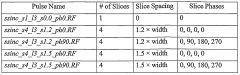
Structural Assignments via Scalar Couplings in NMR
SEP 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Scalar Coupling Background and Objectives
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved significantly since its discovery in the 1940s, becoming an indispensable analytical tool in chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. Scalar coupling, also known as J-coupling, represents one of the fundamental interactions in NMR spectroscopy, arising from the indirect interaction between nuclear spins mediated by bonding electrons. This phenomenon provides critical information about molecular connectivity and stereochemistry, making it essential for structural elucidation.
The evolution of scalar coupling analysis in NMR has progressed from simple first-order interpretation in the 1950s to sophisticated multi-dimensional techniques in contemporary applications. Early work by pioneers such as Ramsey and Purcell established the theoretical foundations, while subsequent developments by Ernst, Wüthrich, and others expanded the practical applications, culminating in the Nobel Prize-winning contributions to NMR methodology.
Current technological trends in this field include the development of higher magnetic field strengths, cryogenic probe technology, and advanced pulse sequence designs that enhance the detection and interpretation of scalar couplings. These advancements have significantly improved spectral resolution and sensitivity, enabling the analysis of increasingly complex molecular structures with greater precision.
The primary technical objectives in scalar coupling-based structural assignments include enhancing the accuracy of coupling constant measurements, developing more robust algorithms for automated structural analysis, and integrating machine learning approaches to interpret complex coupling patterns. Additionally, there is a growing focus on extending these techniques to challenging molecular systems such as intrinsically disordered proteins and complex natural products.
Another significant trend is the integration of scalar coupling data with complementary structural information from techniques such as X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and computational chemistry. This multi-modal approach aims to provide more comprehensive structural insights, particularly for biomolecules in their native environments.
The field is also witnessing increased efforts to standardize scalar coupling data reporting and establish comprehensive databases of coupling constants for various structural motifs. These initiatives seek to facilitate more efficient structure elucidation through pattern recognition and statistical analysis of historical data.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory points toward real-time structural analysis using scalar coupling information, enabling dynamic studies of molecular interactions and conformational changes. This capability would significantly impact drug discovery, materials development, and fundamental understanding of biochemical processes, representing the next frontier in NMR-based structural biology.
The evolution of scalar coupling analysis in NMR has progressed from simple first-order interpretation in the 1950s to sophisticated multi-dimensional techniques in contemporary applications. Early work by pioneers such as Ramsey and Purcell established the theoretical foundations, while subsequent developments by Ernst, Wüthrich, and others expanded the practical applications, culminating in the Nobel Prize-winning contributions to NMR methodology.
Current technological trends in this field include the development of higher magnetic field strengths, cryogenic probe technology, and advanced pulse sequence designs that enhance the detection and interpretation of scalar couplings. These advancements have significantly improved spectral resolution and sensitivity, enabling the analysis of increasingly complex molecular structures with greater precision.
The primary technical objectives in scalar coupling-based structural assignments include enhancing the accuracy of coupling constant measurements, developing more robust algorithms for automated structural analysis, and integrating machine learning approaches to interpret complex coupling patterns. Additionally, there is a growing focus on extending these techniques to challenging molecular systems such as intrinsically disordered proteins and complex natural products.
Another significant trend is the integration of scalar coupling data with complementary structural information from techniques such as X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and computational chemistry. This multi-modal approach aims to provide more comprehensive structural insights, particularly for biomolecules in their native environments.
The field is also witnessing increased efforts to standardize scalar coupling data reporting and establish comprehensive databases of coupling constants for various structural motifs. These initiatives seek to facilitate more efficient structure elucidation through pattern recognition and statistical analysis of historical data.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory points toward real-time structural analysis using scalar coupling information, enabling dynamic studies of molecular interactions and conformational changes. This capability would significantly impact drug discovery, materials development, and fundamental understanding of biochemical processes, representing the next frontier in NMR-based structural biology.
Market Applications of NMR Structural Assignment
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy with structural assignment capabilities has penetrated numerous market sectors, creating substantial economic value across industries. The pharmaceutical sector represents the largest market application, where NMR structural assignments are critical for drug discovery and development processes. Pharmaceutical companies utilize scalar coupling data to determine molecular conformations, stereochemistry, and binding interactions of potential drug candidates, significantly reducing development timelines and costs.
The biotechnology industry has similarly embraced NMR structural assignment techniques for protein structure determination and analysis of biomolecular interactions. This application has proven particularly valuable for companies developing biologics and enzyme-based therapeutics, where understanding three-dimensional structure is paramount to function.
Chemical manufacturing represents another significant market, with NMR structural assignments enabling precise quality control and process optimization. Manufacturers leverage scalar coupling information to verify product purity, identify contaminants, and ensure batch-to-batch consistency. This application extends to specialty chemicals, polymers, and materials science, where structural integrity directly impacts product performance.
The food and beverage industry utilizes NMR structural assignments for authentication of high-value products, detection of adulteration, and quality assurance. For instance, the technique has been applied to verify the origin and quality of olive oils, wines, and natural extracts, providing economic protection for premium products.
Academic and contract research organizations constitute a growing market segment, offering NMR structural assignment services to clients lacking in-house capabilities. This service-based model has expanded accessibility to advanced NMR techniques beyond large corporations with dedicated analytical departments.
Environmental monitoring represents an emerging application area, with NMR structural assignments being used to identify and characterize pollutants, metabolites, and degradation products in environmental samples. This application supports regulatory compliance and remediation efforts across industries.
The agricultural sector has begun implementing NMR structural assignment techniques for soil analysis, crop metabolomics, and development of agrochemicals. These applications help optimize growing conditions, develop more effective pesticides, and understand plant responses to environmental stressors.
Medical diagnostics represents a promising frontier, with research advancing toward using NMR-based metabolomics for disease biomarker discovery and personalized medicine approaches. Though still primarily in research phases, this application holds significant potential for clinical translation and market growth.
The biotechnology industry has similarly embraced NMR structural assignment techniques for protein structure determination and analysis of biomolecular interactions. This application has proven particularly valuable for companies developing biologics and enzyme-based therapeutics, where understanding three-dimensional structure is paramount to function.
Chemical manufacturing represents another significant market, with NMR structural assignments enabling precise quality control and process optimization. Manufacturers leverage scalar coupling information to verify product purity, identify contaminants, and ensure batch-to-batch consistency. This application extends to specialty chemicals, polymers, and materials science, where structural integrity directly impacts product performance.
The food and beverage industry utilizes NMR structural assignments for authentication of high-value products, detection of adulteration, and quality assurance. For instance, the technique has been applied to verify the origin and quality of olive oils, wines, and natural extracts, providing economic protection for premium products.
Academic and contract research organizations constitute a growing market segment, offering NMR structural assignment services to clients lacking in-house capabilities. This service-based model has expanded accessibility to advanced NMR techniques beyond large corporations with dedicated analytical departments.
Environmental monitoring represents an emerging application area, with NMR structural assignments being used to identify and characterize pollutants, metabolites, and degradation products in environmental samples. This application supports regulatory compliance and remediation efforts across industries.
The agricultural sector has begun implementing NMR structural assignment techniques for soil analysis, crop metabolomics, and development of agrochemicals. These applications help optimize growing conditions, develop more effective pesticides, and understand plant responses to environmental stressors.
Medical diagnostics represents a promising frontier, with research advancing toward using NMR-based metabolomics for disease biomarker discovery and personalized medicine approaches. Though still primarily in research phases, this application holds significant potential for clinical translation and market growth.
Current Challenges in Scalar Coupling Analysis
Despite significant advancements in NMR spectroscopy, scalar coupling analysis continues to face several persistent challenges that limit its effectiveness for structural assignments. One fundamental issue is the complexity of coupling patterns in large biomolecules, where signal overlap creates ambiguity in coupling constant measurements. As molecular weight increases, spectral crowding becomes more pronounced, making it difficult to isolate and accurately measure individual coupling constants, particularly in proteins exceeding 25 kDa.
Signal-to-noise ratio limitations present another significant obstacle, especially when attempting to detect long-range couplings that are typically weak (less than 1 Hz) but often contain valuable structural information. These subtle couplings can be obscured by noise or broader signals, requiring extended acquisition times that may not be practical for unstable samples or time-sensitive experiments.
The conformational dynamics of molecules introduces additional complexity, as scalar couplings represent time-averaged values across multiple conformations. For flexible molecules undergoing rapid conformational changes, the measured coupling constants may not accurately reflect any single conformation, complicating structural interpretation. This becomes particularly problematic when analyzing intrinsically disordered proteins or molecules with significant conformational heterogeneity.
Technical limitations in pulse sequence design also hinder progress. While specialized pulse sequences can enhance the detection of specific coupling types, they often come with trade-offs in sensitivity, resolution, or experiment duration. The development of robust pulse sequences that can simultaneously measure multiple coupling constants without compromising spectral quality remains challenging.
Data processing and interpretation present computational challenges as well. Automated algorithms for extracting coupling constants from complex spectra often struggle with overlapping signals or non-first-order coupling patterns. Machine learning approaches show promise but require extensive training datasets that may not be available for novel molecular classes.
The theoretical framework for relating coupling constants to structural parameters also has limitations. While Karplus equations provide valuable correlations between dihedral angles and coupling constants, their empirical nature introduces uncertainties, particularly when applied to non-standard structural motifs or when multiple coupling pathways contribute to the observed constants.
Finally, reference data availability remains problematic. The establishment of comprehensive databases correlating experimental coupling constants with verified structural information across diverse molecular classes would significantly enhance the reliability of structural assignments but requires substantial collaborative efforts across the NMR community.
Signal-to-noise ratio limitations present another significant obstacle, especially when attempting to detect long-range couplings that are typically weak (less than 1 Hz) but often contain valuable structural information. These subtle couplings can be obscured by noise or broader signals, requiring extended acquisition times that may not be practical for unstable samples or time-sensitive experiments.
The conformational dynamics of molecules introduces additional complexity, as scalar couplings represent time-averaged values across multiple conformations. For flexible molecules undergoing rapid conformational changes, the measured coupling constants may not accurately reflect any single conformation, complicating structural interpretation. This becomes particularly problematic when analyzing intrinsically disordered proteins or molecules with significant conformational heterogeneity.
Technical limitations in pulse sequence design also hinder progress. While specialized pulse sequences can enhance the detection of specific coupling types, they often come with trade-offs in sensitivity, resolution, or experiment duration. The development of robust pulse sequences that can simultaneously measure multiple coupling constants without compromising spectral quality remains challenging.
Data processing and interpretation present computational challenges as well. Automated algorithms for extracting coupling constants from complex spectra often struggle with overlapping signals or non-first-order coupling patterns. Machine learning approaches show promise but require extensive training datasets that may not be available for novel molecular classes.
The theoretical framework for relating coupling constants to structural parameters also has limitations. While Karplus equations provide valuable correlations between dihedral angles and coupling constants, their empirical nature introduces uncertainties, particularly when applied to non-standard structural motifs or when multiple coupling pathways contribute to the observed constants.
Finally, reference data availability remains problematic. The establishment of comprehensive databases correlating experimental coupling constants with verified structural information across diverse molecular classes would significantly enhance the reliability of structural assignments but requires substantial collaborative efforts across the NMR community.
Established Protocols for Structural Elucidation
01 NMR spectroscopy techniques for scalar coupling analysis
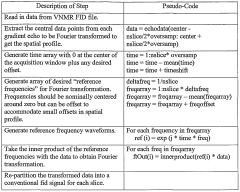
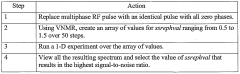
Various NMR spectroscopy techniques are employed to analyze scalar couplings for structural assignments. These techniques include multi-dimensional NMR experiments that provide information about coupling constants between nuclei, which are essential for determining molecular connectivity and configuration. Advanced pulse sequences and data acquisition methods enhance the resolution and sensitivity of scalar coupling measurements, allowing for more accurate structural determinations.- NMR spectroscopy techniques for scalar coupling analysis: Various NMR spectroscopy techniques are employed to analyze scalar couplings for structural assignments. These techniques include multi-dimensional NMR experiments that can detect and measure J-couplings between nuclei, providing valuable information about molecular connectivity and conformation. Advanced pulse sequences and data acquisition methods enhance the resolution and sensitivity of scalar coupling measurements, enabling more accurate structural determinations.
- Computational methods for analyzing scalar coupling data: Computational algorithms and software tools are developed to process and interpret scalar coupling data obtained from NMR experiments. These methods include automated analysis of coupling patterns, simulation of spectra based on molecular structures, and statistical approaches for correlating coupling constants with structural features. Machine learning techniques are increasingly being applied to improve the accuracy of structural assignments based on scalar coupling information.
- Hardware innovations for scalar coupling measurements: Specialized NMR hardware components are designed to enhance the detection and measurement of scalar couplings. These innovations include improved probe designs, gradient coil systems, and signal processing electronics that increase the sensitivity and resolution of coupling measurements. Advanced magnet technologies provide higher field strengths, allowing for better separation of coupling patterns in complex molecular structures.
- Applications of scalar coupling in biomolecular structure determination: Scalar coupling information is crucial for determining the three-dimensional structures of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. The magnitude of coupling constants provides insights into dihedral angles and conformational preferences, while coupling patterns reveal connectivity between atoms. These applications enable researchers to elucidate complex biomolecular structures and understand structure-function relationships in biological systems.
- Integration of scalar coupling data with other structural information: Scalar coupling data is often integrated with other types of structural information to improve the accuracy of molecular structure determinations. This includes combining J-coupling constants with NOE data, chemical shifts, residual dipolar couplings, and computational modeling approaches. Integrated analysis platforms enable researchers to synthesize multiple sources of structural information for more comprehensive and reliable structural assignments.
02 Computational methods for analyzing scalar coupling data
Computational algorithms and software tools are developed to process and interpret scalar coupling data obtained from NMR experiments. These methods include automated analysis of coupling patterns, simulation of spectra based on molecular structures, and prediction of coupling constants from structural parameters. Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to improve the accuracy of structural assignments based on scalar coupling information.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hardware innovations for improved scalar coupling measurements
Specialized NMR hardware components are designed to enhance the measurement of scalar couplings. These innovations include high-field magnets, advanced probe designs, and improved signal processing electronics that increase the sensitivity and resolution of NMR spectrometers. Hardware modifications enable the detection of weak couplings and allow for more precise structural assignments in complex molecules.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of scalar coupling in biomolecular structure determination
Scalar coupling measurements are crucial for determining the three-dimensional structures of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. The coupling constants provide information about dihedral angles and conformational preferences, which are essential for building accurate structural models. Specialized techniques have been developed to measure and interpret scalar couplings in large biomolecules, contributing to advancements in structural biology and drug discovery.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of scalar coupling data with other structural information
Scalar coupling data is often combined with other types of structural information to improve the accuracy of molecular structure determinations. This integration involves correlating coupling constants with chemical shifts, NOE data, and residual dipolar couplings. Computational frameworks have been developed to simultaneously analyze multiple types of NMR parameters, leading to more robust structural assignments and conformational analyses.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Instrument Manufacturers
The field of Structural Assignments via Scalar Couplings in NMR is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated market size of $1.2-1.5 billion and expanding at approximately 5-7% annually. The competitive landscape features established instrumentation companies like JEOL, Bruker BioSpin, and Agilent Technologies leading hardware development, while pharmaceutical giants including Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, and BASF leverage the technology for drug discovery. Academic institutions such as Xiamen University, Rutgers, and Oxford contribute significant research advancements. The technology has reached moderate maturity in traditional applications but is evolving rapidly in areas like RNA structural analysis, where companies like Skyhawk Therapeutics and Base4 Biotechnology are developing innovative therapeutic applications. Integration with AI and computational methods, pioneered by IBM and specialized firms, represents the frontier of this field's development.
JEOL Ltd.
Technical Solution: JEOL has developed advanced NMR spectrometers specifically optimized for structural assignments via scalar couplings. Their JNM-ECZ series incorporates proprietary pulse sequence technologies that enhance the detection of J-couplings across multiple bonds. The system features automated scalar coupling analysis software that can identify and quantify coupling constants with high precision, enabling researchers to determine molecular connectivity patterns without relying solely on chemical shift data. JEOL's technology includes specialized probe designs that maximize signal-to-noise ratios for heteronuclear correlation experiments critical for scalar coupling measurements. Their systems integrate machine learning algorithms to predict coupling patterns based on partial structural information, accelerating the structure elucidation process for complex organic and biomolecules.
Strengths: Superior hardware sensitivity allowing detection of long-range couplings that competitors miss; integrated software suite specifically designed for coupling constant analysis. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some competitors; steeper learning curve for utilizing advanced scalar coupling analysis features.
Bruker BioSpin MRI GmbH
Technical Solution: Bruker BioSpin has pioneered comprehensive solutions for structural assignments via scalar couplings with their AVANCE NEO platform. Their technology incorporates ultra-stable magnets (up to 1.2 GHz) that provide unprecedented resolution for detecting subtle J-coupling patterns. Bruker's TopSpin software includes dedicated modules for automated coupling constant extraction and analysis, with capabilities for simulating complex coupling patterns to match experimental data. Their CryoProbe technology significantly enhances sensitivity, allowing detection of long-range couplings that would otherwise be unobservable. Bruker has also developed specialized pulse sequences like ADEQUATE and INADEQUATE that leverage scalar couplings for carbon-carbon connectivity determination, crucial for complex structure elucidation. Their systems integrate with structure verification software that uses J-coupling data to validate proposed molecular structures against experimental NMR data.
Strengths: Industry-leading magnetic field stability essential for precise J-coupling measurements; comprehensive software ecosystem for coupling analysis and structure verification. Weaknesses: Premium pricing model limits accessibility for smaller research institutions; complex system operation requires specialized training.
Key Innovations in J-Coupling Interpretation
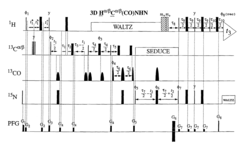
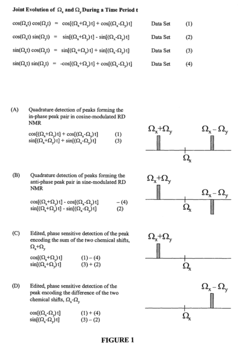
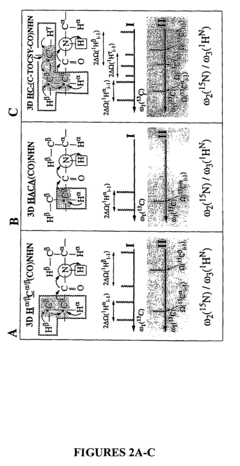
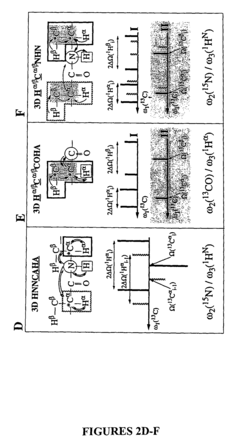
Phase sensitively-detected reduced dimensionality nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for rapid chemical shift assignment and secondary structure determination of proteins
PatentInactiveUS7396685B2
Innovation
- The implementation of reduced dimensionality (RD) TR NMR experiments, such as 3D HA,CA,(CO),N,HN and H,C,(C-TOCSY-CO),N,HN, that use phase-sensitive detection to encode chemical shift values, allowing for sine-modulated 3D NMR spectra generation and frequency discrimination of projected chemical shifts, thereby overcoming sampling limitations.
Simultaneous phase cycling for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
PatentWO2007002464A2
Innovation
- The method of simultaneous phase cycling, which involves applying radiofrequency pulses to multiple spatially discrete slices of a sample to conduct multiple phase cycles in a single transient, using spatial selection and localization techniques from MRI in conjunction with NMR phase cycle schemes, allowing for the simultaneous execution of multiple phase cycles and subsequent signal separation using pulsed magnetic field gradients.
Computational Tools for NMR Data Processing
The evolution of computational tools for NMR data processing has been transformative for structural assignments via scalar couplings. Modern software packages have significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of interpreting complex NMR spectra. These tools typically incorporate sophisticated algorithms for spectral analysis, peak picking, and coupling constant extraction, enabling researchers to rapidly process raw NMR data into meaningful structural information.
Leading software solutions such as MestReNova, TopSpin, and NMRPipe offer comprehensive suites for data processing with specialized modules for scalar coupling analysis. These platforms provide automated methods for multiplet analysis, which can identify coupling patterns and extract J-values with minimal user intervention. The integration of quantum mechanical calculations within these tools has further improved the prediction of coupling constants based on proposed molecular structures.
Machine learning approaches have recently emerged as powerful additions to the computational toolkit. Neural networks trained on extensive databases of known structures and their corresponding coupling constants can now predict structural features with remarkable accuracy. These AI-driven tools are particularly valuable for analyzing complex molecules where traditional methods may struggle to resolve overlapping signals or identify subtle coupling relationships.
Database integration represents another significant advancement in NMR data processing. Modern tools can access and compare experimental data against repositories of known compounds and their spectral characteristics. This capability facilitates rapid identification of structural motifs based on characteristic coupling patterns, substantially accelerating the structure elucidation process.
Cloud-based platforms have democratized access to sophisticated NMR analysis tools. Researchers can now process data remotely using powerful computational resources without requiring extensive local infrastructure. These platforms often feature collaborative capabilities, allowing multiple scientists to simultaneously analyze and annotate spectral data, which is particularly valuable for complex structural assignment problems.
Visualization technologies have also evolved considerably, offering interactive 3D representations that correlate molecular structure with observed coupling constants. These visual interfaces allow researchers to intuitively explore the relationship between structural features and spectral characteristics, facilitating more intuitive interpretation of scalar coupling data for structural assignments.
The integration of these computational tools with other analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography, has created powerful hybrid approaches for structural determination. Modern software increasingly supports multi-modal data analysis, where scalar coupling information from NMR can be combined with complementary structural data to resolve ambiguities and confirm proposed structures with greater confidence.
Leading software solutions such as MestReNova, TopSpin, and NMRPipe offer comprehensive suites for data processing with specialized modules for scalar coupling analysis. These platforms provide automated methods for multiplet analysis, which can identify coupling patterns and extract J-values with minimal user intervention. The integration of quantum mechanical calculations within these tools has further improved the prediction of coupling constants based on proposed molecular structures.
Machine learning approaches have recently emerged as powerful additions to the computational toolkit. Neural networks trained on extensive databases of known structures and their corresponding coupling constants can now predict structural features with remarkable accuracy. These AI-driven tools are particularly valuable for analyzing complex molecules where traditional methods may struggle to resolve overlapping signals or identify subtle coupling relationships.
Database integration represents another significant advancement in NMR data processing. Modern tools can access and compare experimental data against repositories of known compounds and their spectral characteristics. This capability facilitates rapid identification of structural motifs based on characteristic coupling patterns, substantially accelerating the structure elucidation process.
Cloud-based platforms have democratized access to sophisticated NMR analysis tools. Researchers can now process data remotely using powerful computational resources without requiring extensive local infrastructure. These platforms often feature collaborative capabilities, allowing multiple scientists to simultaneously analyze and annotate spectral data, which is particularly valuable for complex structural assignment problems.
Visualization technologies have also evolved considerably, offering interactive 3D representations that correlate molecular structure with observed coupling constants. These visual interfaces allow researchers to intuitively explore the relationship between structural features and spectral characteristics, facilitating more intuitive interpretation of scalar coupling data for structural assignments.
The integration of these computational tools with other analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography, has created powerful hybrid approaches for structural determination. Modern software increasingly supports multi-modal data analysis, where scalar coupling information from NMR can be combined with complementary structural data to resolve ambiguities and confirm proposed structures with greater confidence.
Standardization and Validation Approaches
Standardization of NMR scalar coupling measurements is essential for reliable structural assignments across different laboratories and instruments. Current standardization efforts focus on establishing reference compounds with well-characterized coupling constants that serve as calibration standards. The IUPAC has developed recommendations for reporting scalar coupling data, including specific notation systems and measurement conditions, to ensure consistency in the scientific literature. These standards specify temperature control parameters, solvent selection criteria, and concentration ranges that minimize intermolecular interactions affecting coupling measurements.
Validation approaches for scalar coupling-based structural assignments typically employ multi-tiered verification systems. Primary validation involves comparing experimental coupling constants with theoretical values calculated from proposed structures using density functional theory (DFT) methods. Statistical analysis of these comparisons yields confidence metrics that quantify assignment reliability. Advanced validation protocols incorporate machine learning algorithms trained on extensive databases of known structure-coupling relationships, enabling rapid assessment of structural proposals against established patterns.
Cross-validation techniques have emerged as particularly valuable, combining scalar coupling data with complementary NMR parameters such as chemical shifts, NOE measurements, and residual dipolar couplings. This multi-parameter approach significantly enhances assignment confidence by requiring structural proposals to simultaneously satisfy multiple independent constraints. Round-robin testing among different laboratories has become standard practice for validating new methodologies, with results published in specialized journals dedicated to analytical method validation.
Quality assurance frameworks for scalar coupling measurements now include uncertainty quantification protocols that account for instrumental variations, sample preparation differences, and data processing methods. These frameworks establish minimum reporting requirements for coupling constant measurements, including signal-to-noise ratios, digital resolution parameters, and processing algorithms used. Automated validation software packages have been developed that apply these standardized criteria to evaluate the reliability of structural assignments based on coupling data.
Regulatory bodies in pharmaceutical and chemical industries have incorporated specific guidelines for NMR-based structural verification that emphasize scalar coupling validation. These guidelines mandate minimum validation criteria for structure confirmation in regulatory submissions, particularly for novel chemical entities and complex natural products. The emergence of blockchain-based data validation systems represents the cutting edge of standardization efforts, creating immutable records of raw NMR data and processing parameters that ensure reproducibility and prevent data manipulation.
Validation approaches for scalar coupling-based structural assignments typically employ multi-tiered verification systems. Primary validation involves comparing experimental coupling constants with theoretical values calculated from proposed structures using density functional theory (DFT) methods. Statistical analysis of these comparisons yields confidence metrics that quantify assignment reliability. Advanced validation protocols incorporate machine learning algorithms trained on extensive databases of known structure-coupling relationships, enabling rapid assessment of structural proposals against established patterns.
Cross-validation techniques have emerged as particularly valuable, combining scalar coupling data with complementary NMR parameters such as chemical shifts, NOE measurements, and residual dipolar couplings. This multi-parameter approach significantly enhances assignment confidence by requiring structural proposals to simultaneously satisfy multiple independent constraints. Round-robin testing among different laboratories has become standard practice for validating new methodologies, with results published in specialized journals dedicated to analytical method validation.
Quality assurance frameworks for scalar coupling measurements now include uncertainty quantification protocols that account for instrumental variations, sample preparation differences, and data processing methods. These frameworks establish minimum reporting requirements for coupling constant measurements, including signal-to-noise ratios, digital resolution parameters, and processing algorithms used. Automated validation software packages have been developed that apply these standardized criteria to evaluate the reliability of structural assignments based on coupling data.
Regulatory bodies in pharmaceutical and chemical industries have incorporated specific guidelines for NMR-based structural verification that emphasize scalar coupling validation. These guidelines mandate minimum validation criteria for structure confirmation in regulatory submissions, particularly for novel chemical entities and complex natural products. The emergence of blockchain-based data validation systems represents the cutting edge of standardization efforts, creating immutable records of raw NMR data and processing parameters that ensure reproducibility and prevent data manipulation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!