Market Influence of Regulations on Resistive RAM Expansion
OCT 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ReRAM Regulatory Background and Development Goals
Resistive Random Access Memory (ReRAM) has emerged as a promising next-generation non-volatile memory technology over the past two decades. The technology's development trajectory has been shaped significantly by evolving regulatory frameworks across different regions, with regulations concerning materials usage, manufacturing processes, and environmental impact playing crucial roles in its commercialization journey.
The historical development of ReRAM began in the early 2000s when researchers discovered the resistive switching phenomenon in various oxide materials. Initial research focused primarily on understanding the fundamental mechanisms, with minimal regulatory oversight. As the technology matured from 2010 onwards, increasing attention from regulatory bodies emerged, particularly regarding the use of rare earth elements and potentially hazardous materials in fabrication processes.
Current regulatory landscapes vary significantly across major technology manufacturing regions. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations have imposed strict limitations on certain materials commonly used in ReRAM fabrication. Meanwhile, the United States has focused more on strategic supply chain security through the CHIPS Act, which indirectly influences ReRAM development by prioritizing domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities.
In Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, government initiatives have actively promoted ReRAM development through targeted funding programs while simultaneously implementing environmental regulations that impact manufacturing processes. These regional regulatory differences have created a complex global landscape for ReRAM commercialization and market expansion.
The primary technical goals for ReRAM development within this regulatory context include: achieving compliance with increasingly stringent materials regulations while maintaining performance characteristics; developing environmentally sustainable manufacturing processes that reduce waste and energy consumption; establishing standardized testing protocols that satisfy regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions; and creating supply chain transparency mechanisms to demonstrate regulatory compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
Looking forward, the evolution of ReRAM technology is expected to align with broader regulatory trends toward greater sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Key development targets include reducing or eliminating dependence on rare earth elements, minimizing toxic waste generation during manufacturing, improving energy efficiency metrics to meet emerging regulatory standards, and enhancing end-of-life recyclability to comply with circular economy regulations being implemented globally.
The successful navigation of this complex regulatory landscape will be critical to ReRAM's widespread market adoption, as compliance costs and regulatory uncertainty can significantly impact investment decisions and commercialization timelines for emerging memory technologies.
The historical development of ReRAM began in the early 2000s when researchers discovered the resistive switching phenomenon in various oxide materials. Initial research focused primarily on understanding the fundamental mechanisms, with minimal regulatory oversight. As the technology matured from 2010 onwards, increasing attention from regulatory bodies emerged, particularly regarding the use of rare earth elements and potentially hazardous materials in fabrication processes.
Current regulatory landscapes vary significantly across major technology manufacturing regions. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations have imposed strict limitations on certain materials commonly used in ReRAM fabrication. Meanwhile, the United States has focused more on strategic supply chain security through the CHIPS Act, which indirectly influences ReRAM development by prioritizing domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities.
In Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, government initiatives have actively promoted ReRAM development through targeted funding programs while simultaneously implementing environmental regulations that impact manufacturing processes. These regional regulatory differences have created a complex global landscape for ReRAM commercialization and market expansion.
The primary technical goals for ReRAM development within this regulatory context include: achieving compliance with increasingly stringent materials regulations while maintaining performance characteristics; developing environmentally sustainable manufacturing processes that reduce waste and energy consumption; establishing standardized testing protocols that satisfy regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions; and creating supply chain transparency mechanisms to demonstrate regulatory compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
Looking forward, the evolution of ReRAM technology is expected to align with broader regulatory trends toward greater sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Key development targets include reducing or eliminating dependence on rare earth elements, minimizing toxic waste generation during manufacturing, improving energy efficiency metrics to meet emerging regulatory standards, and enhancing end-of-life recyclability to comply with circular economy regulations being implemented globally.
The successful navigation of this complex regulatory landscape will be critical to ReRAM's widespread market adoption, as compliance costs and regulatory uncertainty can significantly impact investment decisions and commercialization timelines for emerging memory technologies.
Market Demand Analysis for ReRAM Technologies
The global market for Resistive Random Access Memory (ReRAM) technologies has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for high-performance, low-power memory solutions across various sectors. Current market analysis indicates that the ReRAM market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 16% through 2028, with the total addressable market expected to reach approximately 2.5 billion USD by that time.
The primary demand drivers for ReRAM technologies stem from several key industries. The Internet of Things (IoT) sector represents one of the most promising markets, as ReRAM's low power consumption and non-volatile characteristics make it ideal for edge computing devices and sensors that require efficient data storage with minimal energy usage. The automotive industry has also emerged as a significant consumer, particularly for advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous vehicles that demand reliable, high-speed memory capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are increasingly exploring ReRAM integration for next-generation smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The technology's ability to combine storage and computing functions aligns perfectly with the industry's push toward more compact, energy-efficient devices with enhanced performance capabilities. Market research indicates that consumer electronics could account for nearly 35% of total ReRAM demand by 2026.
Enterprise data centers and cloud computing infrastructure providers represent another substantial market segment. These entities are actively seeking memory solutions that can address the growing challenges of data-intensive applications, particularly those involving artificial intelligence and machine learning workloads. ReRAM's potential to reduce latency and power consumption while increasing storage density makes it an attractive alternative to conventional memory technologies in these settings.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption rates across different geographical areas. North America currently leads in ReRAM market share, followed by Asia-Pacific and Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years, primarily due to the strong presence of semiconductor manufacturing facilities and increasing investments in emerging technologies by countries like China, South Korea, and Taiwan.
Market surveys indicate that customers across all segments prioritize several key factors when evaluating ReRAM solutions: cost-effectiveness compared to existing technologies, reliability and endurance metrics, integration capabilities with existing systems, and scalability for future applications. The price-performance ratio remains a critical consideration, as ReRAM must demonstrate clear advantages over established technologies like NAND flash and DRAM to achieve widespread market penetration.
The primary demand drivers for ReRAM technologies stem from several key industries. The Internet of Things (IoT) sector represents one of the most promising markets, as ReRAM's low power consumption and non-volatile characteristics make it ideal for edge computing devices and sensors that require efficient data storage with minimal energy usage. The automotive industry has also emerged as a significant consumer, particularly for advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous vehicles that demand reliable, high-speed memory capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are increasingly exploring ReRAM integration for next-generation smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The technology's ability to combine storage and computing functions aligns perfectly with the industry's push toward more compact, energy-efficient devices with enhanced performance capabilities. Market research indicates that consumer electronics could account for nearly 35% of total ReRAM demand by 2026.
Enterprise data centers and cloud computing infrastructure providers represent another substantial market segment. These entities are actively seeking memory solutions that can address the growing challenges of data-intensive applications, particularly those involving artificial intelligence and machine learning workloads. ReRAM's potential to reduce latency and power consumption while increasing storage density makes it an attractive alternative to conventional memory technologies in these settings.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption rates across different geographical areas. North America currently leads in ReRAM market share, followed by Asia-Pacific and Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years, primarily due to the strong presence of semiconductor manufacturing facilities and increasing investments in emerging technologies by countries like China, South Korea, and Taiwan.
Market surveys indicate that customers across all segments prioritize several key factors when evaluating ReRAM solutions: cost-effectiveness compared to existing technologies, reliability and endurance metrics, integration capabilities with existing systems, and scalability for future applications. The price-performance ratio remains a critical consideration, as ReRAM must demonstrate clear advantages over established technologies like NAND flash and DRAM to achieve widespread market penetration.
Global Regulatory Landscape and Technical Challenges
The global regulatory landscape for Resistive RAM (ReRAM) technology presents a complex interplay of technical standards, data protection laws, and industry-specific regulations that significantly impact market expansion. In North America, the regulatory framework emphasizes data security and privacy, with the U.S. implementing stringent requirements through frameworks like NIST guidelines that directly influence ReRAM adoption in critical infrastructure and government applications. These regulations often mandate specific endurance levels and data retention capabilities that ReRAM manufacturers must meet.
European regulations present additional layers of complexity, particularly through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which imposes strict data sovereignty requirements. This has accelerated interest in ReRAM solutions that offer enhanced security features like physical unclonable functions (PUFs) and built-in encryption capabilities. The European Commission's Chips Act further shapes the landscape by prioritizing memory technologies with reduced environmental footprints, creating both opportunities and compliance challenges for ReRAM developers.
In the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, government initiatives actively promote domestic semiconductor capabilities, including next-generation memory technologies. China's focus on technological self-sufficiency has led to substantial investments in ReRAM research and manufacturing, though export control regulations from Western countries create significant barriers to technology transfer and collaborative development.
Technical challenges intersect with these regulatory frameworks in several critical areas. First, reliability and endurance specifications required by industrial and automotive standards (ISO 26262, IEC 61508) demand ReRAM solutions that can demonstrate consistent performance under extreme conditions. Current ReRAM technologies struggle to simultaneously meet these reliability requirements while maintaining competitive cost structures.
Data retention requirements present another significant challenge, with financial and healthcare sectors requiring decades-long data preservation capabilities that exceed current ReRAM specifications. This gap between regulatory expectations and technical capabilities has slowed adoption in these high-value markets.
Security certification processes, particularly Common Criteria and FIPS 140-3, impose rigorous validation requirements that few ReRAM manufacturers have successfully navigated. The certification timeline often exceeds 18 months, creating a substantial barrier to market entry for emerging ReRAM solutions targeting secure applications.
Environmental regulations, including the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and similar frameworks globally, impact material selection and manufacturing processes for ReRAM. While ReRAM generally offers advantages in power consumption compared to traditional memory technologies, certain implementations utilize materials facing increasing regulatory scrutiny, necessitating ongoing research into alternative compositions.
European regulations present additional layers of complexity, particularly through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which imposes strict data sovereignty requirements. This has accelerated interest in ReRAM solutions that offer enhanced security features like physical unclonable functions (PUFs) and built-in encryption capabilities. The European Commission's Chips Act further shapes the landscape by prioritizing memory technologies with reduced environmental footprints, creating both opportunities and compliance challenges for ReRAM developers.
In the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, government initiatives actively promote domestic semiconductor capabilities, including next-generation memory technologies. China's focus on technological self-sufficiency has led to substantial investments in ReRAM research and manufacturing, though export control regulations from Western countries create significant barriers to technology transfer and collaborative development.
Technical challenges intersect with these regulatory frameworks in several critical areas. First, reliability and endurance specifications required by industrial and automotive standards (ISO 26262, IEC 61508) demand ReRAM solutions that can demonstrate consistent performance under extreme conditions. Current ReRAM technologies struggle to simultaneously meet these reliability requirements while maintaining competitive cost structures.
Data retention requirements present another significant challenge, with financial and healthcare sectors requiring decades-long data preservation capabilities that exceed current ReRAM specifications. This gap between regulatory expectations and technical capabilities has slowed adoption in these high-value markets.
Security certification processes, particularly Common Criteria and FIPS 140-3, impose rigorous validation requirements that few ReRAM manufacturers have successfully navigated. The certification timeline often exceeds 18 months, creating a substantial barrier to market entry for emerging ReRAM solutions targeting secure applications.
Environmental regulations, including the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and similar frameworks globally, impact material selection and manufacturing processes for ReRAM. While ReRAM generally offers advantages in power consumption compared to traditional memory technologies, certain implementations utilize materials facing increasing regulatory scrutiny, necessitating ongoing research into alternative compositions.
Current Regulatory Compliance Solutions
01 Technological advancements in ReRAM devices
Recent technological advancements in Resistive Random Access Memory (ReRAM) have significantly improved device performance and reliability. These innovations include novel materials, structures, and fabrication techniques that enhance switching characteristics, endurance, and retention time. Such improvements are crucial for expanding the ReRAM market as they address previous limitations and enable new applications in various sectors including consumer electronics, automotive, and enterprise storage.- Technological advancements in ReRAM architecture: Recent innovations in resistive RAM architecture have significantly contributed to market expansion. These advancements include improved cell structures, novel materials for switching layers, and enhanced integration techniques that allow for higher density memory arrays. The technological improvements have resulted in better performance characteristics such as faster switching speeds, lower power consumption, and increased reliability, making ReRAM more competitive against traditional memory technologies.
- Manufacturing process optimization: Optimization of manufacturing processes has been crucial for ReRAM market expansion. Innovations in fabrication techniques have enabled cost-effective production of resistive memory devices at scale. These improvements include advanced deposition methods for memory cell materials, integration with standard CMOS processes, and yield enhancement strategies. Such manufacturing advancements have helped reduce production costs and increase output capacity, supporting broader market adoption.
- Application diversification for ReRAM: The expansion of resistive RAM market has been driven by diversification into various application domains. Beyond traditional storage, ReRAM is finding applications in neuromorphic computing, edge AI devices, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and automotive systems. The non-volatile nature, low power consumption, and radiation hardness of ReRAM make it particularly suitable for these emerging applications, opening new market segments and driving overall growth.
- Integration with existing memory ecosystems: Successful integration of resistive RAM with existing memory ecosystems has facilitated market expansion. This includes the development of compatible interfaces, controllers, and software that allow ReRAM to work alongside established memory technologies like DRAM and NAND flash. Hybrid memory systems that leverage the strengths of different memory types are emerging as practical solutions for various computing needs, creating new opportunities for ReRAM adoption in the market.
- Commercial strategies and market development: Strategic commercial approaches have been instrumental in expanding the resistive RAM market. These include partnerships between memory manufacturers and device makers, licensing agreements for ReRAM technology, and targeted marketing to specific industry segments. Investment in production capacity, development of industry standards, and creation of comprehensive product portfolios have also contributed to market growth by addressing diverse customer needs and building confidence in the technology.
02 Integration with existing semiconductor technologies
The successful integration of ReRAM with conventional CMOS technology and other semiconductor platforms has been a key driver for market expansion. This integration allows for the development of hybrid memory solutions that combine the benefits of ReRAM (non-volatility, low power consumption) with traditional memory technologies. Such compatibility with existing manufacturing processes facilitates adoption by reducing implementation barriers and production costs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in emerging markets and IoT
The expansion of the ReRAM market is closely tied to its adoption in emerging applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, wearable technology, and edge computing. ReRAM's characteristics of low power consumption, fast switching speed, and non-volatility make it particularly suitable for these applications where energy efficiency and quick data access are critical. This has opened new market segments beyond traditional computing and storage applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing scale-up and cost reduction
Advancements in manufacturing processes have enabled the scale-up of ReRAM production, leading to significant cost reductions. These improvements include optimized fabrication techniques, increased wafer sizes, and enhanced yield rates. As production volumes increase and manufacturing becomes more efficient, the cost per bit of ReRAM decreases, making it more competitive with established memory technologies and accelerating market adoption across various sectors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market strategies and commercial partnerships
Strategic business approaches and commercial partnerships have played a crucial role in expanding the ReRAM market. Companies are forming alliances to combine technological expertise, manufacturing capabilities, and market access. These collaborations help address challenges in the memory ecosystem and create comprehensive solutions for end-users. Additionally, targeted market strategies focusing on specific applications where ReRAM offers distinct advantages have helped accelerate adoption and market growth.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Positioning
The Resistive RAM market is currently in a growth phase, with regulations significantly influencing its expansion trajectory. The global market size is projected to reach substantial value as emerging applications in IoT, automotive electronics, and data centers drive demand. Technologically, RRAM is approaching maturity with key players demonstrating varied development stages. Industry leaders like Samsung, Micron, and KIOXIA are advancing commercial implementations, while research institutions including Peking University, Tsinghua University, and IMEC are pushing fundamental breakthroughs. Chinese entities such as SMIC and Huawei are rapidly closing technological gaps despite regulatory constraints. Regional regulations, particularly export controls and intellectual property frameworks, are creating distinct competitive landscapes across Asia, North America, and Europe, influencing technology transfer and market access strategies.
KIOXIA Corp.
Technical Solution: KIOXIA (formerly Toshiba Memory) has developed a distinctive approach to ReRAM commercialization that specifically addresses the regulatory challenges unique to different global markets. Their ReRAM technology platform incorporates adaptive design elements that can be configured to meet varying regulatory requirements without fundamental architecture changes. KIOXIA has implemented a comprehensive regulatory intelligence system that monitors evolving memory-related regulations across key markets, with particular focus on data security, environmental compliance, and reliability standards that impact ReRAM adoption. The company has established strategic partnerships with regulatory consultancies in major markets to ensure their ReRAM development roadmap aligns with anticipated regulatory changes. KIOXIA's market strategy includes targeted ReRAM solutions for highly regulated industries such as automotive, medical, and industrial applications, where their expertise in navigating complex approval processes provides competitive advantages. Their approach emphasizes early engagement with standards bodies and regulatory authorities to help shape the regulatory framework for emerging memory technologies rather than simply reacting to established requirements.
Strengths: KIOXIA's focused memory business allows for specialized regulatory expertise specific to memory technologies, enabling more efficient compliance strategies compared to more diversified competitors. Their heritage as part of Toshiba provides established regulatory relationships in key markets. Weaknesses: As a relatively newly independent company, KIOXIA may have less established regulatory affairs infrastructure compared to larger semiconductor conglomerates, potentially creating challenges in simultaneously addressing multiple regulatory environments.
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TSMC has developed a foundry-specific approach to ReRAM implementation that addresses the unique regulatory challenges faced by a manufacturing partner rather than an end-product company. Their ReRAM technology platform offers customizable integration options that can be adapted to meet varying regulatory requirements across different customer applications and target markets. TSMC has invested in developing specialized manufacturing processes that minimize environmental impact while maintaining ReRAM performance characteristics, particularly focusing on reducing hazardous material usage and energy consumption during fabrication. The company has established a comprehensive regulatory compliance framework that helps their customers navigate certification processes for ReRAM-based products across different jurisdictions. This includes detailed documentation of materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures that satisfy regulatory requirements in key markets. TSMC actively participates in international standards development for emerging memory technologies, helping to shape regulatory frameworks that will govern ReRAM adoption. Their approach emphasizes scalable manufacturing solutions that can adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes without requiring fundamental technology redesigns.
Strengths: TSMC's position as a manufacturing partner to multiple ReRAM developers gives them unique insights into diverse regulatory challenges across applications and markets. Their established quality control systems and documentation processes facilitate regulatory approval for customers. Weaknesses: As a foundry, TSMC must support multiple ReRAM architectures and materials systems, potentially creating challenges in optimizing regulatory compliance strategies compared to companies focused on proprietary solutions.
Critical Patents and Technical Standards Analysis
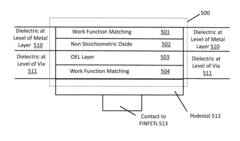
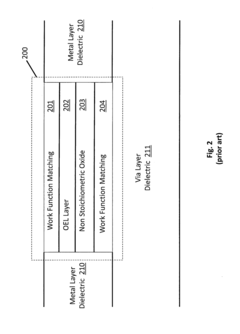
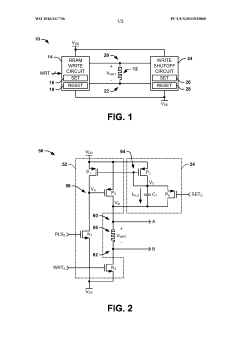
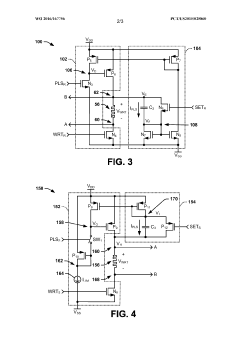
Resistive random access memory cell having bottom-side OEL layer and/or optimized access signaling
PatentInactiveUS20170287555A1
Innovation
- The solution involves modulating the width of the WL signal and adjusting the relative voltage levels of the WL, SL, and BL lines to limit energy application, using asymmetrical voltage levels during SET and RESET phases, and altering the position of the oxide exchange layer (OEL) within the resistive element stack to mitigate source degeneration and control resistive states effectively.
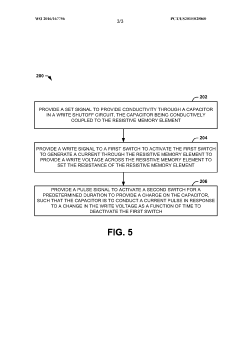
Resistive random access memory (RRAM) system
PatentWO2016167756A1
Innovation
- The RRAM system incorporates a write shutoff circuit that monitors the change in write voltage over time and immediately deactivates the write operation upon detecting a rapid change in resistance, using capacitors and switches to terminate the write stimulus efficiently.
Cross-Border Regulatory Harmonization Strategies
The global regulatory landscape for emerging memory technologies like Resistive RAM (ReRAM) presents significant challenges for market expansion. Divergent regulatory frameworks across major technology markets create barriers to seamless deployment and commercialization. Companies operating in multiple jurisdictions face compliance complexities that increase development costs and delay time-to-market, ultimately impeding ReRAM adoption rates.
Harmonization of cross-border regulations represents a critical pathway to accelerate ReRAM market growth. Strategic alignment of technical standards between North America, Europe, and Asia could reduce certification redundancies and streamline approval processes. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and IEEE have established working groups specifically focused on creating unified standards for non-volatile memory technologies, providing a foundation for regulatory convergence.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between key markets offer another promising harmonization approach. These agreements enable regulatory authorities in different regions to accept each other's conformity assessment results, significantly reducing duplicate testing requirements. The successful implementation of MRAs for semiconductor technologies between the United States and European Union demonstrates a viable model that could be extended to ReRAM technologies.
Industry consortia play an instrumental role in driving regulatory alignment. Organizations like the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association have developed standardized testing protocols for memory technologies that are increasingly recognized across multiple jurisdictions. By expanding these collaborative efforts specifically for ReRAM, stakeholders can advocate for consistent regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with necessary safety and performance requirements.
Data privacy and security regulations present particular harmonization challenges for ReRAM applications in edge computing and IoT devices. The divergence between GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and various Asian data protection frameworks creates compliance complexity. Developing interoperable compliance frameworks that address core security principles while accommodating regional variations would significantly reduce market fragmentation.
Phased implementation strategies offer practical pathways to regulatory harmonization. Beginning with alignment on fundamental technical specifications and gradually expanding to more complex aspects like endurance testing and reliability standards allows for incremental progress. This approach has proven effective in other semiconductor technologies and could be adapted specifically for the unique characteristics of ReRAM technologies.
Harmonization of cross-border regulations represents a critical pathway to accelerate ReRAM market growth. Strategic alignment of technical standards between North America, Europe, and Asia could reduce certification redundancies and streamline approval processes. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and IEEE have established working groups specifically focused on creating unified standards for non-volatile memory technologies, providing a foundation for regulatory convergence.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between key markets offer another promising harmonization approach. These agreements enable regulatory authorities in different regions to accept each other's conformity assessment results, significantly reducing duplicate testing requirements. The successful implementation of MRAs for semiconductor technologies between the United States and European Union demonstrates a viable model that could be extended to ReRAM technologies.
Industry consortia play an instrumental role in driving regulatory alignment. Organizations like the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association have developed standardized testing protocols for memory technologies that are increasingly recognized across multiple jurisdictions. By expanding these collaborative efforts specifically for ReRAM, stakeholders can advocate for consistent regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with necessary safety and performance requirements.
Data privacy and security regulations present particular harmonization challenges for ReRAM applications in edge computing and IoT devices. The divergence between GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and various Asian data protection frameworks creates compliance complexity. Developing interoperable compliance frameworks that address core security principles while accommodating regional variations would significantly reduce market fragmentation.
Phased implementation strategies offer practical pathways to regulatory harmonization. Beginning with alignment on fundamental technical specifications and gradually expanding to more complex aspects like endurance testing and reliability standards allows for incremental progress. This approach has proven effective in other semiconductor technologies and could be adapted specifically for the unique characteristics of ReRAM technologies.
Environmental and Safety Compliance Frameworks
The regulatory landscape governing Resistive RAM (ReRAM) technologies encompasses a complex matrix of environmental and safety compliance frameworks that significantly impact market expansion. These frameworks vary considerably across different regions, with the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) directives establishing some of the most stringent standards globally. These regulations specifically limit the use of certain heavy metals and chemicals that have historically been utilized in semiconductor manufacturing processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have implemented complementary frameworks that focus on workplace safety during ReRAM production and the environmental impact of manufacturing waste. Meanwhile, Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have developed their own regulatory structures that often emphasize different aspects of environmental protection and safety compliance, creating a heterogeneous global compliance landscape.
The materials used in ReRAM fabrication present specific regulatory challenges. Transition metal oxides, commonly employed in ReRAM cells, must meet increasingly strict purity standards and disposal protocols. The manufacturing processes involving these materials generate waste products that require specialized handling and disposal methods to comply with environmental regulations. Companies must invest significantly in waste management systems and pollution control technologies to maintain compliance.
Energy efficiency standards represent another critical dimension of the compliance framework. As data centers increasingly adopt memory-intensive architectures, regulations governing power consumption and heat generation have become more prominent. ReRAM technologies must demonstrate compliance with energy efficiency standards such as the US ENERGY STAR program and the EU Ecodesign Directive to remain competitive in these markets.
Supply chain compliance has emerged as a particularly complex challenge for ReRAM manufacturers. Regulations such as the EU's Conflict Minerals Regulation and the US Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502 require companies to verify that their supply chains are free from minerals sourced from conflict zones. This necessitates comprehensive supply chain auditing and documentation, adding significant operational complexity and cost to ReRAM production and distribution.
End-of-life management regulations, including the EU's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, impose additional requirements on manufacturers regarding product recyclability and take-back programs. These regulations are increasingly influencing product design decisions, pushing manufacturers toward more easily recyclable components and materials, which can impact ReRAM architecture and packaging strategies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have implemented complementary frameworks that focus on workplace safety during ReRAM production and the environmental impact of manufacturing waste. Meanwhile, Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have developed their own regulatory structures that often emphasize different aspects of environmental protection and safety compliance, creating a heterogeneous global compliance landscape.
The materials used in ReRAM fabrication present specific regulatory challenges. Transition metal oxides, commonly employed in ReRAM cells, must meet increasingly strict purity standards and disposal protocols. The manufacturing processes involving these materials generate waste products that require specialized handling and disposal methods to comply with environmental regulations. Companies must invest significantly in waste management systems and pollution control technologies to maintain compliance.
Energy efficiency standards represent another critical dimension of the compliance framework. As data centers increasingly adopt memory-intensive architectures, regulations governing power consumption and heat generation have become more prominent. ReRAM technologies must demonstrate compliance with energy efficiency standards such as the US ENERGY STAR program and the EU Ecodesign Directive to remain competitive in these markets.
Supply chain compliance has emerged as a particularly complex challenge for ReRAM manufacturers. Regulations such as the EU's Conflict Minerals Regulation and the US Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502 require companies to verify that their supply chains are free from minerals sourced from conflict zones. This necessitates comprehensive supply chain auditing and documentation, adding significant operational complexity and cost to ReRAM production and distribution.
End-of-life management regulations, including the EU's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, impose additional requirements on manufacturers regarding product recyclability and take-back programs. These regulations are increasingly influencing product design decisions, pushing manufacturers toward more easily recyclable components and materials, which can impact ReRAM architecture and packaging strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!