How to Prevent GDI Engine Oil Dilution Issues
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
GDI Oil Dilution Background and Objectives
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) technology has emerged as a pivotal advancement in internal combustion engine design over the past two decades. This technology directly injects fuel into the combustion chamber rather than the intake port, offering significant improvements in fuel efficiency and engine performance. However, since its widespread adoption in the 2010s, a persistent challenge has emerged: oil dilution, where unburned fuel contaminates the engine oil, compromising its lubricating properties and potentially leading to accelerated engine wear.
The evolution of GDI technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when automotive manufacturers began seeking solutions to meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations while maintaining or improving performance. By 2015, GDI had become the dominant technology in new gasoline-powered vehicles, with market penetration exceeding 50% in North America and Europe. This rapid adoption, however, brought the oil dilution issue to the forefront, particularly in cold-climate regions and vehicles predominantly used for short-distance driving.
The technical trajectory of GDI systems has seen continuous refinement, with early systems operating at 50-100 bar injection pressures evolving to modern systems exceeding 350 bar. This progression has partially mitigated but not eliminated the oil dilution challenge, indicating the need for comprehensive solutions that address the fundamental mechanisms of fuel-oil interaction under various operating conditions.
Current industry data suggests that GDI engines can experience oil dilution rates 2-3 times higher than port fuel injection engines, with fuel concentration in oil potentially reaching 5-7% in severe cases, well beyond the recommended maximum of 2.5%. This dilution accelerates oil degradation, reduces viscosity, and compromises critical engine protection, potentially reducing engine lifespan by 15-20% if left unaddressed.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the mechanisms behind GDI oil dilution, identify the critical factors contributing to its severity, and develop effective prevention strategies. Specifically, we aim to explore solutions that can be implemented across three domains: engine design modifications, fuel system optimizations, and operational strategy enhancements.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish quantifiable metrics for oil dilution assessment, develop predictive models for dilution rates under various operating conditions, and create a framework for evaluating the effectiveness of proposed solutions. The ultimate goal is to enable GDI technology to fully deliver on its efficiency and performance promises without compromising engine durability or requiring excessive maintenance interventions.
The evolution of GDI technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when automotive manufacturers began seeking solutions to meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations while maintaining or improving performance. By 2015, GDI had become the dominant technology in new gasoline-powered vehicles, with market penetration exceeding 50% in North America and Europe. This rapid adoption, however, brought the oil dilution issue to the forefront, particularly in cold-climate regions and vehicles predominantly used for short-distance driving.
The technical trajectory of GDI systems has seen continuous refinement, with early systems operating at 50-100 bar injection pressures evolving to modern systems exceeding 350 bar. This progression has partially mitigated but not eliminated the oil dilution challenge, indicating the need for comprehensive solutions that address the fundamental mechanisms of fuel-oil interaction under various operating conditions.
Current industry data suggests that GDI engines can experience oil dilution rates 2-3 times higher than port fuel injection engines, with fuel concentration in oil potentially reaching 5-7% in severe cases, well beyond the recommended maximum of 2.5%. This dilution accelerates oil degradation, reduces viscosity, and compromises critical engine protection, potentially reducing engine lifespan by 15-20% if left unaddressed.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the mechanisms behind GDI oil dilution, identify the critical factors contributing to its severity, and develop effective prevention strategies. Specifically, we aim to explore solutions that can be implemented across three domains: engine design modifications, fuel system optimizations, and operational strategy enhancements.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish quantifiable metrics for oil dilution assessment, develop predictive models for dilution rates under various operating conditions, and create a framework for evaluating the effectiveness of proposed solutions. The ultimate goal is to enable GDI technology to fully deliver on its efficiency and performance promises without compromising engine durability or requiring excessive maintenance interventions.
Market Analysis of GDI Engine Technology
The Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) engine technology market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by stringent emission regulations and increasing demand for fuel-efficient vehicles. The global GDI engine market was valued at approximately 7.5 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 12.3 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% during the forecast period.
North America and Europe currently dominate the GDI engine market due to their strict emission standards and high consumer awareness regarding fuel efficiency. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is emerging as the fastest-growing market for GDI technology, fueled by rapid automotive industrialization and increasing disposable income among consumers.
The passenger vehicle segment holds the largest market share for GDI engines, accounting for over 70% of the total market. This dominance is attributed to the higher production volume of passenger vehicles compared to commercial vehicles and the increasing consumer preference for fuel-efficient personal transportation options.
Among the various vehicle classes, mid-sized and compact cars represent the primary application areas for GDI technology. These vehicle segments are particularly sensitive to fuel economy improvements and emission reductions, making them ideal candidates for GDI implementation. Premium and luxury vehicles have already achieved near-complete GDI penetration in many markets.
Market analysis reveals that the oil dilution issue in GDI engines has emerged as a significant concern affecting consumer satisfaction and brand reputation. Vehicle manufacturers that have successfully addressed this issue have gained competitive advantages in terms of warranty claim reductions and improved customer loyalty. This technical challenge represents both a market threat and opportunity for industry players.
The aftermarket sector for GDI-related products, including specialized engine oils designed to mitigate oil dilution effects, has shown substantial growth. This segment is expected to expand at a rate of 9.3% annually through 2028, outpacing the overall GDI market growth.
Consumer awareness regarding GDI oil dilution issues has increased significantly, particularly in cold-weather markets where the problem is more pronounced. Online search data indicates a 215% increase in related queries over the past three years, demonstrating growing consumer concern about this specific technical challenge.
Market research indicates that vehicle manufacturers who effectively communicate their solutions to the oil dilution problem gain measurable advantages in consumer perception scores. Brands that have implemented and marketed specific countermeasures have seen up to 18% improvements in quality perception metrics compared to competitors who have not addressed the issue publicly.
North America and Europe currently dominate the GDI engine market due to their strict emission standards and high consumer awareness regarding fuel efficiency. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is emerging as the fastest-growing market for GDI technology, fueled by rapid automotive industrialization and increasing disposable income among consumers.
The passenger vehicle segment holds the largest market share for GDI engines, accounting for over 70% of the total market. This dominance is attributed to the higher production volume of passenger vehicles compared to commercial vehicles and the increasing consumer preference for fuel-efficient personal transportation options.
Among the various vehicle classes, mid-sized and compact cars represent the primary application areas for GDI technology. These vehicle segments are particularly sensitive to fuel economy improvements and emission reductions, making them ideal candidates for GDI implementation. Premium and luxury vehicles have already achieved near-complete GDI penetration in many markets.
Market analysis reveals that the oil dilution issue in GDI engines has emerged as a significant concern affecting consumer satisfaction and brand reputation. Vehicle manufacturers that have successfully addressed this issue have gained competitive advantages in terms of warranty claim reductions and improved customer loyalty. This technical challenge represents both a market threat and opportunity for industry players.
The aftermarket sector for GDI-related products, including specialized engine oils designed to mitigate oil dilution effects, has shown substantial growth. This segment is expected to expand at a rate of 9.3% annually through 2028, outpacing the overall GDI market growth.
Consumer awareness regarding GDI oil dilution issues has increased significantly, particularly in cold-weather markets where the problem is more pronounced. Online search data indicates a 215% increase in related queries over the past three years, demonstrating growing consumer concern about this specific technical challenge.
Market research indicates that vehicle manufacturers who effectively communicate their solutions to the oil dilution problem gain measurable advantages in consumer perception scores. Brands that have implemented and marketed specific countermeasures have seen up to 18% improvements in quality perception metrics compared to competitors who have not addressed the issue publicly.
Current Challenges in GDI Oil Dilution Prevention
Despite significant advancements in Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) technology, oil dilution remains a persistent challenge for manufacturers and engineers. The fundamental issue stems from the direct injection of fuel into the combustion chamber, where incomplete combustion can lead to fuel mixing with engine oil. This dilution compromises oil viscosity and lubrication properties, potentially causing accelerated engine wear and reduced component lifespan.
One major technical hurdle involves cold-start conditions, where fuel impingement on cylinder walls becomes particularly problematic. At low temperatures, fuel vaporization is significantly reduced, resulting in liquid fuel contacting cylinder surfaces and eventually migrating into the crankcase. Current piston and cylinder designs struggle to fully address this issue, especially in regions with extended cold weather periods.
Combustion chamber geometry presents another significant challenge. The interaction between fuel spray patterns and chamber surfaces remains difficult to optimize across all operating conditions. Even with advanced computational fluid dynamics modeling, achieving ideal spray targeting throughout the engine's operating range continues to elude engineers, particularly during transient operations and varying load conditions.
Fuel injection timing and pressure control systems face limitations in their ability to adapt to rapidly changing driving conditions. While high-pressure injection systems (operating at 200+ bar) have improved atomization, they cannot completely eliminate the risk of wall wetting during certain operating modes, particularly during engine warm-up phases and low-load operation.
Post-injection strategies, intended to raise exhaust temperatures for emissions control, inadvertently contribute to oil dilution. This creates a technical conflict between meeting stringent emissions standards and maintaining oil quality, forcing engineers to make compromises that impact long-term engine durability.
Turbocharging, now common in GDI engines, compounds these challenges by creating complex pressure differentials and flow dynamics within the combustion chamber. The interaction between boosted intake pressure and direct injection timing requires sophisticated control algorithms that current ECU technology struggles to perfect across all operating conditions.
Material limitations also present barriers to solving oil dilution issues. While advanced cylinder coatings and piston ring designs have improved, they cannot completely prevent fuel migration past the rings during certain operating conditions. The cost-effectiveness of implementing exotic materials or complex surface treatments at mass-production scale remains prohibitive for many manufacturers.
Finally, diagnostic capabilities represent a significant gap in addressing oil dilution. Current onboard diagnostic systems lack the sensitivity to detect gradual oil dilution before it reaches problematic levels, leaving vehicle owners unaware until performance issues or premature wear occurs.
One major technical hurdle involves cold-start conditions, where fuel impingement on cylinder walls becomes particularly problematic. At low temperatures, fuel vaporization is significantly reduced, resulting in liquid fuel contacting cylinder surfaces and eventually migrating into the crankcase. Current piston and cylinder designs struggle to fully address this issue, especially in regions with extended cold weather periods.
Combustion chamber geometry presents another significant challenge. The interaction between fuel spray patterns and chamber surfaces remains difficult to optimize across all operating conditions. Even with advanced computational fluid dynamics modeling, achieving ideal spray targeting throughout the engine's operating range continues to elude engineers, particularly during transient operations and varying load conditions.
Fuel injection timing and pressure control systems face limitations in their ability to adapt to rapidly changing driving conditions. While high-pressure injection systems (operating at 200+ bar) have improved atomization, they cannot completely eliminate the risk of wall wetting during certain operating modes, particularly during engine warm-up phases and low-load operation.
Post-injection strategies, intended to raise exhaust temperatures for emissions control, inadvertently contribute to oil dilution. This creates a technical conflict between meeting stringent emissions standards and maintaining oil quality, forcing engineers to make compromises that impact long-term engine durability.
Turbocharging, now common in GDI engines, compounds these challenges by creating complex pressure differentials and flow dynamics within the combustion chamber. The interaction between boosted intake pressure and direct injection timing requires sophisticated control algorithms that current ECU technology struggles to perfect across all operating conditions.
Material limitations also present barriers to solving oil dilution issues. While advanced cylinder coatings and piston ring designs have improved, they cannot completely prevent fuel migration past the rings during certain operating conditions. The cost-effectiveness of implementing exotic materials or complex surface treatments at mass-production scale remains prohibitive for many manufacturers.
Finally, diagnostic capabilities represent a significant gap in addressing oil dilution. Current onboard diagnostic systems lack the sensitivity to detect gradual oil dilution before it reaches problematic levels, leaving vehicle owners unaware until performance issues or premature wear occurs.
Existing Oil Dilution Mitigation Strategies
01 Fuel dilution detection and monitoring systems
Various systems and methods for detecting and monitoring fuel dilution in engine oil of GDI engines. These systems utilize sensors to measure oil properties such as viscosity, density, or dielectric constant to determine the level of fuel contamination. Real-time monitoring allows for early detection of excessive dilution, preventing engine damage and optimizing maintenance intervals.- Detection and measurement of oil dilution in GDI engines: Various methods and systems for detecting and measuring oil dilution in gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines have been developed. These include sensors that can monitor oil quality parameters, analytical techniques to determine fuel contamination levels, and diagnostic systems that can provide real-time feedback on engine oil condition. These detection methods help in early identification of oil dilution issues before they cause significant engine damage.
- Prevention mechanisms for oil dilution: Various prevention mechanisms have been designed to minimize oil dilution in GDI engines. These include improved fuel injection timing and strategies, enhanced combustion chamber designs, optimized piston ring configurations, and advanced thermal management systems. These preventive measures aim to reduce the amount of unburned fuel that reaches the engine oil, thereby extending oil life and protecting engine components.
- Oil formulations resistant to dilution effects: Specialized engine oil formulations have been developed to better withstand the effects of fuel dilution in GDI engines. These oils contain additives that maintain viscosity stability even when contaminated with fuel, provide enhanced oxidation resistance, and offer improved detergency to handle combustion byproducts. These formulations help maintain engine protection even when some level of fuel dilution occurs.
- Engine design modifications to reduce oil dilution: Structural and design modifications to GDI engines have been implemented to address oil dilution issues. These include redesigned cylinder heads, modified piston geometries, improved crankcase ventilation systems, and enhanced oil circulation pathways. Such design changes aim to minimize the contact between unburned fuel and engine oil, thereby reducing dilution and extending oil service life.
- Control strategies for managing oil dilution: Advanced control strategies have been developed to manage oil dilution in GDI engines. These include adaptive engine control algorithms that adjust operating parameters based on oil condition, regeneration cycles to remove fuel contaminants from oil, and intelligent driving mode selections that minimize conditions leading to oil dilution. These control strategies help maintain optimal engine performance while minimizing the negative impacts of oil dilution.
02 Prevention mechanisms for oil dilution
Technical solutions designed to prevent or reduce fuel dilution in GDI engine oil. These include improved fuel injection timing, enhanced combustion chamber designs, and specialized piston ring configurations that minimize fuel spray contact with cylinder walls. Some solutions incorporate heating systems for the engine oil to evaporate fuel contaminants during operation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Oil formulations resistant to dilution effects
Specialized engine oil formulations designed to maintain performance despite fuel dilution in GDI engines. These oils contain additives that help maintain viscosity stability, prevent sludge formation, and protect engine components when diluted with fuel. The formulations often include detergents, dispersants, and viscosity modifiers specifically engineered for GDI applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Diagnostic methods for oil dilution assessment
Methods and techniques for diagnosing the extent of fuel dilution in GDI engine oil. These include laboratory analysis procedures, onboard diagnostic algorithms, and predictive models that can estimate dilution levels based on engine operating conditions. Some methods incorporate machine learning to improve accuracy of dilution predictions based on multiple sensor inputs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Engine design modifications to reduce oil dilution
Structural and design modifications to GDI engines that minimize oil dilution. These include redesigned cylinder heads, optimized spray patterns for fuel injectors, improved crankcase ventilation systems, and enhanced oil separation technologies. Some designs incorporate thermal management systems to maintain optimal oil temperature ranges that facilitate fuel evaporation from the oil.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Automotive OEMs and Suppliers Analysis
The GDI oil dilution market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing focus on prevention technologies as gasoline direct injection engines become more prevalent. The market is expanding due to stricter emissions regulations and consumer demand for fuel-efficient vehicles. Technologically, solutions are advancing from basic to sophisticated approaches, with companies at different maturity levels. The Lubrizol Corp. and Chevron Oronite lead in additive technologies, while major automakers like Hyundai, Ford, Toyota, and Nissan are implementing engineering solutions. OEMs such as Bosch and AVL are developing advanced fuel injection systems to minimize oil dilution. The competitive landscape shows collaboration between oil companies and automakers to address this challenge through both chemical and mechanical approaches.
The Lubrizol Corp.
Technical Solution: Lubrizol has developed advanced additive packages specifically designed to address GDI engine oil dilution. Their technology focuses on maintaining oil viscosity stability even when diluted with fuel. Their Lubrizol PV1559 additive package contains specialized detergents and dispersants that prevent sludge formation when fuel mixes with oil. Additionally, they've engineered anti-wear compounds that remain effective in diluted oil conditions, protecting critical engine components. Their latest innovation includes thermally-activated viscosity stabilizers that respond to temperature changes, maintaining proper lubrication even with 5-7% fuel dilution levels[1]. Lubrizol's solution also incorporates oxidation inhibitors that extend oil life by up to 25% under fuel dilution conditions compared to conventional oils[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in oil additives with proven effectiveness in maintaining viscosity stability and engine protection even with significant fuel dilution. Weaknesses: Their solutions typically require premium pricing, and optimal performance depends on proper oil change intervals being followed.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford has developed a comprehensive approach to mitigate GDI engine oil dilution through both hardware and software solutions. Their EcoBoost GDI engines feature an advanced thermal management system that rapidly brings engines to optimal operating temperature, reducing cold-start fuel condensation. Ford's proprietary cylinder head design incorporates optimized spray targeting with specially angled fuel injectors that minimize wall wetting. Their latest innovation includes a dynamic fuel injection timing control system that adjusts injection patterns based on engine temperature, load, and ambient conditions to minimize fuel impingement on cylinder walls[2]. Additionally, Ford has implemented software calibration strategies that modify the air-fuel ratio and spark timing during cold operation to reduce fuel condensation. Their engines also utilize specialized piston ring designs with enhanced oil control capabilities that better prevent fuel from passing into the crankcase[4].
Strengths: Holistic approach combining hardware design, thermal management, and software calibration to address multiple causes of oil dilution simultaneously. Weaknesses: Some solutions may increase manufacturing complexity and cost, and software calibrations that reduce dilution might slightly impact cold-start performance or fuel economy.
Key Technical Innovations in Fuel System Design
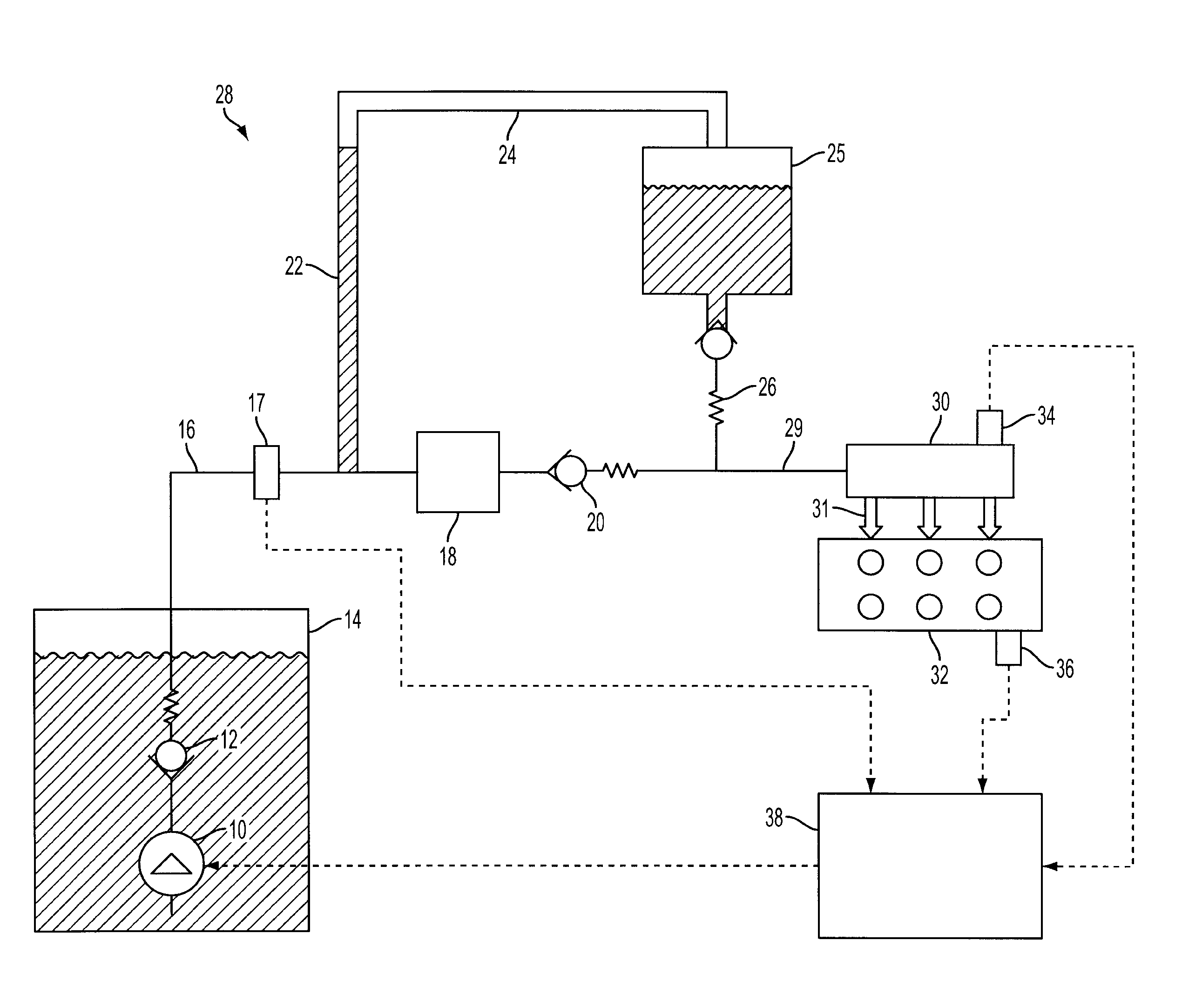
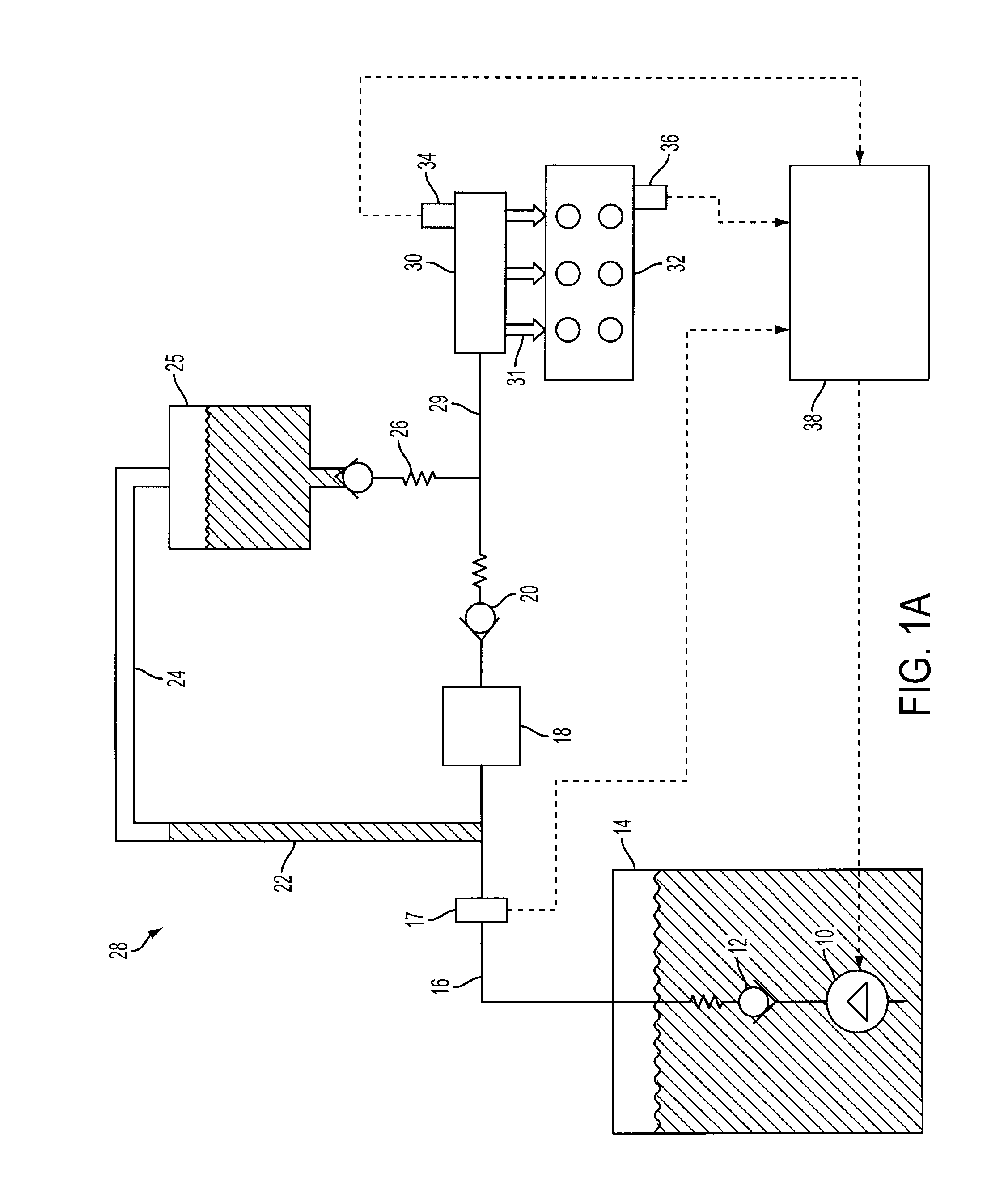
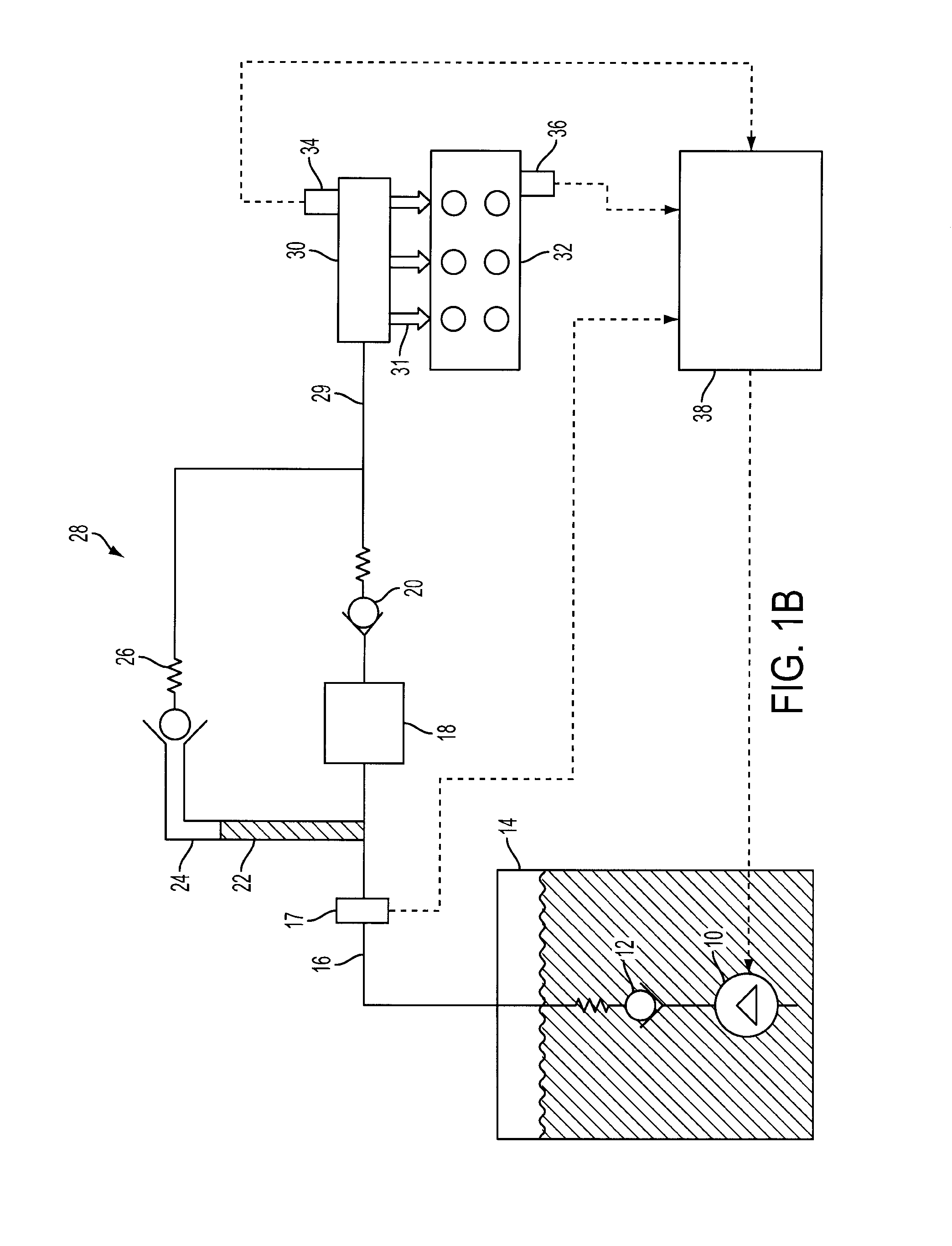
Direct Injection Fuel System with Reservoir
PatentInactiveUS20090107461A1
Innovation
- A fuel delivery system with a lift pump and a high-pressure pump, coupled with a bypass and check valve configuration, where the lift pump is activated during engine shutdown to maintain pressure and fill the fuel rail with liquid fuel, preventing air and vapor ingestion, and a reservoir positioned vertically above the check valve ensures only liquid fuel enters the rail, maintaining pressure and improving fuel pressure rise during engine starts.
Method for maximizing the formation of deposits in injector nozzles of GDI engines
PatentWO2018002610A1
Innovation
- A method to maximize deposit formation in GDI engine injector nozzles by simulating severe conditions through controlled engine speed and load variations, high nozzle temperatures, and moderate fuel flow rates, allowing for automated and unsupervised testing to quickly assess fuel's deposit-forming tendencies.
Emissions Regulations Impact on GDI Technology
The evolution of emissions regulations globally has significantly influenced the development and implementation of Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) technology. Stringent emissions standards, particularly in Europe (Euro 6d), North America (EPA Tier 3, CARB LEV III), and Asia (China 6), have pushed automakers to adopt GDI systems as a primary solution for reducing CO2 emissions and improving fuel efficiency. These regulations typically mandate reductions in nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
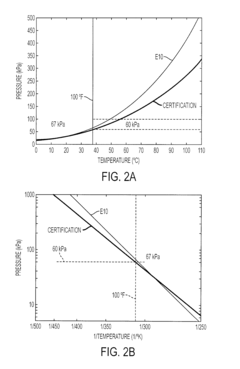
While GDI technology offers substantial benefits in meeting these regulatory requirements through improved combustion efficiency and reduced fuel consumption, the very design changes that enable these improvements can exacerbate oil dilution issues. The higher injection pressures (up to 350 bar in modern systems) and altered spray patterns necessary for emissions compliance can lead to increased fuel impingement on cylinder walls, particularly during cold starts and low-temperature operation.
Regulatory testing cycles have evolved to include more cold-start evaluations and real-world driving emissions (RDE) tests, which have exposed the vulnerability of GDI engines to oil dilution under these conditions. The World Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP), which replaced the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) in many regions, includes more dynamic driving patterns that can trigger increased fuel-oil interaction in GDI systems.
Particulate filter requirements for GDI engines, now mandatory in many markets, create additional challenges. The regeneration cycles necessary for these filters often involve post-injection strategies that can increase the risk of fuel reaching the crankcase. This regulatory-driven technology addition thus creates a secondary pathway for oil dilution beyond the primary wall-wetting mechanism.
Future emissions regulations are projected to become even more stringent, with Euro 7 and equivalent standards in other regions potentially requiring further refinements to GDI technology. These upcoming regulations may necessitate even higher injection pressures, multiple injection events per cycle, and more sophisticated thermal management systems—all of which could potentially exacerbate oil dilution if not properly addressed through concurrent technological innovations.
The regulatory landscape has created a challenging engineering balance: meeting increasingly strict emissions targets while preventing the unintended consequence of increased oil dilution. This tension is driving significant research and development efforts across the automotive industry to develop GDI systems that can satisfy regulatory requirements without compromising engine durability and reliability.
While GDI technology offers substantial benefits in meeting these regulatory requirements through improved combustion efficiency and reduced fuel consumption, the very design changes that enable these improvements can exacerbate oil dilution issues. The higher injection pressures (up to 350 bar in modern systems) and altered spray patterns necessary for emissions compliance can lead to increased fuel impingement on cylinder walls, particularly during cold starts and low-temperature operation.
Regulatory testing cycles have evolved to include more cold-start evaluations and real-world driving emissions (RDE) tests, which have exposed the vulnerability of GDI engines to oil dilution under these conditions. The World Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP), which replaced the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) in many regions, includes more dynamic driving patterns that can trigger increased fuel-oil interaction in GDI systems.
Particulate filter requirements for GDI engines, now mandatory in many markets, create additional challenges. The regeneration cycles necessary for these filters often involve post-injection strategies that can increase the risk of fuel reaching the crankcase. This regulatory-driven technology addition thus creates a secondary pathway for oil dilution beyond the primary wall-wetting mechanism.
Future emissions regulations are projected to become even more stringent, with Euro 7 and equivalent standards in other regions potentially requiring further refinements to GDI technology. These upcoming regulations may necessitate even higher injection pressures, multiple injection events per cycle, and more sophisticated thermal management systems—all of which could potentially exacerbate oil dilution if not properly addressed through concurrent technological innovations.
The regulatory landscape has created a challenging engineering balance: meeting increasingly strict emissions targets while preventing the unintended consequence of increased oil dilution. This tension is driving significant research and development efforts across the automotive industry to develop GDI systems that can satisfy regulatory requirements without compromising engine durability and reliability.
Durability Testing Methodologies for Oil Dilution
Durability testing for oil dilution in GDI (Gasoline Direct Injection) engines requires comprehensive methodologies to accurately simulate real-world conditions and predict long-term performance. The industry has developed several standardized approaches that evaluate how engine oils resist dilution under various operating conditions.
The most widely adopted methodology is the Sequence VH Test, which subjects engines to repeated cold-start cycles followed by short-duration operation. This test specifically targets conditions known to cause fuel dilution in GDI engines by preventing the engine from reaching optimal operating temperatures. Data collection occurs at predetermined intervals, typically measuring fuel content in oil using gas chromatography techniques that can detect concentration levels as low as 0.1%.
Accelerated aging tests represent another critical methodology, where engines operate continuously under varying load conditions while maintaining lower-than-normal operating temperatures. These tests compress years of typical consumer driving patterns into weeks of laboratory testing, allowing engineers to observe cumulative effects of oil dilution on engine components.
Field testing complements laboratory methodologies by deploying instrumented test vehicles in diverse geographic regions with varying climate conditions. These vehicles are equipped with sensors that continuously monitor oil composition, temperature profiles, and engine performance metrics. Fleet testing often involves hundreds of vehicles operating under normal consumer driving patterns, providing statistically significant data on oil dilution rates across different driving styles and environments.
Thermal cycle testing specifically evaluates oil dilution resistance during temperature fluctuations. This methodology subjects engines to programmed temperature variations that mimic seasonal changes and driving patterns, from sub-zero cold starts to high-temperature highway operation, measuring how effectively the oil maintains proper viscosity and chemical properties throughout these transitions.
Component-specific testing isolates critical parts like piston rings and cylinder walls to evaluate how oil dilution affects sealing performance and wear rates. These bench tests allow engineers to focus on specific failure modes without running complete engines, accelerating the development cycle for new materials and designs resistant to oil dilution effects.
Modern durability testing increasingly incorporates digital twin technology, where physical test results calibrate sophisticated simulation models. These models can then predict oil dilution behavior across thousands of virtual operating scenarios, identifying edge cases that might be missed in traditional testing approaches.
The most widely adopted methodology is the Sequence VH Test, which subjects engines to repeated cold-start cycles followed by short-duration operation. This test specifically targets conditions known to cause fuel dilution in GDI engines by preventing the engine from reaching optimal operating temperatures. Data collection occurs at predetermined intervals, typically measuring fuel content in oil using gas chromatography techniques that can detect concentration levels as low as 0.1%.
Accelerated aging tests represent another critical methodology, where engines operate continuously under varying load conditions while maintaining lower-than-normal operating temperatures. These tests compress years of typical consumer driving patterns into weeks of laboratory testing, allowing engineers to observe cumulative effects of oil dilution on engine components.
Field testing complements laboratory methodologies by deploying instrumented test vehicles in diverse geographic regions with varying climate conditions. These vehicles are equipped with sensors that continuously monitor oil composition, temperature profiles, and engine performance metrics. Fleet testing often involves hundreds of vehicles operating under normal consumer driving patterns, providing statistically significant data on oil dilution rates across different driving styles and environments.
Thermal cycle testing specifically evaluates oil dilution resistance during temperature fluctuations. This methodology subjects engines to programmed temperature variations that mimic seasonal changes and driving patterns, from sub-zero cold starts to high-temperature highway operation, measuring how effectively the oil maintains proper viscosity and chemical properties throughout these transitions.
Component-specific testing isolates critical parts like piston rings and cylinder walls to evaluate how oil dilution affects sealing performance and wear rates. These bench tests allow engineers to focus on specific failure modes without running complete engines, accelerating the development cycle for new materials and designs resistant to oil dilution effects.
Modern durability testing increasingly incorporates digital twin technology, where physical test results calibrate sophisticated simulation models. These models can then predict oil dilution behavior across thousands of virtual operating scenarios, identifying edge cases that might be missed in traditional testing approaches.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!