Analysis of Sulfur Cathodes in Electric Vehicle Market
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur cathodes represent a significant evolution in battery technology for electric vehicles, with roots dating back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternatives to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The development trajectory has been marked by incremental advancements addressing fundamental challenges such as the "shuttle effect" and poor cycle life. Initially, sulfur was identified as a promising cathode material due to its high theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds conventional lithium-ion cathodes (typically 250-300 Wh/kg).
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology can be traced through several key phases. The first phase (2000-2010) focused on fundamental research and proof-of-concept demonstrations, establishing the theoretical advantages of lithium-sulfur chemistry. The second phase (2010-2015) saw significant efforts in addressing core challenges through carbon encapsulation techniques and electrolyte modifications. The third phase (2015-2020) brought more sophisticated approaches including functional interlayers and advanced sulfur hosts, resulting in prototype cells with improved stability.
Currently, we are in the fourth phase (2020-present) characterized by commercial viability exploration and scale-up attempts, with companies like OXIS Energy and Sion Power leading development efforts. This phase has seen the emergence of semi-solid sulfur cathodes and hybrid lithium-sulfur-silicon systems that aim to balance energy density with practical performance requirements for electric vehicles.
The primary technical objectives for sulfur cathode development center around five key areas: increasing energy density to exceed 500 Wh/kg at the cell level; improving cycle life to achieve at least 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity fade; enhancing rate capability for fast charging applications; ensuring safety under various operating conditions; and developing cost-effective, environmentally sustainable manufacturing processes.
Long-term objectives include pushing energy density toward the theoretical maximum while maintaining practical performance metrics, developing sulfur cathodes compatible with solid-state electrolytes, and creating manufacturing processes that can be integrated into existing battery production infrastructure. The ultimate goal is to enable electric vehicles with significantly increased range (potentially exceeding 600 miles per charge) while reducing battery costs below $75/kWh.
Industry projections suggest that commercially viable sulfur cathode batteries could reach the market by 2025-2027 for specialized applications, with mainstream electric vehicle adoption potentially following in the 2028-2030 timeframe, contingent upon overcoming remaining technical hurdles related to cycle life and rate capability.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology can be traced through several key phases. The first phase (2000-2010) focused on fundamental research and proof-of-concept demonstrations, establishing the theoretical advantages of lithium-sulfur chemistry. The second phase (2010-2015) saw significant efforts in addressing core challenges through carbon encapsulation techniques and electrolyte modifications. The third phase (2015-2020) brought more sophisticated approaches including functional interlayers and advanced sulfur hosts, resulting in prototype cells with improved stability.
Currently, we are in the fourth phase (2020-present) characterized by commercial viability exploration and scale-up attempts, with companies like OXIS Energy and Sion Power leading development efforts. This phase has seen the emergence of semi-solid sulfur cathodes and hybrid lithium-sulfur-silicon systems that aim to balance energy density with practical performance requirements for electric vehicles.
The primary technical objectives for sulfur cathode development center around five key areas: increasing energy density to exceed 500 Wh/kg at the cell level; improving cycle life to achieve at least 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity fade; enhancing rate capability for fast charging applications; ensuring safety under various operating conditions; and developing cost-effective, environmentally sustainable manufacturing processes.
Long-term objectives include pushing energy density toward the theoretical maximum while maintaining practical performance metrics, developing sulfur cathodes compatible with solid-state electrolytes, and creating manufacturing processes that can be integrated into existing battery production infrastructure. The ultimate goal is to enable electric vehicles with significantly increased range (potentially exceeding 600 miles per charge) while reducing battery costs below $75/kWh.
Industry projections suggest that commercially viable sulfur cathode batteries could reach the market by 2025-2027 for specialized applications, with mainstream electric vehicle adoption potentially following in the 2028-2030 timeframe, contingent upon overcoming remaining technical hurdles related to cycle life and rate capability.
EV Battery Market Demand Analysis
The electric vehicle (EV) battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by increasing consumer adoption of electric vehicles worldwide. Current market projections indicate the global EV battery market will reach approximately $175 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 18% from 2023 to 2028. This remarkable expansion is primarily fueled by stringent environmental regulations, government incentives for EV adoption, and growing consumer awareness about sustainable transportation options.
Within this expanding market, there is a significant demand shift toward batteries with higher energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities. Traditional lithium-ion batteries with conventional cathode materials (NMC, NCA, LFP) are facing limitations in meeting these evolving requirements. This creates a substantial market opportunity for next-generation battery technologies, particularly sulfur-based cathodes, which theoretically offer up to five times the energy density of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Market research indicates that range anxiety remains the primary concern for potential EV buyers, with 67% of consumers citing insufficient driving range as their main hesitation. Consequently, automotive manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can deliver greater energy density at reduced costs. Sulfur cathodes present a compelling value proposition in this context, potentially enabling EVs with ranges exceeding 600 miles on a single charge while reducing battery costs by up to 30%.
The commercial segment of the EV market, including delivery fleets, public transportation, and ride-sharing services, demonstrates particularly strong demand for advanced battery technologies. These commercial applications prioritize total cost of ownership, where the combination of lower battery costs and extended range offered by sulfur cathodes could provide significant competitive advantages.
Regional analysis reveals varying market demands across different territories. European markets show stronger preference for sustainable battery materials with minimal environmental impact, aligning well with sulfur's abundant and environmentally benign nature. Asian markets, particularly China, prioritize cost-effectiveness and manufacturing scalability, while North American consumers emphasize performance metrics such as range and charging speed.
Battery recycling and second-life applications are emerging as critical factors in market acceptance of new battery technologies. Sulfur cathodes potentially offer advantages in this domain due to the relative abundance and lower toxicity of sulfur compared to metals like cobalt and nickel, potentially simplifying end-of-life management and reducing recycling costs.
The market timing for sulfur cathode introduction appears optimal within the 2025-2030 window, coinciding with projected EV adoption inflection points across major automotive markets and the expected maturation of supporting technologies such as solid electrolytes and advanced battery management systems.
Within this expanding market, there is a significant demand shift toward batteries with higher energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities. Traditional lithium-ion batteries with conventional cathode materials (NMC, NCA, LFP) are facing limitations in meeting these evolving requirements. This creates a substantial market opportunity for next-generation battery technologies, particularly sulfur-based cathodes, which theoretically offer up to five times the energy density of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Market research indicates that range anxiety remains the primary concern for potential EV buyers, with 67% of consumers citing insufficient driving range as their main hesitation. Consequently, automotive manufacturers are actively seeking battery technologies that can deliver greater energy density at reduced costs. Sulfur cathodes present a compelling value proposition in this context, potentially enabling EVs with ranges exceeding 600 miles on a single charge while reducing battery costs by up to 30%.
The commercial segment of the EV market, including delivery fleets, public transportation, and ride-sharing services, demonstrates particularly strong demand for advanced battery technologies. These commercial applications prioritize total cost of ownership, where the combination of lower battery costs and extended range offered by sulfur cathodes could provide significant competitive advantages.
Regional analysis reveals varying market demands across different territories. European markets show stronger preference for sustainable battery materials with minimal environmental impact, aligning well with sulfur's abundant and environmentally benign nature. Asian markets, particularly China, prioritize cost-effectiveness and manufacturing scalability, while North American consumers emphasize performance metrics such as range and charging speed.
Battery recycling and second-life applications are emerging as critical factors in market acceptance of new battery technologies. Sulfur cathodes potentially offer advantages in this domain due to the relative abundance and lower toxicity of sulfur compared to metals like cobalt and nickel, potentially simplifying end-of-life management and reducing recycling costs.
The market timing for sulfur cathode introduction appears optimal within the 2025-2030 window, coinciding with projected EV adoption inflection points across major automotive markets and the expected maturation of supporting technologies such as solid electrolytes and advanced battery management systems.
Global Sulfur Cathode R&D Status and Barriers
The global landscape of sulfur cathode research and development presents a complex picture of significant progress alongside persistent challenges. Currently, research institutions and companies across North America, Europe, and Asia are actively pursuing lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology, recognizing its theoretical energy density of approximately 2,600 Wh/kg—nearly five times that of conventional lithium-ion batteries.
In the United States, research efforts are concentrated at institutions like Stanford University, MIT, and Argonne National Laboratory, with substantial funding from the Department of Energy. European research is led by organizations in Germany, France, and the UK, while Asian development is dominated by China, South Korea, and Japan, with companies like CATL and Samsung SDI making significant investments.
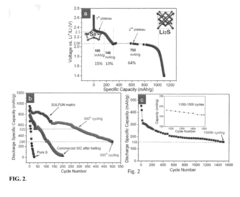
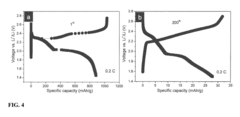
Despite this global interest, several critical barriers impede commercial adoption. The most significant challenge remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss and capacity fade. Current research indicates that after just 100 cycles, many sulfur cathodes retain only 60-70% of their initial capacity.
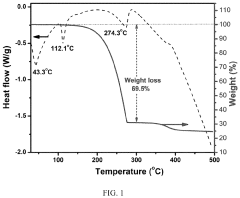
Volume expansion presents another major obstacle, as sulfur experiences approximately 80% volume change during the lithium insertion/extraction process. This expansion leads to mechanical stress, particle fracturing, and eventual electrode degradation, significantly reducing cycle life in practical applications.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates the addition of conductive additives, typically carbon materials comprising 30-40% of cathode weight. This high carbon content reduces the overall energy density advantage of sulfur cathodes in practical cells.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic, with laboratory-scale processes proving difficult to translate to industrial production. Current manufacturing techniques struggle with uniformity, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness when scaled beyond small research batches.
Safety concerns persist regarding the reactivity of lithium polysulfides with conventional electrolytes, potentially leading to thermal runaway under certain conditions. This issue is particularly critical for electric vehicle applications where safety standards are stringent.
Recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and solid-state electrolytes show promise in addressing these challenges, but a comprehensive solution remains elusive. The technology readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathodes currently stands at approximately 4-5, indicating significant development is still required before commercial viability in the electric vehicle market.
In the United States, research efforts are concentrated at institutions like Stanford University, MIT, and Argonne National Laboratory, with substantial funding from the Department of Energy. European research is led by organizations in Germany, France, and the UK, while Asian development is dominated by China, South Korea, and Japan, with companies like CATL and Samsung SDI making significant investments.
Despite this global interest, several critical barriers impede commercial adoption. The most significant challenge remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss and capacity fade. Current research indicates that after just 100 cycles, many sulfur cathodes retain only 60-70% of their initial capacity.
Volume expansion presents another major obstacle, as sulfur experiences approximately 80% volume change during the lithium insertion/extraction process. This expansion leads to mechanical stress, particle fracturing, and eventual electrode degradation, significantly reducing cycle life in practical applications.
The inherently poor electrical conductivity of sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates the addition of conductive additives, typically carbon materials comprising 30-40% of cathode weight. This high carbon content reduces the overall energy density advantage of sulfur cathodes in practical cells.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic, with laboratory-scale processes proving difficult to translate to industrial production. Current manufacturing techniques struggle with uniformity, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness when scaled beyond small research batches.
Safety concerns persist regarding the reactivity of lithium polysulfides with conventional electrolytes, potentially leading to thermal runaway under certain conditions. This issue is particularly critical for electric vehicle applications where safety standards are stringent.
Recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and solid-state electrolytes show promise in addressing these challenges, but a comprehensive solution remains elusive. The technology readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathodes currently stands at approximately 4-5, indicating significant development is still required before commercial viability in the electric vehicle market.
Current Sulfur Cathode Implementation Approaches
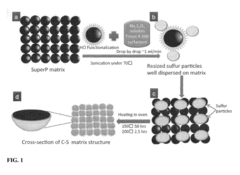
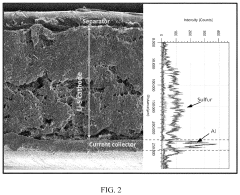
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density.
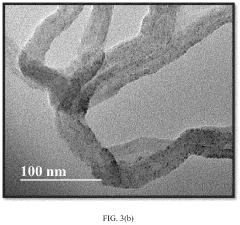
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating specialized architectures at the nanoscale to improve battery performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, hollow carbon spheres containing sulfur, and mesoporous carbon structures that can physically confine sulfur and polysulfides. Nanostructuring helps address issues like volume expansion during cycling and improves electron transport throughout the cathode material, leading to enhanced capacity retention and cycle life.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve electrochemical performance. These protective layers may consist of polymers, metal oxides, or composite materials that act as physical barriers while maintaining ion conductivity. Functional interlayers between the cathode and separator can trap dissolved polysulfides and prevent their migration to the anode, thereby extending battery life and improving coulombic efficiency.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the performance of sulfur cathodes. These may include additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, solvents with reduced polysulfide solubility, or ionic liquids with enhanced stability. Some electrolyte systems incorporate lithium salts with specific anions that interact favorably with polysulfides. These modifications aim to suppress the shuttle effect, enhance ionic conductivity, and improve the overall electrochemical stability of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques can be employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods where sulfur is infiltrated into porous host materials, solution-based processes for creating sulfur-polymer composites, and spray drying or freeze-drying approaches for producing uniform cathode materials. Advanced manufacturing methods focus on achieving homogeneous distribution of sulfur within the conductive matrix, controlling the sulfur loading, and ensuring good adhesion to current collectors for optimal electrochemical performance.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating materials with nanoscale features to improve electrochemical performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, core-shell structures, and nanoparticle assemblies. The nanostructuring helps to contain polysulfides within the cathode structure, provides conductive pathways, and accommodates volume changes during cycling. These materials demonstrate improved capacity retention and cycling stability compared to conventional sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Various protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve battery performance. These include polymer coatings, inorganic layers, and functional separators. The protective materials act as physical barriers to prevent polysulfide migration while maintaining ionic conductivity. Some designs incorporate multiple layers with different functionalities to simultaneously address multiple degradation mechanisms in lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes
Specialized electrolyte systems are developed to work with sulfur cathodes and address the unique challenges of lithium-sulfur chemistry. These include electrolyte additives that suppress polysulfide dissolution, form stable interfaces, or enhance ionic conductivity. Some formulations use high-concentration electrolytes or localized high-concentration electrolytes to minimize polysulfide solubility. Novel electrolyte designs also focus on improving the lithium anode stability in conjunction with sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes at scale. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution processing, spray drying, and electrospinning techniques. Advanced manufacturing approaches focus on achieving uniform sulfur distribution within conductive matrices, controlling porosity, and ensuring structural stability. Some processes incorporate pre-lithiation steps or special thermal treatments to optimize the initial cathode state and subsequent electrochemical performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Sulfur Cathode Technology
The sulfur cathode market for electric vehicles is in an early growth phase, characterized by significant R&D investment but limited commercial deployment. Market size is projected to expand rapidly as manufacturers seek higher energy density and lower-cost alternatives to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Technologically, sulfur cathodes remain in development with key challenges including cycle life and stability. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of maturity: established automotive companies (Toyota, GM) are investing strategically; battery manufacturers (Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, Saft) are advancing commercial prototypes; while research institutions (MIT, Cornell, Central South University) and specialized startups (PolyPlus, Conamix, Sila Nanotechnologies) are driving fundamental innovations through collaborative partnerships to overcome technical barriers and accelerate market adoption.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology specifically targeting the electric vehicle market. Their approach focuses on addressing the "shuttle effect" problem in sulfur cathodes through the implementation of proprietary carbon-sulfur composite materials. The company has engineered a hierarchical porous carbon structure that effectively encapsulates sulfur particles, minimizing polysulfide dissolution and migration. This technology incorporates a specialized protective layer on the cathode surface that acts as a physical barrier against polysulfide shuttling while maintaining excellent ionic conductivity. Samsung's research has demonstrated energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at the cell level, significantly higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. Their manufacturing process integrates these high-capacity sulfur cathodes with compatible electrolyte systems containing lithium nitrate and other additives that form a stable solid electrolyte interphase, further suppressing the shuttle effect and extending cycle life to over 500 cycles with capacity retention above 80%.
Strengths: Superior energy density (400+ Wh/kg) compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, making it ideal for extending EV range. Advanced carbon-sulfur composite structure effectively mitigates the shuttle effect. Weaknesses: Despite improvements, cycle life remains lower than commercial lithium-ion batteries, potentially limiting application in long-life EVs. Higher production costs compared to established battery technologies.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has developed a proprietary sulfur cathode technology for electric vehicles focused on practical implementation in mass-market applications. Their approach centers on a dual-layer cathode design that combines sulfur with a specialized conductive carbon matrix. This structure features a gradient distribution of sulfur concentration, with higher loading in the inner layer and lower loading at the electrolyte interface to minimize polysulfide dissolution. GM's technology incorporates a functional polymer binder system that chemically bonds with lithium polysulfides, significantly reducing their dissolution into the electrolyte. The company has also engineered a novel electrolyte formulation containing specific additives that form a stable cathode-electrolyte interphase, further suppressing the shuttle effect. GM's research demonstrates that this integrated approach enables practical energy densities of 350-400 Wh/kg while maintaining operational stability across a wide temperature range (-20°C to 45°C), which is crucial for automotive applications. Their manufacturing process has been designed for scalability, with techniques compatible with existing battery production infrastructure.
Strengths: Practical implementation focus with manufacturing processes compatible with existing production lines, reducing commercialization barriers. Wide operating temperature range suitable for diverse climate conditions. Weaknesses: Energy density improvements, while significant, are more modest than some laboratory-based approaches. Technology still requires further development to match the cycle life of current lithium-ion batteries in production vehicles.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathode Design
Sulfur nanosponge cathode for lithium-sulfur battery and methods of manufacture thereof
PatentInactiveUS20190006663A1
Innovation
- A method involving the functionalization of conductive carbon black particles to form a sulfur-covering-carbon nanostructured sponge, where sulfur is dispersed and heated to form a coating over the carbon particles, creating a nanostructured sponge cathode that accommodates volume expansion and restricts polysulfide dissolution, enhancing cyclability and capacity retention.
Cathodes for lithium-sulfur batteries with nanocatalysts
PatentPendingUS20240128444A1
Innovation
- A graded structure Li-S cathode with electro-catalyzing and polysulfide-trapping layers, comprising sulfur-rich and conductive carbon layers, is designed to optimize catalyst spatial location and improve sulfur utilization and cycle stability, using nanocatalysts like transition metals and conductive carbon materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries represents a significant advantage over conventional lithium-ion technologies currently dominating the electric vehicle market. Sulfur cathodes utilize abundant, non-toxic materials that can be sourced as byproducts from petroleum refining processes, effectively repurposing industrial waste. This circular economy approach substantially reduces the environmental footprint compared to traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel, which require extensive mining operations with considerable ecological disruption.
Life cycle assessments indicate that Li-S batteries potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 25-30% during manufacturing compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The elimination of cobalt and significant reduction in nickel content addresses critical ethical and environmental concerns related to resource extraction in conflict regions and environmentally sensitive areas. Furthermore, the energy density improvements offered by sulfur cathodes translate to reduced material requirements per kilowatt-hour of storage capacity, optimizing resource utilization across the battery lifecycle.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technology, with preliminary studies suggesting a 15-20% reduction in process water requirements during manufacturing. This advantage becomes particularly significant in regions facing water scarcity challenges, where battery production facilities must compete with agricultural and municipal water needs.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional sustainability benefits. The simpler chemical composition of sulfur cathodes facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with theoretical recovery rates for sulfur exceeding 90% in laboratory conditions. Commercial-scale recycling infrastructure, however, remains underdeveloped and requires significant investment to realize these potential benefits at scale.
Challenges persist regarding the environmental implications of electrolyte components in Li-S batteries, particularly the long-term ecological impacts of lithium salts and organic solvents. Additionally, the polysulfide shuttle effect—while primarily a performance issue—creates potential contamination concerns if batteries are improperly disposed of or damaged. Research into solid-state electrolytes and encapsulation technologies aims to address these environmental vulnerabilities.
Carbon footprint analyses across the full product lifecycle suggest that widespread adoption of sulfur cathode technology could reduce transportation sector emissions by an additional 5-8% beyond the benefits already achieved through electrification. This improvement stems from both manufacturing efficiencies and the potential for extended vehicle range, which enhances the practical utility of electric vehicles in replacing internal combustion engines.
Life cycle assessments indicate that Li-S batteries potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 25-30% during manufacturing compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The elimination of cobalt and significant reduction in nickel content addresses critical ethical and environmental concerns related to resource extraction in conflict regions and environmentally sensitive areas. Furthermore, the energy density improvements offered by sulfur cathodes translate to reduced material requirements per kilowatt-hour of storage capacity, optimizing resource utilization across the battery lifecycle.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technology, with preliminary studies suggesting a 15-20% reduction in process water requirements during manufacturing. This advantage becomes particularly significant in regions facing water scarcity challenges, where battery production facilities must compete with agricultural and municipal water needs.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional sustainability benefits. The simpler chemical composition of sulfur cathodes facilitates more straightforward recycling processes, with theoretical recovery rates for sulfur exceeding 90% in laboratory conditions. Commercial-scale recycling infrastructure, however, remains underdeveloped and requires significant investment to realize these potential benefits at scale.
Challenges persist regarding the environmental implications of electrolyte components in Li-S batteries, particularly the long-term ecological impacts of lithium salts and organic solvents. Additionally, the polysulfide shuttle effect—while primarily a performance issue—creates potential contamination concerns if batteries are improperly disposed of or damaged. Research into solid-state electrolytes and encapsulation technologies aims to address these environmental vulnerabilities.
Carbon footprint analyses across the full product lifecycle suggest that widespread adoption of sulfur cathode technology could reduce transportation sector emissions by an additional 5-8% beyond the benefits already achieved through electrification. This improvement stems from both manufacturing efficiencies and the potential for extended vehicle range, which enhances the practical utility of electric vehicles in replacing internal combustion engines.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Viability
The economic viability of sulfur cathodes represents a pivotal factor in their potential adoption within the electric vehicle market. Current cost analysis indicates that sulfur cathodes offer significant advantages over traditional lithium-ion battery technologies, with raw material costs approximately 80% lower than conventional cathode materials. Sulfur, being an abundant byproduct of petroleum refining, costs merely $0.10-0.20 per kilogram compared to cobalt ($30-60/kg) and nickel ($12-18/kg) used in NMC and NCA cathodes.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes also demonstrate promising cost efficiencies. The synthesis methods require lower energy inputs and fewer complex processing steps than traditional cathode production. Preliminary industrial scale estimates suggest production costs could be reduced by 40-50% compared to current lithium-ion technologies when accounting for materials, processing, and equipment depreciation.
However, several economic challenges remain unresolved. The shorter cycle life of sulfur cathodes (typically 300-500 cycles versus 1,000+ for conventional lithium-ion) negatively impacts the total cost of ownership calculation. This limitation necessitates more frequent battery replacements, potentially offsetting initial cost advantages over the vehicle's lifetime.
Infrastructure considerations also affect commercial viability. Existing battery manufacturing facilities would require significant modifications to accommodate sulfur cathode production, with conversion costs estimated between $50-100 million per gigafactory. This represents a substantial barrier to rapid commercialization despite the lower per-unit production costs.
Market analysis reveals that sulfur cathodes would need to achieve a minimum cycle life of 700 cycles to reach cost parity with current technologies on a lifetime value basis. At current performance levels, the technology remains economically viable primarily for specific applications where initial cost outweighs longevity concerns.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that commercial viability improves dramatically with advances in sulfur utilization efficiency. Increasing active material utilization from current levels (50-60%) to theoretical targets (80%+) would reduce costs by an additional 25-30%, potentially accelerating market adoption despite cycle life limitations.
The economic equation also benefits from environmental considerations, as sulfur cathodes eliminate dependency on critical materials facing supply constraints. This advantage may translate to reduced price volatility and supply chain risks, factors increasingly valued by EV manufacturers seeking stable cost structures.
Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes also demonstrate promising cost efficiencies. The synthesis methods require lower energy inputs and fewer complex processing steps than traditional cathode production. Preliminary industrial scale estimates suggest production costs could be reduced by 40-50% compared to current lithium-ion technologies when accounting for materials, processing, and equipment depreciation.
However, several economic challenges remain unresolved. The shorter cycle life of sulfur cathodes (typically 300-500 cycles versus 1,000+ for conventional lithium-ion) negatively impacts the total cost of ownership calculation. This limitation necessitates more frequent battery replacements, potentially offsetting initial cost advantages over the vehicle's lifetime.
Infrastructure considerations also affect commercial viability. Existing battery manufacturing facilities would require significant modifications to accommodate sulfur cathode production, with conversion costs estimated between $50-100 million per gigafactory. This represents a substantial barrier to rapid commercialization despite the lower per-unit production costs.
Market analysis reveals that sulfur cathodes would need to achieve a minimum cycle life of 700 cycles to reach cost parity with current technologies on a lifetime value basis. At current performance levels, the technology remains economically viable primarily for specific applications where initial cost outweighs longevity concerns.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that commercial viability improves dramatically with advances in sulfur utilization efficiency. Increasing active material utilization from current levels (50-60%) to theoretical targets (80%+) would reduce costs by an additional 25-30%, potentially accelerating market adoption despite cycle life limitations.
The economic equation also benefits from environmental considerations, as sulfur cathodes eliminate dependency on critical materials facing supply constraints. This advantage may translate to reduced price volatility and supply chain risks, factors increasingly valued by EV manufacturers seeking stable cost structures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!