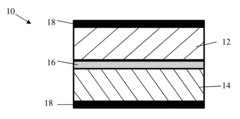
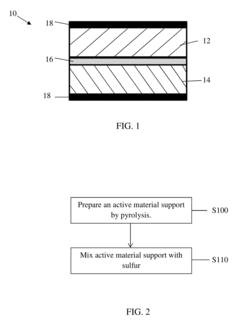
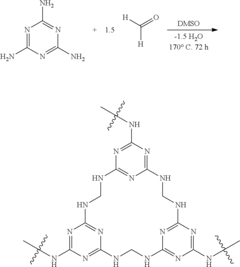
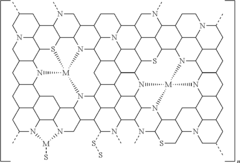
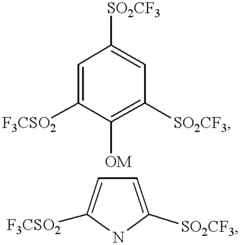
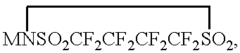Sulfur Cathodes Interface Mechanisms and Material Properties
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 250-300 Wh/kg). The development of sulfur cathodes can be traced back to the 1960s, but significant research momentum has only built up in the past two decades as the limitations of traditional lithium-ion technology have become increasingly apparent in meeting the growing demands for higher energy density applications.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has progressed through several key phases. Initially, research focused on understanding the fundamental electrochemistry of sulfur reduction, which involves multiple complex reactions and the formation of various lithium polysulfide intermediates. Subsequently, efforts shifted toward addressing the "shuttle effect" - the dissolution of polysulfides in the electrolyte leading to capacity fading and poor cycle life. Recent advances have concentrated on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications to improve sulfur utilization and cycling stability.
Current technological trends indicate a convergence of multidisciplinary approaches, combining materials science, electrochemistry, and advanced characterization techniques to develop comprehensive solutions for sulfur cathodes. The interface between sulfur and other battery components has been identified as a critical factor determining overall performance, with particular emphasis on the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation and stability.
The primary objectives of research on sulfur cathode interface mechanisms and material properties are multifaceted. First, to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms governing the formation, evolution, and degradation of interfaces between sulfur, carbon hosts, electrolytes, and other battery components. Second, to establish correlations between material properties (such as porosity, surface functionality, and conductivity) and electrochemical performance metrics. Third, to develop design principles for engineered interfaces that can effectively suppress polysulfide shuttling while maintaining high sulfur utilization and rate capability.
Additionally, research aims to identify sustainable and scalable materials and manufacturing processes that can facilitate the commercial viability of Li-S batteries. This includes exploring earth-abundant materials, environmentally friendly synthesis methods, and processes compatible with existing battery manufacturing infrastructure. The ultimate goal is to enable Li-S batteries that deliver practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle life comparable to current lithium-ion technologies and at competitive costs.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has progressed through several key phases. Initially, research focused on understanding the fundamental electrochemistry of sulfur reduction, which involves multiple complex reactions and the formation of various lithium polysulfide intermediates. Subsequently, efforts shifted toward addressing the "shuttle effect" - the dissolution of polysulfides in the electrolyte leading to capacity fading and poor cycle life. Recent advances have concentrated on nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte modifications to improve sulfur utilization and cycling stability.
Current technological trends indicate a convergence of multidisciplinary approaches, combining materials science, electrochemistry, and advanced characterization techniques to develop comprehensive solutions for sulfur cathodes. The interface between sulfur and other battery components has been identified as a critical factor determining overall performance, with particular emphasis on the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation and stability.
The primary objectives of research on sulfur cathode interface mechanisms and material properties are multifaceted. First, to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms governing the formation, evolution, and degradation of interfaces between sulfur, carbon hosts, electrolytes, and other battery components. Second, to establish correlations between material properties (such as porosity, surface functionality, and conductivity) and electrochemical performance metrics. Third, to develop design principles for engineered interfaces that can effectively suppress polysulfide shuttling while maintaining high sulfur utilization and rate capability.
Additionally, research aims to identify sustainable and scalable materials and manufacturing processes that can facilitate the commercial viability of Li-S batteries. This includes exploring earth-abundant materials, environmentally friendly synthesis methods, and processes compatible with existing battery manufacturing infrastructure. The ultimate goal is to enable Li-S batteries that deliver practical energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, with cycle life comparable to current lithium-ion technologies and at competitive costs.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Sulfur Battery Applications
The lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery market is experiencing significant growth potential due to the inherent advantages of sulfur cathodes, including high theoretical energy density (2600 Wh/kg), abundant sulfur resources, low cost, and environmental friendliness. Current market projections indicate that the global Li-S battery market could reach $2.1 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 35% from 2021 to 2026.
The transportation sector represents the largest potential market for Li-S batteries, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) where the demand for higher energy density and lower cost energy storage solutions continues to grow. Major automotive manufacturers including Toyota, BMW, and Tesla have shown interest in Li-S technology as a potential successor to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The aviation and drone industries also present substantial opportunities, with companies like Airbus exploring Li-S batteries for electric aircraft applications.
Consumer electronics constitutes another significant market segment, where the higher energy density of Li-S batteries could enable longer device operation times between charges. This advantage is particularly valuable for smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices where battery life remains a critical consumer concern.
The stationary energy storage market presents a growing opportunity for Li-S technology, especially in grid-scale applications and renewable energy integration. The lower cost of sulfur compared to traditional cathode materials could make Li-S batteries economically competitive in large-scale energy storage systems.
Market adoption faces several challenges related to the technical limitations of sulfur cathodes. The polysulfide shuttle effect, volume expansion issues, and limited cycle life currently restrict commercial viability. However, recent advancements in interface engineering and material properties have shown promising results in addressing these challenges.
Regional market analysis shows Asia-Pacific leading in Li-S battery development and production, with China, South Korea, and Japan hosting major research initiatives and manufacturing facilities. North America and Europe follow closely, with significant research funding and strategic investments in Li-S technology development.
Market forecasts suggest that as interface mechanisms and material properties of sulfur cathodes improve, commercial adoption will accelerate. The market is expected to follow a similar adoption curve to lithium-ion technology, with initial applications in premium and specialized markets before expanding to mass-market applications as costs decrease and performance improves.
The transportation sector represents the largest potential market for Li-S batteries, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) where the demand for higher energy density and lower cost energy storage solutions continues to grow. Major automotive manufacturers including Toyota, BMW, and Tesla have shown interest in Li-S technology as a potential successor to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The aviation and drone industries also present substantial opportunities, with companies like Airbus exploring Li-S batteries for electric aircraft applications.
Consumer electronics constitutes another significant market segment, where the higher energy density of Li-S batteries could enable longer device operation times between charges. This advantage is particularly valuable for smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices where battery life remains a critical consumer concern.
The stationary energy storage market presents a growing opportunity for Li-S technology, especially in grid-scale applications and renewable energy integration. The lower cost of sulfur compared to traditional cathode materials could make Li-S batteries economically competitive in large-scale energy storage systems.
Market adoption faces several challenges related to the technical limitations of sulfur cathodes. The polysulfide shuttle effect, volume expansion issues, and limited cycle life currently restrict commercial viability. However, recent advancements in interface engineering and material properties have shown promising results in addressing these challenges.
Regional market analysis shows Asia-Pacific leading in Li-S battery development and production, with China, South Korea, and Japan hosting major research initiatives and manufacturing facilities. North America and Europe follow closely, with significant research funding and strategic investments in Li-S technology development.
Market forecasts suggest that as interface mechanisms and material properties of sulfur cathodes improve, commercial adoption will accelerate. The market is expected to follow a similar adoption curve to lithium-ion technology, with initial applications in premium and specialized markets before expanding to mass-market applications as costs decrease and performance improves.
Current Challenges in Sulfur Cathode Interface Engineering
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, several critical challenges persist in sulfur cathode interface engineering that hinder commercial viability. The most prominent issue remains the polysulfide shuttle effect, where soluble lithium polysulfides (Li2Sx, 4≤x≤8) dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, migrate to the anode, and cause parasitic reactions. This phenomenon leads to active material loss, rapid capacity fading, and shortened battery lifespan, presenting a fundamental obstacle to long-term cycling stability.
Interface instability between the sulfur cathode and electrolyte constitutes another major challenge. During charge-discharge cycles, the substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) of sulfur during lithiation creates mechanical stress that disrupts the electrode-electrolyte interface, leading to electrical contact loss and impedance increase. This volumetric change also causes structural degradation of the cathode over time, further compromising performance.
The insulating nature of both sulfur and its end discharge product (Li2S) presents significant electronic conductivity limitations. With conductivity values around 10^-30 S/cm for sulfur and 10^-14 S/cm for Li2S, electron transfer at interfaces becomes severely restricted, resulting in poor reaction kinetics and underutilization of active materials. This challenge necessitates conductive additives that often reduce the overall energy density of the battery system.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate interface engineering. Most conventional electrolytes exhibit poor compatibility with sulfur cathodes, leading to undesirable side reactions, electrolyte decomposition, and the formation of unstable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers. The high reactivity of polysulfides with electrolyte components accelerates these degradation processes, compromising long-term stability.
The heterogeneous distribution of reaction products at interfaces presents additional challenges. During cycling, Li2S and other discharge products tend to deposit unevenly across the cathode surface, creating localized "hot spots" of electrochemical activity. This non-uniform distribution leads to uneven current density, accelerated degradation in certain regions, and overall performance inconsistency.
Finally, the complex multi-phase transitions occurring at sulfur cathode interfaces remain insufficiently understood. The conversion between solid sulfur, dissolved polysulfides, and solid Li2S involves multiple intermediate species and phase transformations that are difficult to characterize and control in real-time. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted interface engineering strategies that could address the fundamental challenges of sulfur cathodes.
Interface instability between the sulfur cathode and electrolyte constitutes another major challenge. During charge-discharge cycles, the substantial volume expansion (approximately 80%) of sulfur during lithiation creates mechanical stress that disrupts the electrode-electrolyte interface, leading to electrical contact loss and impedance increase. This volumetric change also causes structural degradation of the cathode over time, further compromising performance.
The insulating nature of both sulfur and its end discharge product (Li2S) presents significant electronic conductivity limitations. With conductivity values around 10^-30 S/cm for sulfur and 10^-14 S/cm for Li2S, electron transfer at interfaces becomes severely restricted, resulting in poor reaction kinetics and underutilization of active materials. This challenge necessitates conductive additives that often reduce the overall energy density of the battery system.
Electrolyte compatibility issues further complicate interface engineering. Most conventional electrolytes exhibit poor compatibility with sulfur cathodes, leading to undesirable side reactions, electrolyte decomposition, and the formation of unstable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers. The high reactivity of polysulfides with electrolyte components accelerates these degradation processes, compromising long-term stability.
The heterogeneous distribution of reaction products at interfaces presents additional challenges. During cycling, Li2S and other discharge products tend to deposit unevenly across the cathode surface, creating localized "hot spots" of electrochemical activity. This non-uniform distribution leads to uneven current density, accelerated degradation in certain regions, and overall performance inconsistency.
Finally, the complex multi-phase transitions occurring at sulfur cathode interfaces remain insufficiently understood. The conversion between solid sulfur, dissolved polysulfides, and solid Li2S involves multiple intermediate species and phase transformations that are difficult to characterize and control in real-time. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted interface engineering strategies that could address the fundamental challenges of sulfur cathodes.
State-of-the-Art Interface Modification Strategies
01 Interface modification strategies for sulfur cathodes
Various interface modification strategies can be employed to improve the performance of sulfur cathodes in batteries. These include the use of protective coatings, interlayers, and functional additives that help to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and enhance the electrochemical stability of the cathode-electrolyte interface. Such modifications can significantly improve the cycling stability, rate capability, and overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.- Interface modification strategies for sulfur cathodes: Various interface modification strategies can be employed to improve the performance of sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries. These modifications aim to address issues such as polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect at the cathode-electrolyte interface. Techniques include coating the sulfur cathode with protective layers, introducing functional interlayers, and surface modification with polymers or inorganic materials to enhance stability and conductivity at the interface.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured materials are utilized to enhance the performance of sulfur cathodes by providing better confinement of sulfur, improving electronic conductivity, and facilitating ion transport. These materials include carbon-based nanostructures (nanotubes, graphene), mesoporous materials, and metal oxide nanoparticles that can physically trap polysulfides and provide pathways for electron transport. The nanostructured design helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling and improves the overall electrochemical performance.
- Electrolyte interactions with sulfur cathodes: The interactions between electrolytes and sulfur cathodes significantly impact battery performance. Specialized electrolyte formulations can mitigate polysulfide dissolution, enhance ionic conductivity, and stabilize the solid-electrolyte interface. Additives in the electrolyte can form protective films on the cathode surface, while optimized salt concentrations and solvent compositions can reduce side reactions and improve the cycling stability of sulfur cathodes.
- Binder systems for sulfur cathode stability: Binder systems play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and electrochemical performance of sulfur cathodes. Advanced binders provide strong adhesion between active materials and current collectors, accommodate volume changes during cycling, and offer functional groups that can interact with polysulfides to prevent their dissolution. Water-based and functional polymer binders can enhance the mechanical properties and electrochemical stability of sulfur cathodes.
- Conductive additives for enhanced electron transport: Conductive additives are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to overcome the inherent insulating nature of sulfur and improve electron transport throughout the electrode. These additives include carbon-based materials (carbon black, graphene, carbon nanotubes), conductive polymers, and metal-based conductors. The strategic integration of these materials creates efficient electron pathways, reduces internal resistance, and enhances the utilization of active sulfur material, leading to improved capacity and rate capability.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of sulfur cathodes. These include carbon-based nanostructures, metal oxides, and composite materials that provide high surface area, improved conductivity, and efficient polysulfide confinement. The nanoscale architecture helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling, facilitate electron/ion transport, and enhance the utilization of active sulfur material, leading to improved energy density and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte interactions with sulfur cathodes
The interactions between electrolytes and sulfur cathodes significantly influence battery performance. Optimized electrolyte formulations can suppress polysulfide dissolution, enhance ionic conductivity, and stabilize the solid-electrolyte interphase. Additives, solvents, and salt concentrations in the electrolyte can be tailored to improve the compatibility with sulfur cathodes, reduce side reactions, and enhance the overall electrochemical performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Binder systems for sulfur cathode stability
Binder systems play a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity and electrochemical performance of sulfur cathodes. Advanced binders can improve adhesion between active materials and current collectors, accommodate volume changes during cycling, and enhance the mechanical stability of the electrode. Functional binders with specific chemical interactions can also help to trap polysulfides and improve the cycling stability of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Conductive additives for enhanced sulfur cathode performance
Conductive additives are essential components in sulfur cathodes to overcome the inherent insulating nature of sulfur. Various carbon-based materials, metal compounds, and conductive polymers can be incorporated to enhance electron transport, improve sulfur utilization, and facilitate electrochemical reactions. These additives can also provide physical confinement for polysulfides and help maintain the structural integrity of the cathode during cycling, resulting in improved capacity retention and rate capability.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Industrial Players
The sulfur cathode interface research field is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market interest driven by the demand for higher energy density batteries. The global market for sulfur cathode technology is expanding, estimated to reach significant scale as part of the broader $150+ billion battery materials market. Technologically, the field remains in early-to-mid maturity, with key players advancing different approaches. Research institutions like Chinese Academy of Sciences and universities (MIT, Cornell) are establishing fundamental science, while commercial entities represent varying development stages: established manufacturers (Samsung SDI, Toyota, Nissan) are integrating research into product roadmaps; specialized startups (Conamix, Sionic Energy) are developing targeted solutions; and materials companies (Sila Nanotechnologies, Ionic Materials) are addressing interface challenges through novel material approaches.
Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Physics
Technical Solution: The Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Physics has developed innovative approaches to address the "shuttle effect" in lithium-sulfur batteries through interface engineering. Their research focuses on creating functional interlayers between the sulfur cathode and electrolyte, utilizing conductive carbon materials modified with polar metal oxides to trap polysulfides. They've pioneered the use of MXene-based materials as sulfur hosts, demonstrating that Ti3C2Tx MXene can effectively anchor polysulfides through strong chemical interactions. Their recent work includes developing gradient-structured cathodes with varying carbon-sulfur ratios to optimize ion transport while maintaining structural integrity during cycling. The institute has also made significant advances in in-situ characterization techniques to observe real-time interface changes during battery operation.
Strengths: Strong expertise in fundamental interface chemistry and advanced characterization techniques. Their approach combines theoretical modeling with practical material design, allowing for systematic improvement of sulfur cathode performance. Weakness: Some solutions may be too complex or costly for immediate commercial implementation, and scaling up their laboratory techniques remains challenging.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed a comprehensive sulfur cathode technology platform focused on commercial viability. Their approach integrates multiple protection strategies, including carbon-sulfur composite engineering and functional separator coatings. Samsung's proprietary "dual-confinement" technique encapsulates sulfur particles within microporous carbon shells, which are then embedded in a secondary conductive matrix with polysulfide-trapping additives. This hierarchical structure effectively contains sulfur species while maintaining electrical connectivity. Their research also extends to electrolyte engineering, where they've developed fluorinated ether-based formulations that minimize side reactions with lithium metal anodes while remaining compatible with sulfur cathodes. Samsung SDI has demonstrated pouch cells with energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg at practical loading levels, representing significant progress toward commercialization of lithium-sulfur technology.
Strengths: Strong focus on scalable manufacturing processes and practical cell design considerations. Their integrated approach addresses multiple failure mechanisms simultaneously. Weakness: Some solutions involve trade-offs between performance and cost, and their most advanced technologies may rely on proprietary materials that create supply chain dependencies.
Key Scientific Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathode Research
Transition metal containing nitrogen-doped carbon support structure for sulfur active material as a cathode for a lithium-sulfur battery
PatentActiveUS10033046B2
Innovation
- The development of cathodes with a transition metal-containing nitrogen-doped carbon active material support that hosts sulfur and suppresses polysulfide diffusion through high surface area nanostructured pores, using nitrogen-containing polymers doped with transition metals like Fe, V, Mo, W, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn, which anchor soluble species and inhibit polysulfide migration.
Electrochemical cells with carbon nanofibers and electroactive sulfur compounds
PatentInactiveUS6194099B1
Innovation
- Incorporating non-activated carbon nanofibers with diameters less than 1000 nm and specific surface areas less than 600 m^2/g into solid composite cathodes, which contain electroactive sulfur-containing materials with polysulfide moieties, to enhance electrical conductivity and porosity, allowing for increased volumetric density without compromising specific capacity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology represents a critical dimension in evaluating its viability as a next-generation energy storage solution. When compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, Li-S batteries demonstrate significant environmental advantages, primarily due to the abundance and low toxicity of sulfur as a cathode material. Sulfur is an industrial byproduct from petroleum refining processes, making its utilization in batteries an effective form of waste valorization that contributes to circular economy principles.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries potentially have a 20-30% lower carbon footprint than traditional lithium-ion technologies when considering manufacturing processes. This reduction stems from the elimination of cobalt and nickel in cathode materials, both of which are associated with intensive mining operations and significant environmental degradation. The extraction of these conventional battery materials often results in habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial greenhouse gas emissions.
However, challenges remain in the environmental profile of Li-S technology. The dissolution of polysulfides during battery operation can lead to capacity fading and potentially create disposal concerns at end-of-life. Research into encapsulation techniques and stable interfaces is addressing these issues, with recent advancements showing promising results in containing sulfur species within the cathode structure.
Water consumption represents another important sustainability metric. Current manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require less water than conventional cathode production, though the exact reduction varies based on specific manufacturing protocols. Emerging dry processing techniques could further reduce water requirements by up to 60%, significantly enhancing the sustainability profile of these batteries.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. The theoretical recyclability of sulfur cathodes exceeds 90%, substantially higher than many conventional cathode materials. However, practical recovery rates currently average 70-75% due to technological limitations in separation processes. Ongoing research into selective dissolution methods and mechanical separation techniques aims to bridge this gap between theoretical and actual recycling efficiency.
From a regulatory perspective, Li-S batteries align well with emerging sustainability frameworks such as the European Union's Battery Directive and the proposed Battery Passport initiative. These regulatory structures increasingly emphasize reduced environmental footprints, ethical material sourcing, and enhanced recyclability—all areas where sulfur cathode technology demonstrates competitive advantages over incumbent technologies.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries potentially have a 20-30% lower carbon footprint than traditional lithium-ion technologies when considering manufacturing processes. This reduction stems from the elimination of cobalt and nickel in cathode materials, both of which are associated with intensive mining operations and significant environmental degradation. The extraction of these conventional battery materials often results in habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial greenhouse gas emissions.
However, challenges remain in the environmental profile of Li-S technology. The dissolution of polysulfides during battery operation can lead to capacity fading and potentially create disposal concerns at end-of-life. Research into encapsulation techniques and stable interfaces is addressing these issues, with recent advancements showing promising results in containing sulfur species within the cathode structure.
Water consumption represents another important sustainability metric. Current manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require less water than conventional cathode production, though the exact reduction varies based on specific manufacturing protocols. Emerging dry processing techniques could further reduce water requirements by up to 60%, significantly enhancing the sustainability profile of these batteries.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. The theoretical recyclability of sulfur cathodes exceeds 90%, substantially higher than many conventional cathode materials. However, practical recovery rates currently average 70-75% due to technological limitations in separation processes. Ongoing research into selective dissolution methods and mechanical separation techniques aims to bridge this gap between theoretical and actual recycling efficiency.
From a regulatory perspective, Li-S batteries align well with emerging sustainability frameworks such as the European Union's Battery Directive and the proposed Battery Passport initiative. These regulatory structures increasingly emphasize reduced environmental footprints, ethical material sourcing, and enhanced recyclability—all areas where sulfur cathode technology demonstrates competitive advantages over incumbent technologies.
Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
The scalability of sulfur cathode technology from laboratory to industrial production represents a critical challenge in lithium-sulfur battery commercialization. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods often involve complex procedures that are difficult to translate into mass production environments. Processes such as melt-diffusion, chemical vapor deposition, and solution-based methods require precise control of temperature, pressure, and reaction conditions that become increasingly challenging at larger scales.
Material cost considerations significantly impact the commercial viability of sulfur cathodes. While elemental sulfur itself is abundant and inexpensive, the conductive additives and host materials required to enhance performance often involve costly carbon nanostructures or metal compounds. The economic feasibility of these components must be evaluated against performance benefits to determine optimal formulations for mass production.
Manufacturing consistency presents another substantial hurdle. The interface mechanisms between sulfur and host materials are highly sensitive to processing conditions, leading to potential batch-to-batch variations in electrochemical performance. Developing robust quality control protocols and in-line monitoring systems is essential to ensure consistent cathode properties across production runs.
Environmental and safety considerations must also be addressed in scaling up sulfur cathode production. The handling of large quantities of elemental sulfur and potentially toxic solvents requires appropriate engineering controls and waste management systems. Sustainable manufacturing approaches that minimize environmental impact while maintaining economic viability are increasingly important for industry adoption.
Equipment compatibility represents a practical challenge in transitioning from laboratory to industrial scale. Many current synthesis methods rely on specialized equipment that may not have direct industrial equivalents. Adapting these processes to work with existing manufacturing infrastructure or developing new equipment solutions specifically designed for sulfur cathode production will be necessary for successful commercialization.
Roll-to-roll processing compatibility is particularly important for integration with existing battery manufacturing lines. The physical properties of sulfur-based electrode materials, including adhesion characteristics, mechanical stability, and coating uniformity, must be optimized for continuous production methods rather than batch processing typically used in laboratory settings.
Material cost considerations significantly impact the commercial viability of sulfur cathodes. While elemental sulfur itself is abundant and inexpensive, the conductive additives and host materials required to enhance performance often involve costly carbon nanostructures or metal compounds. The economic feasibility of these components must be evaluated against performance benefits to determine optimal formulations for mass production.
Manufacturing consistency presents another substantial hurdle. The interface mechanisms between sulfur and host materials are highly sensitive to processing conditions, leading to potential batch-to-batch variations in electrochemical performance. Developing robust quality control protocols and in-line monitoring systems is essential to ensure consistent cathode properties across production runs.
Environmental and safety considerations must also be addressed in scaling up sulfur cathode production. The handling of large quantities of elemental sulfur and potentially toxic solvents requires appropriate engineering controls and waste management systems. Sustainable manufacturing approaches that minimize environmental impact while maintaining economic viability are increasingly important for industry adoption.
Equipment compatibility represents a practical challenge in transitioning from laboratory to industrial scale. Many current synthesis methods rely on specialized equipment that may not have direct industrial equivalents. Adapting these processes to work with existing manufacturing infrastructure or developing new equipment solutions specifically designed for sulfur cathode production will be necessary for successful commercialization.
Roll-to-roll processing compatibility is particularly important for integration with existing battery manufacturing lines. The physical properties of sulfur-based electrode materials, including adhesion characteristics, mechanical stability, and coating uniformity, must be optimized for continuous production methods rather than batch processing typically used in laboratory settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!