TIM Regulatory Considerations: RoHS, REACH, And Flammability Tests
AUG 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TIM Regulatory Background and Compliance Goals
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) have become increasingly critical components in electronic devices, serving as essential heat transfer media between heat-generating components and heat dissipation systems. As global environmental regulations continue to evolve, the regulatory landscape governing TIMs has become more complex and stringent. The historical development of these regulations traces back to the early 2000s when concerns about hazardous substances in electronic products first gained significant attention.
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, initially implemented in the European Union in 2003 and subsequently revised in 2011 (RoHS 2) and 2015 (RoHS 3), established limitations on the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment. For TIM manufacturers, this has necessitated the elimination or significant reduction of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) from their formulations.
Concurrently, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, implemented in 2007, introduced comprehensive requirements for chemical substances manufactured or imported into the EU. This regulation has profound implications for TIM producers, as it mandates detailed documentation and testing of chemical components, particularly those classified as Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs).
Flammability standards for TIMs have evolved alongside these chemical regulations, with UL 94 emerging as the predominant standard for evaluating the flammability characteristics of materials used in electronic devices. These standards have become increasingly important as electronic devices become more compact and operate at higher temperatures, elevating the risk of thermal-related failures and potential fire hazards.
The primary compliance goals for TIM manufacturers in this regulatory environment are multifaceted. First, they must ensure complete adherence to RoHS directives by eliminating restricted substances while maintaining thermal performance. Second, they must establish comprehensive REACH compliance protocols, including thorough documentation of chemical constituents and ongoing monitoring of the expanding SVHC list.
Third, manufacturers must achieve appropriate flammability ratings for their TIMs based on application requirements, typically targeting V-0, V-1, or V-2 classifications under UL 94 standards. Fourth, they must develop testing methodologies that can simultaneously verify compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks while validating the thermal performance characteristics of their materials.
Finally, TIM producers must establish forward-looking regulatory monitoring systems to anticipate and prepare for emerging regulations, particularly as environmental concerns continue to drive more stringent chemical restrictions globally. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining market access and avoiding costly reformulation efforts in response to sudden regulatory changes.
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, initially implemented in the European Union in 2003 and subsequently revised in 2011 (RoHS 2) and 2015 (RoHS 3), established limitations on the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment. For TIM manufacturers, this has necessitated the elimination or significant reduction of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) from their formulations.
Concurrently, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, implemented in 2007, introduced comprehensive requirements for chemical substances manufactured or imported into the EU. This regulation has profound implications for TIM producers, as it mandates detailed documentation and testing of chemical components, particularly those classified as Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs).
Flammability standards for TIMs have evolved alongside these chemical regulations, with UL 94 emerging as the predominant standard for evaluating the flammability characteristics of materials used in electronic devices. These standards have become increasingly important as electronic devices become more compact and operate at higher temperatures, elevating the risk of thermal-related failures and potential fire hazards.
The primary compliance goals for TIM manufacturers in this regulatory environment are multifaceted. First, they must ensure complete adherence to RoHS directives by eliminating restricted substances while maintaining thermal performance. Second, they must establish comprehensive REACH compliance protocols, including thorough documentation of chemical constituents and ongoing monitoring of the expanding SVHC list.
Third, manufacturers must achieve appropriate flammability ratings for their TIMs based on application requirements, typically targeting V-0, V-1, or V-2 classifications under UL 94 standards. Fourth, they must develop testing methodologies that can simultaneously verify compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks while validating the thermal performance characteristics of their materials.
Finally, TIM producers must establish forward-looking regulatory monitoring systems to anticipate and prepare for emerging regulations, particularly as environmental concerns continue to drive more stringent chemical restrictions globally. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining market access and avoiding costly reformulation efforts in response to sudden regulatory changes.
Market Demand for Compliant Thermal Interface Materials
The global market for thermal interface materials (TIMs) that comply with regulatory standards such as RoHS, REACH, and flammability requirements has experienced significant growth in recent years. This expansion is primarily driven by the increasing thermal management needs across various industries, particularly in electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and renewable energy sectors.
Electronic device miniaturization continues to create substantial demand for compliant TIMs. As devices become smaller while processing power increases, heat dissipation has become a critical challenge. Industry data indicates that thermal management issues account for approximately 55% of electronic component failures, highlighting the essential role of regulatory-compliant thermal interface materials in ensuring product reliability and longevity.
The automotive industry represents another major demand driver for compliant TIMs. The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) has intensified the need for effective thermal management solutions that meet strict regulatory standards. Battery thermal management systems in EVs require TIMs that not only provide excellent thermal conductivity but also comply with stringent safety regulations regarding flammability and hazardous substance restrictions.
Telecommunications infrastructure, particularly with the ongoing global 5G network deployment, has emerged as a significant market for compliant TIMs. The higher power densities and operating temperatures of 5G equipment necessitate advanced thermal management solutions that adhere to international regulatory frameworks.
Consumer awareness regarding environmental and health impacts has further accelerated demand for RoHS and REACH compliant materials. End-users increasingly prefer products manufactured with environmentally responsible materials, creating market pressure for manufacturers to adopt compliant TIMs throughout their supply chains.
Regulatory compliance has evolved from being merely a legal requirement to becoming a competitive advantage. Companies offering TIMs that exceed minimum regulatory standards often command premium pricing and preferred supplier status, particularly in industries with zero-defect tolerance policies such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive safety systems.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the demand for compliant TIMs, followed by North America and Europe. This geographic distribution aligns with electronics manufacturing hubs and stringent regulatory environments. The market is projected to maintain strong growth as regulatory frameworks continue to evolve and expand globally, with particular emphasis on reducing environmental impact and enhancing fire safety standards.
Electronic device miniaturization continues to create substantial demand for compliant TIMs. As devices become smaller while processing power increases, heat dissipation has become a critical challenge. Industry data indicates that thermal management issues account for approximately 55% of electronic component failures, highlighting the essential role of regulatory-compliant thermal interface materials in ensuring product reliability and longevity.
The automotive industry represents another major demand driver for compliant TIMs. The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) has intensified the need for effective thermal management solutions that meet strict regulatory standards. Battery thermal management systems in EVs require TIMs that not only provide excellent thermal conductivity but also comply with stringent safety regulations regarding flammability and hazardous substance restrictions.
Telecommunications infrastructure, particularly with the ongoing global 5G network deployment, has emerged as a significant market for compliant TIMs. The higher power densities and operating temperatures of 5G equipment necessitate advanced thermal management solutions that adhere to international regulatory frameworks.
Consumer awareness regarding environmental and health impacts has further accelerated demand for RoHS and REACH compliant materials. End-users increasingly prefer products manufactured with environmentally responsible materials, creating market pressure for manufacturers to adopt compliant TIMs throughout their supply chains.
Regulatory compliance has evolved from being merely a legal requirement to becoming a competitive advantage. Companies offering TIMs that exceed minimum regulatory standards often command premium pricing and preferred supplier status, particularly in industries with zero-defect tolerance policies such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive safety systems.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the demand for compliant TIMs, followed by North America and Europe. This geographic distribution aligns with electronics manufacturing hubs and stringent regulatory environments. The market is projected to maintain strong growth as regulatory frameworks continue to evolve and expand globally, with particular emphasis on reducing environmental impact and enhancing fire safety standards.
Global Regulatory Challenges for TIM Manufacturers
Thermal Interface Materials (TIM) manufacturers face an increasingly complex global regulatory landscape that significantly impacts product development, market access, and competitive positioning. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive represents one of the most influential regulatory frameworks, restricting the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in electronic equipment. For TIM producers, this necessitates careful material selection and continuous reformulation efforts to maintain compliance while preserving thermal performance characteristics.
The EU's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation presents additional complexity by requiring manufacturers to register substances produced or imported in quantities exceeding one metric ton annually. This regulation's Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) list, which is updated biannually, creates ongoing compliance challenges for TIM manufacturers who must track an ever-expanding list of restricted chemicals that may be present in their formulations.
Flammability testing requirements vary significantly across global markets, with standards such as UL 94, IEC 60695, and ISO 9772 establishing different classification systems and testing methodologies. TIM manufacturers must navigate these disparate requirements while balancing flame retardancy with thermal conductivity—properties that often involve contradictory material characteristics.
The regulatory divergence between major markets creates substantial operational challenges. While the EU maintains stringent chemical restrictions, countries like China are implementing their own frameworks such as China RoHS and China REACH, which feature similar objectives but different implementation requirements and timelines. This regulatory fragmentation necessitates region-specific product formulations and compliance documentation.
Emerging economies are rapidly developing their own regulatory frameworks, often modeling them after established systems but with market-specific modifications. This trend toward regulatory proliferation increases compliance costs and complexity for global TIM manufacturers who must monitor developments across multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
Supply chain transparency has become a critical regulatory challenge, with manufacturers increasingly responsible for documenting compliance throughout their entire supply network. This requires sophisticated tracking systems and supplier qualification processes to ensure that all raw materials and components meet applicable regulations in target markets.
The accelerating pace of regulatory change presents perhaps the greatest challenge, with new substances regularly added to restriction lists and testing methodologies continuously evolving. TIM manufacturers must develop agile regulatory intelligence capabilities and maintain flexible formulation strategies to adapt quickly to these changes while minimizing disruption to product availability and performance.
The EU's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation presents additional complexity by requiring manufacturers to register substances produced or imported in quantities exceeding one metric ton annually. This regulation's Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) list, which is updated biannually, creates ongoing compliance challenges for TIM manufacturers who must track an ever-expanding list of restricted chemicals that may be present in their formulations.
Flammability testing requirements vary significantly across global markets, with standards such as UL 94, IEC 60695, and ISO 9772 establishing different classification systems and testing methodologies. TIM manufacturers must navigate these disparate requirements while balancing flame retardancy with thermal conductivity—properties that often involve contradictory material characteristics.
The regulatory divergence between major markets creates substantial operational challenges. While the EU maintains stringent chemical restrictions, countries like China are implementing their own frameworks such as China RoHS and China REACH, which feature similar objectives but different implementation requirements and timelines. This regulatory fragmentation necessitates region-specific product formulations and compliance documentation.
Emerging economies are rapidly developing their own regulatory frameworks, often modeling them after established systems but with market-specific modifications. This trend toward regulatory proliferation increases compliance costs and complexity for global TIM manufacturers who must monitor developments across multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
Supply chain transparency has become a critical regulatory challenge, with manufacturers increasingly responsible for documenting compliance throughout their entire supply network. This requires sophisticated tracking systems and supplier qualification processes to ensure that all raw materials and components meet applicable regulations in target markets.
The accelerating pace of regulatory change presents perhaps the greatest challenge, with new substances regularly added to restriction lists and testing methodologies continuously evolving. TIM manufacturers must develop agile regulatory intelligence capabilities and maintain flexible formulation strategies to adapt quickly to these changes while minimizing disruption to product availability and performance.
Current TIM Formulations Meeting Regulatory Requirements
01 Environmental compliance for TIM materials
Thermal Interface Materials must comply with environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals). These regulations restrict the use of certain hazardous substances in electronic components, including TIMs. Manufacturers must ensure their thermal interface materials are free from restricted substances like lead, mercury, and certain flame retardants to meet global environmental standards.- Environmental and safety compliance for TIM materials: Thermal Interface Materials must comply with environmental regulations regarding hazardous substances and safety standards. This includes adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals), and other environmental directives that limit or prohibit the use of certain chemicals in electronic components. Manufacturers must ensure their TIM formulations avoid restricted substances while maintaining thermal performance.
- Quality control and testing standards for TIM compliance: Regulatory compliance for Thermal Interface Materials requires adherence to specific testing protocols and quality control standards. These standards ensure consistent performance, reliability, and safety of TIMs in various applications. Testing includes thermal conductivity measurements, aging tests, mechanical property evaluations, and compatibility assessments with different substrate materials to verify compliance with industry specifications and regulatory requirements.
- Supply chain compliance and documentation requirements: Manufacturers of Thermal Interface Materials must maintain comprehensive documentation of material composition, sourcing, and manufacturing processes to demonstrate regulatory compliance. This includes material safety data sheets (MSDS), certificates of compliance, and supply chain verification to ensure all components meet applicable regulations. Proper documentation is essential for product certification, market access, and customer assurance regarding regulatory compliance.
- Industry-specific TIM compliance requirements: Different industries have specific regulatory requirements for Thermal Interface Materials based on their application environments. For example, automotive TIMs must meet additional temperature cycling and vibration standards, while medical device TIMs require biocompatibility testing. Aerospace and military applications have stringent outgassing and reliability requirements. Manufacturers must tailor their compliance strategies to address these industry-specific regulations while maintaining thermal performance.
- Emerging regulations and compliance innovations: The regulatory landscape for Thermal Interface Materials is evolving with increasing focus on sustainability, recyclability, and reduced environmental impact. New regulations are emerging regarding end-of-life management, carbon footprint, and circular economy principles. Innovative approaches to compliance include development of bio-based TIMs, halogen-free formulations, and materials designed for disassembly and recycling, allowing manufacturers to anticipate and adapt to future regulatory requirements.
02 Safety certification requirements for TIMs
Thermal Interface Materials require various safety certifications to ensure they meet industry standards. These include UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, which evaluates flammability and electrical safety properties, and ISO compliance for quality management systems. TIM manufacturers must conduct rigorous testing to demonstrate their products meet thermal performance specifications while maintaining safety standards for use in electronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Material composition documentation and disclosure
Regulatory compliance for Thermal Interface Materials requires comprehensive documentation of material composition. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of all substances used in TIMs and provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheets (SDS). These documents disclose potential hazards, handling procedures, and disposal guidelines. Full disclosure of material composition is essential for downstream manufacturers to ensure their end products comply with relevant regulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Testing and validation protocols for TIMs
Compliance with regulatory standards for Thermal Interface Materials requires specific testing and validation protocols. These include thermal conductivity testing, reliability testing under various environmental conditions, and aging tests to ensure long-term performance. Standardized test methods from organizations like ASTM and JEDEC are used to verify TIM properties. Documentation of these test results is necessary for regulatory approval and customer acceptance in different markets.Expand Specific Solutions05 Supply chain compliance management for TIMs
Managing regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain is critical for Thermal Interface Materials. This includes supplier qualification processes, auditing of material sources, and traceability systems to track components from raw materials to finished products. Companies must implement compliance management systems to monitor changing regulations across different markets and ensure their TIM products meet all applicable standards. This often involves digital solutions for tracking compliance documentation and certifications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Compliant TIM Development
The thermal interface materials (TIM) regulatory landscape is evolving rapidly as the industry matures, with market growth driven by increasing electronic device complexity and thermal management needs. Currently, the market is characterized by stringent compliance requirements across RoHS, REACH, and flammability standards, creating a competitive environment where established players like Intel, 3M Innovative Properties, and Infineon Technologies lead through comprehensive regulatory expertise. Major aerospace manufacturers such as Boeing and automotive companies like Chery Automobile are driving demand for high-performance, regulation-compliant TIMs. The technology has reached moderate maturity, with companies like Hitachi, LG Chem, and Panasonic advancing innovations in environmentally compliant formulations while newer entrants focus on specialized applications meeting regional regulatory variations.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M开发了符合RoHS和REACH标准的热界面材料系列,包括其Thermally Conductive Adhesive Transfer Tapes和Thermally Conductive Epoxy Adhesives。这些产品采用无卤素配方,完全符合欧盟RoHS指令2011/65/EU及其修订案2015/863的要求,不含受限重金属和阻燃剂。3M的TIM解决方案通过UL 94 V-0阻燃测试认证,确保在高温环境下不会产生有害气体。公司实施了全球材料合规管理系统,对供应链进行严格监控,确保所有原材料符合最新的REACH法规要求,包括高度关注物质(SVHC)的申报和替代。3M还开发了专有的环保型导热填充材料,在保持高导热性能的同时,减少了对环境的影响。
优势:全球合规管理系统确保产品在不同市场的合规性;无卤配方减少环境影响;拥有多种符合不同应用场景的TIM解决方案。劣势:某些高性能TIM产品价格较高;部分特殊应用场景可能需要定制解决方案,增加了实施成本和时间。
Intel Corp.
Technical Solution: Intel开发了符合严格环保标准的热界面材料(TIM)解决方案,专为其处理器和数据中心产品设计。Intel的PTIM(Polymer Thermal Interface Material)和STIM(Solder Thermal Interface Material)技术完全符合RoHS指令2011/65/EU及其修订案的要求,不含任何受限重金属和阻燃剂。公司实施了全面的"环保领导计划"(Environmental Leadership Program),确保所有TIM材料符合REACH法规要求,包括对SVHC的严格控制。Intel的TIM产品通过了UL 94 V-0阻燃测试认证,并符合IEC 60695标准。公司开发了无铅焊料TIM技术,在提高散热效率的同时,消除了传统含铅焊料的环境风险。Intel还建立了严格的供应商合规管理体系,要求所有TIM材料供应商提供详细的物质成分申报和合规证明文档。公司的TIM技术路线图包括开发新一代环保型相变材料,在保持卓越导热性能的同时,进一步减少环境足迹。
优势:拥有业界领先的TIM研发能力和专利组合;严格的供应链合规管理确保产品质量和合规性;提供从芯片级到系统级的全面TIM解决方案。劣势:部分高端TIM技术主要用于自有产品,市场可获取性有限;某些特殊TIM解决方案可能需要专门的应用工艺,增加了实施复杂性。
Critical Technologies for RoHS and REACH Compliance
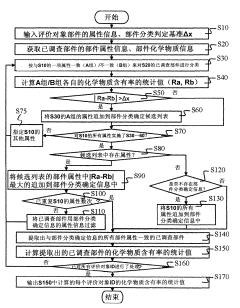
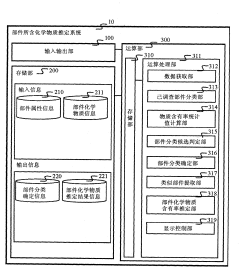
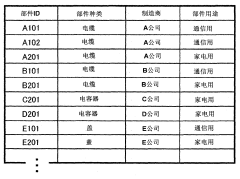
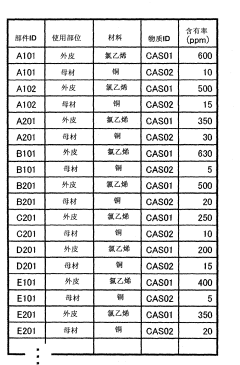
Estimation system for chemical substance included in part and estimation method for chemical substance included in part
PatentInactiveCN102214268A
Innovation
- Provide a system that receives part ID and attribute information, classifies the attributes and chemical substance information of investigated parts, calculates the statistical value of the content rate of specific chemical substances, compares and determines the basis, determines the part classification, and displays the chemical substances in the constituent materials Containment rate, priority is given to investigating substances with higher possibility.
Thermal interface material and solder preforms
PatentInactiveEP1695382A1
Innovation
- A multilayer solder preform comprising a solder component with thermal conductivity enhancement and CTE modifying additives, along with an intrinsic oxygen getter, to enhance thermal conductivity and reduce thermal expansion mismatch, eliminating the need for extrinsic fluxing and improving wetting characteristics.
Supply Chain Implications of Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in thermal interface materials (TIMs) significantly impacts global supply chains, creating a complex web of requirements that manufacturers must navigate. Companies sourcing TIMs must establish robust supplier qualification processes that verify compliance with RoHS, REACH, and flammability standards across their entire supplier network. This often necessitates extensive documentation, material declarations, and regular audit procedures that add administrative overhead to procurement operations.
The geographical fragmentation of regulations creates substantial supply chain complexity. Different regions implement varying interpretations of similar regulations, forcing manufacturers to maintain multiple material formulations or product variants to serve global markets. This regulatory divergence increases inventory management challenges and can lead to longer lead times as suppliers must segregate compliant and non-compliant materials throughout production and distribution channels.
Material substitution requirements driven by regulatory changes frequently trigger supply chain disruptions. When substances are added to restricted lists under RoHS or REACH, manufacturers must rapidly identify alternative materials, validate their performance, and implement changes across production lines. This transition period often results in temporary supply shortages, price volatility, and quality inconsistencies as suppliers adapt formulations to maintain compliance while preserving thermal performance characteristics.
Compliance verification creates additional supply chain checkpoints that extend product development and release timelines. Each material change requires comprehensive testing and certification, which can delay time-to-market for new products. These verification processes also introduce additional costs throughout the supply chain, from raw material suppliers to end-product manufacturers, ultimately affecting product pricing and competitive positioning.
Regulatory non-compliance presents severe supply chain risks, including potential product recalls, market access restrictions, and reputational damage. Forward-thinking companies are implementing digital traceability systems that track compliance data throughout the supply chain, enabling rapid response to regulatory changes and providing transparent documentation for customers and regulatory authorities. These systems help mitigate disruption risks while building trust with increasingly environmentally conscious customers.
The evolving regulatory landscape requires supply chain resilience strategies, including diversified supplier networks, enhanced inventory management practices, and proactive monitoring of regulatory developments. Companies that effectively integrate regulatory compliance into their supply chain management gain competitive advantages through reduced disruption risks and improved market access capabilities.
The geographical fragmentation of regulations creates substantial supply chain complexity. Different regions implement varying interpretations of similar regulations, forcing manufacturers to maintain multiple material formulations or product variants to serve global markets. This regulatory divergence increases inventory management challenges and can lead to longer lead times as suppliers must segregate compliant and non-compliant materials throughout production and distribution channels.
Material substitution requirements driven by regulatory changes frequently trigger supply chain disruptions. When substances are added to restricted lists under RoHS or REACH, manufacturers must rapidly identify alternative materials, validate their performance, and implement changes across production lines. This transition period often results in temporary supply shortages, price volatility, and quality inconsistencies as suppliers adapt formulations to maintain compliance while preserving thermal performance characteristics.
Compliance verification creates additional supply chain checkpoints that extend product development and release timelines. Each material change requires comprehensive testing and certification, which can delay time-to-market for new products. These verification processes also introduce additional costs throughout the supply chain, from raw material suppliers to end-product manufacturers, ultimately affecting product pricing and competitive positioning.
Regulatory non-compliance presents severe supply chain risks, including potential product recalls, market access restrictions, and reputational damage. Forward-thinking companies are implementing digital traceability systems that track compliance data throughout the supply chain, enabling rapid response to regulatory changes and providing transparent documentation for customers and regulatory authorities. These systems help mitigate disruption risks while building trust with increasingly environmentally conscious customers.
The evolving regulatory landscape requires supply chain resilience strategies, including diversified supplier networks, enhanced inventory management practices, and proactive monitoring of regulatory developments. Companies that effectively integrate regulatory compliance into their supply chain management gain competitive advantages through reduced disruption risks and improved market access capabilities.
Environmental Impact Assessment of TIM Materials
The environmental impact of Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) has become increasingly significant as electronic devices proliferate globally. TIMs, while essential for thermal management in electronics, contain various compounds that may pose environmental risks throughout their lifecycle. Understanding these impacts is crucial for sustainable product development and regulatory compliance.
TIM materials typically contain metals, polymers, ceramics, and various chemical additives that can have substantial environmental footprints during extraction, manufacturing, use, and disposal phases. Heavy metals such as silver, copper, and in some cases lead, are common in certain TIM formulations. These metals require energy-intensive mining operations that contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Manufacturing processes for TIMs often involve chemical treatments and energy-intensive production methods that generate additional environmental burdens. Solvent-based processing, common in certain TIM types, can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution and potential health hazards for workers and surrounding communities.
During the use phase, most TIMs remain environmentally inert, though some formulations may gradually degrade and potentially leach compounds into the environment if improperly disposed of. The greatest environmental concern occurs at end-of-life, where improper disposal can lead to contamination of soil and water systems with heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants.
Recent life cycle assessments of various TIM materials have revealed significant differences in environmental impact profiles. Metal-based TIMs typically show higher impacts in resource depletion and energy consumption categories, while polymer-based options often present challenges in biodegradability and potential for microplastic generation.
Carbon-based TIMs, including graphite sheets and carbon nanotubes, present a mixed environmental profile. While their thermal performance can enable more energy-efficient devices, their production may involve energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous chemicals. However, their durability and potential for recovery may offset some environmental concerns.
Emerging bio-based and environmentally friendly TIM alternatives are gaining attention, with materials derived from renewable resources showing promise. These include cellulose-based composites and natural oils modified for thermal conductivity enhancement. Though currently less thermally efficient than conventional options, their reduced environmental footprint makes them attractive for less demanding applications.
The environmental assessment of TIMs must also consider their indirect impacts, particularly how their thermal efficiency affects device energy consumption and lifespan. More efficient TIMs can reduce operational energy requirements and extend product lifespans, potentially offsetting their manufacturing impacts through system-level benefits.
TIM materials typically contain metals, polymers, ceramics, and various chemical additives that can have substantial environmental footprints during extraction, manufacturing, use, and disposal phases. Heavy metals such as silver, copper, and in some cases lead, are common in certain TIM formulations. These metals require energy-intensive mining operations that contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Manufacturing processes for TIMs often involve chemical treatments and energy-intensive production methods that generate additional environmental burdens. Solvent-based processing, common in certain TIM types, can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution and potential health hazards for workers and surrounding communities.
During the use phase, most TIMs remain environmentally inert, though some formulations may gradually degrade and potentially leach compounds into the environment if improperly disposed of. The greatest environmental concern occurs at end-of-life, where improper disposal can lead to contamination of soil and water systems with heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants.
Recent life cycle assessments of various TIM materials have revealed significant differences in environmental impact profiles. Metal-based TIMs typically show higher impacts in resource depletion and energy consumption categories, while polymer-based options often present challenges in biodegradability and potential for microplastic generation.
Carbon-based TIMs, including graphite sheets and carbon nanotubes, present a mixed environmental profile. While their thermal performance can enable more energy-efficient devices, their production may involve energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous chemicals. However, their durability and potential for recovery may offset some environmental concerns.
Emerging bio-based and environmentally friendly TIM alternatives are gaining attention, with materials derived from renewable resources showing promise. These include cellulose-based composites and natural oils modified for thermal conductivity enhancement. Though currently less thermally efficient than conventional options, their reduced environmental footprint makes them attractive for less demanding applications.
The environmental assessment of TIMs must also consider their indirect impacts, particularly how their thermal efficiency affects device energy consumption and lifespan. More efficient TIMs can reduce operational energy requirements and extend product lifespans, potentially offsetting their manufacturing impacts through system-level benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!