How Ethyl Acetate Streamlines Effective Production Pipelines?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Background and Production Goals
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has played a significant role in various industries for decades. Its journey began in the early 20th century when it was first synthesized on an industrial scale. Since then, the production and application of ethyl acetate have evolved dramatically, driven by advancements in chemical engineering and increasing demand across multiple sectors.
The evolution of ethyl acetate production has been marked by continuous improvements in synthesis methods and process efficiency. Initially, the primary production route involved the esterification of ethanol with acetic acid. However, as technology progressed, new pathways emerged, including the Tishchenko process and the dehydrogenation of ethanol. These innovations have significantly enhanced production capacity and reduced costs, making ethyl acetate more accessible for various applications.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry and circular economy principles. Researchers and industry leaders are exploring bio-based feedstocks and catalytic processes that minimize waste and energy consumption, aiming to create a more sustainable production pipeline for ethyl acetate.
The primary goal in ethyl acetate production is to achieve high yield and purity while optimizing resource utilization. This involves developing more efficient catalysts, improving reaction conditions, and implementing advanced separation techniques. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on process intensification, which aims to reduce equipment size, energy consumption, and production time without compromising product quality.
Another crucial objective is to enhance the flexibility of production systems. As market demands fluctuate, manufacturers seek to create adaptable production lines that can quickly adjust output volumes and potentially switch between different ester products. This flexibility is essential for maintaining competitiveness in a dynamic global market.
Safety and environmental considerations are also at the forefront of production goals. Ethyl acetate, being a flammable solvent, requires stringent safety measures throughout its production and handling. Manufacturers are continually working to improve process safety, reduce emissions, and develop closed-loop systems that minimize environmental impact.
As industries strive for more efficient and sustainable operations, the role of ethyl acetate in streamlining production pipelines has become increasingly important. Its excellent solvency properties, low toxicity, and relatively easy recovery make it an ideal candidate for various applications, from coatings and adhesives to pharmaceutical processes. The ongoing research and development in ethyl acetate production aim to further enhance its effectiveness in these applications while addressing the broader challenges of resource efficiency and environmental stewardship.
The evolution of ethyl acetate production has been marked by continuous improvements in synthesis methods and process efficiency. Initially, the primary production route involved the esterification of ethanol with acetic acid. However, as technology progressed, new pathways emerged, including the Tishchenko process and the dehydrogenation of ethanol. These innovations have significantly enhanced production capacity and reduced costs, making ethyl acetate more accessible for various applications.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry and circular economy principles. Researchers and industry leaders are exploring bio-based feedstocks and catalytic processes that minimize waste and energy consumption, aiming to create a more sustainable production pipeline for ethyl acetate.
The primary goal in ethyl acetate production is to achieve high yield and purity while optimizing resource utilization. This involves developing more efficient catalysts, improving reaction conditions, and implementing advanced separation techniques. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on process intensification, which aims to reduce equipment size, energy consumption, and production time without compromising product quality.
Another crucial objective is to enhance the flexibility of production systems. As market demands fluctuate, manufacturers seek to create adaptable production lines that can quickly adjust output volumes and potentially switch between different ester products. This flexibility is essential for maintaining competitiveness in a dynamic global market.
Safety and environmental considerations are also at the forefront of production goals. Ethyl acetate, being a flammable solvent, requires stringent safety measures throughout its production and handling. Manufacturers are continually working to improve process safety, reduce emissions, and develop closed-loop systems that minimize environmental impact.
As industries strive for more efficient and sustainable operations, the role of ethyl acetate in streamlining production pipelines has become increasingly important. Its excellent solvency properties, low toxicity, and relatively easy recovery make it an ideal candidate for various applications, from coatings and adhesives to pharmaceutical processes. The ongoing research and development in ethyl acetate production aim to further enhance its effectiveness in these applications while addressing the broader challenges of resource efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Market Demand Analysis for Ethyl Acetate
The global market for ethyl acetate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key solvent and intermediate in chemical processes, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in streamlining production pipelines, particularly in the manufacturing of paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals.
In the paint and coatings industry, ethyl acetate's demand has been rising due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The increasing construction activities worldwide, coupled with the growing automotive sector, have been major contributors to the market expansion. Ethyl acetate's ability to enhance the drying time and flow characteristics of paints has made it an indispensable component in modern paint formulations.
The adhesives industry has also been a significant driver of ethyl acetate demand. With the rise of e-commerce and packaging requirements, the need for high-performance adhesives has surged. Ethyl acetate's role in improving the bonding strength and reducing curing time has made it a preferred choice among adhesive manufacturers, leading to increased market penetration.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's use as a solvent in drug synthesis and purification processes has been growing. The expanding pharmaceutical industry, particularly in emerging economies, has contributed to the increased demand for ethyl acetate. Its effectiveness in extraction and crystallization processes has made it an essential component in the production of various active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The food and beverage industry has also shown a rising demand for ethyl acetate, primarily due to its application as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences. The growing consumer preference for flavored food and beverages has been a key factor in driving this segment of the market.
From a regional perspective, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, with China and India leading the demand. The rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sectors, and increasing disposable incomes in these countries have been pivotal in driving market growth. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and a focus on eco-friendly solvent alternatives.
The market trend indicates a shift towards bio-based ethyl acetate production, driven by environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives. This trend is expected to open new avenues for market growth, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. The development of efficient production processes using renewable resources is likely to shape the future landscape of the ethyl acetate market.
In the paint and coatings industry, ethyl acetate's demand has been rising due to its excellent solvency properties and low toxicity. The increasing construction activities worldwide, coupled with the growing automotive sector, have been major contributors to the market expansion. Ethyl acetate's ability to enhance the drying time and flow characteristics of paints has made it an indispensable component in modern paint formulations.
The adhesives industry has also been a significant driver of ethyl acetate demand. With the rise of e-commerce and packaging requirements, the need for high-performance adhesives has surged. Ethyl acetate's role in improving the bonding strength and reducing curing time has made it a preferred choice among adhesive manufacturers, leading to increased market penetration.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate's use as a solvent in drug synthesis and purification processes has been growing. The expanding pharmaceutical industry, particularly in emerging economies, has contributed to the increased demand for ethyl acetate. Its effectiveness in extraction and crystallization processes has made it an essential component in the production of various active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The food and beverage industry has also shown a rising demand for ethyl acetate, primarily due to its application as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences. The growing consumer preference for flavored food and beverages has been a key factor in driving this segment of the market.
From a regional perspective, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, with China and India leading the demand. The rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sectors, and increasing disposable incomes in these countries have been pivotal in driving market growth. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and a focus on eco-friendly solvent alternatives.
The market trend indicates a shift towards bio-based ethyl acetate production, driven by environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives. This trend is expected to open new avenues for market growth, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. The development of efficient production processes using renewable resources is likely to shape the future landscape of the ethyl acetate market.
Current State and Challenges in Ethyl Acetate Production
Ethyl acetate production has reached a mature stage globally, with established industrial processes and widespread applications. The current annual production capacity exceeds 3 million tons, driven by its versatile use in various industries such as coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. The dominant production method remains the esterification of ethanol with acetic acid, accounting for approximately 80% of global production.
Despite its maturity, the ethyl acetate industry faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the fluctuation in raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. These price variations significantly impact production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent pricing strategies. Additionally, the industry is grappling with increasing environmental regulations, necessitating the development of more sustainable production methods.
The current production processes, while efficient, still have room for improvement in terms of energy consumption and waste reduction. Many facilities are exploring ways to optimize their energy usage and minimize byproduct formation. The industry is also facing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, prompting research into bio-based feedstocks and greener production technologies.
Another challenge lies in the quality control of ethyl acetate, especially for high-purity applications in electronics and pharmaceuticals. Ensuring consistent product quality while maintaining high production volumes remains a delicate balance for manufacturers. The presence of trace impurities can significantly affect the performance of ethyl acetate in sensitive applications, necessitating advanced purification techniques.
Market competition is intensifying, particularly from emerging economies in Asia. This has led to overcapacity in some regions, putting pressure on profit margins and driving the need for more cost-effective production methods. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on process intensification and automation to stay competitive in the global market.
The industry is also grappling with the need for more flexible production systems that can quickly adapt to changing market demands. This includes the ability to switch between different grades of ethyl acetate or even different products altogether, requiring innovative reactor designs and process control systems.
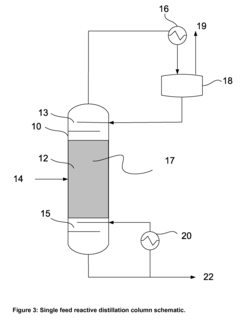
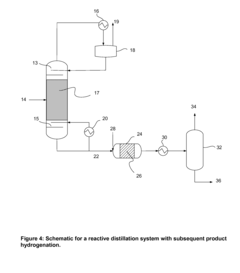
In terms of technological advancements, there is ongoing research into catalytic processes that could improve reaction efficiency and selectivity. Novel reactor designs, such as reactive distillation columns, are being explored to combine reaction and separation steps, potentially reducing energy consumption and equipment footprint.
Despite its maturity, the ethyl acetate industry faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the fluctuation in raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. These price variations significantly impact production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent pricing strategies. Additionally, the industry is grappling with increasing environmental regulations, necessitating the development of more sustainable production methods.
The current production processes, while efficient, still have room for improvement in terms of energy consumption and waste reduction. Many facilities are exploring ways to optimize their energy usage and minimize byproduct formation. The industry is also facing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, prompting research into bio-based feedstocks and greener production technologies.
Another challenge lies in the quality control of ethyl acetate, especially for high-purity applications in electronics and pharmaceuticals. Ensuring consistent product quality while maintaining high production volumes remains a delicate balance for manufacturers. The presence of trace impurities can significantly affect the performance of ethyl acetate in sensitive applications, necessitating advanced purification techniques.
Market competition is intensifying, particularly from emerging economies in Asia. This has led to overcapacity in some regions, putting pressure on profit margins and driving the need for more cost-effective production methods. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on process intensification and automation to stay competitive in the global market.
The industry is also grappling with the need for more flexible production systems that can quickly adapt to changing market demands. This includes the ability to switch between different grades of ethyl acetate or even different products altogether, requiring innovative reactor designs and process control systems.
In terms of technological advancements, there is ongoing research into catalytic processes that could improve reaction efficiency and selectivity. Novel reactor designs, such as reactive distillation columns, are being explored to combine reaction and separation steps, potentially reducing energy consumption and equipment footprint.
Existing Production Pipeline Solutions Using Ethyl Acetate
01 Distillation and separation techniques
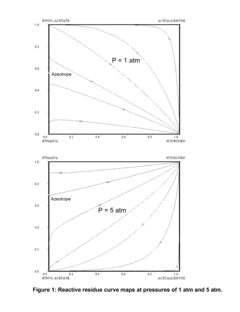
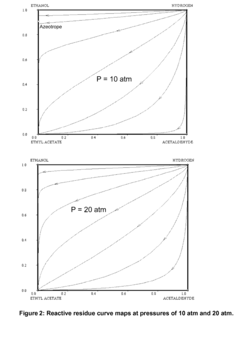
Various distillation and separation techniques are employed to streamline ethyl acetate production and purification. These methods include extractive distillation, azeotropic distillation, and reactive distillation. These processes help to improve the efficiency of ethyl acetate separation from reaction mixtures and increase overall product yield.- Distillation and separation techniques: Various distillation and separation techniques are employed to streamline ethyl acetate production and purification. These methods include extractive distillation, azeotropic distillation, and reactive distillation. These processes help to improve the efficiency of ethyl acetate separation from reaction mixtures and increase overall product yield.
- Catalytic processes for ethyl acetate synthesis: Catalytic processes play a crucial role in streamlining ethyl acetate production. Different catalysts and reaction conditions are utilized to enhance the conversion of raw materials into ethyl acetate. These catalytic methods often involve the use of heterogeneous catalysts, which can improve reaction rates and selectivity while reducing energy consumption.
- Continuous flow reactors and process intensification: Continuous flow reactors and process intensification techniques are implemented to enhance the efficiency of ethyl acetate production. These methods involve the use of microreactors, flow chemistry, and other innovative reactor designs that allow for better control of reaction parameters and improved heat and mass transfer.
- Recycling and waste reduction strategies: Various recycling and waste reduction strategies are employed to improve the sustainability and efficiency of ethyl acetate production. These methods include the recycling of unreacted raw materials, recovery of byproducts, and implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste generation and reduce environmental impact.
- Process control and optimization: Advanced process control and optimization techniques are utilized to streamline ethyl acetate production. These methods involve the use of real-time monitoring systems, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence to optimize reaction conditions, improve product quality, and reduce energy consumption throughout the production process.
02 Catalytic processes for ethyl acetate synthesis
Catalytic processes play a crucial role in streamlining ethyl acetate production. Different catalysts, such as heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts, are used to enhance reaction rates and selectivity. These catalytic processes often involve the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid or the direct synthesis from ethanol and acetaldehyde.Expand Specific Solutions03 Continuous flow reactors and process intensification
Continuous flow reactors and process intensification techniques are implemented to improve ethyl acetate production efficiency. These methods involve the use of microreactors, structured reactors, and other innovative designs that enhance heat and mass transfer, leading to increased productivity and reduced energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and waste reduction strategies
Various recycling and waste reduction strategies are employed to streamline ethyl acetate production and improve overall process sustainability. These include the recycling of unreacted raw materials, recovery of byproducts, and implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize waste generation and maximize resource utilization.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process control and optimization
Advanced process control and optimization techniques are utilized to streamline ethyl acetate production. These methods involve the use of real-time monitoring systems, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence to optimize reaction conditions, improve product quality, and enhance overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Acetate Manufacturing Industry
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand across various industries. The global market size is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by applications in coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Technologically, the production process is well-established, with companies like Celanese International Corp. and Eastman Chemical Co. leading in conventional synthesis methods. However, innovation is ongoing, as evidenced by Viridis Chemical LLC's focus on bio-based ethyl acetate production. Research institutions such as Tianjin University and the University of Campinas are contributing to advancements in sustainable production techniques, indicating a shift towards more environmentally friendly processes in this mature industry.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed an innovative approach to ethyl acetate production that focuses on process integration and sustainability. Their technology utilizes a highly selective heterogeneous catalyst system that enables direct oxidative esterification of ethanol to ethyl acetate[10]. This one-step process eliminates the need for separate acetaldehyde production, significantly simplifying the production pipeline. Wacker has also implemented advanced heat integration techniques, recovering and reusing process heat to reduce overall energy consumption by up to 25%[11]. The company's process incorporates a membrane-based separation system that achieves high-purity ethyl acetate with minimal energy input. Furthermore, Wacker has developed a bio-based route for ethyl acetate production using fermentation-derived ethanol, aligning with circular economy principles and reducing reliance on fossil-based feedstocks[12].
Strengths: Simplified one-step process, reduced energy consumption, efficient separation, and sustainable bio-based production option. Weaknesses: Potential sensitivity to catalyst performance and lifespan. May require careful control of oxidation conditions to prevent over-oxidation.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative ethyl acetate production process that significantly streamlines production pipelines. Their approach utilizes a one-step ethanol dehydrogenation method, which directly converts ethanol to ethyl acetate using a copper-based catalyst[1]. This process achieves high conversion rates of up to 95% and selectivity exceeding 99%[2]. The company has also implemented advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring to optimize production parameters, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced waste. Additionally, Sinopec has integrated a closed-loop recycling system that recovers and purifies unreacted ethanol, further enhancing overall process efficiency[3].
Strengths: High conversion rates, excellent selectivity, improved energy efficiency, and reduced waste. The closed-loop system enhances resource utilization. Weaknesses: Potential dependency on ethanol availability and price fluctuations. The process may require significant initial investment for implementation.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Acetate Synthesis and Application
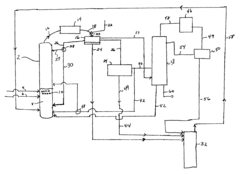
Process improvement for continuous ethyl acetate production
PatentInactiveUS6768021B2
Innovation
- The process involves using a membrane separation unit to remove water from the condensed reaction stream, recycling the dried stream back into the production process, and employing an additional distillation zone to produce purified ethyl acetate with minimal acid content, thereby optimizing water management and increasing process capacity.
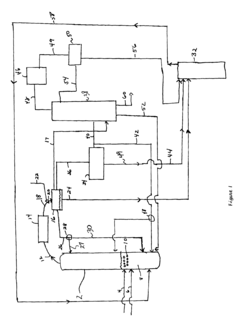
Ethyl Acetate Production
PatentActiveUS20140012037A1
Innovation
- A reactive distillation system that integrates dehydrogenation and dimerization of ethanol using base-metal catalysts, such as copper oxide mixed with other metals, in a single continuous column, allowing for high-purity ethyl acetate production with reduced complexity and cost, and incorporating a stripping unit for impurity separation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The use of ethyl acetate in production pipelines raises important environmental and sustainability considerations. As a solvent widely used in various industries, its impact on the environment and long-term sustainability must be carefully evaluated.
Ethyl acetate is considered a volatile organic compound (VOC), which can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This poses potential risks to both human health and the environment. However, compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate has a relatively low toxicity and is biodegradable, which somewhat mitigates its environmental impact.
In terms of production, the synthesis of ethyl acetate typically involves the reaction of ethanol with acetic acid. While these raw materials can be derived from renewable sources, such as biomass fermentation, the majority of commercial production still relies on petrochemical feedstocks. This dependence on non-renewable resources raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of ethyl acetate production.
To address these environmental challenges, many industries are exploring greener alternatives and implementing more sustainable practices. One approach is the development of bio-based ethyl acetate, produced from renewable feedstocks like corn or sugarcane. This not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also potentially lowers the carbon footprint of the production process.
Another important consideration is the recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate in production pipelines. Implementing efficient solvent recovery systems can significantly reduce emissions and waste, while also improving the overall sustainability of the process. Advanced technologies, such as membrane separation or distillation techniques, are being employed to enhance solvent recovery rates and minimize environmental impact.
The disposal of ethyl acetate waste also requires careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Proper handling, storage, and treatment of waste streams are essential to minimize environmental risks and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
As industries strive for more sustainable operations, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming crucial in evaluating the environmental impact of ethyl acetate use throughout its entire lifecycle. These assessments help identify areas for improvement and guide decision-making towards more environmentally friendly alternatives or process optimizations.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers benefits in streamlining production pipelines, its environmental impact and sustainability considerations cannot be overlooked. Balancing the efficiency gains with responsible environmental stewardship is essential for industries to maintain their social license to operate and ensure long-term sustainability.
Ethyl acetate is considered a volatile organic compound (VOC), which can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This poses potential risks to both human health and the environment. However, compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate has a relatively low toxicity and is biodegradable, which somewhat mitigates its environmental impact.
In terms of production, the synthesis of ethyl acetate typically involves the reaction of ethanol with acetic acid. While these raw materials can be derived from renewable sources, such as biomass fermentation, the majority of commercial production still relies on petrochemical feedstocks. This dependence on non-renewable resources raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of ethyl acetate production.
To address these environmental challenges, many industries are exploring greener alternatives and implementing more sustainable practices. One approach is the development of bio-based ethyl acetate, produced from renewable feedstocks like corn or sugarcane. This not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also potentially lowers the carbon footprint of the production process.
Another important consideration is the recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate in production pipelines. Implementing efficient solvent recovery systems can significantly reduce emissions and waste, while also improving the overall sustainability of the process. Advanced technologies, such as membrane separation or distillation techniques, are being employed to enhance solvent recovery rates and minimize environmental impact.
The disposal of ethyl acetate waste also requires careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Proper handling, storage, and treatment of waste streams are essential to minimize environmental risks and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
As industries strive for more sustainable operations, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming crucial in evaluating the environmental impact of ethyl acetate use throughout its entire lifecycle. These assessments help identify areas for improvement and guide decision-making towards more environmentally friendly alternatives or process optimizations.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers benefits in streamlining production pipelines, its environmental impact and sustainability considerations cannot be overlooked. Balancing the efficiency gains with responsible environmental stewardship is essential for industries to maintain their social license to operate and ensure long-term sustainability.
Safety Regulations and Handling Protocols for Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate is a widely used solvent in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and manufacturing. As its usage in production pipelines increases, it is crucial to establish and adhere to stringent safety regulations and handling protocols. These measures are essential to protect workers, maintain product quality, and ensure environmental compliance.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific exposure limits for ethyl acetate in the workplace. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) is 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. Employers must implement engineering controls and work practices to maintain exposure levels below this threshold. Regular air monitoring and personal exposure assessments are necessary to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in handling ethyl acetate safely. Workers should wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection when working with this solvent. The selection of PPE should be based on a thorough risk assessment and comply with relevant safety standards.
Proper storage and handling of ethyl acetate are critical to prevent accidents and maintain product integrity. The solvent should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition and incompatible materials. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed when not in use. Transfer operations should be conducted using closed systems or in well-ventilated areas to minimize vapor exposure.
Spill response protocols are essential components of ethyl acetate handling procedures. Facilities should have clearly defined spill response plans, including designated personnel, appropriate cleanup materials, and proper disposal methods. Workers must be trained in spill containment and cleanup procedures to minimize environmental impact and potential hazards.
Fire safety is a crucial consideration when working with ethyl acetate due to its flammable nature. Production areas should be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems, and workers must be trained in fire prevention and emergency response procedures. Proper grounding and bonding techniques should be employed during transfer operations to prevent static discharge and potential ignition.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in ethyl acetate handling. Facilities must comply with local, state, and federal regulations regarding emissions, waste disposal, and potential environmental impacts. Implementing proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies is essential to minimize the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
Training and education are fundamental to ensuring the safe handling of ethyl acetate in production pipelines. Comprehensive training programs should cover hazard communication, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses and safety audits help maintain a high level of awareness and compliance among workers.
By implementing these safety regulations and handling protocols, companies can effectively streamline their production pipelines while prioritizing worker safety, product quality, and environmental responsibility. Continuous improvement and adaptation of these measures are necessary to address evolving regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific exposure limits for ethyl acetate in the workplace. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) is 400 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average. Employers must implement engineering controls and work practices to maintain exposure levels below this threshold. Regular air monitoring and personal exposure assessments are necessary to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in handling ethyl acetate safely. Workers should wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection when working with this solvent. The selection of PPE should be based on a thorough risk assessment and comply with relevant safety standards.
Proper storage and handling of ethyl acetate are critical to prevent accidents and maintain product integrity. The solvent should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition and incompatible materials. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed when not in use. Transfer operations should be conducted using closed systems or in well-ventilated areas to minimize vapor exposure.
Spill response protocols are essential components of ethyl acetate handling procedures. Facilities should have clearly defined spill response plans, including designated personnel, appropriate cleanup materials, and proper disposal methods. Workers must be trained in spill containment and cleanup procedures to minimize environmental impact and potential hazards.
Fire safety is a crucial consideration when working with ethyl acetate due to its flammable nature. Production areas should be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems, and workers must be trained in fire prevention and emergency response procedures. Proper grounding and bonding techniques should be employed during transfer operations to prevent static discharge and potential ignition.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in ethyl acetate handling. Facilities must comply with local, state, and federal regulations regarding emissions, waste disposal, and potential environmental impacts. Implementing proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies is essential to minimize the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
Training and education are fundamental to ensuring the safe handling of ethyl acetate in production pipelines. Comprehensive training programs should cover hazard communication, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses and safety audits help maintain a high level of awareness and compliance among workers.
By implementing these safety regulations and handling protocols, companies can effectively streamline their production pipelines while prioritizing worker safety, product quality, and environmental responsibility. Continuous improvement and adaptation of these measures are necessary to address evolving regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!