Sulfur Cathodes Mechanics in High-Capacity Energy Systems
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has undergone significant evolution since its initial conceptualization in the 1960s. The journey began with primary lithium-sulfur batteries, which demonstrated high theoretical energy density but suffered from severe practical limitations. By the early 2000s, researchers shifted focus to rechargeable lithium-sulfur systems, marking a pivotal advancement in high-capacity energy storage technology.
The fundamental attraction of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its impressive theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, substantially surpassing conventional lithium-ion technologies. Additionally, sulfur presents compelling advantages including natural abundance, environmental benignity, and low cost—approximately 1% the cost of cobalt used in traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Despite these promising attributes, sulfur cathode development has been hindered by several persistent challenges. The "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides migrate between electrodes, causes capacity fading and efficiency losses. Furthermore, sulfur's poor electrical conductivity (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates conductive additives, while its substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithiation leads to mechanical degradation.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, electrolyte engineering, and interlayer design. Carbon nanotubes, graphene, and mesoporous carbon frameworks have emerged as effective sulfur hosts, enhancing conductivity while physically constraining polysulfides. Concurrently, electrolyte innovations including solid-state and gel polymer systems have demonstrated improved cycle stability.
The primary objectives of current sulfur cathode research center on achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Researchers aim to mitigate the polysulfide shuttle effect through novel encapsulation strategies and functional interlayers.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap targets commercial viability in specialized applications by 2025, with broader market penetration anticipated by 2030. Key milestones include demonstrating stable performance at commercially relevant loading (>5 mg/cm²), improving rate capability for fast-charging applications, and developing scalable manufacturing techniques that maintain sulfur's cost advantages.
The ultimate goal remains harnessing sulfur's theoretical capacity while overcoming its inherent limitations, potentially revolutionizing energy storage for electric vehicles, grid applications, and portable electronics through significantly enhanced energy density and reduced material costs.
The fundamental attraction of sulfur as a cathode material lies in its impressive theoretical specific capacity of 1,675 mAh/g and energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, substantially surpassing conventional lithium-ion technologies. Additionally, sulfur presents compelling advantages including natural abundance, environmental benignity, and low cost—approximately 1% the cost of cobalt used in traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Despite these promising attributes, sulfur cathode development has been hindered by several persistent challenges. The "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides migrate between electrodes, causes capacity fading and efficiency losses. Furthermore, sulfur's poor electrical conductivity (5×10^-30 S/cm) necessitates conductive additives, while its substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) during lithiation leads to mechanical degradation.
Recent technological breakthroughs have focused on nanostructured carbon hosts, electrolyte engineering, and interlayer design. Carbon nanotubes, graphene, and mesoporous carbon frameworks have emerged as effective sulfur hosts, enhancing conductivity while physically constraining polysulfides. Concurrently, electrolyte innovations including solid-state and gel polymer systems have demonstrated improved cycle stability.
The primary objectives of current sulfur cathode research center on achieving practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life beyond 1,000 cycles with minimal capacity degradation, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Researchers aim to mitigate the polysulfide shuttle effect through novel encapsulation strategies and functional interlayers.
Looking forward, the technology roadmap targets commercial viability in specialized applications by 2025, with broader market penetration anticipated by 2030. Key milestones include demonstrating stable performance at commercially relevant loading (>5 mg/cm²), improving rate capability for fast-charging applications, and developing scalable manufacturing techniques that maintain sulfur's cost advantages.
The ultimate goal remains harnessing sulfur's theoretical capacity while overcoming its inherent limitations, potentially revolutionizing energy storage for electric vehicles, grid applications, and portable electronics through significantly enhanced energy density and reduced material costs.
Market Analysis for High-Capacity Energy Storage Systems
The high-capacity energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the global shift towards renewable energy integration and electrification of transportation. The market for advanced battery technologies, particularly those incorporating sulfur cathodes, is projected to reach $90 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 18.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing governmental policies promoting clean energy adoption across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions.
Consumer electronics currently represent the largest application segment for high-capacity energy storage systems, accounting for approximately 40% of the market share. However, electric vehicles are rapidly gaining ground, with an expected market share increase from 35% in 2023 to potentially 55% by 2028. Grid-scale energy storage applications, though smaller in current market share (15%), show the highest growth potential at 25% annually as utilities seek solutions for renewable energy integration challenges.
Lithium-sulfur batteries, featuring sulfur cathodes, are positioned as a promising next-generation technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which significantly outperforms conventional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg). This performance advantage has attracted substantial investment, with venture capital funding in sulfur cathode technologies reaching $1.2 billion in 2022 alone.
Market demand is increasingly driven by specific performance requirements across different sectors. The automotive industry prioritizes energy density and fast-charging capabilities, while consumer electronics manufacturers focus on cycle life and safety. Grid operators emphasize cost-effectiveness and longevity, with target costs below $100/kWh for widespread adoption.
Regional analysis reveals China leading the manufacturing capacity for high-capacity energy storage systems, controlling 75% of the global supply chain. However, recent policy initiatives in the United States (Inflation Reduction Act) and European Union (European Battery Alliance) aim to reduce this dependency by establishing regional manufacturing capabilities, potentially reshaping market dynamics by 2030.
Customer willingness to pay premium prices for high-capacity energy storage solutions varies significantly by application. Survey data indicates that electric vehicle manufacturers are willing to pay up to 30% premium for batteries offering 50% higher energy density, while grid operators remain highly price-sensitive, with premium acceptance limited to 10-15% for improved performance metrics.
Consumer electronics currently represent the largest application segment for high-capacity energy storage systems, accounting for approximately 40% of the market share. However, electric vehicles are rapidly gaining ground, with an expected market share increase from 35% in 2023 to potentially 55% by 2028. Grid-scale energy storage applications, though smaller in current market share (15%), show the highest growth potential at 25% annually as utilities seek solutions for renewable energy integration challenges.
Lithium-sulfur batteries, featuring sulfur cathodes, are positioned as a promising next-generation technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2,600 Wh/kg, which significantly outperforms conventional lithium-ion batteries (250-300 Wh/kg). This performance advantage has attracted substantial investment, with venture capital funding in sulfur cathode technologies reaching $1.2 billion in 2022 alone.
Market demand is increasingly driven by specific performance requirements across different sectors. The automotive industry prioritizes energy density and fast-charging capabilities, while consumer electronics manufacturers focus on cycle life and safety. Grid operators emphasize cost-effectiveness and longevity, with target costs below $100/kWh for widespread adoption.
Regional analysis reveals China leading the manufacturing capacity for high-capacity energy storage systems, controlling 75% of the global supply chain. However, recent policy initiatives in the United States (Inflation Reduction Act) and European Union (European Battery Alliance) aim to reduce this dependency by establishing regional manufacturing capabilities, potentially reshaping market dynamics by 2030.
Customer willingness to pay premium prices for high-capacity energy storage solutions varies significantly by application. Survey data indicates that electric vehicle manufacturers are willing to pay up to 30% premium for batteries offering 50% higher energy density, while grid operators remain highly price-sensitive, with premium acceptance limited to 10-15% for improved performance metrics.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Mechanics
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology, several critical challenges in sulfur cathode mechanics continue to impede their widespread commercial adoption. The most persistent issue remains the polysulfide shuttle effect, where soluble lithium polysulfides (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during discharge, migrate to the anode, and cause parasitic reactions. This phenomenon leads to rapid capacity fading, low Coulombic efficiency, and shortened battery lifespan, presenting a fundamental obstacle to long-term cycling stability.
The volume expansion problem represents another significant mechanical challenge. During lithiation, sulfur undergoes substantial volumetric expansion (approximately 80%) as it converts to Li2S, causing mechanical stress that can fracture the cathode structure. This expansion-contraction cycle during repeated charging and discharging leads to pulverization of active materials, electrical contact loss, and eventual electrode failure.
Poor electrical conductivity of both sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge product Li2S (10^-31 S/cm) severely limits electron transport within the cathode. This inherent insulating nature necessitates large amounts of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and complicates electrode design and manufacturing processes.
The slow kinetics of sulfur redox reactions, particularly the sluggish conversion between Li2S2 and Li2S during the discharge process, creates significant overpotential and rate capability limitations. This kinetic bottleneck restricts the power performance of Li-S batteries, making them less competitive for applications requiring rapid charging or high power output.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The high reactivity of polysulfides with conventional electrolytes leads to electrolyte degradation and consumption over time. Additionally, the optimal electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio remains excessively high (typically >10 μL/mg), resulting in low energy density at the cell level.
The mechanical integrity of sulfur cathodes is compromised by weak interactions between sulfur species and host materials. Without strong chemical bonding or physical confinement, active material loss occurs continuously during cycling, contributing to capacity decay and performance deterioration.
These interconnected challenges create a complex optimization problem where addressing one issue often exacerbates others. For instance, increasing the sulfur loading to improve energy density typically worsens electronic conductivity and exacerbates volume expansion effects. The multifaceted nature of these challenges necessitates innovative, integrated approaches rather than isolated solutions targeting individual problems.
The volume expansion problem represents another significant mechanical challenge. During lithiation, sulfur undergoes substantial volumetric expansion (approximately 80%) as it converts to Li2S, causing mechanical stress that can fracture the cathode structure. This expansion-contraction cycle during repeated charging and discharging leads to pulverization of active materials, electrical contact loss, and eventual electrode failure.
Poor electrical conductivity of both sulfur (5×10^-30 S/cm) and its discharge product Li2S (10^-31 S/cm) severely limits electron transport within the cathode. This inherent insulating nature necessitates large amounts of conductive additives, which reduces the overall energy density of the battery system and complicates electrode design and manufacturing processes.
The slow kinetics of sulfur redox reactions, particularly the sluggish conversion between Li2S2 and Li2S during the discharge process, creates significant overpotential and rate capability limitations. This kinetic bottleneck restricts the power performance of Li-S batteries, making them less competitive for applications requiring rapid charging or high power output.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate sulfur cathode development. The high reactivity of polysulfides with conventional electrolytes leads to electrolyte degradation and consumption over time. Additionally, the optimal electrolyte-to-sulfur ratio remains excessively high (typically >10 μL/mg), resulting in low energy density at the cell level.
The mechanical integrity of sulfur cathodes is compromised by weak interactions between sulfur species and host materials. Without strong chemical bonding or physical confinement, active material loss occurs continuously during cycling, contributing to capacity decay and performance deterioration.
These interconnected challenges create a complex optimization problem where addressing one issue often exacerbates others. For instance, increasing the sulfur loading to improve energy density typically worsens electronic conductivity and exacerbates volume expansion effects. The multifaceted nature of these challenges necessitates innovative, integrated approaches rather than isolated solutions targeting individual problems.
Current Engineering Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Stability
01 Mechanical stability enhancement of sulfur cathodes
Various approaches are employed to improve the mechanical stability of sulfur cathodes, which is crucial for preventing capacity fading during charge-discharge cycles. These include the use of binders, structural reinforcements, and mechanical confinement strategies that help maintain the integrity of the cathode structure despite volume changes during cycling. Enhanced mechanical stability leads to better cycling performance and longer battery life.- Structural design of sulfur cathodes: Various structural designs are employed to improve the mechanical properties of sulfur cathodes. These include porous structures, carbon-based frameworks, and composite architectures that accommodate volume changes during cycling. Such designs help maintain structural integrity, prevent sulfur dissolution, and enhance the overall mechanical stability of the cathode, leading to improved cycle life and performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Binder systems for sulfur cathode stability: Specialized binder systems are crucial for enhancing the mechanical properties of sulfur cathodes. These binders provide adhesion between active materials and current collectors, maintain electrode integrity during volume changes, and improve the elasticity of the cathode structure. Advanced polymer binders with functional groups can also interact with polysulfides, reducing their dissolution and improving the mechanical stability of the cathode during cycling.
- Carbon-sulfur composites for mechanical enhancement: Carbon-sulfur composites are developed to address the mechanical challenges of sulfur cathodes. Various carbon materials including graphene, carbon nanotubes, and porous carbon are used to encapsulate sulfur, providing conductive networks and mechanical support. These composites effectively accommodate volume expansion, prevent pulverization, and maintain electrical contact throughout cycling, resulting in improved mechanical stability and electrochemical performance.
- Polymer and gel-based sulfur cathode systems: Polymer and gel-based systems are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to enhance their mechanical properties. These materials can form flexible matrices that accommodate volume changes, improve sulfur utilization, and prevent cathode degradation. Gel polymer electrolytes and polymer coatings also help suppress polysulfide shuttling while maintaining good mechanical integrity of the cathode structure during cycling, leading to more stable battery performance.
- Nanostructured materials for sulfur cathode mechanics: Nanostructured materials are employed to improve the mechanical properties of sulfur cathodes. These include metal oxides, metal-organic frameworks, and other nanoscale architectures that provide confinement for sulfur and its discharge products. The nanoscale design helps control volume expansion, enhances structural stability, and improves the mechanical durability of the cathode. Additionally, these materials can offer catalytic effects that facilitate the conversion reactions of sulfur, further enhancing battery performance.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to address challenges related to sulfur's poor conductivity and polysulfide dissolution. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, and other nanoscale materials that provide conductive pathways and physical confinement for sulfur. The nanostructured approach improves electron transport, enhances sulfur utilization, and provides mechanical support to accommodate volume changes during cycling.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polymer and composite binders for sulfur cathodes
Specialized polymers and composite binders are developed to improve the adhesion, flexibility, and mechanical properties of sulfur cathodes. These binders help maintain electrode integrity during the significant volume changes that occur during cycling. Some binders also offer functional properties such as polysulfide trapping or ionic conductivity enhancement, addressing multiple challenges in sulfur cathode mechanics simultaneously.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte interactions with sulfur cathode mechanics
The interaction between electrolytes and sulfur cathodes significantly impacts mechanical performance. Specialized electrolyte formulations can form stable interfaces on the cathode surface, reducing mechanical stress and preventing polysulfide dissolution. Additives in the electrolyte can also enhance the mechanical properties of the cathode-electrolyte interface, leading to improved cycling stability and battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Porous structures for sulfur confinement
Engineered porous structures are designed to physically confine sulfur and its discharge products within the cathode. These structures, including mesoporous carbons, metal-organic frameworks, and hierarchical porous materials, provide mechanical support while accommodating the volume changes during cycling. The pore architecture is optimized to balance sulfur loading, electrolyte accessibility, and mechanical stability, resulting in improved cathode performance and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Sulfur Cathodes
The sulfur cathode mechanics market in high-capacity energy systems is currently in a growth phase, with increasing research activity across academic and commercial sectors. The market is expanding as demand for higher energy density batteries rises, though commercial applications remain limited. Technologically, sulfur cathodes are still evolving toward maturity, with key players driving innovation across different approaches. Academic institutions like MIT, Drexel University, and Rice University are advancing fundamental research, while companies including Sila Nanotechnologies, LG Energy Solution, and Toyota are developing commercial applications. Honeycomb Battery Co. and Nanotek Instruments represent specialized players focusing on novel battery materials and solid-state technologies, respectively. The field is characterized by collaborative efforts between research institutions and industry partners to overcome challenges in sulfur cathode stability and cycle life.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has developed a novel approach to sulfur cathode mechanics focusing on nanostructured sulfur-carbon composites. Their technology employs hollow carbon nanofibers to encapsulate sulfur, creating a physical barrier that contains polysulfides while allowing lithium ions to pass through[1]. This architecture addresses the volume expansion issues during cycling by providing void space within the nanofibers. Additionally, MIT researchers have pioneered the use of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as sulfur hosts, which offer precisely controlled pore structures that can chemically bind with polysulfides[3]. Their recent work includes developing elastomeric binders specifically designed to accommodate the mechanical stress from sulfur's volumetric changes during cycling, significantly improving cycle life in high-capacity lithium-sulfur batteries[5].
Strengths: Superior polysulfide containment through engineered nanostructures; excellent mechanical stability during volume changes; precise control over pore architecture. Weaknesses: Potentially high manufacturing costs for specialized nanostructures; reduced energy density due to inactive carbon components; challenges in scaling laboratory techniques to industrial production.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed a comprehensive approach to sulfur cathode mechanics in high-capacity energy systems through their dual-layer protection strategy. Their technology incorporates a carbon-sulfur composite core with a conductive polymer shell that effectively contains polysulfides while maintaining electrical conductivity[2]. The company has engineered specialized electrolyte additives that form a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the sulfur cathode surface, reducing shuttle effects and enhancing cycling stability[4]. LG's proprietary cathode manufacturing process involves a controlled precipitation method that creates uniform sulfur distribution within the carbon matrix, addressing mechanical stress during volume expansion[7]. They've also implemented a gradient concentration design where sulfur loading varies from the current collector interface to the electrolyte-facing surface, optimizing both energy density and mechanical integrity during cycling[9].
Strengths: Established large-scale manufacturing capabilities; integrated system approach addressing multiple failure mechanisms; commercial viability with existing battery production lines. Weaknesses: Relatively lower energy density compared to theoretical sulfur potential; performance trade-offs to achieve acceptable cycle life; higher costs associated with specialized additives and processing techniques.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathode Mechanics
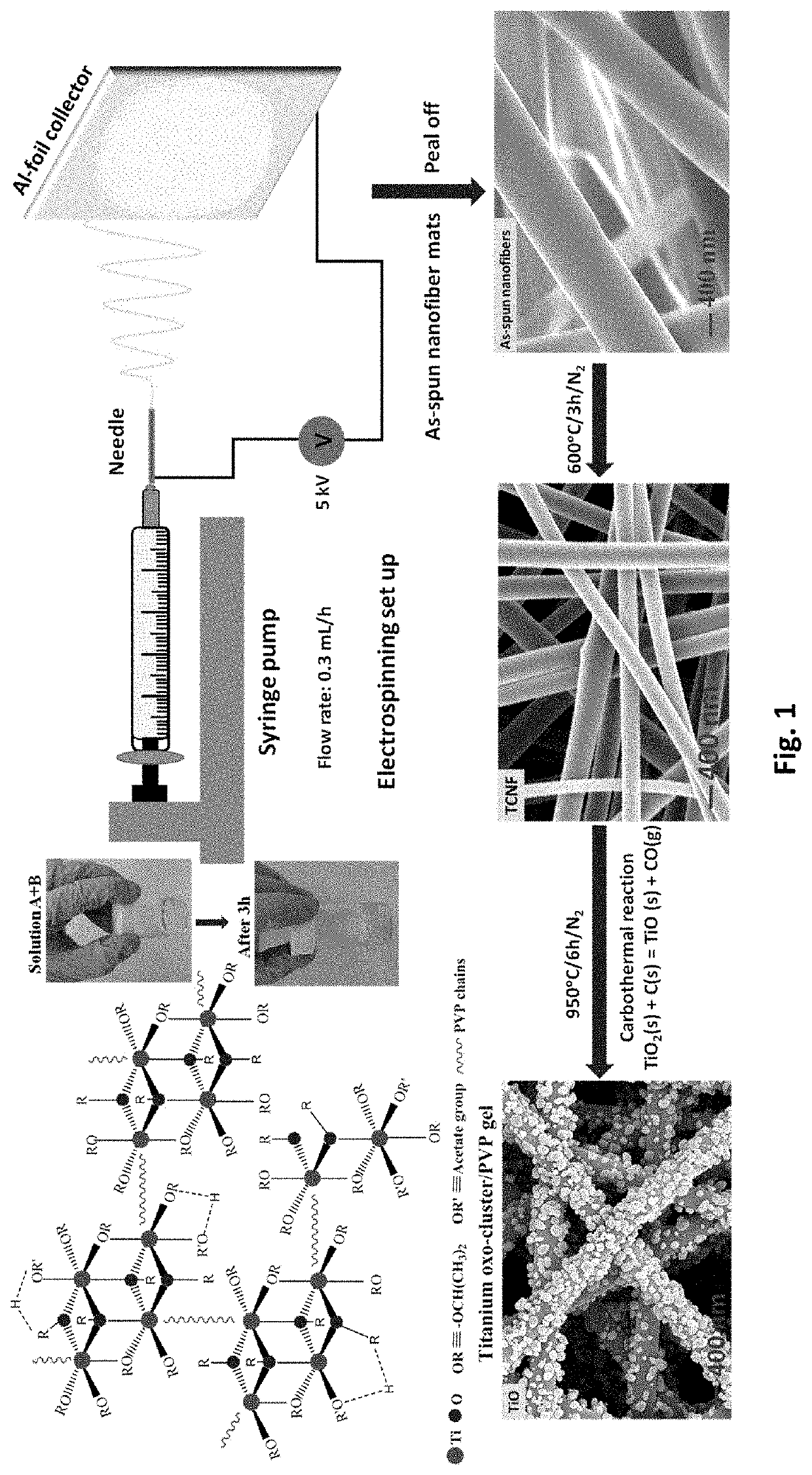
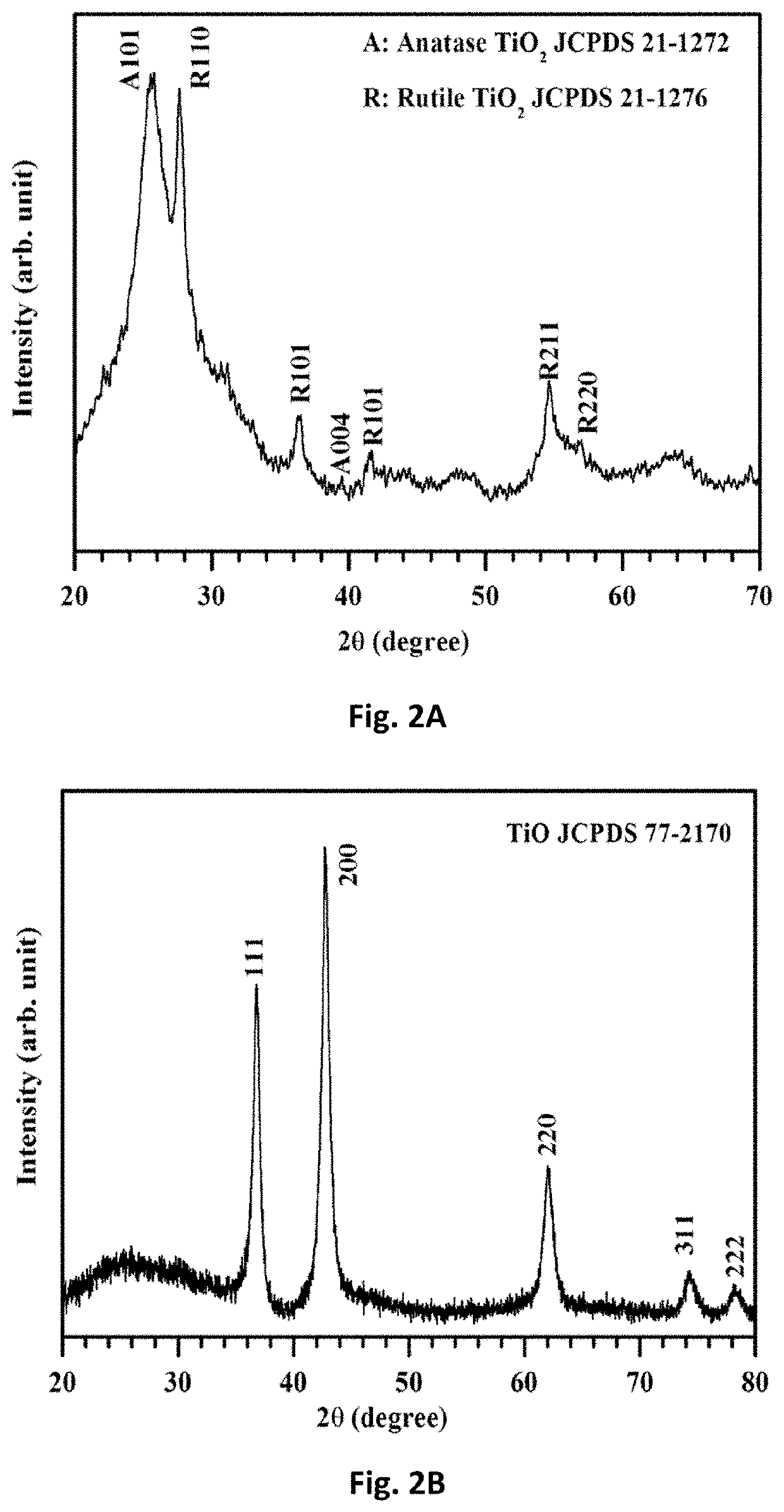
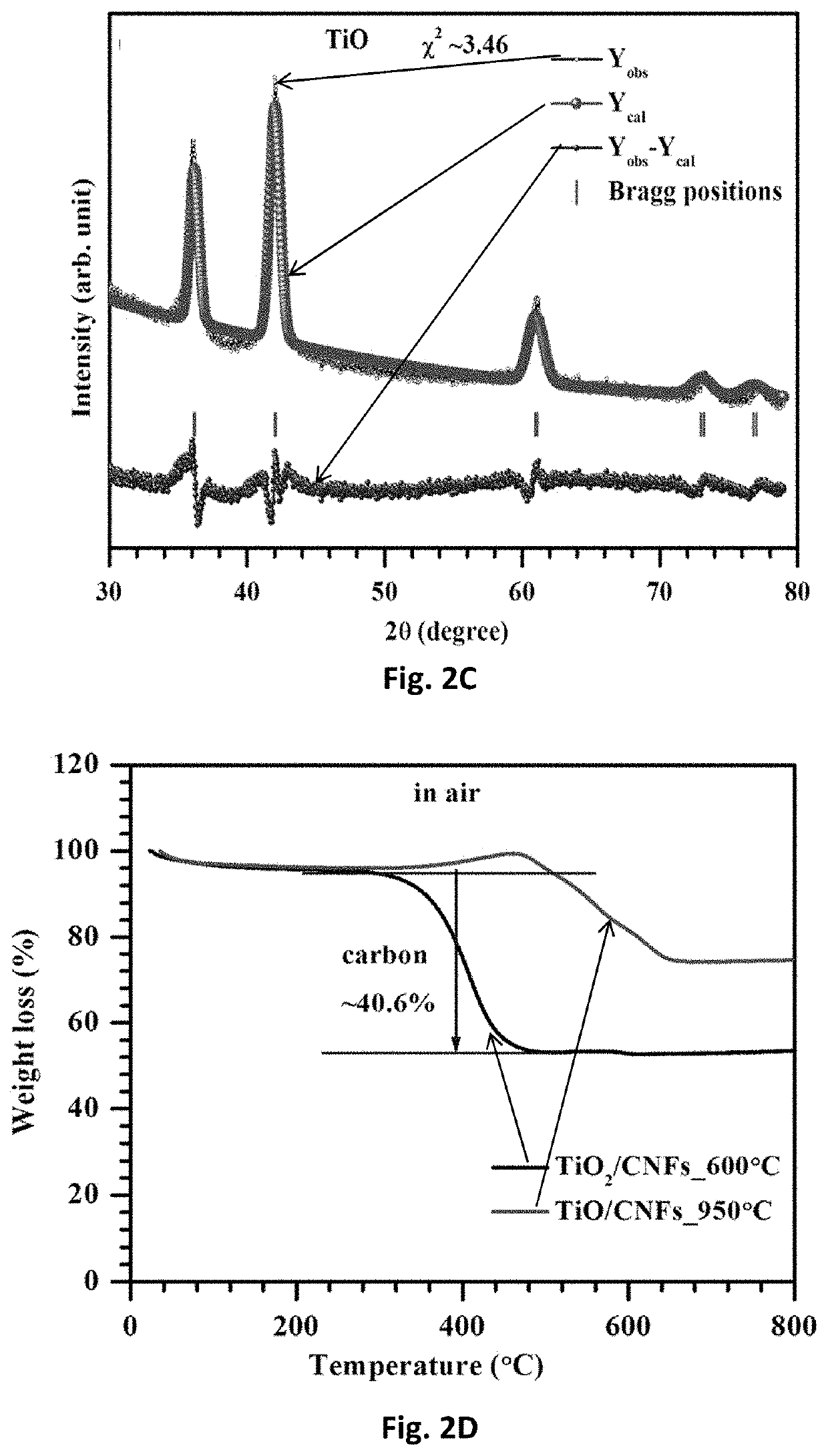
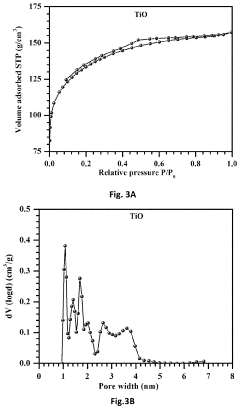
Free-standing, binder-free metal monoxide/suboxide nanofiber as cathodes or anodes for batteries
PatentActiveUS20210111390A1
Innovation
- The development of free-standing, binder-free nanofiber mats with high surface area and conductive metal oxide nanofibers, produced through electrospinning and carbothermal processes, which allow rapid sulfur diffusion and eliminate the need for harsh slurry casting, providing a robust 3D conducting network for uninterrupted electron supply and strong interactions with lithium polysulfides.
Reversible high energy capacity metal-sulfur battery and method of making same
PatentInactiveUS5506072A
Innovation
- A battery system featuring a metal anode, a sulfur-containing cathode, and a specific electrolyte solution with metal and sulfur ions, including a complexing agent and buffering agent, housed in a lightweight, non-reactive case, allowing for high energy storage, long cycle life, and rapid recharge capabilities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Sulfur Cathodes
The environmental implications of sulfur cathodes in high-capacity energy systems represent a critical dimension of their overall viability. Sulfur's abundance in nature—constituting approximately 0.03% of the Earth's crust—positions it as the 16th most common element, with significant deposits available as byproducts from petroleum refining and natural gas processing. This abundance translates to substantially lower environmental impact from extraction compared to traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel, which often involve intensive mining operations in ecologically sensitive regions.
The life cycle assessment of sulfur cathodes reveals promising sustainability metrics. The carbon footprint associated with sulfur cathode production is estimated to be 60-75% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathodes, primarily due to reduced energy requirements during material processing and refinement. Furthermore, the water consumption in manufacturing sulfur-based cathodes is approximately 40% less than their lithium cobalt oxide counterparts, contributing to conservation of this vital resource.
Recycling potential represents another significant environmental advantage of sulfur cathode technologies. Current research indicates recovery rates of up to 85% for sulfur from spent batteries, substantially higher than recovery rates for conventional cathode materials. This circular economy approach minimizes waste generation and reduces dependence on virgin material extraction, further enhancing the sustainability profile of these energy systems.
However, several environmental challenges remain unresolved. The formation of soluble polysulfides during battery operation can lead to potential environmental contamination if improper disposal occurs. These compounds may cause soil and water contamination, necessitating robust end-of-life management protocols. Additionally, while sulfur itself is non-toxic, some additives and electrolytes used in sulfur cathode systems contain fluorinated compounds that present environmental persistence concerns.
From a regulatory perspective, sulfur cathodes generally align well with emerging sustainability legislation worldwide. The European Battery Directive and similar frameworks in North America and Asia increasingly emphasize reduced environmental footprint and improved recyclability—criteria that sulfur-based systems can potentially satisfy. This regulatory compatibility may accelerate commercial adoption and further investment in environmental optimization of these technologies.
The net environmental benefit calculation indicates that widespread adoption of sulfur cathode technologies could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by an estimated 12-18 million metric tons annually by 2030, assuming current projections for electric vehicle and grid storage deployment. This significant potential contribution to climate change mitigation represents a compelling argument for continued development of these high-capacity energy systems.
The life cycle assessment of sulfur cathodes reveals promising sustainability metrics. The carbon footprint associated with sulfur cathode production is estimated to be 60-75% lower than conventional lithium-ion cathodes, primarily due to reduced energy requirements during material processing and refinement. Furthermore, the water consumption in manufacturing sulfur-based cathodes is approximately 40% less than their lithium cobalt oxide counterparts, contributing to conservation of this vital resource.
Recycling potential represents another significant environmental advantage of sulfur cathode technologies. Current research indicates recovery rates of up to 85% for sulfur from spent batteries, substantially higher than recovery rates for conventional cathode materials. This circular economy approach minimizes waste generation and reduces dependence on virgin material extraction, further enhancing the sustainability profile of these energy systems.
However, several environmental challenges remain unresolved. The formation of soluble polysulfides during battery operation can lead to potential environmental contamination if improper disposal occurs. These compounds may cause soil and water contamination, necessitating robust end-of-life management protocols. Additionally, while sulfur itself is non-toxic, some additives and electrolytes used in sulfur cathode systems contain fluorinated compounds that present environmental persistence concerns.
From a regulatory perspective, sulfur cathodes generally align well with emerging sustainability legislation worldwide. The European Battery Directive and similar frameworks in North America and Asia increasingly emphasize reduced environmental footprint and improved recyclability—criteria that sulfur-based systems can potentially satisfy. This regulatory compatibility may accelerate commercial adoption and further investment in environmental optimization of these technologies.
The net environmental benefit calculation indicates that widespread adoption of sulfur cathode technologies could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by an estimated 12-18 million metric tons annually by 2030, assuming current projections for electric vehicle and grid storage deployment. This significant potential contribution to climate change mitigation represents a compelling argument for continued development of these high-capacity energy systems.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability of sulfur cathode manufacturing represents a critical factor in the widespread adoption of high-capacity lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology. Current manufacturing processes face significant challenges when transitioning from laboratory-scale production to industrial-scale manufacturing. The primary obstacle lies in maintaining consistent quality and performance while increasing production volume, particularly due to the complex nature of sulfur cathode structures that often incorporate carbon matrices and functional additives.
Cost analysis reveals that sulfur as a raw material offers substantial economic advantages, with prices approximately 1/150th that of conventional cathode materials like cobalt oxide. This dramatic cost differential provides a compelling economic incentive for commercialization. However, the total manufacturing cost equation must account for additional factors beyond raw material expenses, including specialized processing equipment, quality control systems, and yield rates that currently lag behind established lithium-ion manufacturing processes.
Production yield represents a particular challenge, with current industrial attempts achieving only 60-75% of theoretical capacity in mass-produced cells compared to 80-90% in laboratory settings. This efficiency gap translates directly to increased per-unit costs and represents a significant barrier to market competitiveness. Process optimization focusing on slurry preparation consistency, coating uniformity, and electrolyte infiltration could potentially narrow this gap.
Energy consumption during manufacturing presents another critical cost factor. The thermal treatment processes required for sulfur-carbon composite formation typically demand higher energy inputs than conventional cathode production. Innovative approaches utilizing microwave-assisted synthesis and room-temperature processing techniques have demonstrated potential for reducing these energy requirements by 30-40%, though these methods remain in early development stages.
Equipment compatibility with existing lithium-ion battery production lines varies significantly depending on the specific sulfur cathode formulation. Conventional slurry-based approaches offer greater compatibility, potentially allowing manufacturers to repurpose 60-70% of existing equipment. However, more advanced architectures incorporating specialized nanostructures may require entirely new production systems, substantially increasing capital expenditure requirements.
Scaling considerations must also address safety protocols unique to sulfur processing, including hydrogen sulfide risk mitigation and specialized ventilation systems. These requirements add approximately 15-20% to facility costs compared to conventional battery manufacturing operations. Despite these challenges, economic modeling suggests that at production volumes exceeding 500 MWh annually, sulfur cathode batteries could achieve cost parity with conventional lithium-ion technologies while delivering 2-3 times higher energy density.
Cost analysis reveals that sulfur as a raw material offers substantial economic advantages, with prices approximately 1/150th that of conventional cathode materials like cobalt oxide. This dramatic cost differential provides a compelling economic incentive for commercialization. However, the total manufacturing cost equation must account for additional factors beyond raw material expenses, including specialized processing equipment, quality control systems, and yield rates that currently lag behind established lithium-ion manufacturing processes.
Production yield represents a particular challenge, with current industrial attempts achieving only 60-75% of theoretical capacity in mass-produced cells compared to 80-90% in laboratory settings. This efficiency gap translates directly to increased per-unit costs and represents a significant barrier to market competitiveness. Process optimization focusing on slurry preparation consistency, coating uniformity, and electrolyte infiltration could potentially narrow this gap.
Energy consumption during manufacturing presents another critical cost factor. The thermal treatment processes required for sulfur-carbon composite formation typically demand higher energy inputs than conventional cathode production. Innovative approaches utilizing microwave-assisted synthesis and room-temperature processing techniques have demonstrated potential for reducing these energy requirements by 30-40%, though these methods remain in early development stages.
Equipment compatibility with existing lithium-ion battery production lines varies significantly depending on the specific sulfur cathode formulation. Conventional slurry-based approaches offer greater compatibility, potentially allowing manufacturers to repurpose 60-70% of existing equipment. However, more advanced architectures incorporating specialized nanostructures may require entirely new production systems, substantially increasing capital expenditure requirements.
Scaling considerations must also address safety protocols unique to sulfur processing, including hydrogen sulfide risk mitigation and specialized ventilation systems. These requirements add approximately 15-20% to facility costs compared to conventional battery manufacturing operations. Despite these challenges, economic modeling suggests that at production volumes exceeding 500 MWh annually, sulfur cathode batteries could achieve cost parity with conventional lithium-ion technologies while delivering 2-3 times higher energy density.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!