The Role of Power Steering Fluid in Achieving Precise Steering Control
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Power Steering Evolution
Power steering technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. The journey began with manual steering systems, which required considerable physical effort from drivers, especially when maneuvering vehicles at low speeds or during parking. This limitation led to the development of hydraulic power steering systems in the 1950s, marking a revolutionary change in automotive control.
Hydraulic power steering systems utilize a hydraulic pump driven by the engine to provide assistance to the steering mechanism. This innovation greatly reduced the effort required to steer, particularly in larger vehicles, and quickly became a standard feature in many automobiles. The hydraulic fluid plays a crucial role in transmitting power and ensuring smooth operation of the system.
As automotive technology advanced, electronic power steering (EPS) systems emerged in the 1990s. These systems replaced the hydraulic pump with an electric motor, offering several advantages such as improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance, and more precise control. EPS systems can be tailored to provide varying levels of assistance based on vehicle speed and driving conditions, enhancing both comfort and safety.
The evolution of power steering technology has also seen the development of adaptive steering systems. These advanced systems can adjust the steering ratio based on vehicle speed and driver input, providing more responsive steering at low speeds and increased stability at high speeds. This technology has further refined the driving experience and improved vehicle handling characteristics.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards integrating power steering systems with other vehicle technologies. For instance, the combination of EPS with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) has paved the way for features like lane-keeping assist and automated parking. This integration represents a significant step towards autonomous driving capabilities.
The role of power steering fluid has also evolved alongside these technological advancements. While traditional hydraulic systems rely heavily on power steering fluid for operation, modern EPS systems have reduced or eliminated the need for hydraulic fluid. However, in systems where fluid is still used, its composition and properties have been refined to enhance performance, durability, and environmental compatibility.
Looking ahead, the future of power steering technology is likely to see further integration with electric and autonomous vehicle systems. As vehicles become more electrified and computerized, power steering systems will continue to evolve, potentially incorporating more advanced sensors and artificial intelligence to provide even more precise and adaptive steering control.
Hydraulic power steering systems utilize a hydraulic pump driven by the engine to provide assistance to the steering mechanism. This innovation greatly reduced the effort required to steer, particularly in larger vehicles, and quickly became a standard feature in many automobiles. The hydraulic fluid plays a crucial role in transmitting power and ensuring smooth operation of the system.
As automotive technology advanced, electronic power steering (EPS) systems emerged in the 1990s. These systems replaced the hydraulic pump with an electric motor, offering several advantages such as improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance, and more precise control. EPS systems can be tailored to provide varying levels of assistance based on vehicle speed and driving conditions, enhancing both comfort and safety.
The evolution of power steering technology has also seen the development of adaptive steering systems. These advanced systems can adjust the steering ratio based on vehicle speed and driver input, providing more responsive steering at low speeds and increased stability at high speeds. This technology has further refined the driving experience and improved vehicle handling characteristics.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards integrating power steering systems with other vehicle technologies. For instance, the combination of EPS with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) has paved the way for features like lane-keeping assist and automated parking. This integration represents a significant step towards autonomous driving capabilities.
The role of power steering fluid has also evolved alongside these technological advancements. While traditional hydraulic systems rely heavily on power steering fluid for operation, modern EPS systems have reduced or eliminated the need for hydraulic fluid. However, in systems where fluid is still used, its composition and properties have been refined to enhance performance, durability, and environmental compatibility.
Looking ahead, the future of power steering technology is likely to see further integration with electric and autonomous vehicle systems. As vehicles become more electrified and computerized, power steering systems will continue to evolve, potentially incorporating more advanced sensors and artificial intelligence to provide even more precise and adaptive steering control.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for power steering fluid and its role in achieving precise steering control has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing complexity of automotive steering systems and the rising consumer expectations for vehicle performance and safety. As vehicles become more sophisticated, the need for high-quality power steering fluid that can maintain optimal steering performance under various conditions has become paramount.
The global automotive power steering market, which includes power steering fluids, is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising production of vehicles worldwide, particularly in emerging economies, and the increasing adoption of electric power steering systems. The shift towards electric power steering has not eliminated the need for power steering fluid but has instead created a demand for specialized fluids that can meet the unique requirements of these systems.
In developed markets, there is a growing trend towards premium and high-performance vehicles, which require advanced power steering fluids to ensure precise handling and responsiveness. This trend is driving innovation in fluid formulations, with manufacturers focusing on developing products that offer improved thermal stability, reduced friction, and enhanced protection against wear and corrosion.
The aftermarket segment for power steering fluid also presents a substantial opportunity. As vehicles age, the need for regular maintenance and fluid replacement increases. Consumers are becoming more aware of the importance of using high-quality power steering fluid to maintain their vehicle's performance and extend the life of steering components. This awareness is fueling demand for premium aftermarket products that promise superior protection and longevity.
Environmental concerns are also shaping market demand. There is a growing preference for eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have a reduced environmental impact. Manufacturers are responding to this trend by developing bio-based fluids and formulations that meet stringent environmental standards without compromising on performance.
The commercial vehicle sector represents another significant driver of market demand. Heavy-duty trucks and buses require robust power steering systems that can withstand intense use and harsh operating conditions. This has led to the development of specialized power steering fluids designed to maintain optimal performance under extreme pressure and temperature variations.
As autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, the role of power steering fluid in achieving precise steering control is expected to evolve. These advanced vehicles will require even more precise and responsive steering systems, potentially driving demand for next-generation power steering fluids that can meet these exacting requirements.
The global automotive power steering market, which includes power steering fluids, is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising production of vehicles worldwide, particularly in emerging economies, and the increasing adoption of electric power steering systems. The shift towards electric power steering has not eliminated the need for power steering fluid but has instead created a demand for specialized fluids that can meet the unique requirements of these systems.
In developed markets, there is a growing trend towards premium and high-performance vehicles, which require advanced power steering fluids to ensure precise handling and responsiveness. This trend is driving innovation in fluid formulations, with manufacturers focusing on developing products that offer improved thermal stability, reduced friction, and enhanced protection against wear and corrosion.
The aftermarket segment for power steering fluid also presents a substantial opportunity. As vehicles age, the need for regular maintenance and fluid replacement increases. Consumers are becoming more aware of the importance of using high-quality power steering fluid to maintain their vehicle's performance and extend the life of steering components. This awareness is fueling demand for premium aftermarket products that promise superior protection and longevity.
Environmental concerns are also shaping market demand. There is a growing preference for eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have a reduced environmental impact. Manufacturers are responding to this trend by developing bio-based fluids and formulations that meet stringent environmental standards without compromising on performance.
The commercial vehicle sector represents another significant driver of market demand. Heavy-duty trucks and buses require robust power steering systems that can withstand intense use and harsh operating conditions. This has led to the development of specialized power steering fluids designed to maintain optimal performance under extreme pressure and temperature variations.
As autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, the role of power steering fluid in achieving precise steering control is expected to evolve. These advanced vehicles will require even more precise and responsive steering systems, potentially driving demand for next-generation power steering fluids that can meet these exacting requirements.
Current Challenges
Power steering fluid plays a crucial role in achieving precise steering control, yet several challenges persist in its application and performance. One of the primary issues is fluid degradation over time, which can lead to reduced steering responsiveness and increased wear on system components. Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures and humidity, can accelerate this degradation process, affecting the fluid's viscosity and lubricating properties.
Another significant challenge is the potential for contamination within the power steering system. Debris, metal particles, and moisture can enter the system, compromising the fluid's effectiveness and potentially causing damage to sensitive components. This contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced hydraulic efficiency, and ultimately, a loss of steering precision.
Maintaining proper fluid levels presents an ongoing challenge for vehicle owners and technicians. Insufficient fluid levels can result in inadequate hydraulic pressure, leading to steering difficulties and potential system damage. Conversely, overfilling can cause fluid expansion and leakage, particularly under high-temperature conditions.
The compatibility of power steering fluids with different vehicle makes and models poses another challenge. With various fluid formulations available, selecting the correct type for a specific vehicle is critical to ensure optimal performance and prevent system damage. Using incompatible fluids can lead to seal degradation, corrosion, and reduced steering efficiency.
Leakage remains a persistent issue in power steering systems. Worn seals, damaged hoses, or loose connections can result in fluid loss, compromising the system's ability to maintain proper hydraulic pressure. Detecting and addressing leaks promptly is essential to prevent steering failure and ensure safety.
The increasing complexity of modern steering systems, including electric power steering (EPS) and hybrid systems, presents new challenges in fluid management. These advanced systems may require specialized fluids or different maintenance approaches, necessitating ongoing research and development to meet evolving technological demands.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures also pose challenges to the power steering fluid industry. There is a growing need for more environmentally friendly fluid formulations that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact. This includes developing biodegradable options and reducing the use of harmful additives.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in power steering fluid specifications across manufacturers creates difficulties in fluid selection and maintenance. This variability can lead to confusion among consumers and technicians, potentially resulting in the use of incorrect fluids and subsequent system issues.
Another significant challenge is the potential for contamination within the power steering system. Debris, metal particles, and moisture can enter the system, compromising the fluid's effectiveness and potentially causing damage to sensitive components. This contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced hydraulic efficiency, and ultimately, a loss of steering precision.
Maintaining proper fluid levels presents an ongoing challenge for vehicle owners and technicians. Insufficient fluid levels can result in inadequate hydraulic pressure, leading to steering difficulties and potential system damage. Conversely, overfilling can cause fluid expansion and leakage, particularly under high-temperature conditions.
The compatibility of power steering fluids with different vehicle makes and models poses another challenge. With various fluid formulations available, selecting the correct type for a specific vehicle is critical to ensure optimal performance and prevent system damage. Using incompatible fluids can lead to seal degradation, corrosion, and reduced steering efficiency.
Leakage remains a persistent issue in power steering systems. Worn seals, damaged hoses, or loose connections can result in fluid loss, compromising the system's ability to maintain proper hydraulic pressure. Detecting and addressing leaks promptly is essential to prevent steering failure and ensure safety.
The increasing complexity of modern steering systems, including electric power steering (EPS) and hybrid systems, presents new challenges in fluid management. These advanced systems may require specialized fluids or different maintenance approaches, necessitating ongoing research and development to meet evolving technological demands.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures also pose challenges to the power steering fluid industry. There is a growing need for more environmentally friendly fluid formulations that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact. This includes developing biodegradable options and reducing the use of harmful additives.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in power steering fluid specifications across manufacturers creates difficulties in fluid selection and maintenance. This variability can lead to confusion among consumers and technicians, potentially resulting in the use of incorrect fluids and subsequent system issues.
Existing Fluid Solutions
01 Power steering fluid composition
Specialized fluid compositions for power steering systems, designed to improve performance and durability. These fluids may include additives to enhance lubrication, reduce wear, and maintain viscosity under various operating conditions.- Power steering fluid composition: Specialized fluid compositions for power steering systems are developed to improve performance and durability. These fluids often include additives to enhance lubrication, reduce wear, and maintain viscosity under various operating conditions. The composition may also incorporate anti-foaming agents and corrosion inhibitors to protect steering system components.
- Hydraulic control systems for power steering: Advanced hydraulic control systems are designed to optimize power steering performance. These systems may include pressure regulation mechanisms, flow control valves, and hydraulic circuits that respond to driver input and vehicle speed. The goal is to provide smooth, responsive steering assistance while maintaining efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
- Electric power steering control: Electric power steering systems utilize electric motors and control units to provide steering assistance. These systems often incorporate sensors to detect steering input, vehicle speed, and road conditions. Advanced control algorithms are used to adjust the level of assistance and improve steering feel, enhancing overall vehicle handling and safety.
- Steering fluid reservoirs and circulation systems: Innovative designs for power steering fluid reservoirs and circulation systems aim to improve fluid management and system efficiency. These may include features such as integrated filtration systems, temperature control mechanisms, and optimized fluid routing to ensure proper lubrication and cooling of steering components.
- Hybrid steering systems: Hybrid steering systems combine hydraulic and electric components to optimize performance and efficiency. These systems may use electric pumps to provide hydraulic pressure or incorporate both hydraulic and electric assist mechanisms. The goal is to leverage the advantages of both technologies while minimizing their respective drawbacks.
02 Steering control mechanisms
Innovative designs for steering control systems, including hydraulic and electric power steering mechanisms. These systems aim to enhance steering responsiveness, reduce driver effort, and improve overall vehicle handling.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fluid circulation and management
Systems and methods for efficient circulation and management of power steering fluid within the steering system. This includes pumps, reservoirs, and flow control devices designed to optimize fluid distribution and pressure regulation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Steering system diagnostics and maintenance
Technologies for monitoring, diagnosing, and maintaining power steering systems. This includes sensors, diagnostic tools, and maintenance procedures to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the steering system and its fluid.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with vehicle control systems
Methods for integrating power steering fluid control with other vehicle systems, such as engine management, suspension, and stability control. This integration aims to improve overall vehicle performance, efficiency, and safety.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The power steering fluid market is in a mature stage, with a global market size expected to reach several billion dollars by 2025. The technology is well-established, with major automotive manufacturers and component suppliers dominating the landscape. Companies like Ford, ZF Friedrichshafen, and JTEKT Corp. are key players, leveraging their extensive experience in automotive systems. The market is characterized by incremental innovations focused on improving fluid performance, longevity, and environmental impact. Emerging trends include the development of electric power steering systems, which may impact the traditional hydraulic fluid market in the long term. However, the widespread use of hydraulic power steering in existing vehicles ensures continued demand for power steering fluid in the foreseeable future.
ZF Friedrichshafen AG
Technical Solution: ZF has pioneered the development of electric power steering (EPS) systems that work alongside traditional hydraulic power steering fluid. Their latest innovation is the OnAxis steer-by-wire system, which completely eliminates the mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels. This system uses advanced sensors and actuators to translate driver input into precise wheel movements, with power steering fluid playing a crucial role in dampening vibrations and providing tactile feedback[4]. ZF's system incorporates redundant electronic control units and power supplies to ensure fail-operational capability, meeting the highest safety standards for autonomous driving applications[5].
Strengths: Enables advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving features, improved packaging flexibility, and enhanced steering feel. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost and potential concerns about system reliability in extreme conditions.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has developed a Variable Flow Control (VFC) power steering system that optimizes the flow of power steering fluid based on driving conditions. This system uses an electric pump to control fluid pressure and flow, reducing energy consumption during straight-line driving and increasing assist during low-speed maneuvers. Toyota's VFC system also incorporates a fluid temperature sensor to adjust performance in various climate conditions, ensuring consistent steering feel[6]. Additionally, Toyota has implemented a regenerative power steering system in some hybrid models, which recovers energy during steering operations to improve overall vehicle efficiency[7].
Strengths: Improved fuel efficiency, consistent steering feel across various conditions, and integration with hybrid powertrains. Weaknesses: Increased system complexity and potential for higher costs in entry-level vehicles.
Innovative Fluid Formulas
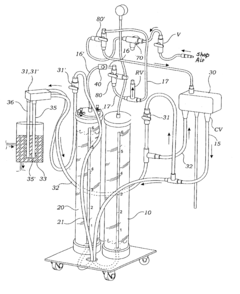
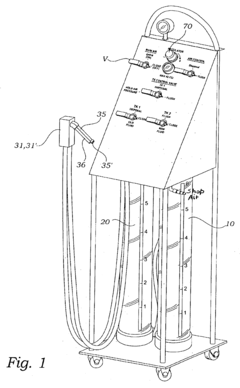
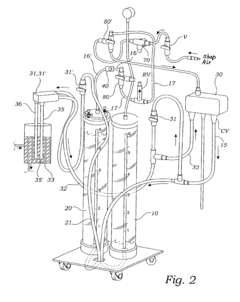
Power steering fluid exchange system and method of use
PatentInactiveUS6772803B2
Innovation
- An apparatus comprising a fluid receiving container, a fluid supply container, a utility fluid pump, and a pressure actuated fluid valve, where air is compressed by spent fluid to open the valve when 80-90% of spent fluid is removed, allowing replacement fluid to enter the power steering system, ensuring minimal mixing with the spent fluid.
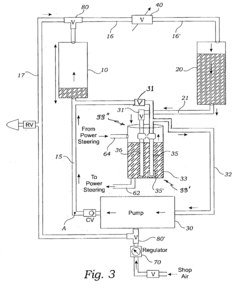
Power steering apparatus
PatentActiveUS20060015230A1
Innovation
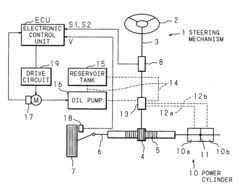
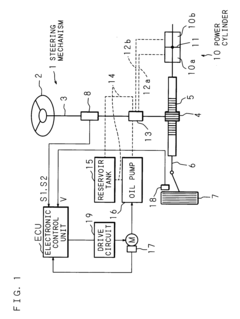
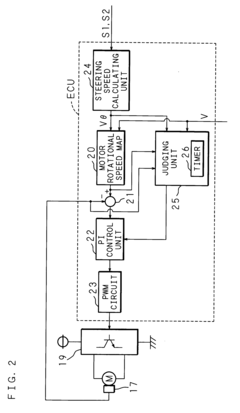
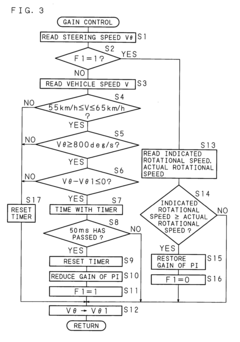
- A power steering apparatus that includes an oil pump, an electric motor, vehicle speed and steering speed detectors, and a control system that adjusts the motor's rotational speed through feedback control. The system reduces the feedback control gain when the steering speed change is minimal and holds the target rotational speed when the steering speed is high, ensuring smooth steering assistance without obstruction.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development and use of power steering fluid in automotive systems. As concerns about environmental protection and sustainability continue to grow, manufacturers and regulators are increasingly focused on minimizing the environmental impact of power steering fluids.
One of the primary environmental considerations for power steering fluids is their potential for leakage and contamination. Traditional mineral-based fluids can pose significant risks to soil and water resources if they leak from vehicles or are improperly disposed of. In response, many jurisdictions have implemented strict regulations governing the handling, storage, and disposal of these fluids. These regulations often require automotive service centers and manufacturers to implement proper containment measures and follow specific disposal protocols to prevent environmental contamination.
The push for more environmentally friendly alternatives has led to the development of synthetic and biodegradable power steering fluids. These newer formulations are designed to break down more quickly in the environment, reducing their long-term impact on ecosystems. Some jurisdictions have begun to incentivize or mandate the use of these more sustainable options, particularly in areas with sensitive ecological habitats or stringent environmental protection laws.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from power steering fluids have also come under scrutiny. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse health effects. As a result, regulations in many regions now limit the VOC content of automotive fluids, including power steering fluids. This has driven innovation in fluid formulations to reduce or eliminate volatile components while maintaining the necessary performance characteristics for precise steering control.
The automotive industry has also seen a trend towards extended service intervals for power steering fluids. This approach, encouraged by both environmental regulations and consumer demand for lower maintenance vehicles, aims to reduce the overall volume of fluid consumed and disposed of over a vehicle's lifetime. Manufacturers have responded by developing more durable fluid formulations that can maintain their performance characteristics for longer periods, thereby reducing the frequency of fluid changes and the associated environmental impact.
Recycling and reclamation of power steering fluids have become important aspects of environmental compliance. Many regions now require automotive service providers to participate in fluid recycling programs, where used power steering fluid is collected, processed, and either reused or repurposed. This circular economy approach helps to reduce the demand for new fluid production and minimizes the environmental footprint of power steering systems.
As electric power steering systems become more prevalent, the environmental regulations surrounding traditional hydraulic power steering fluids are evolving. While electric systems eliminate the need for hydraulic fluid, they introduce new environmental considerations related to the production and disposal of electronic components and batteries. Regulators are adapting their frameworks to address these emerging technologies, focusing on issues such as rare earth element extraction and electronic waste management.
One of the primary environmental considerations for power steering fluids is their potential for leakage and contamination. Traditional mineral-based fluids can pose significant risks to soil and water resources if they leak from vehicles or are improperly disposed of. In response, many jurisdictions have implemented strict regulations governing the handling, storage, and disposal of these fluids. These regulations often require automotive service centers and manufacturers to implement proper containment measures and follow specific disposal protocols to prevent environmental contamination.
The push for more environmentally friendly alternatives has led to the development of synthetic and biodegradable power steering fluids. These newer formulations are designed to break down more quickly in the environment, reducing their long-term impact on ecosystems. Some jurisdictions have begun to incentivize or mandate the use of these more sustainable options, particularly in areas with sensitive ecological habitats or stringent environmental protection laws.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from power steering fluids have also come under scrutiny. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse health effects. As a result, regulations in many regions now limit the VOC content of automotive fluids, including power steering fluids. This has driven innovation in fluid formulations to reduce or eliminate volatile components while maintaining the necessary performance characteristics for precise steering control.
The automotive industry has also seen a trend towards extended service intervals for power steering fluids. This approach, encouraged by both environmental regulations and consumer demand for lower maintenance vehicles, aims to reduce the overall volume of fluid consumed and disposed of over a vehicle's lifetime. Manufacturers have responded by developing more durable fluid formulations that can maintain their performance characteristics for longer periods, thereby reducing the frequency of fluid changes and the associated environmental impact.
Recycling and reclamation of power steering fluids have become important aspects of environmental compliance. Many regions now require automotive service providers to participate in fluid recycling programs, where used power steering fluid is collected, processed, and either reused or repurposed. This circular economy approach helps to reduce the demand for new fluid production and minimizes the environmental footprint of power steering systems.
As electric power steering systems become more prevalent, the environmental regulations surrounding traditional hydraulic power steering fluids are evolving. While electric systems eliminate the need for hydraulic fluid, they introduce new environmental considerations related to the production and disposal of electronic components and batteries. Regulators are adapting their frameworks to address these emerging technologies, focusing on issues such as rare earth element extraction and electronic waste management.
Safety Considerations
Power steering fluid plays a crucial role in ensuring precise steering control, but it also presents several safety considerations that must be carefully addressed. The primary concern is the potential for fluid leaks, which can lead to a loss of steering assistance and compromise vehicle control. Regular inspections of the power steering system, including hoses, seals, and connections, are essential to detect and prevent leaks before they become critical safety issues.
Another safety consideration is the risk of contamination in the power steering fluid. Contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, or water can enter the system through damaged seals or during maintenance procedures. These impurities can cause accelerated wear on components, leading to premature failure and potentially dangerous steering malfunctions. Implementing proper filtration systems and maintaining a clean working environment during servicing can mitigate these risks.
The chemical composition of power steering fluid also raises safety concerns. Many power steering fluids contain petroleum-based compounds that can be harmful if ingested or if they come into contact with skin or eyes. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures must be established to protect both service technicians and the environment. Additionally, the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with power steering fluid is essential to prevent accidental exposure.
Temperature management is another critical safety aspect of power steering fluid. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect the fluid's viscosity and performance. In high-temperature conditions, the fluid may break down more quickly, leading to reduced lubrication and increased wear on steering components. Conversely, in very cold temperatures, the fluid may become too thick, causing sluggish steering response. Proper fluid selection based on the vehicle's operating conditions and regular fluid changes can help maintain optimal performance and safety across various temperature ranges.
The potential for fire hazards associated with power steering fluid must also be considered. While not as flammable as some other automotive fluids, power steering fluid can still ignite under certain conditions, particularly if it comes into contact with hot engine components. Proper routing of power steering lines away from heat sources and prompt cleanup of any spills are important safety measures to reduce fire risks.
Lastly, the environmental impact of power steering fluid disposal is a growing safety concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Implementing responsible disposal practices, such as recycling programs or using biodegradable fluid alternatives, is crucial for minimizing environmental hazards and ensuring long-term safety for communities.
Another safety consideration is the risk of contamination in the power steering fluid. Contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, or water can enter the system through damaged seals or during maintenance procedures. These impurities can cause accelerated wear on components, leading to premature failure and potentially dangerous steering malfunctions. Implementing proper filtration systems and maintaining a clean working environment during servicing can mitigate these risks.
The chemical composition of power steering fluid also raises safety concerns. Many power steering fluids contain petroleum-based compounds that can be harmful if ingested or if they come into contact with skin or eyes. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures must be established to protect both service technicians and the environment. Additionally, the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with power steering fluid is essential to prevent accidental exposure.
Temperature management is another critical safety aspect of power steering fluid. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect the fluid's viscosity and performance. In high-temperature conditions, the fluid may break down more quickly, leading to reduced lubrication and increased wear on steering components. Conversely, in very cold temperatures, the fluid may become too thick, causing sluggish steering response. Proper fluid selection based on the vehicle's operating conditions and regular fluid changes can help maintain optimal performance and safety across various temperature ranges.
The potential for fire hazards associated with power steering fluid must also be considered. While not as flammable as some other automotive fluids, power steering fluid can still ignite under certain conditions, particularly if it comes into contact with hot engine components. Proper routing of power steering lines away from heat sources and prompt cleanup of any spills are important safety measures to reduce fire risks.
Lastly, the environmental impact of power steering fluid disposal is a growing safety concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Implementing responsible disposal practices, such as recycling programs or using biodegradable fluid alternatives, is crucial for minimizing environmental hazards and ensuring long-term safety for communities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!