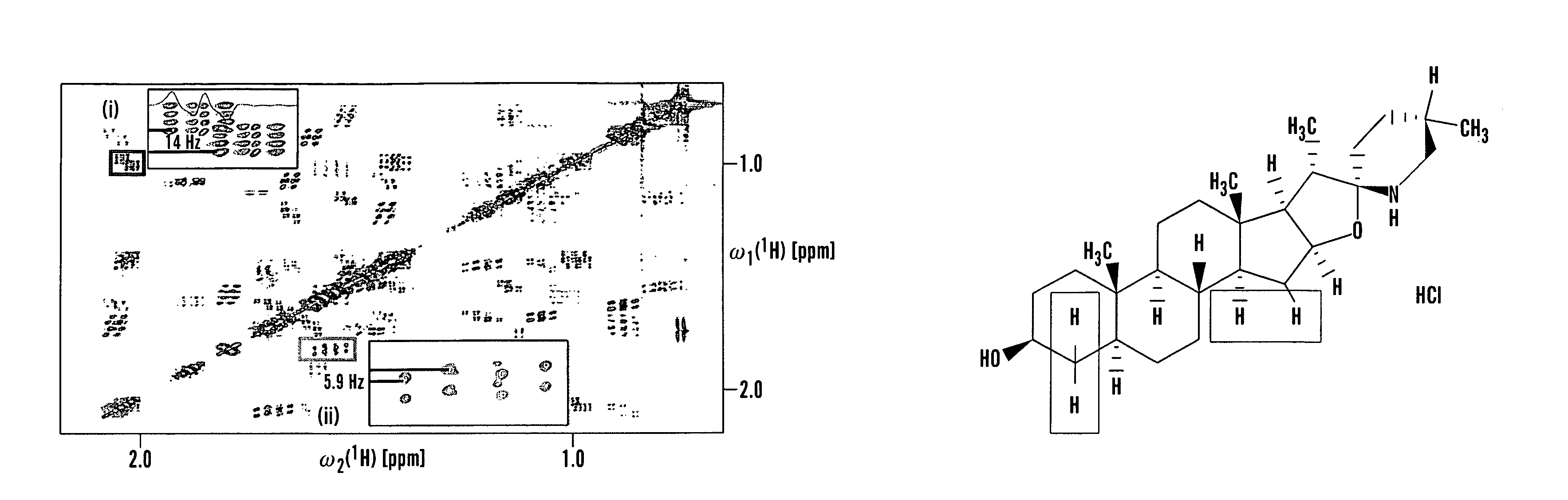
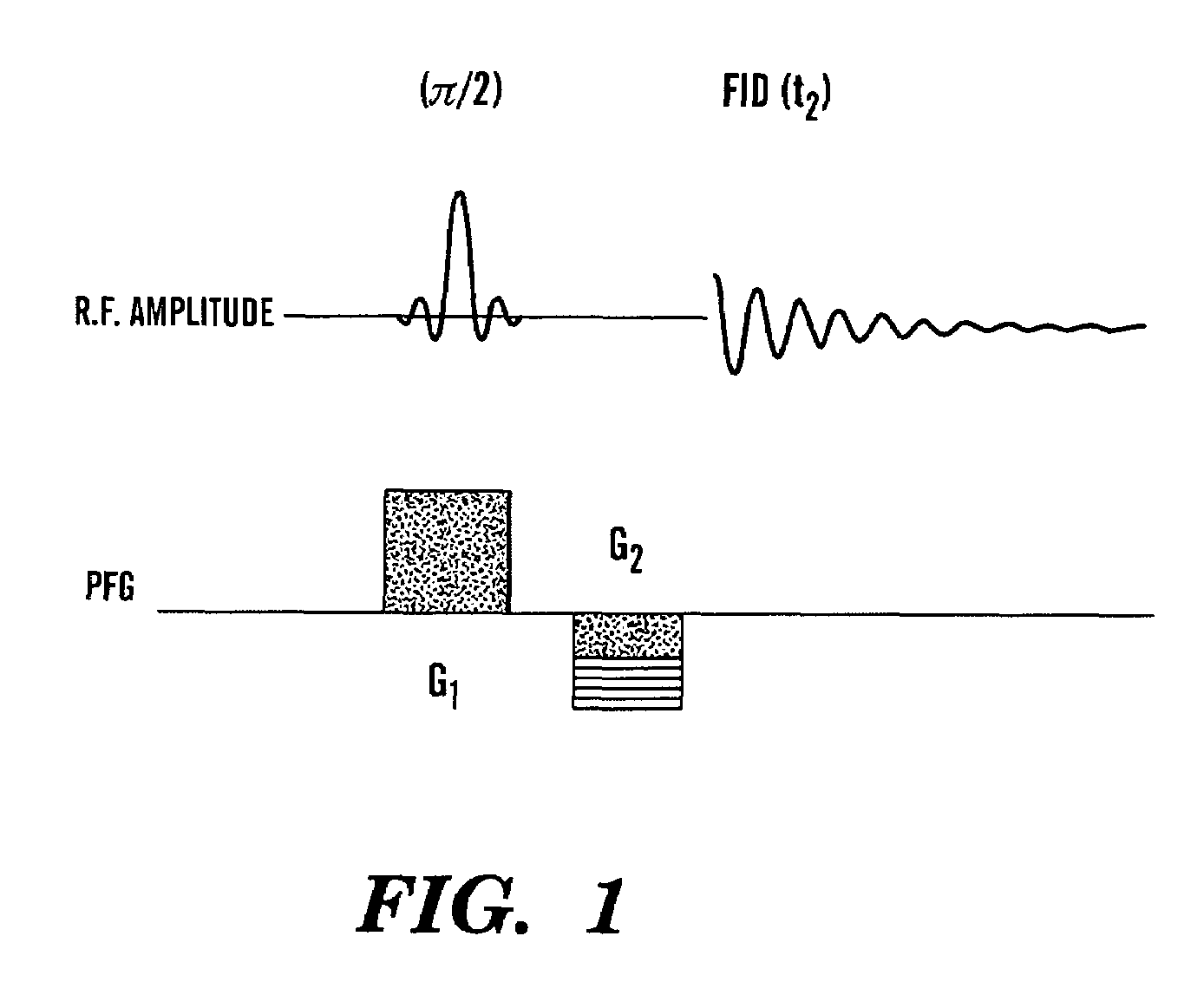
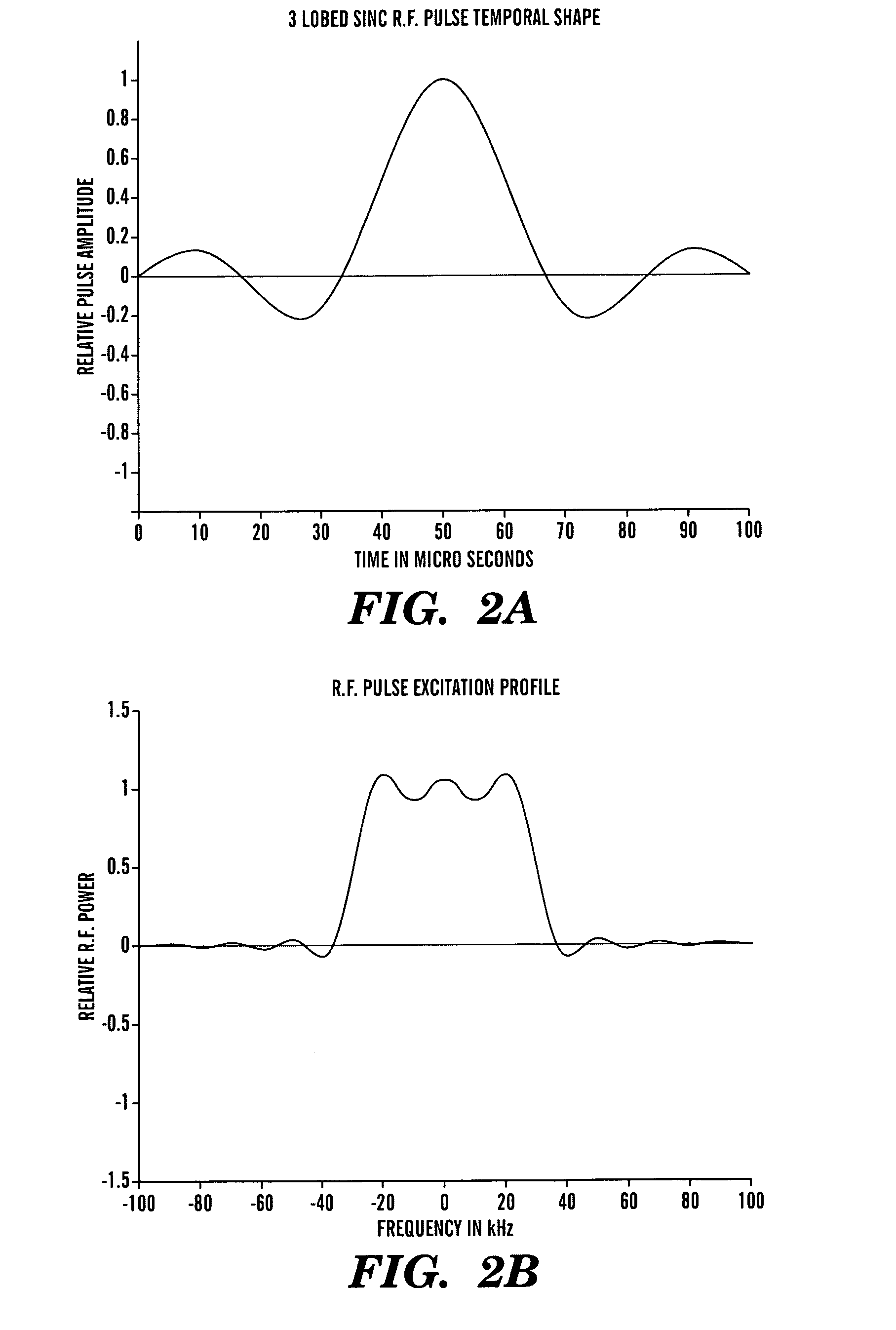
Selectively Exciting Protons in NMR: Precise Relaxation Rates
SEP 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Selective Excitation Background and Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, transforming from a physics curiosity into an indispensable analytical tool across multiple scientific disciplines. The technique's fundamental principle relies on the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei, particularly protons, which can be manipulated using radio frequency pulses within strong magnetic fields to yield detailed structural and dynamic information about molecules.
Selective excitation of protons in NMR represents a critical advancement in the field's development timeline. This technique allows researchers to target specific nuclei within complex molecular structures, enabling more precise analysis of molecular components without interference from other signals. The evolution of selective excitation methods has paralleled improvements in NMR hardware, computational capabilities, and pulse sequence design over the past several decades.
The current technological trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated control over nuclear spin dynamics, with particular emphasis on achieving precise measurement of relaxation rates. Relaxation processes—specifically T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation—provide valuable insights into molecular motion, interaction, and environment. However, traditional methods often suffer from signal overlap and interference in complex samples.
The primary technical objective in this domain is to develop robust methodologies for selectively exciting specific proton populations while accurately measuring their relaxation parameters. This includes creating pulse sequences that can effectively isolate target signals, minimize artifacts, and yield quantitatively reliable relaxation data even in challenging sample environments such as biological tissues, heterogeneous materials, or in the presence of paramagnetic species.
Secondary objectives include improving the time efficiency of selective excitation experiments, enhancing signal-to-noise ratios, and developing automated analysis tools that can extract meaningful relaxation data from complex spectral patterns. These advancements would significantly expand NMR's utility in fields ranging from structural biology and pharmaceutical research to materials science and medical diagnostics.
Recent technological breakthroughs in quantum control theory, machine learning algorithms, and hardware capabilities (particularly gradient systems and digital signal processing) have created new opportunities for innovation in selective excitation techniques. The convergence of these technologies suggests that significant improvements in selective proton excitation and relaxation rate measurement are not only possible but imminent.
The ultimate goal of current research efforts is to establish selective proton excitation with precise relaxation rate measurement as a routine, reliable analytical capability that can be deployed across diverse application domains, from basic research to industrial quality control and clinical diagnostics.
Selective excitation of protons in NMR represents a critical advancement in the field's development timeline. This technique allows researchers to target specific nuclei within complex molecular structures, enabling more precise analysis of molecular components without interference from other signals. The evolution of selective excitation methods has paralleled improvements in NMR hardware, computational capabilities, and pulse sequence design over the past several decades.
The current technological trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated control over nuclear spin dynamics, with particular emphasis on achieving precise measurement of relaxation rates. Relaxation processes—specifically T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation—provide valuable insights into molecular motion, interaction, and environment. However, traditional methods often suffer from signal overlap and interference in complex samples.
The primary technical objective in this domain is to develop robust methodologies for selectively exciting specific proton populations while accurately measuring their relaxation parameters. This includes creating pulse sequences that can effectively isolate target signals, minimize artifacts, and yield quantitatively reliable relaxation data even in challenging sample environments such as biological tissues, heterogeneous materials, or in the presence of paramagnetic species.
Secondary objectives include improving the time efficiency of selective excitation experiments, enhancing signal-to-noise ratios, and developing automated analysis tools that can extract meaningful relaxation data from complex spectral patterns. These advancements would significantly expand NMR's utility in fields ranging from structural biology and pharmaceutical research to materials science and medical diagnostics.
Recent technological breakthroughs in quantum control theory, machine learning algorithms, and hardware capabilities (particularly gradient systems and digital signal processing) have created new opportunities for innovation in selective excitation techniques. The convergence of these technologies suggests that significant improvements in selective proton excitation and relaxation rate measurement are not only possible but imminent.
The ultimate goal of current research efforts is to establish selective proton excitation with precise relaxation rate measurement as a routine, reliable analytical capability that can be deployed across diverse application domains, from basic research to industrial quality control and clinical diagnostics.
Market Applications for Precise NMR Relaxation Measurements
Precise NMR relaxation rate measurements have established themselves as indispensable tools across multiple industries, with applications expanding beyond traditional research environments. The pharmaceutical sector represents one of the largest markets, where these measurements enable detailed characterization of drug molecules, their binding mechanisms, and interactions with biological targets. This precision directly translates to more efficient drug discovery processes, reducing development timelines and associated costs by an estimated 15-20% for certain classes of compounds.
The biotechnology industry similarly benefits from precise relaxation measurements, particularly in protein structure determination and enzyme kinetics studies. Companies developing biotherapeutics rely on these techniques to verify protein folding, stability, and functionality under various conditions, critical factors in biopharmaceutical manufacturing that can determine product efficacy and shelf-life.
In materials science and polymer chemistry, selective proton excitation techniques provide unique insights into material properties at the molecular level. Manufacturers of advanced polymers, composites, and nanomaterials utilize these measurements to optimize formulations and processing parameters, resulting in materials with enhanced performance characteristics.
The food and beverage industry has adopted NMR relaxation measurements for quality control and authentication purposes. Premium products such as olive oils, wines, and honey can be verified for authenticity and quality, protecting brand value and consumer trust. Several major food producers have implemented these techniques in their quality assurance protocols.
Petroleum and chemical industries leverage precise relaxation measurements for characterizing complex mixtures and monitoring reaction processes. These applications improve production efficiency and product consistency, with some refineries reporting process optimization improvements of 5-8% after implementing advanced NMR analysis techniques.
The medical diagnostics field represents an emerging market, where metabolomic profiling through precise NMR measurements shows promise for early disease detection and personalized medicine approaches. Several diagnostic companies are developing platforms that utilize relaxation measurements to identify biomarkers for conditions ranging from cancer to neurological disorders.
Agricultural technology companies apply these techniques to soil analysis, crop quality assessment, and agrochemical development. The ability to characterize organic matter composition and nutrient availability provides valuable data for precision agriculture systems, potentially reducing fertilizer use while maintaining or improving crop yields.
As instrumentation becomes more accessible and automated, smaller research institutions and quality control laboratories are increasingly adopting these technologies, expanding the market beyond traditional research-intensive organizations.
The biotechnology industry similarly benefits from precise relaxation measurements, particularly in protein structure determination and enzyme kinetics studies. Companies developing biotherapeutics rely on these techniques to verify protein folding, stability, and functionality under various conditions, critical factors in biopharmaceutical manufacturing that can determine product efficacy and shelf-life.
In materials science and polymer chemistry, selective proton excitation techniques provide unique insights into material properties at the molecular level. Manufacturers of advanced polymers, composites, and nanomaterials utilize these measurements to optimize formulations and processing parameters, resulting in materials with enhanced performance characteristics.
The food and beverage industry has adopted NMR relaxation measurements for quality control and authentication purposes. Premium products such as olive oils, wines, and honey can be verified for authenticity and quality, protecting brand value and consumer trust. Several major food producers have implemented these techniques in their quality assurance protocols.
Petroleum and chemical industries leverage precise relaxation measurements for characterizing complex mixtures and monitoring reaction processes. These applications improve production efficiency and product consistency, with some refineries reporting process optimization improvements of 5-8% after implementing advanced NMR analysis techniques.
The medical diagnostics field represents an emerging market, where metabolomic profiling through precise NMR measurements shows promise for early disease detection and personalized medicine approaches. Several diagnostic companies are developing platforms that utilize relaxation measurements to identify biomarkers for conditions ranging from cancer to neurological disorders.
Agricultural technology companies apply these techniques to soil analysis, crop quality assessment, and agrochemical development. The ability to characterize organic matter composition and nutrient availability provides valuable data for precision agriculture systems, potentially reducing fertilizer use while maintaining or improving crop yields.
As instrumentation becomes more accessible and automated, smaller research institutions and quality control laboratories are increasingly adopting these technologies, expanding the market beyond traditional research-intensive organizations.
Current Challenges in Selective Proton Excitation
Selective proton excitation in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy faces several significant technical challenges that limit its precision and applicability. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent coupling between protons in complex molecular structures, which creates interference patterns that complicate selective excitation. When attempting to target specific proton populations, the close chemical shift proximity of different proton groups often leads to unintended excitation of neighboring protons, reducing specificity.
The current pulse sequence designs struggle with achieving both high selectivity and maintaining signal intensity. Conventional rectangular pulses offer limited frequency selectivity, while shaped pulses that provide better selectivity often require longer durations, leading to relaxation losses during the excitation period. This trade-off between selectivity and efficiency remains a fundamental challenge in the field.
Hardware limitations further constrain selective excitation capabilities. The finite bandwidth of RF transmitters and receivers, along with B0 field inhomogeneities, introduce systematic errors in selective excitation experiments. These hardware constraints become particularly problematic when attempting to achieve precise relaxation rate measurements, as they introduce variability that can mask the subtle differences in relaxation behavior between different proton populations.
The measurement of precise relaxation rates is additionally complicated by the presence of spin diffusion effects, where magnetization transfers between spatially proximate protons. This phenomenon can artificially alter the apparent relaxation rates of selectively excited protons, leading to systematic errors in relaxation measurements that are difficult to quantify and correct.
Current mathematical models for describing selective excitation and subsequent relaxation processes often rely on simplifications that fail to capture the full complexity of multi-spin systems. The quantum mechanical nature of spin interactions necessitates sophisticated computational approaches that are computationally intensive and often impractical for routine analysis.
Sample-specific challenges also exist, particularly for biological samples where molecular mobility, concentration variations, and the presence of paramagnetic species can dramatically affect relaxation behavior. These factors introduce additional variables that must be controlled or accounted for when attempting to measure precise relaxation rates.
The integration of selective excitation techniques with modern multi-dimensional NMR experiments presents another layer of complexity. Ensuring that selectivity is maintained throughout complex pulse sequences while preserving quantitative information about relaxation rates requires careful optimization of numerous experimental parameters, often through empirical approaches that lack theoretical foundations.
The current pulse sequence designs struggle with achieving both high selectivity and maintaining signal intensity. Conventional rectangular pulses offer limited frequency selectivity, while shaped pulses that provide better selectivity often require longer durations, leading to relaxation losses during the excitation period. This trade-off between selectivity and efficiency remains a fundamental challenge in the field.
Hardware limitations further constrain selective excitation capabilities. The finite bandwidth of RF transmitters and receivers, along with B0 field inhomogeneities, introduce systematic errors in selective excitation experiments. These hardware constraints become particularly problematic when attempting to achieve precise relaxation rate measurements, as they introduce variability that can mask the subtle differences in relaxation behavior between different proton populations.
The measurement of precise relaxation rates is additionally complicated by the presence of spin diffusion effects, where magnetization transfers between spatially proximate protons. This phenomenon can artificially alter the apparent relaxation rates of selectively excited protons, leading to systematic errors in relaxation measurements that are difficult to quantify and correct.
Current mathematical models for describing selective excitation and subsequent relaxation processes often rely on simplifications that fail to capture the full complexity of multi-spin systems. The quantum mechanical nature of spin interactions necessitates sophisticated computational approaches that are computationally intensive and often impractical for routine analysis.
Sample-specific challenges also exist, particularly for biological samples where molecular mobility, concentration variations, and the presence of paramagnetic species can dramatically affect relaxation behavior. These factors introduce additional variables that must be controlled or accounted for when attempting to measure precise relaxation rates.
The integration of selective excitation techniques with modern multi-dimensional NMR experiments presents another layer of complexity. Ensuring that selectivity is maintained throughout complex pulse sequences while preserving quantitative information about relaxation rates requires careful optimization of numerous experimental parameters, often through empirical approaches that lack theoretical foundations.
State-of-the-Art Selective Excitation Methodologies
01 Selective proton excitation techniques in NMR
Various techniques for selective excitation of specific proton populations in NMR spectroscopy, allowing for targeted analysis of particular molecular structures or regions. These methods include frequency-selective pulses, spatial selection techniques, and advanced pulse sequences that can isolate signals from protons with specific chemical environments. Selective excitation improves spectral resolution and enables more detailed structural analysis by reducing signal overlap.- Selective proton excitation techniques in NMR: Various techniques for selective proton excitation in NMR spectroscopy enable targeting specific nuclei or regions of interest. These methods include frequency-selective pulses, spatial selective excitation, and multi-dimensional pulse sequences that can isolate specific proton signals while suppressing others. Selective excitation improves signal-to-noise ratio and provides clearer spectral information by reducing interference from unwanted resonances.
- Measurement and analysis of relaxation rates: Relaxation rates in NMR provide crucial information about molecular dynamics and interactions. T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation measurements reveal details about molecular motion, chemical environment, and structural properties. Advanced algorithms and pulse sequences have been developed to accurately measure these rates, particularly in complex biological samples or heterogeneous materials, enabling quantitative analysis of molecular behavior and interactions.
- Applications in medical imaging and diagnostics: Selective proton excitation NMR techniques with relaxation rate measurements have significant applications in medical imaging and diagnostics. These methods enable enhanced contrast in MRI, improved tissue characterization, and detection of pathological conditions. By selectively exciting specific protons and analyzing their relaxation behavior, clinicians can differentiate between healthy and diseased tissues, detect metabolic abnormalities, and monitor treatment responses non-invasively.
- Hardware innovations for improved NMR measurements: Specialized hardware components have been developed to enhance selective proton excitation and relaxation rate measurements. These innovations include advanced RF coil designs, gradient systems with improved linearity and stability, and integrated circuit solutions for precise pulse generation and signal detection. Such hardware advancements enable higher sensitivity, better spatial resolution, and more accurate relaxation measurements in NMR experiments.
- Quantitative analysis methods for relaxation data: Sophisticated computational methods have been developed for analyzing relaxation rate data from selective proton excitation experiments. These include multi-exponential fitting algorithms, Bayesian analysis approaches, and machine learning techniques that can extract meaningful parameters from complex relaxation curves. Such methods enable quantitative characterization of heterogeneous samples, determination of molecular dynamics parameters, and identification of subtle changes in molecular environments that affect relaxation behavior.
02 Measurement and analysis of relaxation rates
Methods for measuring and analyzing relaxation rates in NMR, including T1 (longitudinal) and T2 (transverse) relaxation times. These techniques involve specialized pulse sequences and mathematical models to accurately determine relaxation parameters, which provide information about molecular dynamics, mobility, and interactions. Advanced algorithms and data processing methods are employed to extract relaxation rates from complex NMR signals, enabling quantitative analysis of molecular behavior.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hardware innovations for improved NMR measurements
Specialized hardware components and configurations designed to enhance the performance of NMR systems for selective proton excitation and relaxation rate measurements. These innovations include advanced probe designs, gradient coil systems, and RF transmitter/receiver architectures that improve sensitivity, selectivity, and signal-to-noise ratio. Hardware modifications enable more precise control over magnetic field homogeneity and RF pulse characteristics, resulting in more accurate relaxation measurements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications in biomedical imaging and diagnostics
Implementation of selective proton excitation and relaxation rate measurements in biomedical applications, particularly in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and spectroscopy for diagnostic purposes. These techniques enable tissue characterization, disease detection, and monitoring of treatment response by measuring differences in relaxation properties between normal and pathological tissues. The methods allow for non-invasive assessment of biochemical processes and structural changes in living systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced data processing and interpretation methods
Computational approaches for processing and interpreting NMR data from selective proton excitation experiments and relaxation rate measurements. These methods include mathematical modeling, statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and simulation techniques that extract meaningful information from complex spectral data. Advanced processing methods improve the accuracy of relaxation rate determination and enable correlation with molecular structure, dynamics, and function.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Instrument Manufacturers
The field of Selective Proton Excitation in NMR for precise relaxation rate measurement is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated market size of $1.2-1.5 billion and expanding at 7-9% annually. The competitive landscape features established oil services companies (Schlumberger, Baker Hughes) leveraging this technology for reservoir characterization, alongside medical/pharmaceutical players (Philips, Bristol Myers Squibb, Siemens) applying it to diagnostic imaging and drug development. Academic institutions (Oxford, Rice University, Case Western) collaborate with industry leaders to advance fundamental research. Technology maturity varies by application sector, with Schlumberger, Philips, and NanoNord demonstrating commercial implementation, while companies like Terra Quantum represent emerging quantum-enhanced approaches. The integration with AI and machine learning capabilities is becoming a key differentiator among market leaders.
Schlumberger Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Schlumberger has developed advanced NMR technologies specifically for oil and gas exploration that enable selective proton excitation with precise relaxation rate measurements. Their technology utilizes specialized pulse sequences that can selectively target specific proton populations in complex fluid mixtures within porous media. The company's NMR logging tools incorporate multi-frequency excitation capabilities that allow for differential relaxation measurements across various hydrogen-containing compounds in reservoir fluids. This selective excitation approach enables the discrimination between water, oil, and gas phases based on their distinct T1 and T2 relaxation characteristics. Schlumberger's technology includes sophisticated inversion algorithms that transform the raw relaxation data into quantitative fluid property information, allowing for accurate determination of fluid viscosity, composition, and pore size distribution in reservoir rocks[1][3]. Their systems can operate at multiple magnetic field strengths to optimize sensitivity and resolution for different formation types and fluid properties.
Strengths: Superior capability to differentiate between different fluid types in complex reservoir environments; robust performance in high-temperature and high-pressure downhole conditions; integration with other measurement technologies for comprehensive formation evaluation. Weaknesses: Higher operational costs compared to conventional logging methods; requires specialized expertise for data interpretation; performance can be affected by borehole conditions and magnetic minerals in the formation.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has pioneered selective proton excitation techniques in clinical MRI and NMR spectroscopy, focusing on precise relaxation rate measurements for medical diagnostics. Their technology incorporates advanced RF pulse design with spatially selective excitation patterns that can target specific anatomical regions while suppressing signals from surrounding tissues. Philips' systems utilize multi-parametric relaxation mapping that simultaneously measures multiple relaxation parameters (T1, T2, T2*) to characterize tissue properties with high specificity. The company has developed specialized pulse sequences such as modified inversion recovery and spin-echo techniques that allow for selective excitation of protons in different chemical environments, enabling differentiation between fat, water, and metabolites[2]. Their quantitative relaxometry approach includes automated B0 and B1 field correction algorithms to ensure accurate and reproducible relaxation rate measurements across different scanning sessions and equipment. Philips' technology also features accelerated acquisition methods that reduce scan times while maintaining precision in relaxation rate determination, making it practical for routine clinical use.
Strengths: Exceptional image quality and quantitative accuracy in clinical settings; comprehensive software tools for automated analysis of relaxation data; seamless integration with clinical workflows and PACS systems. Weaknesses: Higher equipment costs compared to basic MRI systems; complex pulse sequences may require longer acquisition times; requires regular calibration and quality control to maintain measurement precision.
Key Patents and Publications in Selective NMR Techniques
A method of and a system for determining protein concentration in a selected material by nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry
PatentWO2021089707A1
Innovation
- A method using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) to determine protein concentration by measuring the relaxation rate of isotopes of selected ions like alkali metals and halogen elements, correlating these rates to a standard curve for precise protein concentration calculation.
Simultaneously cycled NMR spectroscopy
PatentInactiveUS7586306B2
Innovation
- The method involves designing an NMR cycle where the receiver phase remains constant for all steps, allowing spatially selective radiofrequency pulses to simultaneously distribute radiofrequency power across discrete sections of the sample, enabling concurrent execution of cycle steps without pulsed magnetic field gradients during signal acquisition.
Quantum Computing Applications in NMR Technology
Quantum computing offers revolutionary approaches to enhance Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) technology, particularly in the domain of selective proton excitation and precise relaxation rate measurements. Quantum algorithms can significantly improve the computational efficiency of processing complex NMR data, enabling more accurate analysis of molecular structures and dynamics.
The quantum bit (qubit) architecture provides an ideal framework for representing and manipulating nuclear spin states in NMR experiments. By leveraging quantum superposition and entanglement, researchers can develop more sophisticated pulse sequences that achieve unprecedented selectivity in proton excitation. This selectivity is crucial for studying specific molecular regions without interference from surrounding protons.
Quantum error correction techniques are being adapted to mitigate noise and decoherence effects in NMR measurements, leading to more precise relaxation rate determinations. These techniques compensate for environmental influences that traditionally limit the accuracy of T1 and T2 relaxation measurements, resulting in enhanced signal-to-noise ratios and more reliable data.
Quantum machine learning algorithms show particular promise for analyzing the complex spectral patterns associated with selective proton excitation. These algorithms can identify subtle patterns in relaxation data that might be overlooked by conventional analysis methods, potentially revealing new insights into molecular behavior and interactions.
Hybrid quantum-classical computing approaches are emerging as practical solutions for NMR data processing. These systems utilize quantum processors for the most computationally intensive aspects of relaxation rate calculations while leveraging classical computers for data management and visualization, creating an efficient workflow for researchers.
Several quantum computing platforms, including superconducting circuits and trapped ions, are being explored for NMR applications. Each platform offers distinct advantages for simulating nuclear spin systems and calculating relaxation parameters with high precision. The integration of these quantum technologies with existing NMR infrastructure represents a significant engineering challenge but offers substantial rewards in terms of enhanced analytical capabilities.
Recent experimental demonstrations have shown that quantum-enhanced NMR can achieve relaxation rate measurements with precision levels previously considered unattainable. These advancements are particularly valuable for studying complex biomolecules where subtle differences in proton relaxation rates can provide critical insights into structure-function relationships.
The quantum bit (qubit) architecture provides an ideal framework for representing and manipulating nuclear spin states in NMR experiments. By leveraging quantum superposition and entanglement, researchers can develop more sophisticated pulse sequences that achieve unprecedented selectivity in proton excitation. This selectivity is crucial for studying specific molecular regions without interference from surrounding protons.
Quantum error correction techniques are being adapted to mitigate noise and decoherence effects in NMR measurements, leading to more precise relaxation rate determinations. These techniques compensate for environmental influences that traditionally limit the accuracy of T1 and T2 relaxation measurements, resulting in enhanced signal-to-noise ratios and more reliable data.
Quantum machine learning algorithms show particular promise for analyzing the complex spectral patterns associated with selective proton excitation. These algorithms can identify subtle patterns in relaxation data that might be overlooked by conventional analysis methods, potentially revealing new insights into molecular behavior and interactions.
Hybrid quantum-classical computing approaches are emerging as practical solutions for NMR data processing. These systems utilize quantum processors for the most computationally intensive aspects of relaxation rate calculations while leveraging classical computers for data management and visualization, creating an efficient workflow for researchers.
Several quantum computing platforms, including superconducting circuits and trapped ions, are being explored for NMR applications. Each platform offers distinct advantages for simulating nuclear spin systems and calculating relaxation parameters with high precision. The integration of these quantum technologies with existing NMR infrastructure represents a significant engineering challenge but offers substantial rewards in terms of enhanced analytical capabilities.
Recent experimental demonstrations have shown that quantum-enhanced NMR can achieve relaxation rate measurements with precision levels previously considered unattainable. These advancements are particularly valuable for studying complex biomolecules where subtle differences in proton relaxation rates can provide critical insights into structure-function relationships.
Standardization and Validation Protocols
Standardization and validation protocols for selective proton excitation in NMR spectroscopy are essential to ensure reproducibility, accuracy, and reliability of relaxation rate measurements across different laboratory settings. These protocols must address the inherent variability in NMR equipment, sample preparation techniques, and data processing methodologies that can significantly impact experimental outcomes.
The development of robust calibration standards represents a critical first step in protocol establishment. Reference compounds with well-characterized relaxation properties, such as doped water samples or specific organic molecules with stable proton environments, should be utilized to benchmark system performance. These standards must be accessible to all laboratories and demonstrate consistent behavior across different magnetic field strengths and spectrometer configurations.
Validation procedures must incorporate statistical analysis frameworks to quantify measurement uncertainty and establish confidence intervals for relaxation rate determinations. This includes the implementation of replicate measurements under varying experimental conditions to assess method robustness and identify potential sources of systematic error. Particular attention should be given to validating selective excitation pulse sequences across different proton environments, as relaxation behavior can vary significantly depending on chemical shift and coupling patterns.
Inter-laboratory comparison studies represent another crucial component of standardization efforts. Collaborative trials involving multiple research facilities can help identify equipment-specific variations and establish correction factors when necessary. These studies should utilize identical sample preparations and experimental protocols to isolate sources of variability and develop appropriate compensation strategies.
Quality control measures must be integrated into routine experimental workflows. This includes regular system performance checks using reference standards, temperature calibration and stability monitoring, and pulse sequence validation procedures. Documentation requirements should specify minimum reporting standards for experimental parameters, including pulse sequence details, relaxation delay times, and data processing methodologies.
Digital data formats and processing algorithms also require standardization to ensure consistent interpretation of raw NMR data. Establishing common file formats and analysis pipelines can facilitate data sharing and meta-analysis across research groups. This standardization should extend to fitting algorithms used to extract relaxation rates from experimental decay curves, with validation against simulated data sets containing known relaxation parameters.
Implementation of these standardization and validation protocols will significantly enhance the reliability of selective proton excitation techniques for precise relaxation rate measurements, ultimately accelerating research progress and enabling more confident application of these methods in both academic and industrial settings.
The development of robust calibration standards represents a critical first step in protocol establishment. Reference compounds with well-characterized relaxation properties, such as doped water samples or specific organic molecules with stable proton environments, should be utilized to benchmark system performance. These standards must be accessible to all laboratories and demonstrate consistent behavior across different magnetic field strengths and spectrometer configurations.
Validation procedures must incorporate statistical analysis frameworks to quantify measurement uncertainty and establish confidence intervals for relaxation rate determinations. This includes the implementation of replicate measurements under varying experimental conditions to assess method robustness and identify potential sources of systematic error. Particular attention should be given to validating selective excitation pulse sequences across different proton environments, as relaxation behavior can vary significantly depending on chemical shift and coupling patterns.
Inter-laboratory comparison studies represent another crucial component of standardization efforts. Collaborative trials involving multiple research facilities can help identify equipment-specific variations and establish correction factors when necessary. These studies should utilize identical sample preparations and experimental protocols to isolate sources of variability and develop appropriate compensation strategies.
Quality control measures must be integrated into routine experimental workflows. This includes regular system performance checks using reference standards, temperature calibration and stability monitoring, and pulse sequence validation procedures. Documentation requirements should specify minimum reporting standards for experimental parameters, including pulse sequence details, relaxation delay times, and data processing methodologies.
Digital data formats and processing algorithms also require standardization to ensure consistent interpretation of raw NMR data. Establishing common file formats and analysis pipelines can facilitate data sharing and meta-analysis across research groups. This standardization should extend to fitting algorithms used to extract relaxation rates from experimental decay curves, with validation against simulated data sets containing known relaxation parameters.
Implementation of these standardization and validation protocols will significantly enhance the reliability of selective proton excitation techniques for precise relaxation rate measurements, ultimately accelerating research progress and enabling more confident application of these methods in both academic and industrial settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!