Technological advancements in gate valve sensors for increased accuracy
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Gate Valve Sensor Evolution and Objectives
Gate valve sensors have undergone significant evolution since their inception, driven by the increasing demand for precision and reliability in various industries. The journey of these sensors began with simple mechanical indicators, progressing through electromechanical devices, and now entering the era of advanced digital and smart sensing technologies. This technological progression has been fueled by the need for more accurate, real-time monitoring of valve positions and operational status in critical applications such as oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
The primary objective of gate valve sensor advancements is to enhance accuracy in position detection and feedback. This goal is crucial for ensuring optimal valve performance, preventing failures, and improving overall system efficiency. Increased accuracy allows for better control of fluid flow, pressure regulation, and process optimization. Additionally, improved sensors aim to provide more detailed diagnostics, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Another key objective is the integration of sensors with modern industrial control systems and IoT platforms. This integration facilitates remote monitoring, data analytics, and automated decision-making processes. The ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of operational data in real-time is becoming increasingly important for industries seeking to optimize their processes and reduce operational costs.
Miniaturization and robustness are also significant goals in gate valve sensor development. As industrial environments become more compact and challenging, there is a growing need for sensors that can operate reliably in confined spaces and harsh conditions. This includes resistance to extreme temperatures, pressures, vibrations, and corrosive substances.
Energy efficiency and environmental considerations are driving the development of low-power sensors and environmentally friendly materials. The aim is to create sensors that can operate for extended periods without frequent battery replacements or maintenance, while also aligning with sustainability goals.
Lastly, the evolution of gate valve sensors is focused on enhancing their versatility and adaptability. The objective is to develop sensors that can be easily retrofitted to existing valve systems and are compatible with a wide range of valve types and sizes. This adaptability is crucial for industries looking to upgrade their infrastructure without significant overhauls.
As we look to the future, the objectives for gate valve sensor technology continue to expand. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into sensor systems is becoming a priority, aiming to provide predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making capabilities. These advancements are set to revolutionize valve management, offering unprecedented levels of control, efficiency, and reliability in industrial processes.
The primary objective of gate valve sensor advancements is to enhance accuracy in position detection and feedback. This goal is crucial for ensuring optimal valve performance, preventing failures, and improving overall system efficiency. Increased accuracy allows for better control of fluid flow, pressure regulation, and process optimization. Additionally, improved sensors aim to provide more detailed diagnostics, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Another key objective is the integration of sensors with modern industrial control systems and IoT platforms. This integration facilitates remote monitoring, data analytics, and automated decision-making processes. The ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of operational data in real-time is becoming increasingly important for industries seeking to optimize their processes and reduce operational costs.
Miniaturization and robustness are also significant goals in gate valve sensor development. As industrial environments become more compact and challenging, there is a growing need for sensors that can operate reliably in confined spaces and harsh conditions. This includes resistance to extreme temperatures, pressures, vibrations, and corrosive substances.
Energy efficiency and environmental considerations are driving the development of low-power sensors and environmentally friendly materials. The aim is to create sensors that can operate for extended periods without frequent battery replacements or maintenance, while also aligning with sustainability goals.
Lastly, the evolution of gate valve sensors is focused on enhancing their versatility and adaptability. The objective is to develop sensors that can be easily retrofitted to existing valve systems and are compatible with a wide range of valve types and sizes. This adaptability is crucial for industries looking to upgrade their infrastructure without significant overhauls.
As we look to the future, the objectives for gate valve sensor technology continue to expand. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into sensor systems is becoming a priority, aiming to provide predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making capabilities. These advancements are set to revolutionize valve management, offering unprecedented levels of control, efficiency, and reliability in industrial processes.
Market Demand Analysis for Precision Gate Valve Sensors
The market demand for precision gate valve sensors has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing need for accurate flow control and monitoring across various industries. Industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and power generation are particularly fueling this demand as they seek to optimize their operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
In the oil and gas sector, precision gate valve sensors play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient transport of fluids through pipelines. The industry's focus on minimizing leaks and maximizing throughput has led to a surge in demand for advanced sensor technologies that can provide real-time, accurate measurements of valve positions and flow rates.
The water treatment industry is another major contributor to the growing market for precision gate valve sensors. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is an increasing emphasis on efficient water management systems. Precision sensors enable better control of water distribution networks, helping to reduce water loss and improve overall system performance.
Chemical processing plants require highly accurate flow control to maintain product quality and ensure safety. The demand for precision gate valve sensors in this sector is driven by the need for precise control of chemical reactions and the ability to quickly respond to process variations.
In the power generation industry, the push for greater energy efficiency and reduced emissions has led to increased adoption of advanced control systems, including precision gate valve sensors. These sensors help optimize combustion processes, improve steam management, and enhance overall plant performance.
The market for precision gate valve sensors is also benefiting from the broader trend of industrial automation and the Internet of Things (IoT). As more industries embrace smart manufacturing concepts, the integration of advanced sensors into existing infrastructure is becoming increasingly common. This trend is expected to continue driving demand for precision gate valve sensors in the coming years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for precision gate valve sensors, owing to their well-established industrial bases and early adoption of advanced technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing investments in automation technologies.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, industries are under pressure to improve their monitoring and control capabilities. This regulatory landscape is further boosting the demand for high-precision sensors that can help companies comply with emissions standards and resource management requirements.
In the oil and gas sector, precision gate valve sensors play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient transport of fluids through pipelines. The industry's focus on minimizing leaks and maximizing throughput has led to a surge in demand for advanced sensor technologies that can provide real-time, accurate measurements of valve positions and flow rates.
The water treatment industry is another major contributor to the growing market for precision gate valve sensors. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is an increasing emphasis on efficient water management systems. Precision sensors enable better control of water distribution networks, helping to reduce water loss and improve overall system performance.
Chemical processing plants require highly accurate flow control to maintain product quality and ensure safety. The demand for precision gate valve sensors in this sector is driven by the need for precise control of chemical reactions and the ability to quickly respond to process variations.
In the power generation industry, the push for greater energy efficiency and reduced emissions has led to increased adoption of advanced control systems, including precision gate valve sensors. These sensors help optimize combustion processes, improve steam management, and enhance overall plant performance.
The market for precision gate valve sensors is also benefiting from the broader trend of industrial automation and the Internet of Things (IoT). As more industries embrace smart manufacturing concepts, the integration of advanced sensors into existing infrastructure is becoming increasingly common. This trend is expected to continue driving demand for precision gate valve sensors in the coming years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for precision gate valve sensors, owing to their well-established industrial bases and early adoption of advanced technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing investments in automation technologies.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, industries are under pressure to improve their monitoring and control capabilities. This regulatory landscape is further boosting the demand for high-precision sensors that can help companies comply with emissions standards and resource management requirements.
Current Challenges in Gate Valve Sensor Technology
Gate valve sensor technology, while advanced, still faces several significant challenges that hinder its ability to provide consistently accurate measurements in various operational environments. One of the primary issues is the susceptibility of sensors to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and pressure changes. These external influences can lead to sensor drift and calibration errors, compromising the reliability of valve position readings.
Another critical challenge lies in the miniaturization of sensor components without sacrificing performance. As industrial processes demand more compact and efficient valve systems, engineers struggle to design sensors that maintain high accuracy while fitting into increasingly confined spaces. This size constraint often leads to trade-offs between sensor sensitivity and robustness, potentially impacting long-term reliability.
The integration of sensors with existing valve infrastructure presents another hurdle. Many industrial facilities utilize legacy equipment, making it difficult to retrofit advanced sensors without significant modifications or downtime. This compatibility issue slows the adoption of new sensor technologies and limits the potential for widespread improvements in valve monitoring accuracy.
Durability and longevity of sensors in harsh industrial environments remain ongoing concerns. Exposure to corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high-pressure conditions can degrade sensor components over time, leading to reduced accuracy and increased maintenance requirements. Developing materials and protective coatings that can withstand these conditions without compromising sensor performance is a complex engineering challenge.
Power consumption and energy efficiency of sensor systems also pose significant obstacles, particularly in remote or hazardous locations where frequent battery replacements are impractical or dangerous. Balancing the need for continuous, high-precision monitoring with low power requirements is a delicate task that often involves compromises in sampling rates or data transmission frequencies.
Data processing and interpretation present additional challenges. As sensors become more sophisticated, they generate increasingly large volumes of data. Developing algorithms and software systems capable of efficiently processing this information and extracting meaningful insights in real-time is crucial for leveraging the full potential of advanced sensor technologies.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of implementing high-accuracy sensor systems across large-scale industrial operations remains a significant barrier. While the benefits of improved accuracy are clear, justifying the substantial investment required for widespread sensor upgrades can be difficult, especially in industries with tight profit margins or those facing economic uncertainties.
Another critical challenge lies in the miniaturization of sensor components without sacrificing performance. As industrial processes demand more compact and efficient valve systems, engineers struggle to design sensors that maintain high accuracy while fitting into increasingly confined spaces. This size constraint often leads to trade-offs between sensor sensitivity and robustness, potentially impacting long-term reliability.
The integration of sensors with existing valve infrastructure presents another hurdle. Many industrial facilities utilize legacy equipment, making it difficult to retrofit advanced sensors without significant modifications or downtime. This compatibility issue slows the adoption of new sensor technologies and limits the potential for widespread improvements in valve monitoring accuracy.
Durability and longevity of sensors in harsh industrial environments remain ongoing concerns. Exposure to corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high-pressure conditions can degrade sensor components over time, leading to reduced accuracy and increased maintenance requirements. Developing materials and protective coatings that can withstand these conditions without compromising sensor performance is a complex engineering challenge.
Power consumption and energy efficiency of sensor systems also pose significant obstacles, particularly in remote or hazardous locations where frequent battery replacements are impractical or dangerous. Balancing the need for continuous, high-precision monitoring with low power requirements is a delicate task that often involves compromises in sampling rates or data transmission frequencies.
Data processing and interpretation present additional challenges. As sensors become more sophisticated, they generate increasingly large volumes of data. Developing algorithms and software systems capable of efficiently processing this information and extracting meaningful insights in real-time is crucial for leveraging the full potential of advanced sensor technologies.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of implementing high-accuracy sensor systems across large-scale industrial operations remains a significant barrier. While the benefits of improved accuracy are clear, justifying the substantial investment required for widespread sensor upgrades can be difficult, especially in industries with tight profit margins or those facing economic uncertainties.
State-of-the-Art Gate Valve Sensor Solutions
01 Sensor integration for improved accuracy
Gate valves can be equipped with integrated sensors to enhance accuracy in position detection and control. These sensors can include position sensors, pressure sensors, or flow sensors that provide real-time data on valve status and performance. The integration of sensors allows for more precise monitoring and control of valve operations, leading to improved accuracy in various industrial applications.- Sensor integration for improved accuracy: Gate valves can be equipped with integrated sensors to enhance accuracy in position detection and control. These sensors provide real-time feedback on valve position, enabling precise monitoring and adjustment. Advanced sensor technologies, such as Hall effect sensors or optical encoders, can be utilized to achieve high accuracy in valve position measurement.
- Calibration techniques for sensor accuracy: Implementing proper calibration techniques is crucial for maintaining sensor accuracy in gate valve systems. Regular calibration procedures can compensate for environmental factors, wear, and drift, ensuring consistent and reliable measurements over time. Advanced calibration methods may involve automated processes or self-calibrating sensors to minimize human error and improve overall accuracy.
- Multi-sensor systems for enhanced accuracy: Utilizing multiple sensors in gate valve systems can significantly improve accuracy by providing redundant measurements and cross-validation. This approach helps to eliminate errors from individual sensor failures or inaccuracies. Different types of sensors can be combined to measure various parameters, such as position, pressure, and flow, for a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of valve performance.
- Digital signal processing for improved accuracy: Implementing advanced digital signal processing techniques can enhance the accuracy of gate valve sensors. These methods can include noise reduction algorithms, data fusion from multiple sensors, and adaptive filtering. By processing raw sensor data through sophisticated algorithms, the system can achieve higher precision in valve position and control, even in challenging operating conditions.
- Environmental compensation for sensor accuracy: Developing sensors with built-in environmental compensation can improve accuracy in varying operating conditions. These sensors can account for factors such as temperature, pressure, and vibration that may affect measurements. By incorporating compensation mechanisms, the sensors can maintain high accuracy across a wide range of environmental conditions, ensuring reliable gate valve operation in diverse applications.
02 Advanced sensor technologies for gate valves
Implementing advanced sensor technologies in gate valves can significantly improve accuracy. These may include optical sensors, ultrasonic sensors, or magnetic sensors that offer high-precision measurements of valve position and movement. Such technologies can provide more accurate readings even in challenging environments, enhancing overall valve performance and reliability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Calibration and compensation techniques
To enhance gate valve sensor accuracy, various calibration and compensation techniques can be employed. These may involve software algorithms that account for environmental factors, wear and tear, or other variables that could affect sensor readings. Regular calibration procedures and adaptive compensation methods can help maintain high accuracy over the valve's operational lifetime.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multi-sensor systems for redundancy and accuracy
Implementing multi-sensor systems in gate valves can improve overall accuracy through redundancy and cross-validation. By using multiple sensors of the same or different types, the system can compare readings and identify discrepancies, leading to more reliable and accurate measurements. This approach can also provide fail-safe operation in case of individual sensor malfunction.Expand Specific Solutions05 Digital signal processing for enhanced accuracy
Incorporating digital signal processing (DSP) techniques in gate valve sensor systems can significantly improve accuracy. DSP can filter out noise, compensate for environmental factors, and apply advanced algorithms to raw sensor data. This results in more precise and reliable measurements of valve position, pressure, and flow, leading to improved overall performance and control of gate valves.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Gate Valve Sensor Industry
The technological advancements in gate valve sensors for increased accuracy are currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for precision in industrial processes. The global market size for smart valve sensors is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by the need for improved efficiency and automation in various industries. The technology's maturity varies among key players, with companies like Siemens AG, Honeywell International Technologies Ltd., and Emerson Electric Co. leading in innovation. These firms are developing advanced sensor technologies, integrating IoT capabilities, and improving data analytics for predictive maintenance. Other players like Fujikin, Inc. and Azbil Corp. are also making significant strides in sensor accuracy and reliability, contributing to the overall advancement of the field.
Siemens AG
Technical Solution: Siemens AG has developed advanced gate valve sensors utilizing digital twin technology and IoT integration. Their solution incorporates smart sensors with built-in diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities. The sensors use high-precision measurement techniques, including ultrasonic and electromagnetic methods, to accurately detect valve position and flow rates[1]. Siemens' gate valve sensors also feature real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to continuously improve accuracy and performance over time[2]. The system integrates seamlessly with industrial control systems and cloud platforms for comprehensive monitoring and optimization[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive solution with digital twin integration, advanced analytics, and predictive maintenance. Weaknesses: May require significant infrastructure upgrades and initial investment for full implementation.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has innovated in gate valve sensor technology by developing a new generation of MEMS-based sensors. These sensors utilize microelectromechanical systems to achieve high accuracy and reliability in valve position sensing. Bosch's solution incorporates advanced signal processing algorithms and temperature compensation techniques to ensure precise measurements across various operating conditions[4]. The company has also integrated their sensors with wireless communication protocols, enabling real-time monitoring and remote diagnostics[5]. Bosch's gate valve sensors feature self-calibration capabilities, reducing maintenance requirements and improving long-term accuracy[6].
Strengths: High precision MEMS technology, wireless connectivity, and self-calibration features. Weaknesses: May have higher unit costs compared to traditional sensor technologies.
Innovative Sensor Technologies for Gate Valves
Flow control device
PatentInactiveUS6810906B2
Innovation
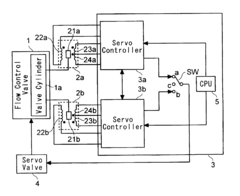
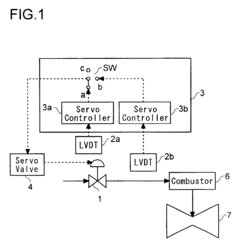
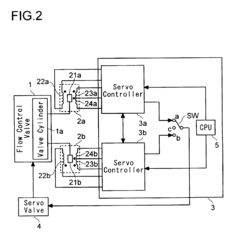
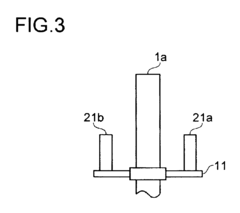
- A flow control device employing first and second linear variable differential transformers (LVDTs) with parallel secondary coils and servo controllers to monitor voltages, a switch selecting control signals based on normal performance ranges, ensuring accurate detection and fault tolerance by isolating faulty components.
Throttle valve control apparatus of internal combustion engine and automobile using the same
PatentInactiveUS7367315B2
Innovation
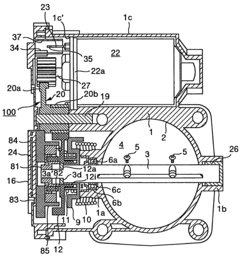
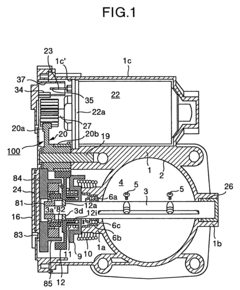
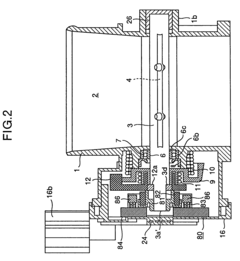
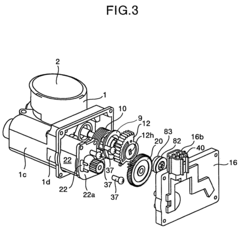
- A non-contact magnetic type throttle valve control apparatus is introduced, featuring a magnet on the throttle valve axis and a cover with hole elements that detect changes in magnetic flux, providing a long-lasting and accurate sensor system by minimizing magnetic interference and using a resin gear to prevent magnetic field leakage.
Industrial Standards for Gate Valve Sensors
Industrial standards play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of gate valve sensors across various industries. These standards provide a framework for manufacturers, operators, and regulatory bodies to maintain consistency and quality in sensor design, implementation, and operation.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards specifically addressing valve sensors and related technologies. ISO 5208 outlines the pressure testing requirements for industrial valves, including those equipped with sensors. This standard ensures that valve sensors can withstand operational pressures and maintain accuracy under various conditions.
Another relevant standard is IEC 60534, which focuses on industrial-process control valves. It includes specifications for sensor integration, signal processing, and communication protocols. This standard is particularly important for ensuring compatibility between gate valve sensors and control systems across different manufacturers.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) has also established standards relevant to gate valve sensors, particularly in the oil and gas industry. API 6D provides specifications for pipeline valves, including requirements for sensor integration and performance. This standard is widely adopted in the petroleum sector and influences sensor design for high-pressure applications.
In the process industry, the NAMUR recommendation NE 107 has gained significant traction. While not a formal standard, it provides guidelines for self-monitoring and diagnosis of field devices, including valve sensors. This recommendation has been instrumental in improving sensor reliability and predictive maintenance capabilities.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed IEC 61508, a standard focusing on functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard is particularly relevant for gate valve sensors used in safety-critical applications, ensuring that sensor failures do not compromise overall system safety.
Compliance with these standards often requires rigorous testing and certification processes. Organizations like TÜV and UL provide third-party verification services to ensure that gate valve sensors meet the required standards. This certification process adds an extra layer of assurance for end-users regarding the reliability and accuracy of the sensors.
As technology advances, these standards are regularly reviewed and updated to incorporate new developments. For instance, the increasing use of digital communication protocols in valve sensors has led to the development of standards like HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) and FOUNDATION Fieldbus, which specify communication interfaces for industrial sensors and actuators.
The adoption of these standards has significantly contributed to the increased accuracy and reliability of gate valve sensors. By providing a common framework for design and performance criteria, these standards have driven innovation while ensuring interoperability and safety across different industries and applications.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards specifically addressing valve sensors and related technologies. ISO 5208 outlines the pressure testing requirements for industrial valves, including those equipped with sensors. This standard ensures that valve sensors can withstand operational pressures and maintain accuracy under various conditions.
Another relevant standard is IEC 60534, which focuses on industrial-process control valves. It includes specifications for sensor integration, signal processing, and communication protocols. This standard is particularly important for ensuring compatibility between gate valve sensors and control systems across different manufacturers.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) has also established standards relevant to gate valve sensors, particularly in the oil and gas industry. API 6D provides specifications for pipeline valves, including requirements for sensor integration and performance. This standard is widely adopted in the petroleum sector and influences sensor design for high-pressure applications.
In the process industry, the NAMUR recommendation NE 107 has gained significant traction. While not a formal standard, it provides guidelines for self-monitoring and diagnosis of field devices, including valve sensors. This recommendation has been instrumental in improving sensor reliability and predictive maintenance capabilities.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed IEC 61508, a standard focusing on functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard is particularly relevant for gate valve sensors used in safety-critical applications, ensuring that sensor failures do not compromise overall system safety.
Compliance with these standards often requires rigorous testing and certification processes. Organizations like TÜV and UL provide third-party verification services to ensure that gate valve sensors meet the required standards. This certification process adds an extra layer of assurance for end-users regarding the reliability and accuracy of the sensors.
As technology advances, these standards are regularly reviewed and updated to incorporate new developments. For instance, the increasing use of digital communication protocols in valve sensors has led to the development of standards like HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) and FOUNDATION Fieldbus, which specify communication interfaces for industrial sensors and actuators.
The adoption of these standards has significantly contributed to the increased accuracy and reliability of gate valve sensors. By providing a common framework for design and performance criteria, these standards have driven innovation while ensuring interoperability and safety across different industries and applications.
Environmental Impact of Advanced Sensor Technologies
The integration of advanced sensor technologies in gate valve systems has significant environmental implications that extend beyond operational efficiency. These sensors, designed to enhance accuracy and control in valve operations, contribute to reduced resource waste and improved environmental stewardship in industrial processes.
One of the primary environmental benefits of advanced gate valve sensors is the substantial reduction in fluid leakage. By providing more precise measurements and control, these sensors enable tighter sealing and more accurate valve positioning. This results in minimized losses of potentially hazardous or environmentally harmful substances, reducing the risk of soil and water contamination. In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment, this improvement translates to a notable decrease in environmental incidents and associated cleanup costs.
Energy efficiency is another key area where advanced sensor technologies make a positive environmental impact. The increased accuracy in valve control allows for optimized flow rates and pressure management, leading to reduced energy consumption in pumping and processing systems. This efficiency gain not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to decreased carbon emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
The longevity and reliability of gate valves equipped with advanced sensors also play a role in environmental conservation. These sensors enable predictive maintenance strategies, allowing operators to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach extends the lifespan of valve systems, reducing the frequency of replacements and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing and disposing of valve components.
In water management applications, the precision offered by advanced gate valve sensors contributes to more effective conservation efforts. By enabling finer control over water distribution and usage, these technologies help minimize water waste in agricultural, municipal, and industrial settings. This is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity, where every drop saved has significant environmental value.
The environmental benefits of these sensor technologies extend to air quality management as well. In industrial processes where gas flows are controlled by gate valves, improved accuracy leads to better emission control. This is particularly relevant in industries subject to strict environmental regulations, where precise monitoring and control of gaseous emissions are essential for compliance and environmental protection.
However, it's important to consider the environmental impact of the sensors themselves. The production of advanced electronic components often involves rare earth elements and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. As the adoption of these technologies increases, there is a growing need for sustainable production methods and responsible end-of-life management for these sensor systems to ensure their overall environmental benefit remains positive.
One of the primary environmental benefits of advanced gate valve sensors is the substantial reduction in fluid leakage. By providing more precise measurements and control, these sensors enable tighter sealing and more accurate valve positioning. This results in minimized losses of potentially hazardous or environmentally harmful substances, reducing the risk of soil and water contamination. In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment, this improvement translates to a notable decrease in environmental incidents and associated cleanup costs.
Energy efficiency is another key area where advanced sensor technologies make a positive environmental impact. The increased accuracy in valve control allows for optimized flow rates and pressure management, leading to reduced energy consumption in pumping and processing systems. This efficiency gain not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to decreased carbon emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
The longevity and reliability of gate valves equipped with advanced sensors also play a role in environmental conservation. These sensors enable predictive maintenance strategies, allowing operators to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach extends the lifespan of valve systems, reducing the frequency of replacements and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing and disposing of valve components.
In water management applications, the precision offered by advanced gate valve sensors contributes to more effective conservation efforts. By enabling finer control over water distribution and usage, these technologies help minimize water waste in agricultural, municipal, and industrial settings. This is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity, where every drop saved has significant environmental value.
The environmental benefits of these sensor technologies extend to air quality management as well. In industrial processes where gas flows are controlled by gate valves, improved accuracy leads to better emission control. This is particularly relevant in industries subject to strict environmental regulations, where precise monitoring and control of gaseous emissions are essential for compliance and environmental protection.
However, it's important to consider the environmental impact of the sensors themselves. The production of advanced electronic components often involves rare earth elements and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. As the adoption of these technologies increases, there is a growing need for sustainable production methods and responsible end-of-life management for these sensor systems to ensure their overall environmental benefit remains positive.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!