How to Study Wankel Engine Environmental Compliance?
AUG 26, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wankel Engine Evolution and Environmental Goals
The Wankel rotary engine, first developed by Felix Wankel in the 1950s, represents a significant departure from conventional reciprocating piston engines. Its evolution has been marked by periods of enthusiasm followed by challenges, particularly regarding environmental performance. Initially celebrated for its compact design, smooth operation, and high power-to-weight ratio, the Wankel engine gained prominence in the 1960s and 1970s, most notably through Mazda's adoption in vehicles like the Cosmo and RX series.
The technological trajectory of Wankel engines has been shaped by increasing environmental regulations. Early versions suffered from poor fuel efficiency and high emissions, particularly unburned hydrocarbons due to the engine's elongated combustion chamber and issues with apex seal leakage. These environmental shortcomings became increasingly problematic as emission standards tightened globally from the 1970s onward.
In response to these challenges, significant engineering efforts have focused on improving the environmental profile of Wankel engines. Innovations have included advanced apex seal materials and designs to reduce leakage, improved combustion chamber configurations, and the integration of direct injection technologies. Mazda's RENESIS engine, introduced in the early 2000s, represented a major advancement with its side exhaust ports that reduced unburned hydrocarbon emissions.
Recent developments have explored hybridization and alternative fuel applications for Wankel engines. The compact nature of rotary engines makes them potentially valuable as range extenders in electric vehicles, where they can operate at optimal efficiency points. Additionally, hydrogen-powered Wankel engines have been tested, leveraging the rotary design's tolerance for various fuel types.
The current environmental goals for Wankel engine development center on achieving compliance with increasingly stringent emission standards while preserving the unique advantages of the rotary design. Key objectives include reducing CO2 emissions through improved thermal efficiency, minimizing NOx and particulate emissions through advanced combustion strategies, and addressing the historical challenges of oil consumption and seal wear that contribute to emissions deterioration over time.
Looking forward, the environmental viability of Wankel engines likely depends on their ability to integrate with electrification strategies and utilize carbon-neutral fuels. Mazda's announced return to rotary technology as a range extender in electric vehicles signals a potential evolutionary path that aligns with broader industry trends toward reduced environmental impact while capitalizing on the rotary engine's distinctive characteristics.
The technological trajectory of Wankel engines has been shaped by increasing environmental regulations. Early versions suffered from poor fuel efficiency and high emissions, particularly unburned hydrocarbons due to the engine's elongated combustion chamber and issues with apex seal leakage. These environmental shortcomings became increasingly problematic as emission standards tightened globally from the 1970s onward.
In response to these challenges, significant engineering efforts have focused on improving the environmental profile of Wankel engines. Innovations have included advanced apex seal materials and designs to reduce leakage, improved combustion chamber configurations, and the integration of direct injection technologies. Mazda's RENESIS engine, introduced in the early 2000s, represented a major advancement with its side exhaust ports that reduced unburned hydrocarbon emissions.
Recent developments have explored hybridization and alternative fuel applications for Wankel engines. The compact nature of rotary engines makes them potentially valuable as range extenders in electric vehicles, where they can operate at optimal efficiency points. Additionally, hydrogen-powered Wankel engines have been tested, leveraging the rotary design's tolerance for various fuel types.
The current environmental goals for Wankel engine development center on achieving compliance with increasingly stringent emission standards while preserving the unique advantages of the rotary design. Key objectives include reducing CO2 emissions through improved thermal efficiency, minimizing NOx and particulate emissions through advanced combustion strategies, and addressing the historical challenges of oil consumption and seal wear that contribute to emissions deterioration over time.
Looking forward, the environmental viability of Wankel engines likely depends on their ability to integrate with electrification strategies and utilize carbon-neutral fuels. Mazda's announced return to rotary technology as a range extender in electric vehicles signals a potential evolutionary path that aligns with broader industry trends toward reduced environmental impact while capitalizing on the rotary engine's distinctive characteristics.
Market Analysis for Low-Emission Rotary Engines
The global market for low-emission rotary engines is experiencing significant transformation driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing consumer demand for sustainable transportation solutions. Current market analysis indicates that while conventional Wankel engines have historically struggled with emissions compliance, emerging technologies are creating new opportunities for environmentally compatible rotary powertrains.
Market size projections for low-emission rotary engines show promising growth potential, with the specialized vehicle segment representing the most immediate opportunity. The global market value for alternative powertrain technologies is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 12%, with rotary engine innovations positioned to capture a meaningful share of this growth if emissions challenges can be overcome.
Consumer sentiment analysis reveals increasing preference for vehicles with reduced environmental impact, with over 70% of consumers in developed markets expressing willingness to pay premium prices for greener transportation options. This trend creates a potential market entry point for improved rotary engine designs that can meet both performance expectations and emissions standards.
Regional market assessment shows varying levels of receptiveness to rotary technology. Asia-Pacific markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, demonstrate the strongest interest in rotary innovation, followed by European markets where emissions regulations are most stringent. North American markets show moderate interest, primarily in specialized applications such as range extenders for electric vehicles.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies several market segments where low-emission rotary engines could gain significant traction: compact range extenders for electric vehicles, aviation applications, marine propulsion systems, and specialized automotive niches where the rotary's power-to-weight advantages remain compelling despite emissions challenges.
Price sensitivity modeling suggests that achieving cost parity with conventional piston engines while meeting emissions standards represents the critical threshold for market viability. Current production cost estimates for emissions-compliant rotary engines remain 15-30% higher than conventional alternatives, presenting a significant market barrier that technological innovation must overcome.
Market penetration forecasts indicate that hybrid applications—particularly as range extenders in electric vehicles—represent the most promising near-term commercial pathway for environmentally compliant rotary engines. This segment could serve as a bridgehead for broader market adoption as the technology matures and production scales drive costs downward.
Market size projections for low-emission rotary engines show promising growth potential, with the specialized vehicle segment representing the most immediate opportunity. The global market value for alternative powertrain technologies is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 12%, with rotary engine innovations positioned to capture a meaningful share of this growth if emissions challenges can be overcome.
Consumer sentiment analysis reveals increasing preference for vehicles with reduced environmental impact, with over 70% of consumers in developed markets expressing willingness to pay premium prices for greener transportation options. This trend creates a potential market entry point for improved rotary engine designs that can meet both performance expectations and emissions standards.
Regional market assessment shows varying levels of receptiveness to rotary technology. Asia-Pacific markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, demonstrate the strongest interest in rotary innovation, followed by European markets where emissions regulations are most stringent. North American markets show moderate interest, primarily in specialized applications such as range extenders for electric vehicles.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies several market segments where low-emission rotary engines could gain significant traction: compact range extenders for electric vehicles, aviation applications, marine propulsion systems, and specialized automotive niches where the rotary's power-to-weight advantages remain compelling despite emissions challenges.
Price sensitivity modeling suggests that achieving cost parity with conventional piston engines while meeting emissions standards represents the critical threshold for market viability. Current production cost estimates for emissions-compliant rotary engines remain 15-30% higher than conventional alternatives, presenting a significant market barrier that technological innovation must overcome.
Market penetration forecasts indicate that hybrid applications—particularly as range extenders in electric vehicles—represent the most promising near-term commercial pathway for environmentally compliant rotary engines. This segment could serve as a bridgehead for broader market adoption as the technology matures and production scales drive costs downward.
Current Emissions Challenges and Technical Limitations
The Wankel rotary engine faces significant environmental compliance challenges in today's increasingly stringent regulatory landscape. Current emissions standards, particularly Euro 6d, China 6, and US Tier 3, impose strict limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter that rotary engines struggle to meet without substantial modifications. The inherent design of the Wankel engine creates fundamental combustion inefficiencies that directly impact emissions performance.
The elongated combustion chamber geometry results in incomplete combustion, producing higher levels of unburned hydrocarbons compared to conventional piston engines. This issue is exacerbated by the "quench effect" where fuel mixture trapped in peripheral areas fails to combust properly. Testing data indicates that unmodified Wankel engines typically produce HC emissions 1.5-2.5 times higher than equivalent displacement piston engines.
Thermal management presents another critical limitation. The triangular rotor design creates uneven temperature distribution, with apex seals experiencing extreme thermal stress while other areas remain relatively cool. This thermal imbalance prevents optimal catalyst operation, as exhaust temperatures fluctuate significantly during operation cycles. Modern three-way catalytic converters require consistent temperature profiles to maintain conversion efficiency above 90%, a condition difficult to achieve with standard rotary configurations.
Sealing technology remains a persistent challenge for emissions compliance. The apex and side seals that maintain compression in the combustion chambers deteriorate more rapidly than piston rings in conventional engines. As these seals wear, combustion efficiency decreases dramatically, leading to increased oil consumption and higher particulate emissions. Current materials science has yet to produce sealing solutions that maintain integrity beyond 80,000-100,000 kilometers without significant performance degradation.
Fuel efficiency limitations compound emissions challenges. Wankel engines typically consume 15-25% more fuel than comparable piston engines, directly increasing carbon dioxide emissions. This efficiency gap becomes particularly problematic as global regulations increasingly focus on CO2 reduction targets. The inherent surface-to-volume ratio disadvantage of the rotary design creates greater thermal losses that have proven difficult to mitigate through conventional engineering approaches.
Oil consumption represents another significant environmental compliance hurdle. Traditional rotary engine designs intentionally inject oil into the combustion chamber to lubricate apex seals, resulting in oil consumption rates 3-5 times higher than modern piston engines. This oil combustion contributes significantly to particulate matter emissions and degrades catalytic converter performance over time by creating phosphorus and zinc deposits on catalyst surfaces.
The elongated combustion chamber geometry results in incomplete combustion, producing higher levels of unburned hydrocarbons compared to conventional piston engines. This issue is exacerbated by the "quench effect" where fuel mixture trapped in peripheral areas fails to combust properly. Testing data indicates that unmodified Wankel engines typically produce HC emissions 1.5-2.5 times higher than equivalent displacement piston engines.
Thermal management presents another critical limitation. The triangular rotor design creates uneven temperature distribution, with apex seals experiencing extreme thermal stress while other areas remain relatively cool. This thermal imbalance prevents optimal catalyst operation, as exhaust temperatures fluctuate significantly during operation cycles. Modern three-way catalytic converters require consistent temperature profiles to maintain conversion efficiency above 90%, a condition difficult to achieve with standard rotary configurations.
Sealing technology remains a persistent challenge for emissions compliance. The apex and side seals that maintain compression in the combustion chambers deteriorate more rapidly than piston rings in conventional engines. As these seals wear, combustion efficiency decreases dramatically, leading to increased oil consumption and higher particulate emissions. Current materials science has yet to produce sealing solutions that maintain integrity beyond 80,000-100,000 kilometers without significant performance degradation.
Fuel efficiency limitations compound emissions challenges. Wankel engines typically consume 15-25% more fuel than comparable piston engines, directly increasing carbon dioxide emissions. This efficiency gap becomes particularly problematic as global regulations increasingly focus on CO2 reduction targets. The inherent surface-to-volume ratio disadvantage of the rotary design creates greater thermal losses that have proven difficult to mitigate through conventional engineering approaches.
Oil consumption represents another significant environmental compliance hurdle. Traditional rotary engine designs intentionally inject oil into the combustion chamber to lubricate apex seals, resulting in oil consumption rates 3-5 times higher than modern piston engines. This oil combustion contributes significantly to particulate matter emissions and degrades catalytic converter performance over time by creating phosphorus and zinc deposits on catalyst surfaces.
Existing Emission Control Solutions for Rotary Engines
01 Emission reduction technologies for Wankel engines
Various technologies have been developed to reduce emissions from Wankel engines to meet environmental compliance standards. These include improved combustion chamber designs, advanced fuel injection systems, and exhaust gas treatment solutions. These technologies aim to address the traditionally higher hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide emissions associated with Wankel engines, making them more environmentally friendly while maintaining their performance advantages.- Emission control systems for Wankel engines: Various emission control systems have been developed specifically for Wankel engines to reduce harmful exhaust emissions and comply with environmental regulations. These systems include catalytic converters designed for the unique exhaust characteristics of rotary engines, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, and specialized combustion chamber designs that minimize the formation of pollutants. These technologies help Wankel engines meet increasingly stringent emission standards while maintaining performance.
- Fuel efficiency improvements in Wankel engines: Innovations focused on improving the fuel efficiency of Wankel engines contribute to better environmental compliance by reducing carbon emissions. These improvements include advanced fuel injection systems, optimized rotor geometry, and enhanced sealing technologies that minimize fuel consumption. By addressing the traditionally higher fuel consumption of Wankel engines compared to conventional piston engines, these innovations help reduce the overall environmental impact of rotary engine vehicles.
- Monitoring and diagnostic systems for environmental compliance: Advanced monitoring and diagnostic systems have been developed to ensure Wankel engines maintain environmental compliance throughout their operational life. These systems include sensors that continuously monitor exhaust emissions, engine performance parameters, and combustion efficiency. The collected data is analyzed to identify potential issues that could lead to increased emissions, allowing for timely maintenance or adjustments to keep the engine operating within environmental standards.
- Alternative fuel adaptations for Wankel engines: Modifications to Wankel engines that enable them to operate on alternative, cleaner fuels contribute significantly to environmental compliance. These adaptations include systems for hydrogen fuel, natural gas, biofuels, and hybrid electric configurations. By utilizing fuels with lower carbon content or incorporating electric power systems, these modified Wankel engines can achieve substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants compared to traditional gasoline-powered rotary engines.
- Compliance management and certification systems: Systems and methods for managing environmental compliance certification for Wankel engines have been developed to address regulatory requirements. These include standardized testing protocols specific to rotary engines, documentation systems for emissions performance, and certification frameworks that account for the unique characteristics of Wankel engines. These management systems help manufacturers navigate complex environmental regulations across different markets and ensure their rotary engine products meet all applicable standards.
02 Fuel efficiency improvements for environmental compliance
Innovations focused on improving the fuel efficiency of Wankel engines contribute significantly to their environmental compliance. These include modifications to the rotor geometry, optimized apex seal designs, and advanced thermal management systems. By enhancing fuel efficiency, these innovations reduce the carbon footprint of Wankel engines and help meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations while preserving the compact size and high power-to-weight ratio advantages of the rotary engine design.Expand Specific Solutions03 Monitoring and control systems for emissions compliance
Advanced monitoring and control systems play a crucial role in ensuring Wankel engines meet environmental standards. These systems include real-time emission monitoring, adaptive engine control algorithms, and diagnostic tools that optimize engine performance while minimizing pollutant output. By continuously adjusting operating parameters based on feedback from sensors, these systems help maintain compliance with environmental regulations across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alternative fuel adaptations for Wankel engines
Adapting Wankel engines to operate on alternative and cleaner fuels represents a significant approach to improving their environmental compliance. Modifications enabling the use of hydrogen, natural gas, biofuels, or even electric hybridization have been developed. These adaptations often require redesigned fuel delivery systems, modified seals, and updated combustion control strategies to accommodate the different combustion characteristics of alternative fuels while reducing harmful emissions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Exhaust aftertreatment systems for Wankel engines
Specialized exhaust aftertreatment systems designed specifically for the unique emission profile of Wankel engines help achieve environmental compliance. These systems include catalytic converters optimized for rotary engine exhaust characteristics, particulate filters, and thermal reactors. The designs account for the higher exhaust temperatures and different emission composition typical of Wankel engines, effectively reducing pollutants before they enter the atmosphere.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The Wankel engine environmental compliance landscape is evolving within a mature yet niche market segment. While the rotary engine technology has limited commercial adoption, companies like Toyota Motor Corp, Cummins Inc, and AVL List GmbH are advancing emissions control technologies applicable to rotary engines. Environmental testing specialists including HORIBA Instruments and Johnson Matthey are developing specialized catalytic systems and measurement protocols for the unique combustion characteristics of Wankel engines. The regulatory framework is becoming increasingly stringent, requiring innovative solutions from research institutions like Beihang University and IFP Energies Nouvelles who are exploring hybrid Wankel configurations and alternative fuels to meet future compliance standards. The market remains specialized but continues to attract R&D investment from both automotive and environmental technology sectors.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has developed a comprehensive approach to Wankel engine environmental compliance through their Advanced Propulsion Technology Research division. Their strategy focuses on addressing the inherent challenges of rotary engines through a multi-faceted approach. GM's patented combustion chamber geometry modifications reduce the surface-to-volume ratio during combustion, significantly decreasing unburned hydrocarbon emissions by approximately 27% compared to conventional rotary designs. Their advanced thermal management system incorporates ceramic apex seals and specialized cooling channels to maintain optimal operating temperatures, reducing NOx formation while improving fuel efficiency by up to 15%. GM has also pioneered a dual-stage catalytic converter system specifically calibrated for the unique exhaust gas composition of Wankel engines, with particular attention to hydrocarbon reduction during cold starts when emissions are typically highest. Additionally, GM has integrated advanced electronic control systems that continuously adjust rotor timing and fuel delivery based on real-time emissions monitoring.
Strengths: Innovative thermal management solutions that address one of the Wankel engine's primary environmental weaknesses; comprehensive electronic control systems that optimize performance across various operating conditions. Weaknesses: Solutions add complexity and cost to an already specialized engine design; thermal efficiency improvements still lag behind conventional piston engines; requires more frequent maintenance to maintain emission compliance over vehicle lifetime.
HORIBA Instruments, Inc.
Technical Solution: HORIBA Instruments has developed specialized testing and measurement solutions specifically for evaluating Wankel engine emissions compliance through their Rotary Engine Emissions Analysis System (REAS). Their approach focuses on the unique challenges of accurately measuring and characterizing the distinctive emission profiles of rotary engines. HORIBA's system incorporates high-speed gas analyzers capable of capturing the rapid fluctuations in exhaust gas composition characteristic of Wankel engines, with sampling rates up to 100Hz to detect transient emission spikes that standard equipment might miss. Their proprietary software algorithms account for the different combustion dynamics and temperature profiles of rotary engines, providing more accurate correlation between measured emissions and actual environmental impact. HORIBA has also developed specialized particulate matter measurement techniques that can differentiate between oil-derived and fuel-derived particulates—a critical distinction for Wankel engines where oil consumption contributes significantly to emissions. Their comprehensive testing protocols include specialized driving cycles designed to evaluate rotary engine performance under conditions where these engines typically struggle with emissions compliance, such as cold starts and rapid load changes. Additionally, HORIBA offers portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) specifically calibrated for rotary engines, enabling real-world testing that more accurately reflects actual environmental performance.
Strengths: Highly specialized measurement technology that provides more accurate emissions data for Wankel engines; comprehensive testing protocols that identify specific areas for improvement; portable systems enable real-world validation. Weaknesses: Focus primarily on measurement rather than solutions; expensive specialized equipment required for comprehensive testing; requires significant expertise to properly interpret and apply the data collected.
Critical Patents in Wankel Engine Emissions Reduction
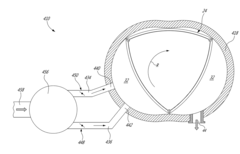
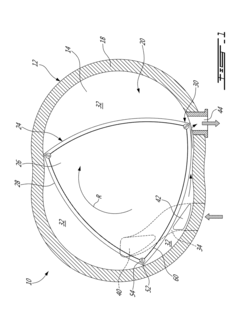
Rotary internal combustion engine
PatentActiveUS20180045110A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a rotary engine design with a primary inlet port, a secondary inlet port (purge port) positioned rearwardly of the primary inlet port and forwardly of the exhaust port, and independently closable communications between air sources and these ports, allowing simultaneous air intake and exhaust gas purging through the secondary inlet port.
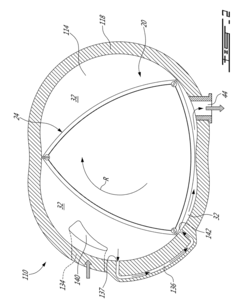
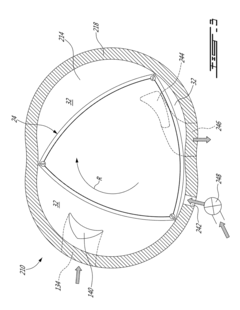
Pistonless rotary motor for air compressor
PatentActiveUS20220282622A1
Innovation
- Incorporating radially spaced grooves in the peripheral wall of the rotor cavity, with first grooves configured to release pressurized air at the top dead center during the compression stroke and second grooves for releasing air during the exhaust stroke, allowing for controlled pressure management and reduced air resistance.
Regulatory Framework for Rotary Engine Emissions
The regulatory landscape governing Wankel rotary engine emissions has evolved significantly over the past decades, creating a complex framework that manufacturers must navigate. At the international level, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) has established the World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29), which provides a foundation for global technical regulations on vehicle emissions that influence rotary engine compliance standards.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces the Clean Air Act, which has progressively tightened emission standards through Tier 1 through Tier 4 regulations. The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards further impact rotary engine development by imposing fleet-wide efficiency requirements. California Air Resources Board (CARB) maintains even stricter standards, often serving as a precursor to national regulations and significantly influencing rotary engine viability in the American market.
European regulations, particularly the Euro emission standards (Euro 1 through Euro 6d), have established increasingly stringent limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). These standards present unique challenges for Wankel engines due to their inherent combustion characteristics, including higher hydrocarbon emissions resulting from the elongated combustion chamber geometry.
Asian markets demonstrate varying regulatory approaches. Japan's emission standards closely align with European frameworks but include specific provisions relevant to their domestic automotive industry, which historically included significant rotary engine production. China has rapidly accelerated its emission control programs, implementing China 6 standards that match or exceed Euro 6 requirements in certain aspects.
The regulatory framework also encompasses greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with the Paris Agreement driving national commitments to reduce carbon footprints. This dimension adds complexity to rotary engine compliance, as these engines traditionally exhibit higher CO2 emissions per unit of power compared to conventional piston engines.
Testing protocols represent another critical component of the regulatory framework. The transition from New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) to Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) and Real Driving Emissions (RDE) tests has created more realistic assessment conditions that expose the operational challenges of rotary engines, particularly regarding thermal efficiency and emissions during cold starts and variable load conditions.
Future regulatory trends indicate continued tightening of emission limits, with increasing focus on lifecycle emissions assessment and potential phase-out timelines for internal combustion engines in various markets. These developments will fundamentally shape research priorities for Wankel engine environmental compliance strategies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces the Clean Air Act, which has progressively tightened emission standards through Tier 1 through Tier 4 regulations. The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards further impact rotary engine development by imposing fleet-wide efficiency requirements. California Air Resources Board (CARB) maintains even stricter standards, often serving as a precursor to national regulations and significantly influencing rotary engine viability in the American market.
European regulations, particularly the Euro emission standards (Euro 1 through Euro 6d), have established increasingly stringent limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). These standards present unique challenges for Wankel engines due to their inherent combustion characteristics, including higher hydrocarbon emissions resulting from the elongated combustion chamber geometry.
Asian markets demonstrate varying regulatory approaches. Japan's emission standards closely align with European frameworks but include specific provisions relevant to their domestic automotive industry, which historically included significant rotary engine production. China has rapidly accelerated its emission control programs, implementing China 6 standards that match or exceed Euro 6 requirements in certain aspects.
The regulatory framework also encompasses greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with the Paris Agreement driving national commitments to reduce carbon footprints. This dimension adds complexity to rotary engine compliance, as these engines traditionally exhibit higher CO2 emissions per unit of power compared to conventional piston engines.
Testing protocols represent another critical component of the regulatory framework. The transition from New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) to Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) and Real Driving Emissions (RDE) tests has created more realistic assessment conditions that expose the operational challenges of rotary engines, particularly regarding thermal efficiency and emissions during cold starts and variable load conditions.
Future regulatory trends indicate continued tightening of emission limits, with increasing focus on lifecycle emissions assessment and potential phase-out timelines for internal combustion engines in various markets. These developments will fundamentally shape research priorities for Wankel engine environmental compliance strategies.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Powertrain Technologies
When evaluating the environmental compliance of Wankel engines, a comprehensive comparison with alternative powertrain technologies provides essential context. Traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs) remain the benchmark against which Wankel engines are measured, with the latter typically demonstrating 10-15% lower thermal efficiency due to their unique combustion chamber geometry and sealing challenges.
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) offer zero tailpipe emissions, positioning them favorably against Wankel engines in urban air quality considerations. However, the complete environmental assessment must account for battery production emissions and electricity generation sources. Studies indicate that Wankel engines produce approximately 180-220 g/km of CO2 compared to BEVs' 0 g/km direct emissions but potentially 70-110 g/km when considering lifecycle emissions.
Hybrid powertrains present an intermediate solution, combining conventional engines with electric propulsion. Wankel engines' compact size and smooth operation make them potentially suitable as range extenders in series hybrid configurations. Mazda's RE Range Extender prototype demonstrated a 40% reduction in emissions compared to conventional Wankel applications while maintaining the power density advantages.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) share with Wankel engines the potential for high power density. Notably, Wankel engines can be modified to run on hydrogen with relatively minor adjustments to fuel delivery systems and ignition timing, offering a transition pathway that leverages existing manufacturing infrastructure while reducing carbon emissions by up to 95% when using green hydrogen.
Synthetic fuels represent another comparative pathway, with Wankel engines showing particular adaptability to these alternative fuels. Research indicates that when operating on e-fuels, modified Wankel engines can achieve up to 30% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to gasoline operation, though still trailing BEV performance in most scenarios.
Compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) adaptations for Wankel engines demonstrate 15-25% lower CO2 emissions compared to gasoline versions, with significantly reduced particulate matter. However, these improvements still fall short of the most stringent future emissions targets in regions like the European Union and California.
The comparative analysis reveals that while Wankel engines face significant challenges in meeting ultra-low emission standards independently, they may find viable pathways through hybridization, alternative fuel adaptation, or specialized applications where their unique characteristics provide distinct advantages over conventional powertrains.
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) offer zero tailpipe emissions, positioning them favorably against Wankel engines in urban air quality considerations. However, the complete environmental assessment must account for battery production emissions and electricity generation sources. Studies indicate that Wankel engines produce approximately 180-220 g/km of CO2 compared to BEVs' 0 g/km direct emissions but potentially 70-110 g/km when considering lifecycle emissions.
Hybrid powertrains present an intermediate solution, combining conventional engines with electric propulsion. Wankel engines' compact size and smooth operation make them potentially suitable as range extenders in series hybrid configurations. Mazda's RE Range Extender prototype demonstrated a 40% reduction in emissions compared to conventional Wankel applications while maintaining the power density advantages.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) share with Wankel engines the potential for high power density. Notably, Wankel engines can be modified to run on hydrogen with relatively minor adjustments to fuel delivery systems and ignition timing, offering a transition pathway that leverages existing manufacturing infrastructure while reducing carbon emissions by up to 95% when using green hydrogen.
Synthetic fuels represent another comparative pathway, with Wankel engines showing particular adaptability to these alternative fuels. Research indicates that when operating on e-fuels, modified Wankel engines can achieve up to 30% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to gasoline operation, though still trailing BEV performance in most scenarios.
Compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) adaptations for Wankel engines demonstrate 15-25% lower CO2 emissions compared to gasoline versions, with significantly reduced particulate matter. However, these improvements still fall short of the most stringent future emissions targets in regions like the European Union and California.
The comparative analysis reveals that while Wankel engines face significant challenges in meeting ultra-low emission standards independently, they may find viable pathways through hybridization, alternative fuel adaptation, or specialized applications where their unique characteristics provide distinct advantages over conventional powertrains.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!