structural anisotropy in biological samples, helping to diagnose pathological conditions and understand tissue organization. The methods are also useful for monitoring changes in tissue anisotropy during disease progression or treatment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced data processing for anisotropic NMR signals
Sophisticated data processing algorithms have been developed to extract meaningful information from anisotropic NMR signals. These include tensor analysis methods, multidimensional signal processing, and machine learning approaches that can separate overlapping signals based on their anisotropic properties. Such computational techniques enhance the resolution and information content of NMR data from complex anisotropic samples.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in NMR Instrumentation and Research
The NMR sample analysis technology landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with an estimated market size exceeding $1.5 billion and steady annual growth. Leading players include JEOL Ltd. and Bruker, who dominate the high-end instrumentation segment, while Waters Technology Corp. focuses on specialized separation technologies. F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Otsuka Pharmaceutical represent pharmaceutical industry applications, with significant R&D investments in anisotropic separation techniques. Academic institutions like University of Tokyo and University of California contribute fundamental research, while Hitachi and Rigaku provide complementary analytical technologies. The ecosystem demonstrates a balanced mix of established commercial solutions and ongoing innovation, particularly in resolving complex molecular structures through advanced NMR methodologies.
Waters Technology Corp.
Technical Solution: Waters Technology has developed a sophisticated approach to resolving anisotropic separations in NMR sample analysis through their integrated chromatography-NMR platform. Their technology combines advanced liquid chromatography (LC) separation techniques with specialized NMR detection methods optimized for anisotropic samples. Waters' systems feature unique flow-cell designs that preserve molecular orientation during the transition from separation to detection phases. Their proprietary software algorithms can distinguish between isotropic and anisotropic contributions to the NMR signal, enabling researchers to extract orientation-dependent information even from complex mixtures. Waters has also developed specialized sample preparation protocols that enhance anisotropic effects through the use of alignment media such as stretched polymer gels and liquid crystalline phases. Their technology incorporates advanced pulse sequences specifically designed to measure residual dipolar couplings and other anisotropic NMR parameters that provide critical structural information. The integration of LC with NMR allows for the analysis of complex mixtures where anisotropic effects might otherwise be obscured by signal overlap[6][8].
Strengths: Unique integration of chromatographic separation with NMR analysis provides superior resolution for complex mixtures exhibiting anisotropic properties. Specialized flow-cell technology preserves molecular orientation throughout the analytical process. Weaknesses: The combined LC-NMR approach requires expertise in both chromatography and NMR spectroscopy, potentially limiting user accessibility. System complexity can lead to higher maintenance requirements and operational costs.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed a comprehensive platform for resolving anisotropic separations in NMR sample analysis, primarily focused on applications in pharmaceutical research and development. Their approach combines high-field NMR spectroscopy with specialized sample preparation techniques designed to enhance and control molecular orientation. Roche's technology utilizes custom-designed alignment media, including stretched polymer gels and liquid crystalline phases, that induce partial molecular alignment while maintaining compatibility with biological samples. Their NMR systems incorporate advanced pulse sequences specifically optimized for measuring residual dipolar couplings (RDCs), residual chemical shift anisotropy (RCSA), and other anisotropic parameters that provide critical information about molecular conformation and interactions. Roche has also developed proprietary software algorithms for extracting structural information from anisotropic NMR data and integrating this with computational modeling to generate accurate three-dimensional structures of drug candidates and their target proteins. Their approach has been particularly valuable for analyzing the conformational preferences of flexible pharmaceutical compounds and understanding their binding modes with biological targets[9][11].
Strengths: Specialized expertise in pharmaceutical applications allows for optimized protocols specifically relevant to drug discovery and development. Integration with computational modeling enhances the structural insights gained from anisotropic NMR data. Weaknesses: Solutions are primarily optimized for pharmaceutical applications and may require significant adaptation for other fields. The proprietary nature of some components may limit accessibility and customization options for researchers outside Roche's collaborative network.
Key Technical Innovations in NMR Sample Analysis
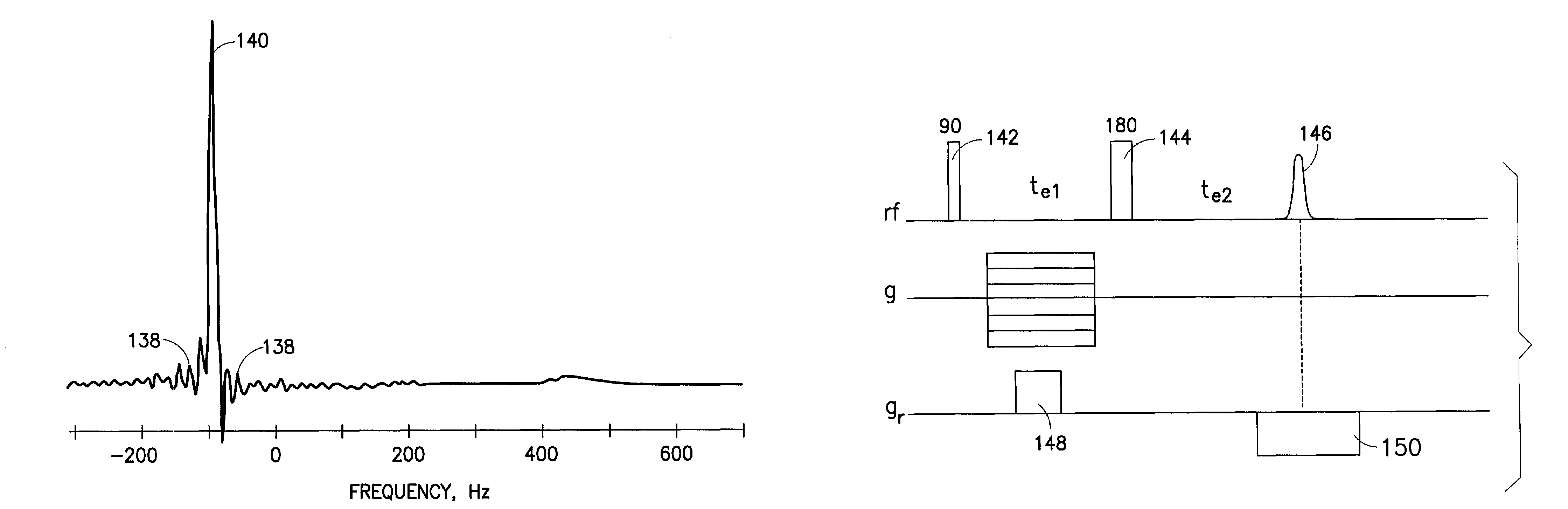
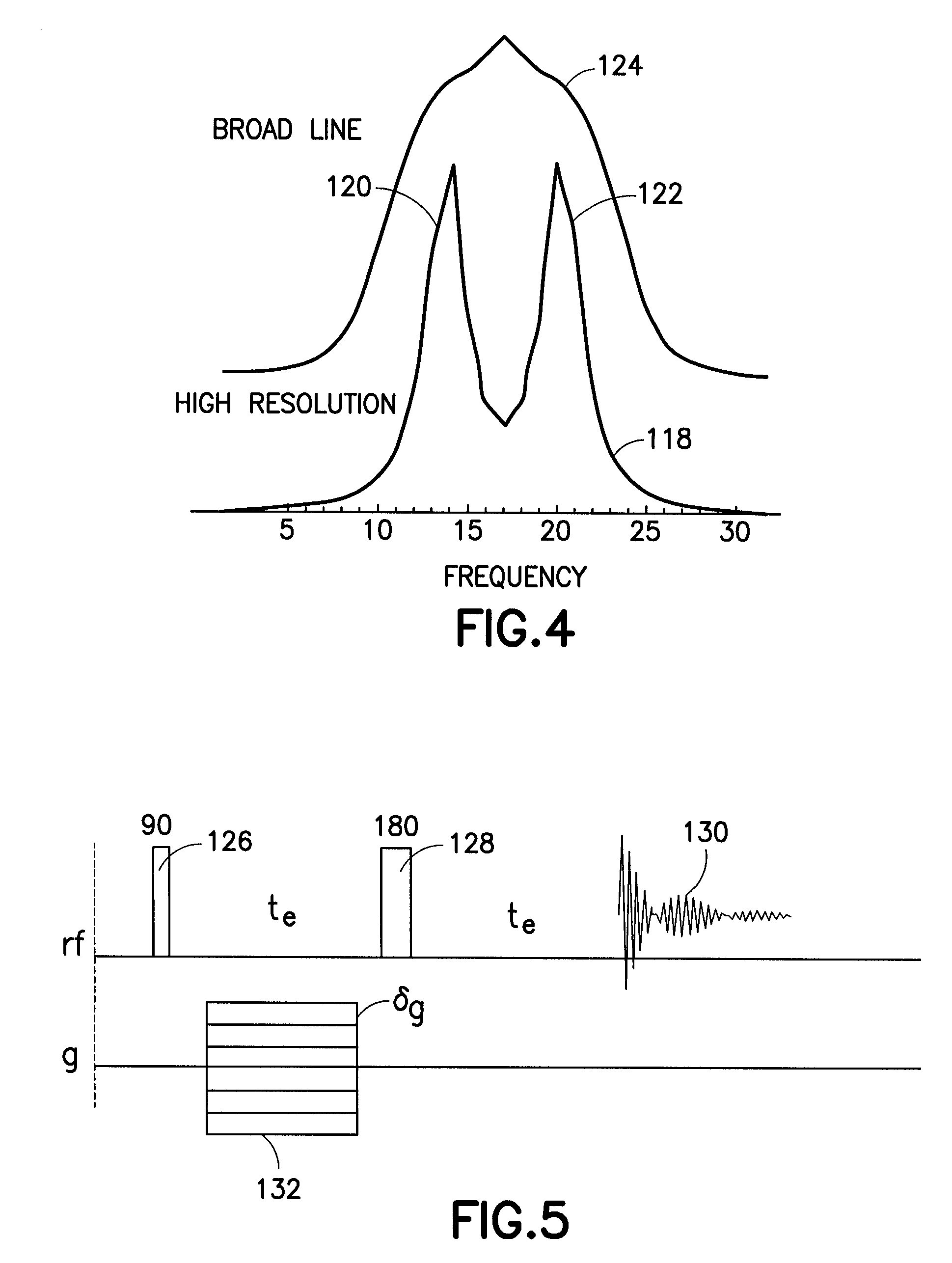
Method and apparatus to improve NMR spectral resolution in an inhomogeneous magnetic field
PatentActiveUS7683615B2
Innovation
- A method involving the generation of magnetic pulses and gradient pulses to produce a reconstructed high-resolution NMR spectrum by determining the spatial dependence of the inhomogeneous magnetic field, allowing for the correction and summation of spectra to improve spectral resolution without requiring more homogeneous magnetic fields.
NMR-MAS turbine assembly
PatentActiveUS20170108561A1
Innovation
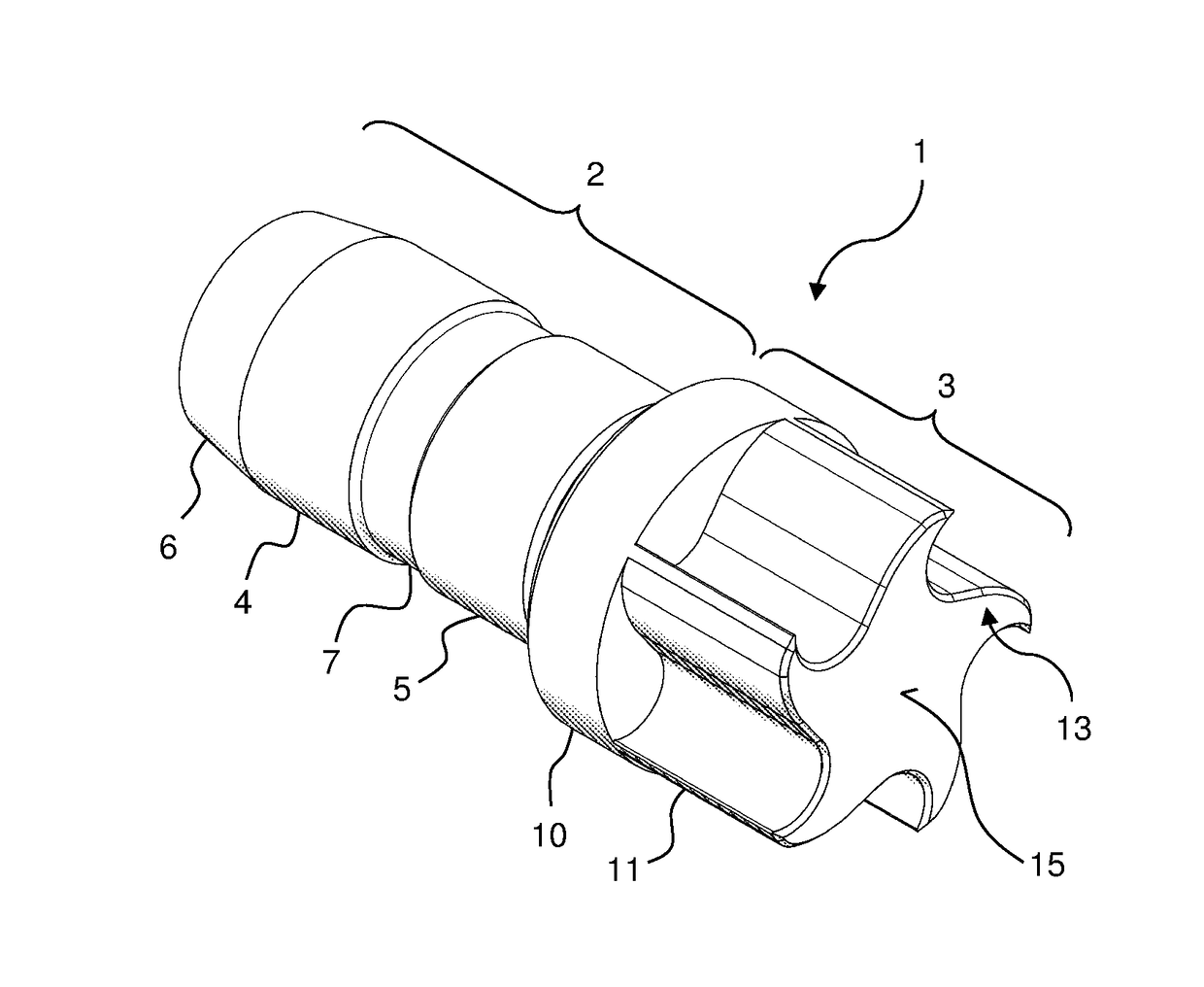
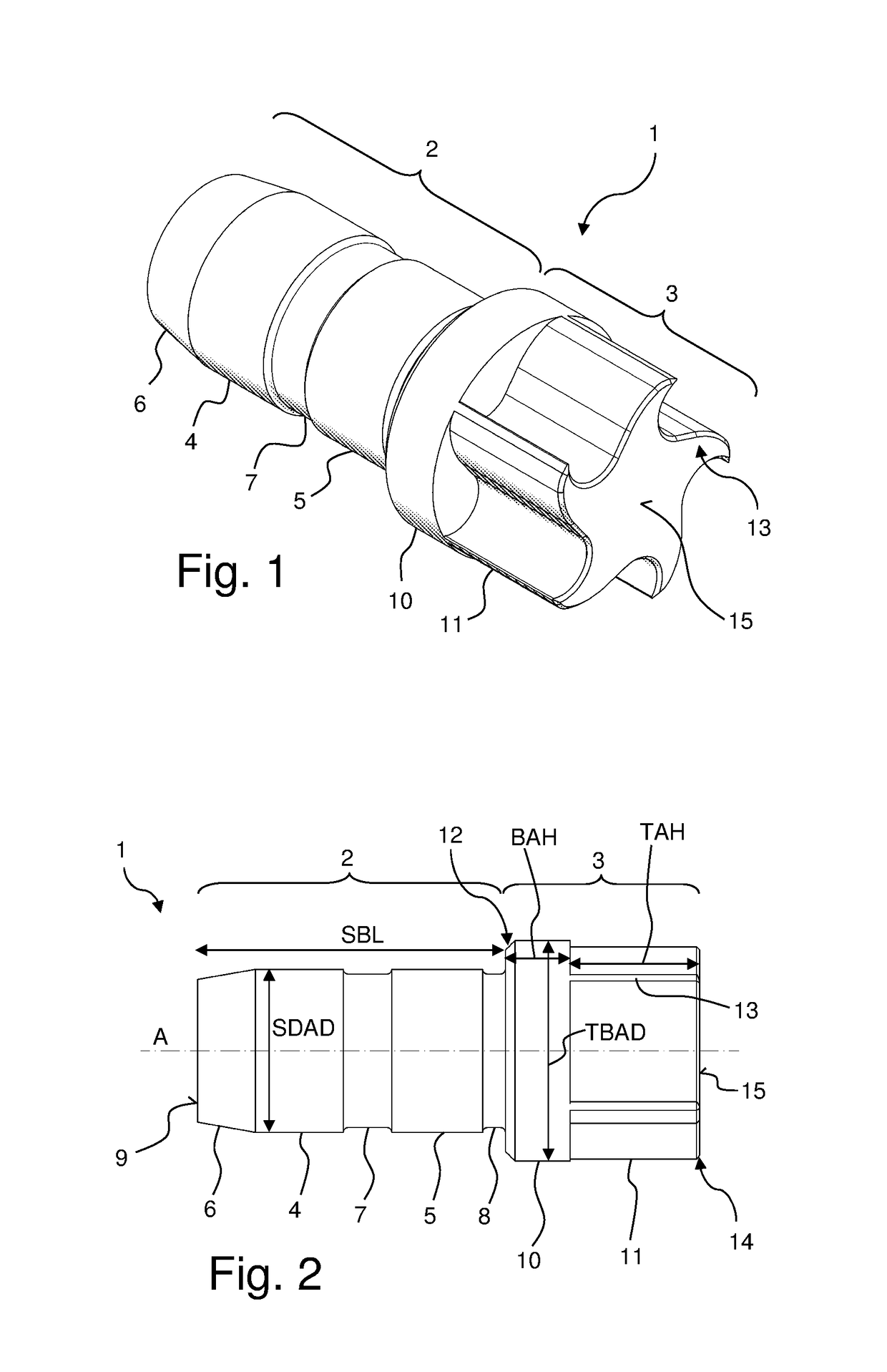
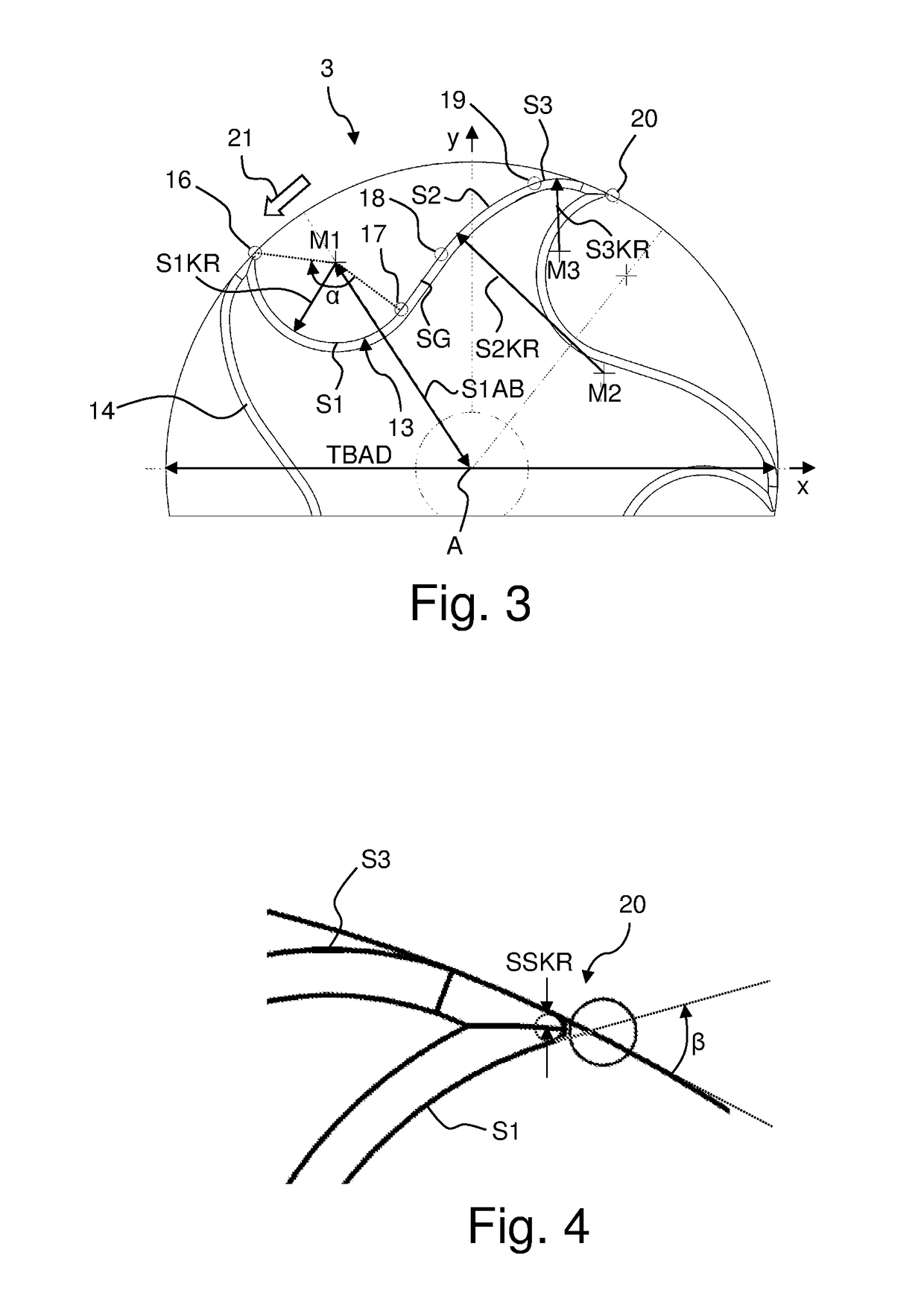
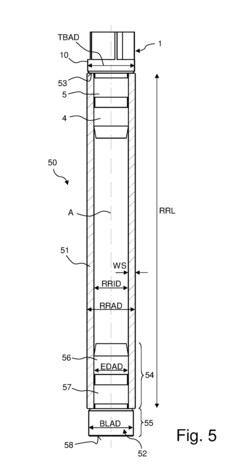
- A turbine cap with a specific blade geometry and design, featuring a stopper region with a sealing section and a turbine region with five blades, where the blades have a sharp radius of curvature and a concave first blade piece, is used to drive the NMR-MAS rotor, allowing for rotation frequencies up to 111 kHz with improved running stability and efficiency.
Interdisciplinary Applications of Improved NMR Separations
The improved resolution of anisotropic separations in NMR spectroscopy has opened significant opportunities for cross-disciplinary applications beyond traditional chemistry and structural biology domains. These advancements are particularly transformative in pharmaceutical development, where enhanced NMR separation techniques enable more precise characterization of drug candidates, especially those with complex stereochemistry or conformational variability.
In materials science, the ability to resolve anisotropic separations has revolutionized the analysis of polymer structures, liquid crystals, and advanced composite materials. Researchers can now accurately determine molecular orientation, domain structures, and phase transitions that were previously indistinguishable using conventional analytical methods. This has accelerated the development of novel materials with tailored properties for specific industrial applications.
The medical diagnostics field has embraced these improved NMR separation techniques for metabolomics studies, where the enhanced resolution allows for more accurate identification of biomarkers in complex biological samples. This capability has proven invaluable for early disease detection and personalized medicine approaches, as subtle metabolic changes can now be detected with greater sensitivity and specificity.
Environmental science applications have expanded significantly, with improved NMR separations enabling more detailed analysis of complex environmental samples such as soil organic matter, pollutants in water systems, and atmospheric particulates. The ability to distinguish between structurally similar compounds in these heterogeneous matrices provides critical information for environmental monitoring and remediation strategies.
Food science and agriculture have benefited through enhanced quality control processes that can now detect minute variations in food composition, authenticate product origins, and identify adulterants with unprecedented accuracy. The non-destructive nature of NMR analysis makes it particularly valuable for high-value agricultural products and processed foods where quality verification is essential.
Forensic science has incorporated these advanced NMR separation techniques to improve the characterization of trace evidence, particularly in cases involving complex mixtures of organic compounds. The enhanced discriminatory power has strengthened the evidentiary value of chemical analyses in legal proceedings.
The integration of improved NMR separation techniques with artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches has further expanded interdisciplinary applications, enabling automated pattern recognition in complex spectral data and facilitating knowledge discovery across scientific domains that were previously considered unrelated.
In materials science, the ability to resolve anisotropic separations has revolutionized the analysis of polymer structures, liquid crystals, and advanced composite materials. Researchers can now accurately determine molecular orientation, domain structures, and phase transitions that were previously indistinguishable using conventional analytical methods. This has accelerated the development of novel materials with tailored properties for specific industrial applications.
The medical diagnostics field has embraced these improved NMR separation techniques for metabolomics studies, where the enhanced resolution allows for more accurate identification of biomarkers in complex biological samples. This capability has proven invaluable for early disease detection and personalized medicine approaches, as subtle metabolic changes can now be detected with greater sensitivity and specificity.
Environmental science applications have expanded significantly, with improved NMR separations enabling more detailed analysis of complex environmental samples such as soil organic matter, pollutants in water systems, and atmospheric particulates. The ability to distinguish between structurally similar compounds in these heterogeneous matrices provides critical information for environmental monitoring and remediation strategies.
Food science and agriculture have benefited through enhanced quality control processes that can now detect minute variations in food composition, authenticate product origins, and identify adulterants with unprecedented accuracy. The non-destructive nature of NMR analysis makes it particularly valuable for high-value agricultural products and processed foods where quality verification is essential.
Forensic science has incorporated these advanced NMR separation techniques to improve the characterization of trace evidence, particularly in cases involving complex mixtures of organic compounds. The enhanced discriminatory power has strengthened the evidentiary value of chemical analyses in legal proceedings.
The integration of improved NMR separation techniques with artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches has further expanded interdisciplinary applications, enabling automated pattern recognition in complex spectral data and facilitating knowledge discovery across scientific domains that were previously considered unrelated.
Standardization and Quality Control in NMR Analysis
Standardization and quality control in NMR analysis are critical components for addressing anisotropic separations in NMR sample analysis. The inherent variability in sample preparation, instrument performance, and data processing necessitates robust standardization protocols to ensure reliable and reproducible results.
The establishment of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation is fundamental to minimizing anisotropic effects. These procedures must account for factors such as sample concentration, solvent selection, temperature control, and tube positioning within the magnetic field. Research indicates that even minor deviations in these parameters can significantly amplify anisotropic separations, leading to spectral distortions and misinterpretation of data.
Quality control measures for NMR instrumentation play an equally important role. Regular calibration of magnetic field homogeneity, probe tuning, and pulse sequence optimization are essential practices. The implementation of reference standards, such as tetramethylsilane (TMS) for proton NMR, provides crucial benchmarks for chemical shift calibration and spectral alignment, helping to distinguish genuine anisotropic effects from instrumental artifacts.
Data processing standardization represents another critical dimension. The development of automated processing workflows with defined parameters for phase correction, baseline adjustment, and peak integration helps minimize operator-dependent variations. Advanced algorithms specifically designed to account for anisotropic effects during spectral processing have shown promising results in recent studies, particularly when applied to complex biomolecular samples.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have demonstrated that standardization efforts significantly reduce variability in anisotropic separation measurements. A 2022 multi-center study involving 15 research facilities showed that implementation of standardized protocols reduced inter-laboratory variation by 68% when analyzing identical anisotropic samples, highlighting the efficacy of these approaches.
Regulatory bodies and industry consortia have begun developing comprehensive guidelines specifically addressing anisotropic challenges in NMR analysis. The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) has incorporated specific recommendations for anisotropic sample handling in their latest analytical method validation guidelines, while the ASTM International has published standards for quantitative NMR that include provisions for anisotropic effects.
Future standardization efforts are focusing on machine learning approaches to automatically detect and correct for anisotropic artifacts. These computational methods promise to establish new quality control paradigms that adapt to sample-specific characteristics rather than applying generic correction factors, potentially revolutionizing how anisotropic separations are managed in routine NMR analysis.
The establishment of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation is fundamental to minimizing anisotropic effects. These procedures must account for factors such as sample concentration, solvent selection, temperature control, and tube positioning within the magnetic field. Research indicates that even minor deviations in these parameters can significantly amplify anisotropic separations, leading to spectral distortions and misinterpretation of data.
Quality control measures for NMR instrumentation play an equally important role. Regular calibration of magnetic field homogeneity, probe tuning, and pulse sequence optimization are essential practices. The implementation of reference standards, such as tetramethylsilane (TMS) for proton NMR, provides crucial benchmarks for chemical shift calibration and spectral alignment, helping to distinguish genuine anisotropic effects from instrumental artifacts.
Data processing standardization represents another critical dimension. The development of automated processing workflows with defined parameters for phase correction, baseline adjustment, and peak integration helps minimize operator-dependent variations. Advanced algorithms specifically designed to account for anisotropic effects during spectral processing have shown promising results in recent studies, particularly when applied to complex biomolecular samples.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have demonstrated that standardization efforts significantly reduce variability in anisotropic separation measurements. A 2022 multi-center study involving 15 research facilities showed that implementation of standardized protocols reduced inter-laboratory variation by 68% when analyzing identical anisotropic samples, highlighting the efficacy of these approaches.
Regulatory bodies and industry consortia have begun developing comprehensive guidelines specifically addressing anisotropic challenges in NMR analysis. The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) has incorporated specific recommendations for anisotropic sample handling in their latest analytical method validation guidelines, while the ASTM International has published standards for quantitative NMR that include provisions for anisotropic effects.
Future standardization efforts are focusing on machine learning approaches to automatically detect and correct for anisotropic artifacts. These computational methods promise to establish new quality control paradigms that adapt to sample-specific characteristics rather than applying generic correction factors, potentially revolutionizing how anisotropic separations are managed in routine NMR analysis.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!