The Role of Battery Pack Design in Energy Resilience Planning
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Battery Technology Evolution and Resilience Goals
Battery technology has evolved significantly over the past decades, transitioning from simple lead-acid configurations to advanced lithium-ion chemistries and beyond. This evolution has been driven by increasing demands for energy density, longevity, safety, and sustainability across various applications. The early 2000s marked a pivotal shift with the commercialization of lithium-ion batteries, which offered substantially higher energy densities compared to previous technologies. By 2010, these batteries had become the dominant technology for portable electronics and were beginning to penetrate the electric vehicle market.
The mid-2010s witnessed accelerated innovation in battery management systems (BMS), thermal regulation, and cell chemistry optimization. Energy densities improved from approximately 100 Wh/kg to over 250 Wh/kg in commercial applications, while costs decreased from over $1,000/kWh to under $200/kWh by 2020. This dramatic cost reduction, coupled with performance improvements, has transformed batteries from specialized components to critical infrastructure elements.
In parallel with these technological advancements, the concept of energy resilience has gained prominence in response to increasing climate-related disruptions, cybersecurity threats, and grid instability events. Energy resilience refers to the ability of energy systems to prepare for, withstand, and recover from disruptions while maintaining critical functions. Battery systems have emerged as key enablers of resilience strategies due to their ability to store energy during normal operations and discharge during emergencies.
The convergence of battery technology evolution and resilience goals has created new design imperatives for battery pack systems. Modern battery packs must not only deliver high energy density and long cycle life but also incorporate features that enhance system resilience. These include rapid response capabilities, islanding functionality, black start capability, and intelligent load management. The resilience goals for battery systems typically include providing backup power for critical loads, supporting microgrid operations during grid outages, enabling peak shaving to reduce strain on aging infrastructure, and facilitating the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Looking forward, battery technology evolution is increasingly being shaped by resilience requirements. Next-generation battery packs are being designed with modular architectures that allow for redundancy and graceful degradation rather than catastrophic failure. Advanced BMS designs incorporate predictive analytics and machine learning to anticipate potential failures and optimize performance under stress conditions. Materials science innovations are focusing on chemistries that offer improved thermal stability and resistance to extreme environmental conditions, directly addressing resilience concerns in regions facing increasing climate volatility.
The mid-2010s witnessed accelerated innovation in battery management systems (BMS), thermal regulation, and cell chemistry optimization. Energy densities improved from approximately 100 Wh/kg to over 250 Wh/kg in commercial applications, while costs decreased from over $1,000/kWh to under $200/kWh by 2020. This dramatic cost reduction, coupled with performance improvements, has transformed batteries from specialized components to critical infrastructure elements.
In parallel with these technological advancements, the concept of energy resilience has gained prominence in response to increasing climate-related disruptions, cybersecurity threats, and grid instability events. Energy resilience refers to the ability of energy systems to prepare for, withstand, and recover from disruptions while maintaining critical functions. Battery systems have emerged as key enablers of resilience strategies due to their ability to store energy during normal operations and discharge during emergencies.
The convergence of battery technology evolution and resilience goals has created new design imperatives for battery pack systems. Modern battery packs must not only deliver high energy density and long cycle life but also incorporate features that enhance system resilience. These include rapid response capabilities, islanding functionality, black start capability, and intelligent load management. The resilience goals for battery systems typically include providing backup power for critical loads, supporting microgrid operations during grid outages, enabling peak shaving to reduce strain on aging infrastructure, and facilitating the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Looking forward, battery technology evolution is increasingly being shaped by resilience requirements. Next-generation battery packs are being designed with modular architectures that allow for redundancy and graceful degradation rather than catastrophic failure. Advanced BMS designs incorporate predictive analytics and machine learning to anticipate potential failures and optimize performance under stress conditions. Materials science innovations are focusing on chemistries that offer improved thermal stability and resistance to extreme environmental conditions, directly addressing resilience concerns in regions facing increasing climate volatility.
Market Analysis for Energy Storage Solutions
The global energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and the growing need for grid resilience. As of 2023, the market valuation stands at approximately $27 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 20-25% over the next decade. Battery energy storage systems (BESS) dominate this landscape, accounting for over 70% of new installations, with lithium-ion technologies maintaining market leadership despite emerging alternatives.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a significant shift toward distributed energy resources, with residential and commercial sectors showing increased interest in behind-the-meter storage solutions. This trend is particularly evident in regions with high electricity costs or vulnerable grid infrastructure. Market research indicates that energy resilience has become a primary purchase driver, surpassing even cost savings in some segments, especially following major climate-related disruptions.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to accommodate and incentivize energy storage deployment. Several major markets have introduced capacity payments, time-of-use rate structures, and specific resilience incentives that directly benefit battery storage systems. These policy developments have created market opportunities valued at approximately $5 billion annually across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions.
Competitive analysis reveals a market bifurcation between large-scale utility solutions and modular commercial/residential offerings. The former segment is dominated by established energy conglomerates and specialized storage providers, while the latter shows greater fragmentation with numerous innovative startups gaining market share. Battery pack design has emerged as a critical differentiator, with companies investing heavily in thermal management, modular architectures, and intelligent battery management systems.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across market segments. Utility-scale projects remain highly cost-driven, with levelized cost of storage (LCOS) being the primary metric. In contrast, commercial and residential customers demonstrate willingness to pay premiums of 15-30% for systems offering enhanced resilience features, such as rapid response capabilities, longer duration discharge, and intelligent load management during outages.
Market forecasts indicate that battery pack designs optimized specifically for resilience applications will capture an increasing share of new installations, potentially reaching 40% of the commercial market by 2028. This represents a significant opportunity for manufacturers who can effectively balance energy density, cycle life, safety features, and intelligent control systems in their battery pack designs.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a significant shift toward distributed energy resources, with residential and commercial sectors showing increased interest in behind-the-meter storage solutions. This trend is particularly evident in regions with high electricity costs or vulnerable grid infrastructure. Market research indicates that energy resilience has become a primary purchase driver, surpassing even cost savings in some segments, especially following major climate-related disruptions.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to accommodate and incentivize energy storage deployment. Several major markets have introduced capacity payments, time-of-use rate structures, and specific resilience incentives that directly benefit battery storage systems. These policy developments have created market opportunities valued at approximately $5 billion annually across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions.
Competitive analysis reveals a market bifurcation between large-scale utility solutions and modular commercial/residential offerings. The former segment is dominated by established energy conglomerates and specialized storage providers, while the latter shows greater fragmentation with numerous innovative startups gaining market share. Battery pack design has emerged as a critical differentiator, with companies investing heavily in thermal management, modular architectures, and intelligent battery management systems.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across market segments. Utility-scale projects remain highly cost-driven, with levelized cost of storage (LCOS) being the primary metric. In contrast, commercial and residential customers demonstrate willingness to pay premiums of 15-30% for systems offering enhanced resilience features, such as rapid response capabilities, longer duration discharge, and intelligent load management during outages.
Market forecasts indicate that battery pack designs optimized specifically for resilience applications will capture an increasing share of new installations, potentially reaching 40% of the commercial market by 2028. This represents a significant opportunity for manufacturers who can effectively balance energy density, cycle life, safety features, and intelligent control systems in their battery pack designs.
Current Challenges in Battery Pack Design
Battery pack design for energy resilience faces significant technical challenges that must be addressed to meet growing demands for reliable energy storage solutions. Current battery pack designs struggle with thermal management issues, particularly in high-power applications where heat generation can lead to reduced efficiency, accelerated degradation, and safety concerns. Conventional cooling systems often prove inadequate for maintaining optimal temperature ranges across all cells within large-scale battery packs, resulting in thermal gradients that create performance inconsistencies.
Energy density limitations represent another major challenge, as current lithium-ion technologies approach their theoretical limits. While incremental improvements continue, the energy-to-weight and energy-to-volume ratios remain insufficient for many resilience applications that require extended backup power capabilities without excessive space requirements or weight constraints.
Safety concerns persist despite advances in battery management systems. Thermal runaway events, though rare, continue to pose significant risks, especially in large-scale installations where cascading failures could have catastrophic consequences. Current protection mechanisms add complexity, weight, and cost while sometimes reducing overall energy density.
Lifecycle management presents ongoing difficulties, with battery degradation patterns proving difficult to predict accurately across varied usage conditions. Current battery management systems struggle to optimize charging and discharging protocols to maximize longevity while maintaining performance, particularly when batteries experience irregular usage patterns typical in resilience applications.
Standardization remains elusive across the industry, with proprietary designs limiting interoperability and increasing costs. The lack of universal standards for battery pack interfaces, communication protocols, and physical dimensions complicates integration into broader energy systems and hinders the development of modular solutions that could enhance resilience through redundancy and scalability.
Cost factors continue to challenge widespread adoption, with high-quality battery packs requiring expensive materials, sophisticated management systems, and complex manufacturing processes. While prices have declined, the total cost of ownership remains prohibitive for many potential applications, especially when factoring in maintenance, replacement, and end-of-life disposal considerations.
Integration with renewable energy sources presents additional technical hurdles, as battery systems must accommodate the variable and sometimes unpredictable nature of renewable generation. Current battery management algorithms struggle to optimize charging cycles when paired with intermittent sources like solar or wind, potentially reducing overall system efficiency and battery lifespan.
Energy density limitations represent another major challenge, as current lithium-ion technologies approach their theoretical limits. While incremental improvements continue, the energy-to-weight and energy-to-volume ratios remain insufficient for many resilience applications that require extended backup power capabilities without excessive space requirements or weight constraints.
Safety concerns persist despite advances in battery management systems. Thermal runaway events, though rare, continue to pose significant risks, especially in large-scale installations where cascading failures could have catastrophic consequences. Current protection mechanisms add complexity, weight, and cost while sometimes reducing overall energy density.
Lifecycle management presents ongoing difficulties, with battery degradation patterns proving difficult to predict accurately across varied usage conditions. Current battery management systems struggle to optimize charging and discharging protocols to maximize longevity while maintaining performance, particularly when batteries experience irregular usage patterns typical in resilience applications.
Standardization remains elusive across the industry, with proprietary designs limiting interoperability and increasing costs. The lack of universal standards for battery pack interfaces, communication protocols, and physical dimensions complicates integration into broader energy systems and hinders the development of modular solutions that could enhance resilience through redundancy and scalability.
Cost factors continue to challenge widespread adoption, with high-quality battery packs requiring expensive materials, sophisticated management systems, and complex manufacturing processes. While prices have declined, the total cost of ownership remains prohibitive for many potential applications, especially when factoring in maintenance, replacement, and end-of-life disposal considerations.
Integration with renewable energy sources presents additional technical hurdles, as battery systems must accommodate the variable and sometimes unpredictable nature of renewable generation. Current battery management algorithms struggle to optimize charging cycles when paired with intermittent sources like solar or wind, potentially reducing overall system efficiency and battery lifespan.
Current Battery Pack Design Approaches
01 Battery Management Systems for Energy Resilience
Advanced battery management systems (BMS) are crucial for enhancing energy resilience in battery packs. These systems monitor and control battery parameters such as state of charge, temperature, and voltage to optimize performance and prevent failures. By implementing intelligent algorithms and control strategies, BMS can extend battery life, improve safety, and ensure reliable operation during power disruptions, contributing significantly to overall energy resilience.- Battery Management Systems for Energy Resilience: Advanced battery management systems (BMS) are crucial for enhancing energy resilience in battery packs. These systems monitor and control battery parameters such as state of charge, temperature, and voltage to optimize performance and prevent failures. By implementing intelligent algorithms and predictive analytics, BMS can extend battery life, improve safety, and ensure reliable operation during power disruptions, contributing significantly to overall energy resilience.
- Modular Battery Pack Architectures: Modular battery pack designs enhance energy resilience by allowing for flexible configuration, easy maintenance, and fault isolation. These architectures enable the replacement of individual modules without compromising the entire system, improving overall reliability. Modular designs also facilitate scalability, allowing systems to be expanded or reduced based on energy requirements, and can incorporate redundancy features that maintain power supply even when some modules fail.
- Thermal Management Solutions: Effective thermal management is essential for battery pack resilience, as temperature extremes can significantly impact performance and longevity. Advanced cooling and heating systems maintain optimal operating temperatures across various environmental conditions. These solutions include liquid cooling circuits, phase-change materials, and intelligent thermal control algorithms that prevent thermal runaway and ensure consistent performance, thereby enhancing the overall energy resilience of battery systems.
- Energy Storage Integration with Renewable Sources: Battery pack designs that integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources significantly enhance energy resilience. These systems incorporate smart charging algorithms that optimize energy capture from intermittent sources like solar and wind. By effectively storing excess energy during peak production periods and releasing it during shortages, these integrated systems provide consistent power supply despite fluctuations in renewable generation, creating more resilient and sustainable energy ecosystems.
- Fault Detection and Self-Healing Capabilities: Advanced battery packs incorporate sophisticated fault detection systems and self-healing capabilities to maintain energy resilience. These features include real-time monitoring sensors, diagnostic algorithms, and automated response mechanisms that can identify potential failures before they occur. Some designs implement redundant pathways for current flow, allowing the system to automatically reroute power around damaged cells or components, thereby maintaining operation during partial failures and enhancing overall system reliability.
02 Thermal Management Solutions for Battery Packs
Effective thermal management is essential for battery pack resilience and longevity. Innovative cooling and heating systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures across all cells, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring consistent performance under various environmental conditions. These solutions include liquid cooling circuits, phase change materials, and intelligent thermal control systems that adapt to changing conditions, thereby enhancing the energy resilience of battery storage systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modular and Scalable Battery Pack Architectures
Modular battery pack designs improve energy resilience by allowing for flexible configuration, easier maintenance, and fault isolation. These architectures enable the system to continue functioning even if individual modules fail, providing redundancy and enhanced reliability. Scalable designs also facilitate capacity expansion and technology upgrades without replacing the entire system, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term energy resilience and adaptability to changing energy demands.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy Storage System Integration and Grid Support
Battery packs designed for energy resilience incorporate advanced integration capabilities with power grids and renewable energy sources. These systems feature bidirectional power flow, enabling functions such as peak shaving, load shifting, and grid stabilization. During outages, they can provide backup power through seamless transition mechanisms. Sophisticated control algorithms optimize energy flow between multiple sources and loads, enhancing overall system resilience and supporting critical infrastructure during disruptions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced Materials and Cell Technologies for Resilient Battery Packs
Innovative materials and cell technologies significantly improve battery pack resilience. These include high-energy density cathode materials, solid-state electrolytes, and advanced anode compositions that enhance safety, cycle life, and performance under stress conditions. Structural battery designs that integrate energy storage into load-bearing components offer additional resilience benefits. These material innovations enable battery packs to withstand harsh environments, rapid charge/discharge cycles, and extended periods of operation, critical for energy resilience applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Energy Storage
The battery pack design market for energy resilience is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by renewable energy integration and grid stability concerns. The market is expected to reach significant scale as energy storage becomes critical for resilience planning. Technologically, established players like LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and SK On lead with advanced lithium-ion technologies, while companies like Huawei Digital Power and EVE Energy are rapidly advancing in integrated energy management systems. Traditional automotive manufacturers such as Nissan are leveraging their EV expertise to develop stationary storage solutions. Research institutions like Tsinghua University and Huazhong University of Science & Technology are contributing breakthrough innovations, positioning battery pack design as a critical component in future energy infrastructure.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed advanced battery pack designs that integrate intelligent Battery Management Systems (BMS) with predictive analytics capabilities. Their modular battery architecture allows for flexible deployment in various energy resilience applications, from residential to utility-scale installations. The company's battery packs feature advanced thermal management systems that utilize phase-change materials and liquid cooling technologies to maintain optimal operating temperatures even during extreme weather events[1]. Their energy storage solutions incorporate AI-driven load forecasting and energy management algorithms that can predict grid instabilities and automatically switch to backup power mode with minimal transition time[3]. LG Energy Solution's battery packs also feature bidirectional charging capabilities, enabling them to participate in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) applications, further enhancing energy resilience by creating distributed energy resources that can be aggregated during grid emergencies[5].
Strengths: Superior thermal management technology provides exceptional performance during extreme weather events; AI-driven energy management optimizes battery utilization and extends lifespan; modular design allows for scalable solutions across different applications. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to some competitors; proprietary BMS may limit integration with third-party systems; dependency on specific rare earth materials could create supply chain vulnerabilities.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has pioneered a comprehensive battery pack design approach focused on energy resilience through their E-PACK platform. This system integrates high-energy density lithium-ion cells with advanced safety features including multi-layer protection circuits and real-time monitoring capabilities. Their battery packs employ a proprietary cell-to-pack technology that eliminates module housings, increasing energy density by approximately 10% while reducing weight[2]. For energy resilience applications, Samsung has developed specialized Battery Management Systems that can operate in islanded mode during grid outages, with response times under 20 milliseconds to ensure uninterrupted power supply to critical infrastructure[4]. The company's battery packs feature advanced thermal runaway prevention through their "Thermal Barrier" technology, which physically isolates cells to prevent cascading failures. Additionally, Samsung's energy storage solutions incorporate predictive maintenance algorithms that can detect potential failures before they occur, significantly enhancing system reliability during critical grid events[7].
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density provides longer backup times in smaller footprints; ultra-fast response times ensure seamless transition during outages; advanced thermal management prevents catastrophic failures. Weaknesses: Premium pricing positions products at the higher end of the market; complex integration requirements may increase installation costs; limited compatibility with some third-party energy management systems.
Critical Patents in Battery Pack Architecture
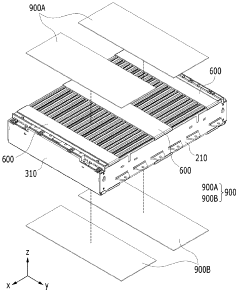
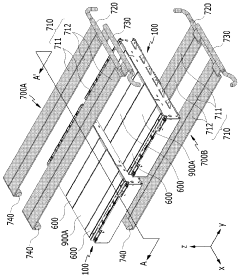
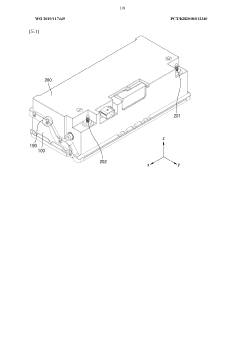
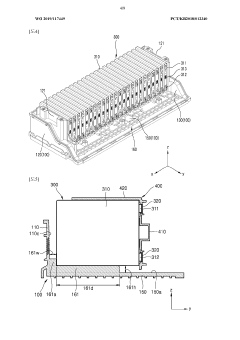
Battery pack and device comprising same
PatentWO2023172106A1
Innovation
- The battery pack design incorporates a battery cell stack with side plates and a connecting member, a pack tray, and a heat sink with upper and lower cooling units through which refrigerant flows, allowing for improved heat dissipation and reduced weight by integrating the cooling structure within the module housing.
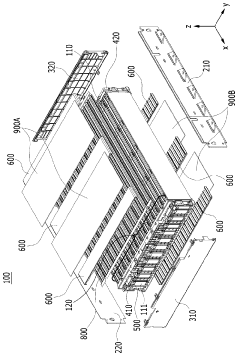
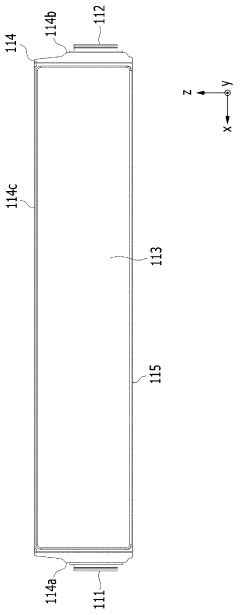
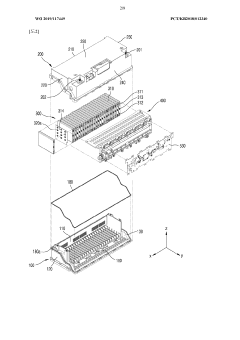
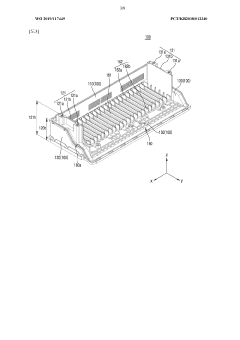
Battery pack
PatentWO2019117449A1
Innovation
- A battery pack design with reduced components, featuring a lower and upper case structure with specific side wall configurations, fastening members, and a holder unit for efficient temperature control and weight reduction, allowing for direct seating of battery cells without a module structure.
Grid Integration Strategies
Effective grid integration of battery systems represents a critical component in maximizing the value of battery pack designs for energy resilience planning. The integration approach must consider both technical compatibility and operational synergy between battery systems and existing grid infrastructure. Modern grid integration strategies typically follow a multi-layered framework that addresses physical connections, communication protocols, and operational coordination.
Primary integration methodologies include direct coupling, where battery systems connect directly to distribution networks, and indirect coupling through intermediary power conversion systems that provide additional control capabilities. The selection between these approaches depends on voltage levels, response time requirements, and the specific resilience objectives being targeted. Advanced battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in facilitating seamless grid integration by enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy flows.
Communication protocols represent another essential aspect of grid integration. Standards such as IEEE 2030.5, IEC 61850, and OpenADR have emerged as dominant frameworks for enabling interoperability between battery systems and grid operators. These protocols support critical functions including automated demand response, frequency regulation, and coordinated islanding during grid disturbances. The implementation of secure, low-latency communication channels ensures that battery resources can respond rapidly to grid signals.
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence integration strategies across different markets. In regions with established ancillary service markets, battery systems can be configured to prioritize frequency regulation and voltage support capabilities. Conversely, in areas focused on resilience against extreme weather events, integration strategies may emphasize islanding capabilities and black start functionality. The regulatory environment also determines interconnection requirements, which must be carefully considered during battery pack design phases.
Virtual power plant (VPP) architectures represent an emerging integration approach that aggregates distributed battery resources to provide grid services at scale. This model enables smaller battery installations to collectively participate in wholesale markets and provide meaningful grid support. For resilience planning, VPP frameworks can coordinate distributed battery resources during emergencies to maintain power to critical infrastructure while supporting broader grid stability.
Future grid integration strategies are increasingly focused on predictive capabilities that leverage weather forecasting, load prediction, and machine learning algorithms to optimize battery operation. These advanced approaches enable proactive management of battery resources in anticipation of grid disturbances rather than reactive responses after disruptions occur. The integration of these predictive elements represents a significant advancement in maximizing the resilience value of battery systems within modern grid architectures.
Primary integration methodologies include direct coupling, where battery systems connect directly to distribution networks, and indirect coupling through intermediary power conversion systems that provide additional control capabilities. The selection between these approaches depends on voltage levels, response time requirements, and the specific resilience objectives being targeted. Advanced battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in facilitating seamless grid integration by enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy flows.
Communication protocols represent another essential aspect of grid integration. Standards such as IEEE 2030.5, IEC 61850, and OpenADR have emerged as dominant frameworks for enabling interoperability between battery systems and grid operators. These protocols support critical functions including automated demand response, frequency regulation, and coordinated islanding during grid disturbances. The implementation of secure, low-latency communication channels ensures that battery resources can respond rapidly to grid signals.
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence integration strategies across different markets. In regions with established ancillary service markets, battery systems can be configured to prioritize frequency regulation and voltage support capabilities. Conversely, in areas focused on resilience against extreme weather events, integration strategies may emphasize islanding capabilities and black start functionality. The regulatory environment also determines interconnection requirements, which must be carefully considered during battery pack design phases.
Virtual power plant (VPP) architectures represent an emerging integration approach that aggregates distributed battery resources to provide grid services at scale. This model enables smaller battery installations to collectively participate in wholesale markets and provide meaningful grid support. For resilience planning, VPP frameworks can coordinate distributed battery resources during emergencies to maintain power to critical infrastructure while supporting broader grid stability.
Future grid integration strategies are increasingly focused on predictive capabilities that leverage weather forecasting, load prediction, and machine learning algorithms to optimize battery operation. These advanced approaches enable proactive management of battery resources in anticipation of grid disturbances rather than reactive responses after disruptions occur. The integration of these predictive elements represents a significant advancement in maximizing the resilience value of battery systems within modern grid architectures.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Battery pack design plays a crucial role in determining the environmental footprint of energy resilience systems. The materials used in battery manufacturing, particularly lithium, cobalt, and nickel, involve resource-intensive extraction processes that can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and significant carbon emissions. Modern battery pack designs increasingly incorporate recycled materials and sustainable sourcing practices to mitigate these impacts, with some manufacturers achieving up to 30% reduction in carbon footprint through these approaches.
The lifecycle assessment of battery packs reveals that production phase accounts for approximately 70% of their total environmental impact. However, innovative designs focusing on longevity and efficiency can substantially reduce the cumulative environmental burden by extending operational lifespans from the current average of 8-10 years to potentially 15-20 years. This extension significantly improves the environmental return on investment for energy resilience infrastructure.
End-of-life management represents another critical environmental consideration. Advanced battery pack designs now incorporate modular components that facilitate easier disassembly and material recovery. These design innovations have increased recycling efficiency rates from below 50% to over 80% for certain battery chemistries, dramatically reducing waste and the need for virgin material extraction.
Thermal management systems within battery packs also influence environmental performance. Passive cooling designs that minimize or eliminate the need for energy-intensive active cooling can reduce operational carbon emissions by 15-25% compared to conventional systems. This improvement becomes particularly significant in off-grid resilience applications where energy efficiency directly translates to reduced fossil fuel consumption.
The environmental impact of battery packs extends to their integration with renewable energy sources. Optimized battery designs that efficiently capture and store intermittent renewable energy can displace up to 90% of fossil fuel generation in hybrid systems, substantially reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Studies indicate that each kilowatt-hour of properly designed battery storage integrated with renewables can prevent approximately 0.5-0.7 kg of CO2 emissions compared to traditional backup power solutions.
Water usage represents an often overlooked environmental aspect of battery systems. Advanced manufacturing processes for next-generation battery packs have reduced water requirements by up to 60% compared to earlier designs, addressing concerns about water scarcity in regions where battery production is concentrated. This improvement is particularly relevant as climate change exacerbates water security challenges globally.
The lifecycle assessment of battery packs reveals that production phase accounts for approximately 70% of their total environmental impact. However, innovative designs focusing on longevity and efficiency can substantially reduce the cumulative environmental burden by extending operational lifespans from the current average of 8-10 years to potentially 15-20 years. This extension significantly improves the environmental return on investment for energy resilience infrastructure.
End-of-life management represents another critical environmental consideration. Advanced battery pack designs now incorporate modular components that facilitate easier disassembly and material recovery. These design innovations have increased recycling efficiency rates from below 50% to over 80% for certain battery chemistries, dramatically reducing waste and the need for virgin material extraction.
Thermal management systems within battery packs also influence environmental performance. Passive cooling designs that minimize or eliminate the need for energy-intensive active cooling can reduce operational carbon emissions by 15-25% compared to conventional systems. This improvement becomes particularly significant in off-grid resilience applications where energy efficiency directly translates to reduced fossil fuel consumption.
The environmental impact of battery packs extends to their integration with renewable energy sources. Optimized battery designs that efficiently capture and store intermittent renewable energy can displace up to 90% of fossil fuel generation in hybrid systems, substantially reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Studies indicate that each kilowatt-hour of properly designed battery storage integrated with renewables can prevent approximately 0.5-0.7 kg of CO2 emissions compared to traditional backup power solutions.
Water usage represents an often overlooked environmental aspect of battery systems. Advanced manufacturing processes for next-generation battery packs have reduced water requirements by up to 60% compared to earlier designs, addressing concerns about water scarcity in regions where battery production is concentrated. This improvement is particularly relevant as climate change exacerbates water security challenges globally.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!