How to Reduce Boiling Loss in Liquid Nitrogen Dewar Vessels
OCT 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cryogenic Storage Technology Background and Objectives
Cryogenic storage technology has evolved significantly since the early 20th century, with the development of vacuum-insulated vessels by Sir James Dewar in 1892 marking a pivotal moment in the field. These vessels, now commonly known as Dewar flasks or vessels, have become fundamental components in various industries requiring the storage and transportation of cryogenic liquids, particularly liquid nitrogen which maintains a temperature of -196°C under normal atmospheric pressure.
The evolution of cryogenic storage technology has been driven by increasing demands from scientific research, healthcare, industrial manufacturing, and space exploration sectors. Early Dewar vessels suffered from significant boiling losses, often exceeding 5-10% per day, severely limiting their practical applications and economic viability for long-term storage solutions.
Over the decades, technological advancements have focused on improving insulation techniques, materials science, and design optimization to minimize heat transfer pathways. The introduction of multi-layer insulation (MLI), advanced vacuum technologies, and specialized neck tube designs has progressively reduced boiling losses to current industry standards of 1-3% per day for standard commercial vessels.
Despite these improvements, the persistent challenge of boiling loss remains a critical limitation in cryogenic storage applications. Boiling loss occurs when ambient heat penetrates the vessel, causing the liquid nitrogen to evaporate. This not only results in the wastage of valuable cryogenic fluid but also necessitates frequent refilling, increases operational costs, and can compromise sample integrity in scientific and medical applications.
The current technological landscape shows a clear trend toward developing more efficient insulation systems, exploring novel materials with lower thermal conductivity, and implementing advanced vacuum maintenance technologies. Recent innovations include the integration of active cooling systems, phase change materials, and smart monitoring solutions to further reduce boiling losses.
The primary objective of current research efforts is to achieve substantial reductions in boiling loss rates, ideally below 0.5% per day for standard vessels and approaching 0.1% for high-performance applications. Such improvements would revolutionize numerous fields, enabling longer-term storage of biological samples, reducing operational costs in industrial applications, and expanding the feasibility of cryogenic technologies in remote or resource-limited settings.
Additionally, there is growing emphasis on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly cryogenic storage solutions, as the production and transportation of liquid nitrogen have significant carbon footprints. The integration of renewable energy sources for cooling systems and the development of more energy-efficient manufacturing processes represent important secondary objectives in this technological domain.
The evolution of cryogenic storage technology has been driven by increasing demands from scientific research, healthcare, industrial manufacturing, and space exploration sectors. Early Dewar vessels suffered from significant boiling losses, often exceeding 5-10% per day, severely limiting their practical applications and economic viability for long-term storage solutions.
Over the decades, technological advancements have focused on improving insulation techniques, materials science, and design optimization to minimize heat transfer pathways. The introduction of multi-layer insulation (MLI), advanced vacuum technologies, and specialized neck tube designs has progressively reduced boiling losses to current industry standards of 1-3% per day for standard commercial vessels.
Despite these improvements, the persistent challenge of boiling loss remains a critical limitation in cryogenic storage applications. Boiling loss occurs when ambient heat penetrates the vessel, causing the liquid nitrogen to evaporate. This not only results in the wastage of valuable cryogenic fluid but also necessitates frequent refilling, increases operational costs, and can compromise sample integrity in scientific and medical applications.
The current technological landscape shows a clear trend toward developing more efficient insulation systems, exploring novel materials with lower thermal conductivity, and implementing advanced vacuum maintenance technologies. Recent innovations include the integration of active cooling systems, phase change materials, and smart monitoring solutions to further reduce boiling losses.
The primary objective of current research efforts is to achieve substantial reductions in boiling loss rates, ideally below 0.5% per day for standard vessels and approaching 0.1% for high-performance applications. Such improvements would revolutionize numerous fields, enabling longer-term storage of biological samples, reducing operational costs in industrial applications, and expanding the feasibility of cryogenic technologies in remote or resource-limited settings.
Additionally, there is growing emphasis on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly cryogenic storage solutions, as the production and transportation of liquid nitrogen have significant carbon footprints. The integration of renewable energy sources for cooling systems and the development of more energy-efficient manufacturing processes represent important secondary objectives in this technological domain.
Market Demand Analysis for Efficient Liquid Nitrogen Storage
The global market for efficient liquid nitrogen storage solutions has been experiencing steady growth, driven primarily by expanding applications across healthcare, biotechnology, and industrial sectors. The demand for Dewar vessels with reduced boiling loss is particularly pronounced in research institutions, biobanks, and pharmaceutical companies where sample preservation is critical and operational costs are closely monitored.
Market research indicates that the global cryogenic equipment market, which includes liquid nitrogen storage systems, was valued at approximately $16 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2030. Within this broader market, specialized Dewar vessels with enhanced thermal efficiency represent a high-growth segment due to increasing awareness of operational cost savings and environmental considerations.
Healthcare and life sciences sectors constitute the largest market segment, accounting for nearly 45% of demand for advanced liquid nitrogen storage solutions. The rapid expansion of biobanking facilities worldwide, estimated to be growing at 8.5% annually, is creating substantial demand for Dewar vessels with minimal boiling loss characteristics. This growth is particularly evident in emerging markets where healthcare infrastructure is developing rapidly.
Industrial applications represent another significant market segment, with food processing, metal manufacturing, and electronics industries increasingly adopting cryogenic technologies. These sectors are especially sensitive to operational efficiency, creating demand for storage solutions that minimize nitrogen loss and reduce refilling frequency.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the highest growth rates are being observed in Asia-Pacific markets, particularly China and India, where healthcare infrastructure development and industrial modernization are creating new demand centers for efficient cryogenic storage solutions.
Customer surveys indicate that end-users prioritize three key factors when selecting liquid nitrogen storage systems: operational cost efficiency (including minimized boiling loss), reliability, and safety features. Price sensitivity varies significantly by region and application, with research institutions demonstrating greater willingness to invest in premium solutions that offer superior thermal efficiency and reduced nitrogen consumption over time.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for Dewar vessels with advanced insulation technologies capable of reducing boiling loss by more than 30% compared to conventional designs could capture premium pricing and significant market share. This represents a strategic opportunity for manufacturers who can develop and commercialize innovative solutions addressing this specific market need.
Market research indicates that the global cryogenic equipment market, which includes liquid nitrogen storage systems, was valued at approximately $16 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2030. Within this broader market, specialized Dewar vessels with enhanced thermal efficiency represent a high-growth segment due to increasing awareness of operational cost savings and environmental considerations.
Healthcare and life sciences sectors constitute the largest market segment, accounting for nearly 45% of demand for advanced liquid nitrogen storage solutions. The rapid expansion of biobanking facilities worldwide, estimated to be growing at 8.5% annually, is creating substantial demand for Dewar vessels with minimal boiling loss characteristics. This growth is particularly evident in emerging markets where healthcare infrastructure is developing rapidly.
Industrial applications represent another significant market segment, with food processing, metal manufacturing, and electronics industries increasingly adopting cryogenic technologies. These sectors are especially sensitive to operational efficiency, creating demand for storage solutions that minimize nitrogen loss and reduce refilling frequency.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the highest growth rates are being observed in Asia-Pacific markets, particularly China and India, where healthcare infrastructure development and industrial modernization are creating new demand centers for efficient cryogenic storage solutions.
Customer surveys indicate that end-users prioritize three key factors when selecting liquid nitrogen storage systems: operational cost efficiency (including minimized boiling loss), reliability, and safety features. Price sensitivity varies significantly by region and application, with research institutions demonstrating greater willingness to invest in premium solutions that offer superior thermal efficiency and reduced nitrogen consumption over time.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for Dewar vessels with advanced insulation technologies capable of reducing boiling loss by more than 30% compared to conventional designs could capture premium pricing and significant market share. This represents a strategic opportunity for manufacturers who can develop and commercialize innovative solutions addressing this specific market need.
Current Challenges in Dewar Vessel Insulation Technology
Despite significant advancements in cryogenic technology, Dewar vessel insulation continues to face several critical challenges that limit their thermal efficiency and contribute to liquid nitrogen boiling loss. The primary challenge remains the vacuum integrity maintenance in the vessel's double-walled structure. Even microscopic leaks can dramatically compromise the vacuum insulation, leading to increased heat transfer and accelerated evaporation rates. Current manufacturing processes struggle to consistently produce perfect vacuum seals that maintain their integrity over extended operational periods.
Material limitations present another significant obstacle. Traditional insulation materials like multilayer insulation (MLI) and aerogels, while effective, still permit considerable radiative and conductive heat transfer. The degradation of these materials over time due to thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and radiation exposure further compromises their insulating properties, resulting in gradually increasing boiling loss rates throughout the vessel's operational life.
Thermal bridging through necessary structural supports and access ports represents a persistent engineering challenge. These components create unavoidable pathways for heat to enter the cryogenic environment. Current designs attempt to minimize these effects through strategic placement and material selection, but they remain significant contributors to overall thermal losses.
Cost-effectiveness constraints often limit the implementation of advanced insulation technologies. Many superior insulation solutions exist in laboratory settings but remain economically unfeasible for commercial production. This creates a significant gap between theoretical performance capabilities and practical market implementations, particularly in price-sensitive applications.
Size and weight considerations further complicate insulation optimization. Enhanced insulation typically requires increased wall thickness or additional components, creating trade-offs between thermal efficiency and practical usability. This is especially problematic in portable applications where dimensional constraints are strict.
The industry also faces challenges in standardized performance measurement and comparison methodologies. Different manufacturers employ varying testing protocols, making it difficult for end-users to accurately compare boiling loss rates across different products and technologies.
Emerging technologies like vacuum super insulation panels (VSIPs) and advanced nanomaterials show promise but face integration challenges with existing manufacturing processes. The transition from laboratory-scale success to industrial implementation remains problematic due to scalability issues, long-term reliability concerns, and initial investment requirements.
Material limitations present another significant obstacle. Traditional insulation materials like multilayer insulation (MLI) and aerogels, while effective, still permit considerable radiative and conductive heat transfer. The degradation of these materials over time due to thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and radiation exposure further compromises their insulating properties, resulting in gradually increasing boiling loss rates throughout the vessel's operational life.
Thermal bridging through necessary structural supports and access ports represents a persistent engineering challenge. These components create unavoidable pathways for heat to enter the cryogenic environment. Current designs attempt to minimize these effects through strategic placement and material selection, but they remain significant contributors to overall thermal losses.
Cost-effectiveness constraints often limit the implementation of advanced insulation technologies. Many superior insulation solutions exist in laboratory settings but remain economically unfeasible for commercial production. This creates a significant gap between theoretical performance capabilities and practical market implementations, particularly in price-sensitive applications.
Size and weight considerations further complicate insulation optimization. Enhanced insulation typically requires increased wall thickness or additional components, creating trade-offs between thermal efficiency and practical usability. This is especially problematic in portable applications where dimensional constraints are strict.
The industry also faces challenges in standardized performance measurement and comparison methodologies. Different manufacturers employ varying testing protocols, making it difficult for end-users to accurately compare boiling loss rates across different products and technologies.
Emerging technologies like vacuum super insulation panels (VSIPs) and advanced nanomaterials show promise but face integration challenges with existing manufacturing processes. The transition from laboratory-scale success to industrial implementation remains problematic due to scalability issues, long-term reliability concerns, and initial investment requirements.
Current Boil-Off Reduction Methods and Technologies
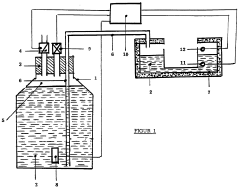
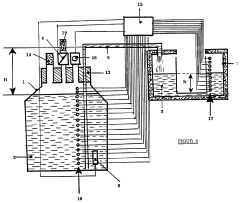
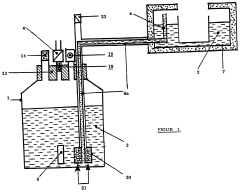
01 Vacuum insulation technology for reducing boiling loss
Dewar vessels utilize vacuum insulation technology to minimize heat transfer and reduce liquid nitrogen boiling loss. The vacuum layer between the inner and outer walls creates an effective thermal barrier that prevents heat from the environment from reaching the cryogenic liquid. Advanced multi-layer vacuum insulation systems with specialized materials can further enhance thermal efficiency and extend holding times for liquid nitrogen storage.- Vacuum insulation technologies for reducing boiling loss: Advanced vacuum insulation technologies are employed in Dewar vessels to minimize heat transfer and reduce liquid nitrogen boiling loss. These include multi-layer vacuum insulation, specialized vacuum sealing methods, and improved vacuum maintenance systems. The vacuum layers create effective thermal barriers that significantly reduce heat ingress from the environment, thereby extending the holding time of liquid nitrogen and minimizing evaporation rates.
- Structural design improvements to minimize heat transfer: Innovative structural designs in Dewar vessels focus on minimizing heat transfer pathways to reduce boiling loss. These designs include optimized neck tube configurations, strategic placement of support structures, and improved vessel geometry. By reducing thermal bridges and creating more efficient container shapes, these structural improvements help maintain lower temperatures for longer periods, resulting in decreased evaporation rates of liquid nitrogen.
- Advanced materials for enhanced thermal insulation: The use of advanced materials with superior thermal insulation properties significantly reduces liquid nitrogen boiling loss in Dewar vessels. These materials include specialized composites, novel metal alloys, and engineered polymers that offer lower thermal conductivity. The implementation of these materials in vessel construction creates more effective barriers against heat transfer, thereby minimizing evaporation and extending the storage duration of liquid nitrogen.
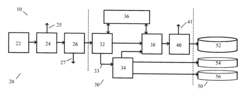
- Monitoring and control systems for evaporation management: Sophisticated monitoring and control systems are integrated into Dewar vessels to manage liquid nitrogen evaporation rates. These systems include temperature sensors, pressure monitors, and automated control mechanisms that optimize storage conditions. By continuously tracking critical parameters and making automatic adjustments, these systems help maintain optimal conditions that minimize boiling loss, improving efficiency and extending the usable life of stored liquid nitrogen.
- Pressure regulation and vapor recovery techniques: Advanced pressure regulation and vapor recovery techniques are implemented to manage boiling loss in liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels. These include pressure relief systems, vapor recondensation mechanisms, and pressure balancing technologies. By effectively managing internal pressure and recapturing evaporated nitrogen, these techniques significantly reduce overall loss rates and improve the economic efficiency of liquid nitrogen storage systems.
02 Neck tube design and sealing mechanisms
The design of the neck tube and sealing mechanisms significantly impacts boiling loss in liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels. Optimized neck geometries with reduced cross-sectional areas minimize heat conduction pathways. Advanced sealing technologies prevent air infiltration and maintain vacuum integrity. Some designs incorporate multi-layer radiation shields in the neck region to reflect thermal radiation and further reduce evaporation rates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pressure regulation and venting systems
Effective pressure regulation and venting systems are crucial for controlling boiling loss in liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels. These systems maintain optimal internal pressure while safely releasing excess gas to prevent pressure buildup. Advanced designs incorporate pressure relief valves, burst discs, and regulated venting mechanisms that minimize nitrogen loss during normal operation while ensuring safety during pressure fluctuations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Structural materials and surface treatments
The selection of structural materials and surface treatments significantly affects the thermal performance of liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels. Low thermal conductivity materials for inner vessels and support structures minimize heat transfer pathways. Specialized surface treatments and coatings on internal surfaces reduce radiation heat transfer. Some designs incorporate composite materials with optimized thermal properties to further reduce boiling loss.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and automated control systems
Advanced monitoring and automated control systems help minimize boiling loss in liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels. These systems continuously track temperature, pressure, and liquid level parameters to optimize storage conditions. Intelligent control algorithms can adjust cooling systems and venting mechanisms based on real-time data. Some designs incorporate predictive maintenance features that identify potential issues before they lead to increased evaporation rates.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Cryogenics
The liquid nitrogen dewar vessel market is currently in a growth phase, driven by increasing applications in healthcare, electronics, and research sectors. The global market size is estimated to exceed $250 million, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% through 2028. Technologically, boiling loss reduction has seen significant advancements, with industry leaders Air Liquide and Air Products & Chemicals developing multi-layer vacuum insulation systems and advanced pressure management technologies. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Messer SE have focused on innovative material science solutions, while Kawasaki Heavy Industries has pioneered cryogenic fluid dynamics improvements. Emerging players like Gaztransport & Technigaz are introducing specialized membrane containment systems, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established industrial gas companies and specialized cryogenic equipment manufacturers.
Air Liquide SA
Technical Solution: Air Liquide has developed advanced multi-layer super insulation (MLI) technology for their Dewar vessels, utilizing up to 80 layers of aluminized Mylar with spacer materials to minimize radiative heat transfer. Their proprietary vacuum maintenance system maintains high vacuum levels (10^-6 torr) between the inner and outer vessels, significantly reducing conductive heat transfer. Air Liquide's vessels incorporate specialized neck tube designs made from low thermal conductivity composite materials that reduce heat leakage by up to 40% compared to conventional designs. Their automated liquid level monitoring system optimizes filling schedules and prevents unnecessary venting, while advanced pressure relief systems manage boil-off gas efficiently.
Strengths: Industry-leading vacuum technology and multi-layer insulation systems provide exceptional thermal efficiency. Their global service network ensures proper maintenance of vacuum integrity. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to basic Dewar vessels, and the sophisticated systems require specialized maintenance.
Air Products & Chemicals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Air Products has pioneered an integrated approach to Dewar vessel design focusing on thermal efficiency optimization. Their vessels feature proprietary "CryoGuard" technology, a multi-component insulation system that combines radiation shields, vacuum space optimization, and specialized getter materials that continuously absorb residual gases in the vacuum space, maintaining insulation performance over extended periods. The company has developed specialized neck plugs that reduce heat ingress by up to 50% during non-use periods. Their vessels incorporate phase-change material (PCM) buffers in strategic locations to absorb thermal energy before it reaches the liquid nitrogen, effectively extending hold times by 15-20%. Air Products also utilizes advanced pressure management systems that recapture boil-off gas for reuse or controlled venting.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach addressing multiple heat transfer pathways simultaneously, with particularly effective solutions for maintaining vacuum integrity over time. Weaknesses: System complexity requires more sophisticated manufacturing processes and may present challenges for field repairs in remote locations.
Key Innovations in Vacuum Insulation and Thermal Barrier Systems
Liquid nitrogen refilling device
PatentWO1991003679A1
Innovation
- A device that maintains a constant flow of liquid nitrogen into the cooling chamber by controlling the excess pressure in the Dewar vessel based on the detected liquid nitrogen level, using a heating element and a porous element to regulate evaporation and pressure, ensuring a steady state and minimizing mechanical and thermal interference.
Method for Nitrogen Rejection and or Helium Recovery in an Liquefaction Plant
PatentActiveUS20100162755A1
Innovation
- A method involving passing an initial LNG stream through heat exchangers and liquid expanders for dynamic decompression, followed by flash equilibrium separation in pre-fractionation vessels and fractionation columns to separate nitrogen and helium, utilizing vapor and liquid streams for cooling and further processing.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
Energy efficiency in liquid nitrogen storage systems represents a critical intersection of operational cost management and environmental responsibility. The boiling loss in Dewar vessels not only translates to direct economic waste but also contributes to unnecessary energy consumption across the supply chain. When considering that industrial gas production, including nitrogen liquefaction, accounts for approximately 2% of global electricity consumption, any improvement in storage efficiency creates significant sustainability benefits.
The energy footprint of liquid nitrogen begins with its production process, which requires approximately 0.5-0.7 kWh of electricity per kilogram of liquid nitrogen produced. Each liter of nitrogen lost through boil-off represents wasted energy that must be replaced through additional production, creating a cascading energy penalty throughout the system. Modern advancements in insulation technology can reduce evaporation rates from traditional 2-3% daily loss to below 0.5% in advanced systems, representing substantial energy savings.
From a lifecycle assessment perspective, reducing boiling loss addresses multiple sustainability dimensions. Primary energy savings occur at the point of use, while secondary benefits manifest in reduced transportation requirements, as fewer deliveries are needed to maintain operational levels. This translates to lower carbon emissions across the distribution network, particularly significant when considering that cryogenic transport vehicles are typically diesel-powered with substantial fuel consumption rates.
The circular economy potential of improved Dewar vessel design should not be overlooked. Advanced materials used in multi-layer insulation systems often incorporate recyclable components, while longer-lasting vacuum integrity reduces the frequency of vessel replacement. Furthermore, the recovery and reuse of boil-off gas through recondensation systems represents an emerging approach to closed-loop operation in laboratory and industrial settings.
Economic incentives for energy efficiency improvements align with environmental goals in this technology space. The payback period for investments in advanced insulation technologies typically ranges from 8-24 months depending on usage patterns and nitrogen costs, making efficiency upgrades financially attractive even without considering broader sustainability benefits. Additionally, as carbon pricing mechanisms expand globally, the economic case for reducing unnecessary energy consumption in cryogenic storage will strengthen further.
The energy footprint of liquid nitrogen begins with its production process, which requires approximately 0.5-0.7 kWh of electricity per kilogram of liquid nitrogen produced. Each liter of nitrogen lost through boil-off represents wasted energy that must be replaced through additional production, creating a cascading energy penalty throughout the system. Modern advancements in insulation technology can reduce evaporation rates from traditional 2-3% daily loss to below 0.5% in advanced systems, representing substantial energy savings.
From a lifecycle assessment perspective, reducing boiling loss addresses multiple sustainability dimensions. Primary energy savings occur at the point of use, while secondary benefits manifest in reduced transportation requirements, as fewer deliveries are needed to maintain operational levels. This translates to lower carbon emissions across the distribution network, particularly significant when considering that cryogenic transport vehicles are typically diesel-powered with substantial fuel consumption rates.
The circular economy potential of improved Dewar vessel design should not be overlooked. Advanced materials used in multi-layer insulation systems often incorporate recyclable components, while longer-lasting vacuum integrity reduces the frequency of vessel replacement. Furthermore, the recovery and reuse of boil-off gas through recondensation systems represents an emerging approach to closed-loop operation in laboratory and industrial settings.
Economic incentives for energy efficiency improvements align with environmental goals in this technology space. The payback period for investments in advanced insulation technologies typically ranges from 8-24 months depending on usage patterns and nitrogen costs, making efficiency upgrades financially attractive even without considering broader sustainability benefits. Additionally, as carbon pricing mechanisms expand globally, the economic case for reducing unnecessary energy consumption in cryogenic storage will strengthen further.
Safety Standards and Compliance Requirements
Compliance with safety standards is paramount when designing and operating liquid nitrogen Dewar vessels to minimize boiling loss while ensuring user protection. The primary regulatory frameworks governing these vessels include ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section VIII, which establishes design requirements for pressure vessels, and ISO 21009-1:2008, which specifically addresses vacuum-insulated vessels for cryogenic liquids.
These standards mandate specific design features that impact boiling loss management, including pressure relief mechanisms, vacuum integrity requirements, and material specifications. For instance, all Dewar vessels must incorporate pressure relief valves calibrated to release at pressures below the vessel's maximum allowable working pressure, preventing catastrophic failures while managing evaporation rates.
Material selection requirements further influence boiling loss performance, as standards specify materials that maintain structural integrity at cryogenic temperatures while minimizing heat transfer. Commonly approved materials include austenitic stainless steels (304L, 316L) and certain aluminum alloys, which must undergo rigorous testing to verify their suitability for cryogenic applications.
Operational safety requirements also impact boiling loss management strategies. Standards mandate minimum ventilation requirements for indoor storage areas, limiting the implementation of certain insulation approaches that might otherwise reduce heat ingress. Additionally, regulations often specify maximum allowable external surface temperatures to prevent cold burns, which can constrain certain super-insulation techniques.
Labeling and documentation requirements ensure users understand proper handling procedures that minimize unnecessary heat introduction. These include clear markings for fill levels, handling instructions, and hazard warnings that promote practices reducing unnecessary boiling losses during operation and maintenance.
Recent regulatory developments have introduced more stringent requirements for energy efficiency in cryogenic storage systems, particularly in the European Union and parts of Asia. These emerging standards establish maximum allowable evaporation rates for different vessel sizes and applications, directly influencing design approaches to boiling loss reduction.
Compliance testing protocols require manufacturers to demonstrate boiling loss performance under standardized conditions, typically measuring normal evaporation rate (NER) over specified time periods. These tests must be conducted by certified laboratories following procedures outlined in standards such as EN 1251 or equivalent national regulations.
For transportation of liquid nitrogen in Dewar vessels, additional regulations apply, including DOT/ADR requirements that may impact vessel design and insulation approaches. These regulations often impose additional constraints on pressure management systems that must be considered when implementing boiling loss reduction strategies.
These standards mandate specific design features that impact boiling loss management, including pressure relief mechanisms, vacuum integrity requirements, and material specifications. For instance, all Dewar vessels must incorporate pressure relief valves calibrated to release at pressures below the vessel's maximum allowable working pressure, preventing catastrophic failures while managing evaporation rates.
Material selection requirements further influence boiling loss performance, as standards specify materials that maintain structural integrity at cryogenic temperatures while minimizing heat transfer. Commonly approved materials include austenitic stainless steels (304L, 316L) and certain aluminum alloys, which must undergo rigorous testing to verify their suitability for cryogenic applications.
Operational safety requirements also impact boiling loss management strategies. Standards mandate minimum ventilation requirements for indoor storage areas, limiting the implementation of certain insulation approaches that might otherwise reduce heat ingress. Additionally, regulations often specify maximum allowable external surface temperatures to prevent cold burns, which can constrain certain super-insulation techniques.
Labeling and documentation requirements ensure users understand proper handling procedures that minimize unnecessary heat introduction. These include clear markings for fill levels, handling instructions, and hazard warnings that promote practices reducing unnecessary boiling losses during operation and maintenance.
Recent regulatory developments have introduced more stringent requirements for energy efficiency in cryogenic storage systems, particularly in the European Union and parts of Asia. These emerging standards establish maximum allowable evaporation rates for different vessel sizes and applications, directly influencing design approaches to boiling loss reduction.
Compliance testing protocols require manufacturers to demonstrate boiling loss performance under standardized conditions, typically measuring normal evaporation rate (NER) over specified time periods. These tests must be conducted by certified laboratories following procedures outlined in standards such as EN 1251 or equivalent national regulations.
For transportation of liquid nitrogen in Dewar vessels, additional regulations apply, including DOT/ADR requirements that may impact vessel design and insulation approaches. These regulations often impose additional constraints on pressure management systems that must be considered when implementing boiling loss reduction strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!