Key Markets for Ethyl Acetate: Opportunities and Challenges
JUN 27, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, also known as ethyl ethanoate, is a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5. This colorless liquid is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties and characteristics. As an ester formed by the reaction between ethanol and acetic acid, ethyl acetate possesses a fruity odor and is commonly recognized for its sweet smell, often associated with nail polish remover or certain types of glue.
The compound's low boiling point of 77.1°C (170.8°F) and high volatility make it an excellent solvent for a wide range of applications. Its ability to dissolve many organic compounds, coupled with its relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents, has led to its widespread adoption in industrial processes and consumer products.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. Its reactivity and stability under certain conditions make it an ideal starting material for synthesizing more complex molecules. Additionally, its use as an extraction solvent in the production of pharmaceuticals and food additives highlights its importance in these sectors.
The paint and coatings industry heavily relies on ethyl acetate as a solvent and diluent. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to form homogeneous mixtures with many resins and pigments make it an essential component in formulating paints, varnishes, and lacquers. This property also extends to its use in the printing industry, where it is employed in flexographic and rotogravure printing inks.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl acetate plays a dual role. Naturally occurring in many fruits, it is used as a flavoring agent to enhance or impart fruity notes in various food products. Moreover, its solvent properties make it valuable in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, offering a less toxic alternative to traditional methods.
The electronics industry utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of circuit boards and semiconductor devices. Its ability to clean and remove flux residues without damaging sensitive components has made it a preferred choice in electronics manufacturing processes.
As environmental concerns grow, the biodegradability and lower toxicity of ethyl acetate compared to some alternative solvents have increased its appeal across industries. This has led to its adoption in eco-friendly products and processes, aligning with the global shift towards more sustainable industrial practices.
The compound's low boiling point of 77.1°C (170.8°F) and high volatility make it an excellent solvent for a wide range of applications. Its ability to dissolve many organic compounds, coupled with its relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents, has led to its widespread adoption in industrial processes and consumer products.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. Its reactivity and stability under certain conditions make it an ideal starting material for synthesizing more complex molecules. Additionally, its use as an extraction solvent in the production of pharmaceuticals and food additives highlights its importance in these sectors.
The paint and coatings industry heavily relies on ethyl acetate as a solvent and diluent. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to form homogeneous mixtures with many resins and pigments make it an essential component in formulating paints, varnishes, and lacquers. This property also extends to its use in the printing industry, where it is employed in flexographic and rotogravure printing inks.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl acetate plays a dual role. Naturally occurring in many fruits, it is used as a flavoring agent to enhance or impart fruity notes in various food products. Moreover, its solvent properties make it valuable in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, offering a less toxic alternative to traditional methods.
The electronics industry utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of circuit boards and semiconductor devices. Its ability to clean and remove flux residues without damaging sensitive components has made it a preferred choice in electronics manufacturing processes.
As environmental concerns grow, the biodegradability and lower toxicity of ethyl acetate compared to some alternative solvents have increased its appeal across industries. This has led to its adoption in eco-friendly products and processes, aligning with the global shift towards more sustainable industrial practices.
Market Demand Analysis
The global ethyl acetate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The demand for ethyl acetate is primarily fueled by its extensive use as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives, which collectively account for a significant portion of the market share. The construction and automotive sectors, in particular, have been key contributors to the increasing demand for ethyl acetate-based products.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate finds application as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. The growing consumer preference for flavored food products and the rising popularity of decaffeinated beverages have positively impacted the market demand. Additionally, the pharmaceutical sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of various drugs and as a reagent in laboratory applications, further bolstering market growth.
The packaging industry represents another substantial market for ethyl acetate, particularly in flexible packaging applications. The shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions has led to increased adoption of ethyl acetate-based adhesives and coatings, as they offer improved recyclability compared to some alternatives.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, with China and India leading the demand. The rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sector, and increasing disposable income in these countries have been driving factors. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets showing steady demand primarily from established end-use industries.
The market is also witnessing a trend towards bio-based ethyl acetate, driven by growing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for market players, as they navigate the transition to more sustainable production methods while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Despite the overall positive outlook, the ethyl acetate market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and competition from alternative solvents. The fluctuating prices of ethanol and acetic acid, the primary raw materials for ethyl acetate production, can impact profit margins and market stability. Moreover, the increasing focus on reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in various industries may pose challenges to ethyl acetate usage in certain applications.
In conclusion, the ethyl acetate market demonstrates a complex interplay of growth drivers and potential obstacles. While traditional applications continue to support market expansion, emerging trends in sustainability and regulatory pressures are shaping the future landscape of the industry. Market players must adapt to these evolving dynamics to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this versatile chemical compound.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate finds application as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. The growing consumer preference for flavored food products and the rising popularity of decaffeinated beverages have positively impacted the market demand. Additionally, the pharmaceutical sector utilizes ethyl acetate in the production of various drugs and as a reagent in laboratory applications, further bolstering market growth.
The packaging industry represents another substantial market for ethyl acetate, particularly in flexible packaging applications. The shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions has led to increased adoption of ethyl acetate-based adhesives and coatings, as they offer improved recyclability compared to some alternatives.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of ethyl acetate, with China and India leading the demand. The rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sector, and increasing disposable income in these countries have been driving factors. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets showing steady demand primarily from established end-use industries.
The market is also witnessing a trend towards bio-based ethyl acetate, driven by growing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for market players, as they navigate the transition to more sustainable production methods while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Despite the overall positive outlook, the ethyl acetate market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and competition from alternative solvents. The fluctuating prices of ethanol and acetic acid, the primary raw materials for ethyl acetate production, can impact profit margins and market stability. Moreover, the increasing focus on reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in various industries may pose challenges to ethyl acetate usage in certain applications.
In conclusion, the ethyl acetate market demonstrates a complex interplay of growth drivers and potential obstacles. While traditional applications continue to support market expansion, emerging trends in sustainability and regulatory pressures are shaping the future landscape of the industry. Market players must adapt to these evolving dynamics to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this versatile chemical compound.
Industry Challenges
The ethyl acetate industry faces several significant challenges that impact its growth and sustainability. One of the primary concerns is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. These fluctuations can significantly affect production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent pricing strategies.
Environmental regulations pose another major challenge for the industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt to more stringent emission control standards and waste management practices. This often requires substantial investments in cleaner production technologies and processes, which can be financially burdensome for smaller manufacturers.
The industry also grapples with intense competition from alternative solvents and technologies. As companies seek more environmentally friendly and cost-effective solutions, ethyl acetate faces competition from bio-based solvents and water-based alternatives in various applications. This competition puts pressure on ethyl acetate producers to innovate and differentiate their products.
Safety concerns related to the flammability and toxicity of ethyl acetate present ongoing challenges for manufacturers, transporters, and end-users. Ensuring proper handling, storage, and use of the solvent requires continuous training and implementation of safety protocols, which can increase operational costs and complexity.
The global nature of the ethyl acetate market introduces challenges related to trade barriers, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions. These factors can disrupt supply chains, affect pricing, and create market uncertainties. Manufacturers must navigate complex international trade regulations and adapt to changing global market dynamics.
Technological advancements in production processes present both opportunities and challenges for the industry. While new technologies can improve efficiency and reduce costs, they also require significant capital investments and may render existing production facilities obsolete. This creates a dilemma for manufacturers in deciding when and how to upgrade their facilities.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in meeting the evolving needs of end-users across various sectors. As industries such as coatings, pharmaceuticals, and electronics advance, they demand higher purity grades and specialized formulations of ethyl acetate. Meeting these requirements often necessitates ongoing research and development efforts, as well as investments in quality control and product customization capabilities.
Environmental regulations pose another major challenge for the industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt to more stringent emission control standards and waste management practices. This often requires substantial investments in cleaner production technologies and processes, which can be financially burdensome for smaller manufacturers.
The industry also grapples with intense competition from alternative solvents and technologies. As companies seek more environmentally friendly and cost-effective solutions, ethyl acetate faces competition from bio-based solvents and water-based alternatives in various applications. This competition puts pressure on ethyl acetate producers to innovate and differentiate their products.
Safety concerns related to the flammability and toxicity of ethyl acetate present ongoing challenges for manufacturers, transporters, and end-users. Ensuring proper handling, storage, and use of the solvent requires continuous training and implementation of safety protocols, which can increase operational costs and complexity.
The global nature of the ethyl acetate market introduces challenges related to trade barriers, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions. These factors can disrupt supply chains, affect pricing, and create market uncertainties. Manufacturers must navigate complex international trade regulations and adapt to changing global market dynamics.
Technological advancements in production processes present both opportunities and challenges for the industry. While new technologies can improve efficiency and reduce costs, they also require significant capital investments and may render existing production facilities obsolete. This creates a dilemma for manufacturers in deciding when and how to upgrade their facilities.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in meeting the evolving needs of end-users across various sectors. As industries such as coatings, pharmaceuticals, and electronics advance, they demand higher purity grades and specialized formulations of ethyl acetate. Meeting these requirements often necessitates ongoing research and development efforts, as well as investments in quality control and product customization capabilities.
Current Applications
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The production methods aim to optimize the reaction conditions and separation processes to obtain high-quality ethyl acetate efficiently.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in industrial processes: Ethyl acetate finds diverse applications in industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in various industries, including coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. The compound is also employed in extraction processes, as a reaction medium, and in the production of other chemicals. Its properties make it suitable for use in cleaning and degreasing applications.
- Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate: Methods for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial processes are described. These include adsorption techniques, membrane separation, and distillation processes. The recovery methods aim to reduce waste, improve process efficiency, and minimize environmental impact by reusing the solvent in various applications.
- Ethyl acetate as a component in formulations: Ethyl acetate is used as a component in various formulations, including coatings, adhesives, and personal care products. Its properties as a solvent and its ability to enhance certain characteristics of formulations make it valuable in product development. The compound is often combined with other ingredients to achieve desired performance attributes.
- Safety and environmental considerations for ethyl acetate use: Safety measures and environmental considerations related to the use of ethyl acetate are addressed. This includes handling procedures, storage requirements, and emission control strategies. Methods for reducing the environmental impact of ethyl acetate production and use, such as improved process efficiency and waste reduction techniques, are also discussed.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in chemical synthesis is highlighted.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
The use of ethyl acetate as an extraction solvent and in separation processes is described. Its properties make it suitable for extracting various compounds from mixtures and for use in chromatographic techniques.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Methods for handling, storing, and disposing of ethyl acetate are discussed, considering its flammability and potential environmental impact. Techniques for reducing emissions and improving safety in industrial settings are presented.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate
Research into novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate is presented. These include the development of new compounds based on ethyl acetate structure and modifications to improve its properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Market Players
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature growth stage, characterized by steady demand across various industries. The global market size is projected to reach approximately $4.5 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of around 5%. Technologically, ethyl acetate production is well-established, with major players like Celanese International Corp., BASF Corp., and Eastman Chemical Co. leading in process efficiency and product quality. However, emerging companies such as China Catalyst Holding Co., Ltd. and HighChem Co., Ltd. are driving innovation in catalysts and production methods. Research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Tianjin University are contributing to advancements in green synthesis and bio-based ethyl acetate production, indicating potential for future market disruption and sustainability improvements.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed a proprietary technology for ethyl acetate production using ethylene and acetic acid as raw materials. Their process employs a heterogeneous catalyst system that allows for high selectivity and yield[1]. The company has also implemented advanced process control systems to optimize production efficiency and reduce energy consumption[2]. Celanese's ethyl acetate is widely used in coatings, adhesives, and flexible packaging industries due to its high purity and consistent quality[3]. The company has strategically positioned its production facilities near key markets to ensure reliable supply and reduce transportation costs[4].
Strengths: Proprietary technology, high-quality product, strategic global presence. Weaknesses: Dependence on volatile raw material prices, potential environmental concerns related to ethylene-based production.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative ethyl acetate production process using bio-ethanol as a feedstock. This approach aligns with the growing demand for sustainable chemical production[1]. The company's process integrates fermentation technology with catalytic esterification, allowing for the use of renewable resources[2]. Sinopec has also implemented advanced separation techniques to achieve high-purity ethyl acetate, meeting the stringent requirements of electronic and pharmaceutical industries[3]. The company's large-scale production facilities are equipped with energy recovery systems, significantly reducing overall energy consumption and carbon footprint[4].
Strengths: Sustainable production method, large-scale facilities, diverse market applications. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs compared to traditional methods, dependence on bio-ethanol availability.
Innovative Technologies
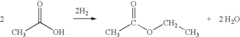
Direct and selective production of ethyl acetate from acetic acid utilizing a bimetal supported catalyst
PatentWO2010014145A2
Innovation
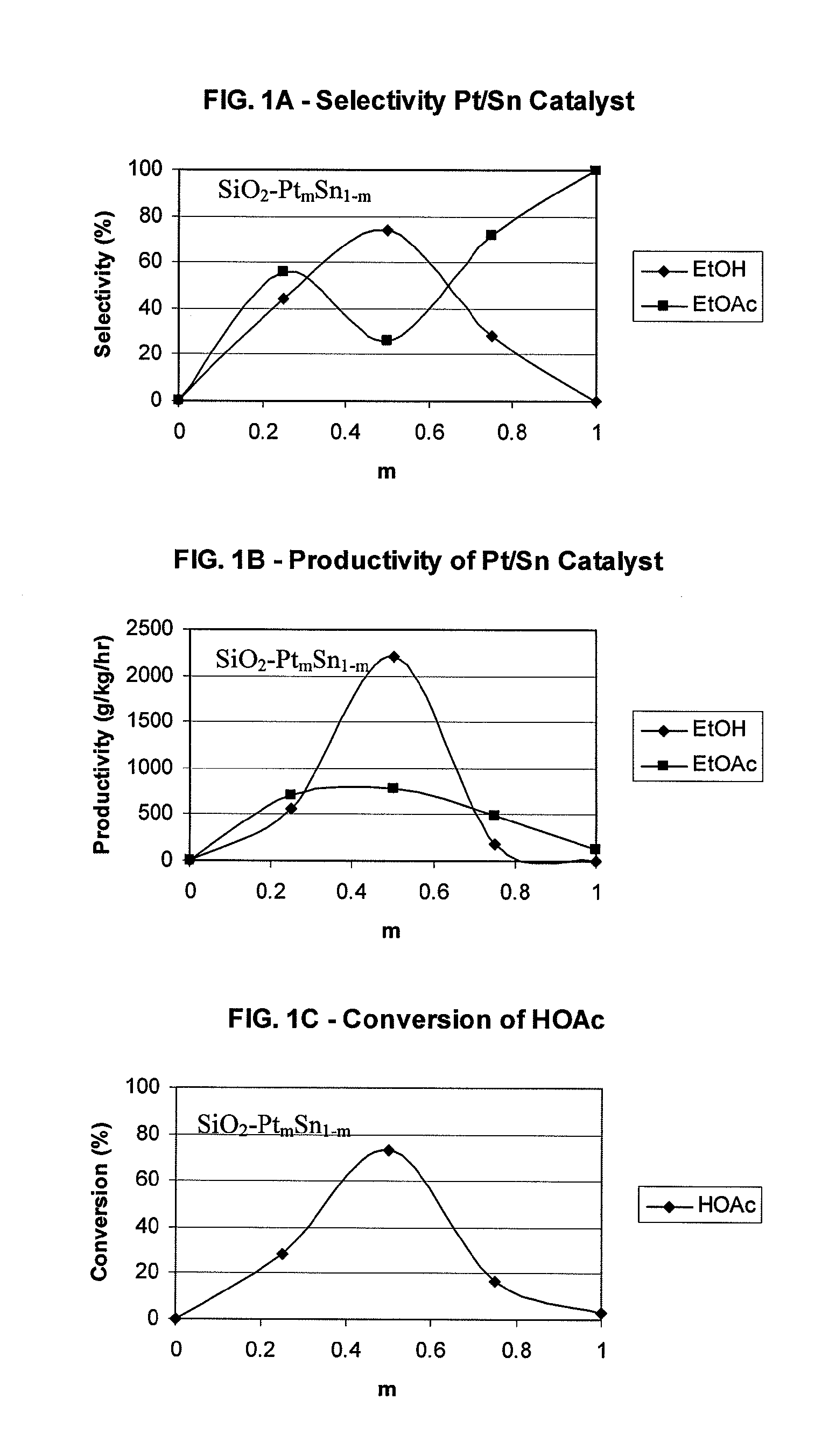
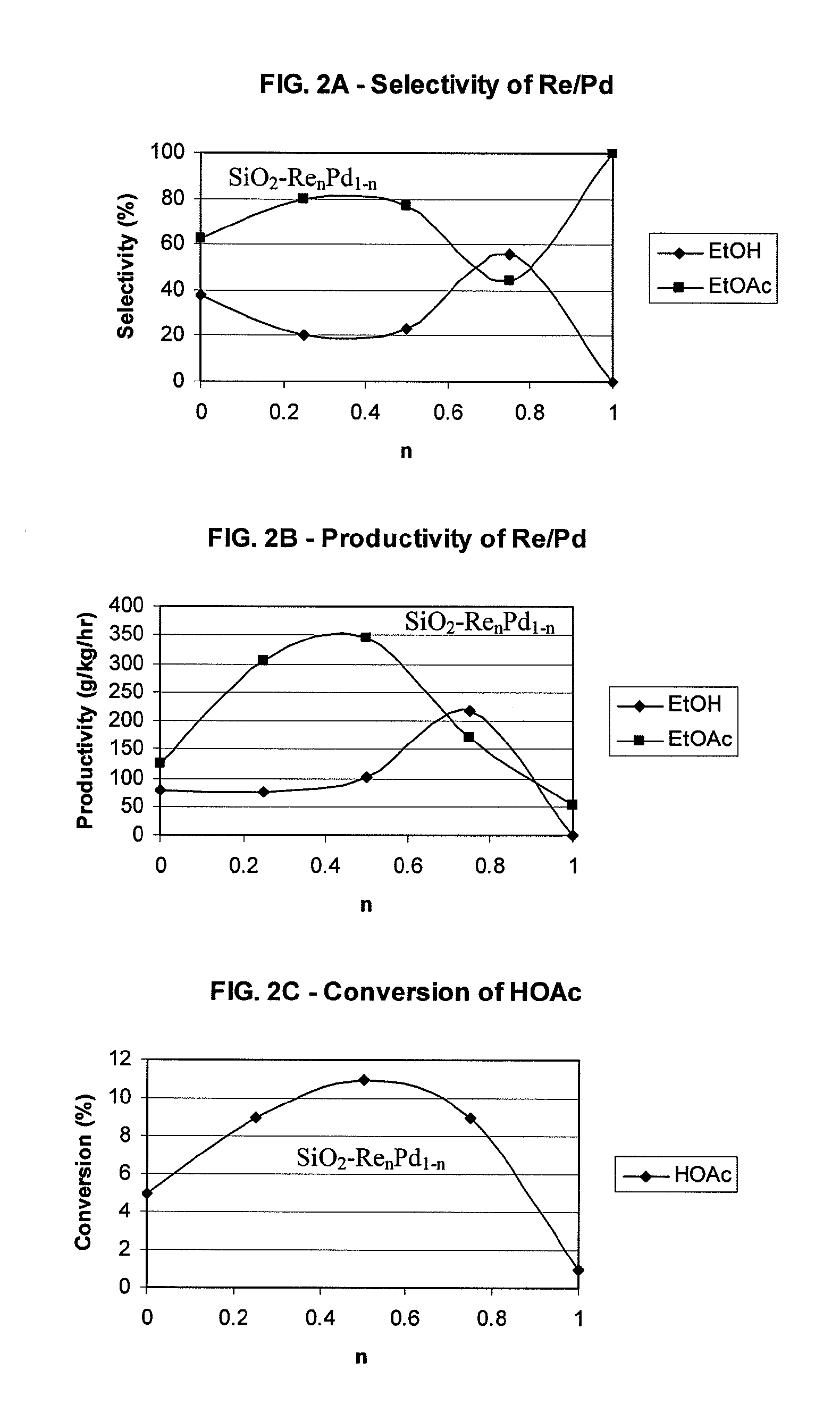
- A process utilizing a bimetallic catalyst supported on a suitable catalyst support, comprising metals like platinum, palladium, copper, and cobalt, which selectively hydrogenates acetic acid to ethyl acetate with high yield and selectivity, minimizing by-product formation.
Processes for making ethyl acetate from acetic acid
PatentInactiveUS20100197959A1
Innovation
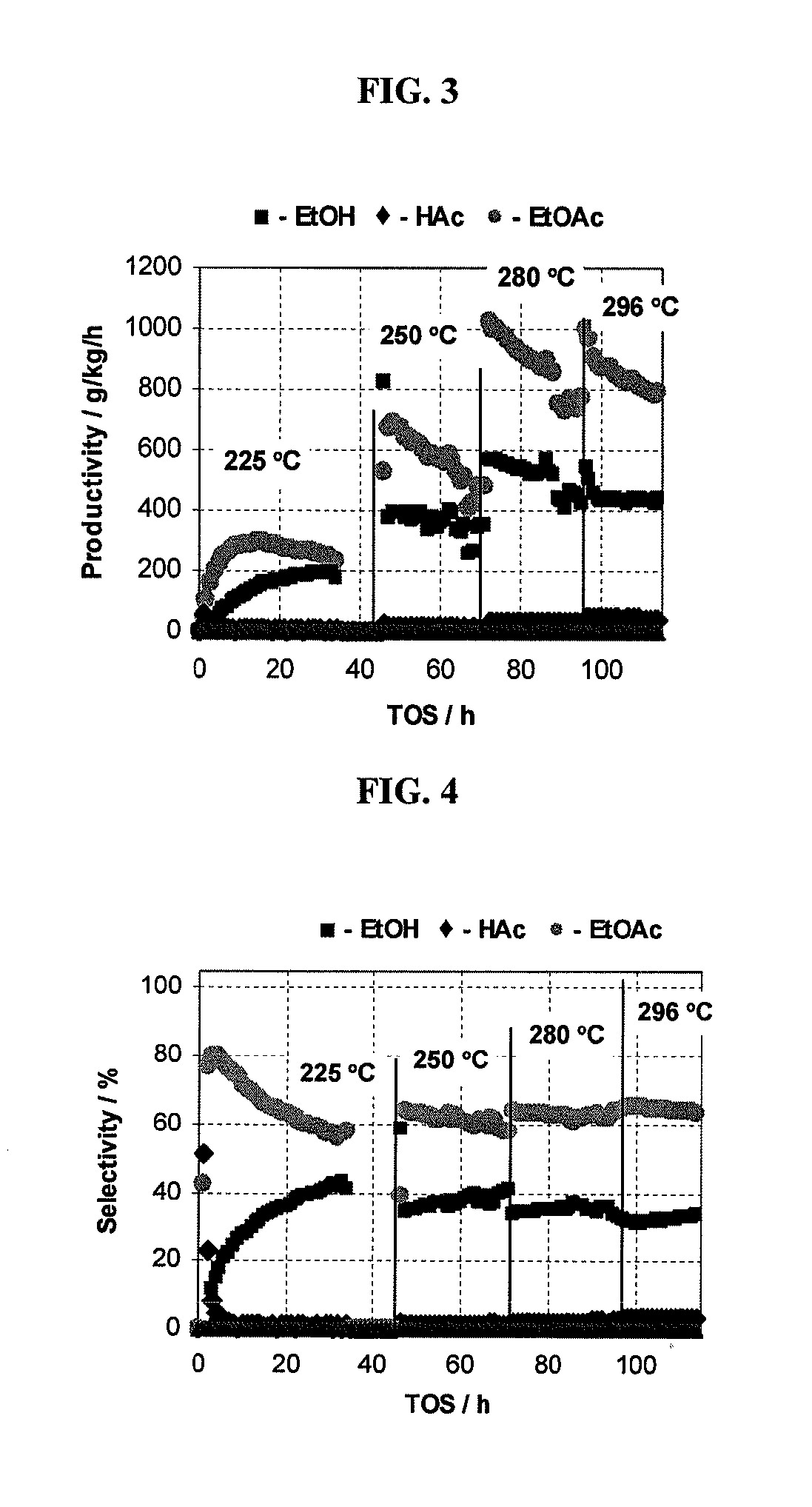
- A process utilizing catalysts comprising metals like nickel, palladium, or platinum, combined with support materials like silica or titania, and modified with oxides of Group IVB, VB, or VIB metals, which are effective in hydrogenating acetic acid to produce ethyl acetate with high selectivity and minimizing by-product formation.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in shaping its market dynamics and applications across various industries. As a widely used solvent and chemical intermediate, ethyl acetate is subject to diverse regulations that vary by region and sector.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory and is subject to reporting requirements for manufacturers and importers. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for workers handling ethyl acetate in industrial settings.
The European Union's regulatory approach to ethyl acetate is governed by the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register ethyl acetate and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which provides valuable information on its properties, hazards, and safe use.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is regulated by food safety authorities. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ethyl acetate as a food additive, while the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has established specific purity criteria for its use in food processing.
Environmental regulations also impact the ethyl acetate market. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission controls, which affect industries using ethyl acetate as a solvent. These regulations drive the development of low-VOC and VOC-free alternatives, influencing market trends and product formulations.
The pharmaceutical industry faces stringent regulations regarding the use of ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, enforced by agencies like the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), set standards for the quality and purity of ethyl acetate used in pharmaceutical applications.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations promoting circular economy principles are emerging. These may impact the ethyl acetate market by encouraging recycling and recovery processes, as well as the development of bio-based alternatives.
Understanding and navigating this complex regulatory landscape is essential for stakeholders in the ethyl acetate market. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures legal operation but also opens opportunities for innovation and market differentiation.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory and is subject to reporting requirements for manufacturers and importers. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for workers handling ethyl acetate in industrial settings.
The European Union's regulatory approach to ethyl acetate is governed by the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register ethyl acetate and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which provides valuable information on its properties, hazards, and safe use.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is regulated by food safety authorities. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ethyl acetate as a food additive, while the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has established specific purity criteria for its use in food processing.
Environmental regulations also impact the ethyl acetate market. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission controls, which affect industries using ethyl acetate as a solvent. These regulations drive the development of low-VOC and VOC-free alternatives, influencing market trends and product formulations.
The pharmaceutical industry faces stringent regulations regarding the use of ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, enforced by agencies like the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), set standards for the quality and purity of ethyl acetate used in pharmaceutical applications.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations promoting circular economy principles are emerging. These may impact the ethyl acetate market by encouraging recycling and recovery processes, as well as the development of bio-based alternatives.
Understanding and navigating this complex regulatory landscape is essential for stakeholders in the ethyl acetate market. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures legal operation but also opens opportunities for innovation and market differentiation.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate production and usage is a critical consideration in its key markets. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), ethyl acetate contributes to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the implementation of stricter emission controls in many regions.
In the manufacturing process, the production of ethyl acetate can result in the release of various pollutants, including VOCs, carbon dioxide, and other greenhouse gases. These emissions contribute to climate change and air quality degradation. Additionally, the use of fossil fuel-based feedstocks in traditional ethyl acetate production methods further exacerbates its carbon footprint.
Water pollution is another environmental concern associated with ethyl acetate. Improper disposal or accidental spills can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and human health. This risk necessitates stringent handling and disposal protocols in industries that utilize ethyl acetate.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not entirely negative. When compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively less harmful. It has a lower ozone depletion potential and global warming potential than many chlorinated solvents. Furthermore, ethyl acetate is biodegradable, which reduces its long-term environmental persistence.
The push for sustainability has driven research into greener production methods for ethyl acetate. Bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offers a more environmentally friendly alternative. This approach reduces reliance on fossil fuels and can significantly lower the overall carbon footprint of ethyl acetate production.
In response to environmental concerns, many industries are adopting closed-loop systems and solvent recovery technologies to minimize ethyl acetate emissions and waste. These practices not only reduce environmental impact but also offer economic benefits through improved resource efficiency.
The environmental challenges associated with ethyl acetate have also spurred innovation in alternative solvents and technologies. This has led to the development of water-based and solvent-free systems in some applications, potentially reducing the overall market demand for ethyl acetate in certain sectors.
In the manufacturing process, the production of ethyl acetate can result in the release of various pollutants, including VOCs, carbon dioxide, and other greenhouse gases. These emissions contribute to climate change and air quality degradation. Additionally, the use of fossil fuel-based feedstocks in traditional ethyl acetate production methods further exacerbates its carbon footprint.
Water pollution is another environmental concern associated with ethyl acetate. Improper disposal or accidental spills can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and human health. This risk necessitates stringent handling and disposal protocols in industries that utilize ethyl acetate.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not entirely negative. When compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively less harmful. It has a lower ozone depletion potential and global warming potential than many chlorinated solvents. Furthermore, ethyl acetate is biodegradable, which reduces its long-term environmental persistence.
The push for sustainability has driven research into greener production methods for ethyl acetate. Bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offers a more environmentally friendly alternative. This approach reduces reliance on fossil fuels and can significantly lower the overall carbon footprint of ethyl acetate production.
In response to environmental concerns, many industries are adopting closed-loop systems and solvent recovery technologies to minimize ethyl acetate emissions and waste. These practices not only reduce environmental impact but also offer economic benefits through improved resource efficiency.
The environmental challenges associated with ethyl acetate have also spurred innovation in alternative solvents and technologies. This has led to the development of water-based and solvent-free systems in some applications, potentially reducing the overall market demand for ethyl acetate in certain sectors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!