Application of Sulfur Cathodes in High-Power Energy Systems
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has evolved significantly over the past few decades, emerging as a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. The journey began in the 1960s with initial explorations into lithium-sulfur electrochemistry, but meaningful progress was limited by fundamental challenges including polysulfide shuttling and poor electrical conductivity. The 2000s marked a renaissance in sulfur cathode research, driven by increasing demands for higher energy density storage solutions and the theoretical capacity of sulfur reaching 1,675 mAh/g—approximately five times higher than traditional lithium-ion cathodes.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by progressive improvements in three key areas: sulfur utilization efficiency, cycle stability, and power performance. Early implementations struggled with rapid capacity fading and low practical energy densities, but recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte engineering have significantly enhanced performance metrics.
Current technological trajectories indicate a convergence toward integrated design approaches that simultaneously address multiple challenges inherent to sulfur electrochemistry. The development of hierarchical porous carbon architectures, polar functional interfaces, and advanced electrolyte formulations represents the cutting edge of contemporary research efforts.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development for high-power energy systems is to achieve commercially viable performance metrics that capitalize on sulfur's theoretical advantages while mitigating its inherent limitations. Specifically, researchers aim to develop cathodes capable of delivering energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, maintaining stable performance over 1,000+ cycles, and supporting high discharge rates necessary for demanding applications such as electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage.
Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing complexity and cost, enhancing safety profiles through thermal stability improvements, and developing environmentally sustainable production methods that leverage sulfur's abundance and low environmental impact. The ultimate goal is to position sulfur cathodes as a viable alternative to conventional lithium-ion technologies in applications where high energy density and power capability are paramount.
The technological roadmap for sulfur cathodes in high-power systems anticipates gradual implementation, beginning with specialized applications tolerant of current limitations before expanding to mainstream markets as performance metrics improve. This staged approach allows for iterative refinement while establishing manufacturing infrastructure and supply chains necessary for large-scale commercialization.
The evolution of sulfur cathode technology has been characterized by progressive improvements in three key areas: sulfur utilization efficiency, cycle stability, and power performance. Early implementations struggled with rapid capacity fading and low practical energy densities, but recent advancements in nanostructured carbon hosts, functional polymer binders, and electrolyte engineering have significantly enhanced performance metrics.
Current technological trajectories indicate a convergence toward integrated design approaches that simultaneously address multiple challenges inherent to sulfur electrochemistry. The development of hierarchical porous carbon architectures, polar functional interfaces, and advanced electrolyte formulations represents the cutting edge of contemporary research efforts.
The primary objective of sulfur cathode technology development for high-power energy systems is to achieve commercially viable performance metrics that capitalize on sulfur's theoretical advantages while mitigating its inherent limitations. Specifically, researchers aim to develop cathodes capable of delivering energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg at the cell level, maintaining stable performance over 1,000+ cycles, and supporting high discharge rates necessary for demanding applications such as electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage.
Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing complexity and cost, enhancing safety profiles through thermal stability improvements, and developing environmentally sustainable production methods that leverage sulfur's abundance and low environmental impact. The ultimate goal is to position sulfur cathodes as a viable alternative to conventional lithium-ion technologies in applications where high energy density and power capability are paramount.
The technological roadmap for sulfur cathodes in high-power systems anticipates gradual implementation, beginning with specialized applications tolerant of current limitations before expanding to mainstream markets as performance metrics improve. This staged approach allows for iterative refinement while establishing manufacturing infrastructure and supply chains necessary for large-scale commercialization.
Market Analysis for High-Power Energy Storage Systems
The high-power energy storage systems market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy integration, grid stabilization, and electrification of transportation. The global market for high-power energy storage reached approximately $12 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18-20% through 2030, potentially reaching $45-50 billion by the end of the decade.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate this market segment, accounting for roughly 70% of installed high-power storage capacity. However, their limitations in energy density, cost, and safety concerns have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies like sulfur-based cathodes, which offer theoretical energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion systems.
The transportation sector represents the largest application segment for high-power energy storage, particularly in electric vehicles requiring rapid acceleration and fast-charging capabilities. This sector alone constitutes approximately 45% of the market demand, followed by grid services (30%) and industrial applications (15%).
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, holding about 40% of the global share, primarily due to extensive manufacturing capabilities in China, Japan, and South Korea. North America follows with 30% market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Europe accounts for 25%, with particularly strong growth in countries with aggressive renewable energy targets.
Customer requirements in high-power applications emphasize power density, cycle life, safety, and increasingly, sustainability metrics. The market shows willingness to pay premium prices for solutions offering 20-30% improvements in power density or cycle life compared to standard lithium-ion systems.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market dynamics, with policies promoting renewable energy integration and carbon reduction creating favorable conditions for advanced energy storage technologies. The European Union's Green Deal and similar initiatives in North America and Asia have established supportive frameworks for next-generation storage solutions, including those utilizing sulfur cathodes.
Market barriers include technology maturity concerns, established supply chains for incumbent technologies, and initial cost considerations. However, the projected decline in manufacturing costs for sulfur-based cathodes (estimated at 8-12% annually) is expected to substantially improve market penetration over the next five years.
The competitive landscape features both established energy storage providers expanding their technology portfolios and specialized startups focused exclusively on sulfur-based solutions, creating a dynamic environment for innovation and commercial deployment.
Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate this market segment, accounting for roughly 70% of installed high-power storage capacity. However, their limitations in energy density, cost, and safety concerns have created significant opportunities for alternative technologies like sulfur-based cathodes, which offer theoretical energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion systems.
The transportation sector represents the largest application segment for high-power energy storage, particularly in electric vehicles requiring rapid acceleration and fast-charging capabilities. This sector alone constitutes approximately 45% of the market demand, followed by grid services (30%) and industrial applications (15%).
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, holding about 40% of the global share, primarily due to extensive manufacturing capabilities in China, Japan, and South Korea. North America follows with 30% market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Europe accounts for 25%, with particularly strong growth in countries with aggressive renewable energy targets.
Customer requirements in high-power applications emphasize power density, cycle life, safety, and increasingly, sustainability metrics. The market shows willingness to pay premium prices for solutions offering 20-30% improvements in power density or cycle life compared to standard lithium-ion systems.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market dynamics, with policies promoting renewable energy integration and carbon reduction creating favorable conditions for advanced energy storage technologies. The European Union's Green Deal and similar initiatives in North America and Asia have established supportive frameworks for next-generation storage solutions, including those utilizing sulfur cathodes.
Market barriers include technology maturity concerns, established supply chains for incumbent technologies, and initial cost considerations. However, the projected decline in manufacturing costs for sulfur-based cathodes (estimated at 8-12% annually) is expected to substantially improve market penetration over the next five years.
The competitive landscape features both established energy storage providers expanding their technology portfolios and specialized startups focused exclusively on sulfur-based solutions, creating a dynamic environment for innovation and commercial deployment.
Current Status and Technical Challenges of Sulfur Cathodes
Sulfur cathodes have emerged as a promising technology in high-power energy systems due to their high theoretical energy density (2600 Wh/kg) and cost-effectiveness. Currently, the global research landscape shows significant advancements in sulfur cathode technology, with major research centers in North America, Europe, and East Asia leading development efforts. Laboratory-scale lithium-sulfur batteries have demonstrated energy densities of 400-600 Wh/kg, substantially exceeding conventional lithium-ion batteries, though still far from theoretical limits.
Despite these achievements, sulfur cathodes face several critical technical challenges that hinder their widespread commercial adoption. The most significant issue is the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. Current solutions involving electrolyte modifications and physical barriers show promise but remain insufficient for long-term stability.
Poor electrical conductivity represents another major obstacle, as elemental sulfur and its discharge products (Li2S/Li2S2) are inherently insulating. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations (typically 30-40% by weight), which significantly reduces the practical energy density of the entire system. Various conductive frameworks and sulfur hosts have been developed, but balancing conductivity enhancement with high sulfur loading remains challenging.
Volume expansion during cycling presents a substantial mechanical challenge, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% volume change during lithiation/delithiation processes. This expansion leads to structural degradation, particle isolation, and eventual capacity loss. Current mitigation strategies include flexible electrode designs and specialized binders, though long-term mechanical stability remains elusive.
For high-power applications specifically, sulfur cathodes exhibit poor rate capability due to slow reaction kinetics and mass transport limitations. The conversion reaction mechanism between sulfur and lithium involves multiple steps and phase transitions, resulting in significant polarization at high current densities. Recent research has focused on catalytic materials to accelerate these reactions, but substantial improvements are still needed to meet the demands of high-power applications.
The geographical distribution of sulfur cathode technology development shows concentration in regions with established battery research infrastructure. China leads in patent applications, while the United States and Germany contribute significant fundamental research. Japan and South Korea focus on industrial applications, leveraging their existing battery manufacturing expertise to accelerate commercialization efforts.
Despite these achievements, sulfur cathodes face several critical technical challenges that hinder their widespread commercial adoption. The most significant issue is the "shuttle effect," where soluble polysulfide intermediates dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing active material loss, reduced coulombic efficiency, and accelerated capacity fading. Current solutions involving electrolyte modifications and physical barriers show promise but remain insufficient for long-term stability.
Poor electrical conductivity represents another major obstacle, as elemental sulfur and its discharge products (Li2S/Li2S2) are inherently insulating. This limitation necessitates high carbon content in cathode formulations (typically 30-40% by weight), which significantly reduces the practical energy density of the entire system. Various conductive frameworks and sulfur hosts have been developed, but balancing conductivity enhancement with high sulfur loading remains challenging.
Volume expansion during cycling presents a substantial mechanical challenge, with sulfur cathodes experiencing up to 80% volume change during lithiation/delithiation processes. This expansion leads to structural degradation, particle isolation, and eventual capacity loss. Current mitigation strategies include flexible electrode designs and specialized binders, though long-term mechanical stability remains elusive.
For high-power applications specifically, sulfur cathodes exhibit poor rate capability due to slow reaction kinetics and mass transport limitations. The conversion reaction mechanism between sulfur and lithium involves multiple steps and phase transitions, resulting in significant polarization at high current densities. Recent research has focused on catalytic materials to accelerate these reactions, but substantial improvements are still needed to meet the demands of high-power applications.
The geographical distribution of sulfur cathode technology development shows concentration in regions with established battery research infrastructure. China leads in patent applications, while the United States and Germany contribute significant fundamental research. Japan and South Korea focus on industrial applications, leveraging their existing battery manufacturing expertise to accelerate commercialization efforts.
Current Technical Solutions for Sulfur Cathode Implementation
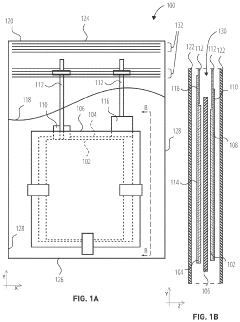
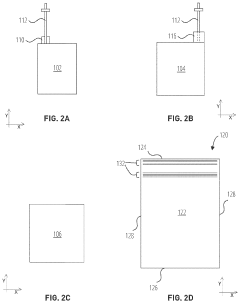
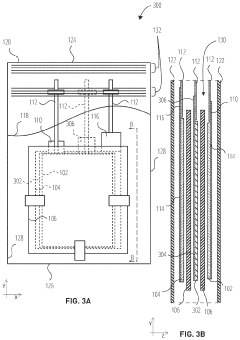
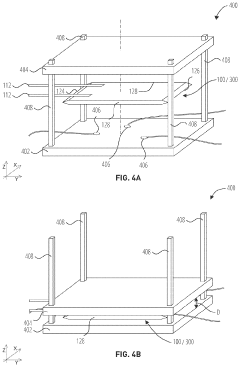
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive additives, binders, and other materials to improve conductivity and stability. The cathode composition directly affects energy density, cycle life, and overall battery performance. Advanced formulations aim to address challenges such as sulfur dissolution and polysulfide shuttling.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides to improve conductivity, cycle life, and capacity retention.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating specialized architectures at the nanoscale to improve battery performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, core-shell structures, and hierarchical porous materials that can effectively trap polysulfides while maintaining good electronic conductivity. Nanostructuring helps to accommodate volume changes during cycling and provides shorter diffusion paths for lithium ions, resulting in improved capacity and cycling stability.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to mitigate polysulfide shuttling and improve electrochemical performance. These protective layers may consist of polymers, metal oxides, or composite materials that act as physical barriers while allowing lithium ion transport. Functional interlayers between the cathode and separator can also trap dissolved polysulfides and prevent their migration to the anode, thereby extending battery life and improving coulombic efficiency.
- Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the performance of sulfur cathodes. These may include additives that form protective films on the cathode surface, solvents with reduced polysulfide solubility, or ionic liquids that enhance ionic conductivity while suppressing polysulfide dissolution. Some electrolyte systems incorporate lithium salts with specific anions that interact favorably with polysulfides or form stable solid electrolyte interphases, leading to improved cycling stability and reduced capacity fade.
- Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques can be employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods where sulfur is infiltrated into porous host materials, solution-based processes for creating uniform sulfur-carbon composites, and advanced coating techniques for applying protective layers. Some processes involve high-temperature treatment to optimize sulfur distribution within the conductive matrix, while others focus on environmentally friendly, scalable approaches suitable for industrial production. The manufacturing method significantly impacts the cathode's structure, sulfur loading, and electrochemical performance.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured materials are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to improve electrochemical performance. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, mesoporous carbon, and other nanoscale materials that provide high surface area and conductive pathways. Nanostructuring helps contain sulfur within the cathode structure, mitigates polysulfide shuttling, and enhances electron transport. These approaches significantly improve capacity retention and cycling stability of sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to prevent polysulfide dissolution and migration. These include polymer coatings, metal oxide layers, and functional separators that act as physical barriers. Such protective structures help maintain the integrity of the cathode during cycling, reduce capacity fading, and extend battery life. Advanced coating technologies enable controlled ion transport while blocking polysulfide diffusion.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sulfur cathode binders and electrolyte systems
Specialized binders and electrolyte systems are developed for sulfur cathodes to enhance performance and stability. Novel polymer binders provide mechanical strength and help retain active material during cycling. Advanced electrolyte formulations, including additives and ionic liquids, suppress polysulfide dissolution and promote stable solid-electrolyte interphase formation. The combination of optimized binders and electrolytes significantly improves the cycling performance of sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based techniques, and advanced deposition processes. Manufacturing considerations include sulfur loading, electrode thickness, porosity control, and scalability. Innovative production methods aim to achieve uniform sulfur distribution, optimal pore structure, and strong adhesion to current collectors, all of which are critical for commercial viability of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Sulfur Cathode Development
The sulfur cathode technology in high-power energy systems is currently in a transitional phase from early development to commercial application, with the market expected to grow significantly due to increasing demand for higher energy density batteries. The global market for sulfur-based battery technologies is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2030, driven by electric vehicle and grid storage applications. Leading companies like Sion Power, PolyPlus Battery, and Sila Nanotechnologies have made significant advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology, while established players such as Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and Nissan are investing heavily in research. Academic institutions including MIT, Nankai University, and Drexel University are contributing fundamental research to overcome key challenges of sulfur cathodes, particularly addressing cycle life limitations and sulfur dissolution issues.
Ionic Materials Inc.
Technical Solution: Ionic Materials has developed a revolutionary solid polymer electrolyte that enables stable operation of sulfur cathodes in high-power energy systems. Their proprietary polymer conducts lithium ions at room temperature without liquid components, fundamentally addressing the polysulfide shuttle effect that typically plagues sulfur cathodes. The solid-state nature of their electrolyte prevents dissolution of sulfur reaction products, maintaining cathode integrity over extended cycling. Ionic Materials' technology allows for direct contact between lithium metal anodes and sulfur cathodes without dendrite formation or internal shorting. Their sulfur cathode formulation incorporates the polymer electrolyte directly into the cathode structure, creating a single-phase system with improved interfacial properties. The company has demonstrated cells with energy densities approaching 500 Wh/kg while maintaining stable performance at high discharge rates. Recent developments include optimization for power applications through electrode architecture modifications and polymer composition tuning.
Strengths: Solid-state design eliminates fundamental polysulfide shuttle issues; Enhanced safety due to non-flammable electrolyte; Compatible with high-energy lithium metal anodes. Weaknesses: Lower ionic conductivity than liquid electrolytes, potentially limiting high-power applications; Manufacturing challenges for solid-state cells at scale; Temperature sensitivity of polymer performance.
PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: PolyPlus has pioneered a protected lithium electrode (PLE) technology that enables stable cycling of sulfur cathodes in high-power applications. Their approach uses a ceramic membrane that prevents direct contact between lithium metal and the electrolyte while allowing efficient lithium-ion transport. This technology addresses the fundamental challenge of lithium-sulfur batteries by protecting the lithium anode from polysulfide shuttling and dendrite formation. PolyPlus's sulfur cathode design incorporates a hierarchical carbon framework with optimized pore structure to accommodate sulfur expansion during discharge while maintaining electrical connectivity. The company has demonstrated cells with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg and improved cycle life compared to conventional lithium-sulfur designs. Their technology also features a specialized electrolyte system that enhances sulfur utilization and reduces capacity fade. Recent developments include adapting their technology for high-power applications through electrode architecture optimization.
Strengths: Unique protected lithium electrode technology that addresses fundamental lithium-sulfur challenges; Very high energy density potential; Applicable to multiple battery chemistries beyond sulfur. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process for the ceramic membrane; Higher cost structure than conventional approaches; Challenges with mechanical stability during repeated cycling.
Critical Patents and Research Breakthroughs in Sulfur Cathodes
Methods for operating energy storage devices with sulfur-based cathodes, and related systems and methods
PatentPendingUS20230268568A1
Innovation
- Applying external pressure to the electrochemical cell during charging and discharging, which optimizes the performance parameters such as energy density and cycling properties by inhibiting dendrite growth and maintaining the structural integrity of the cathode, thereby enhancing the electrochemical performance of sulfur-based cathodes.
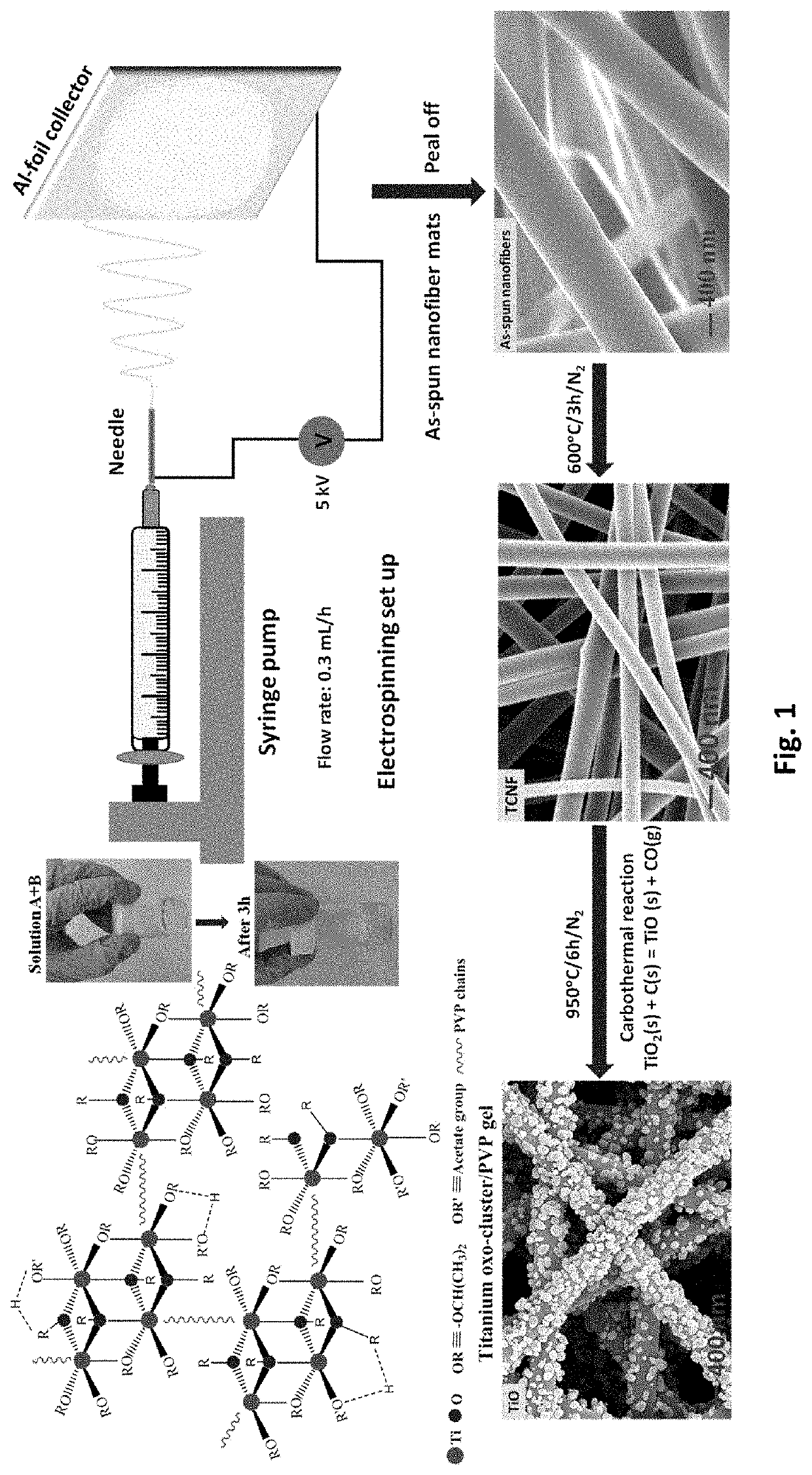
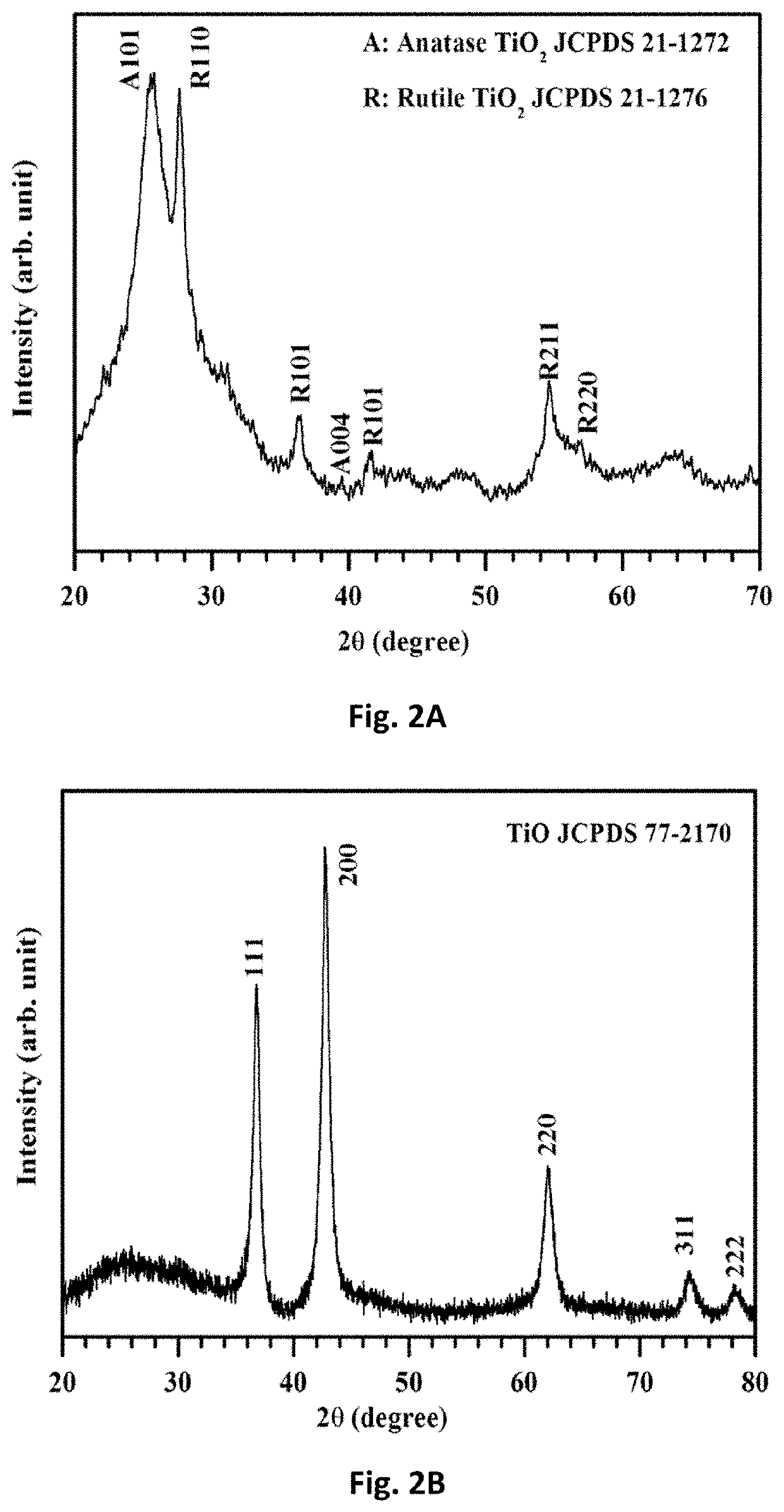
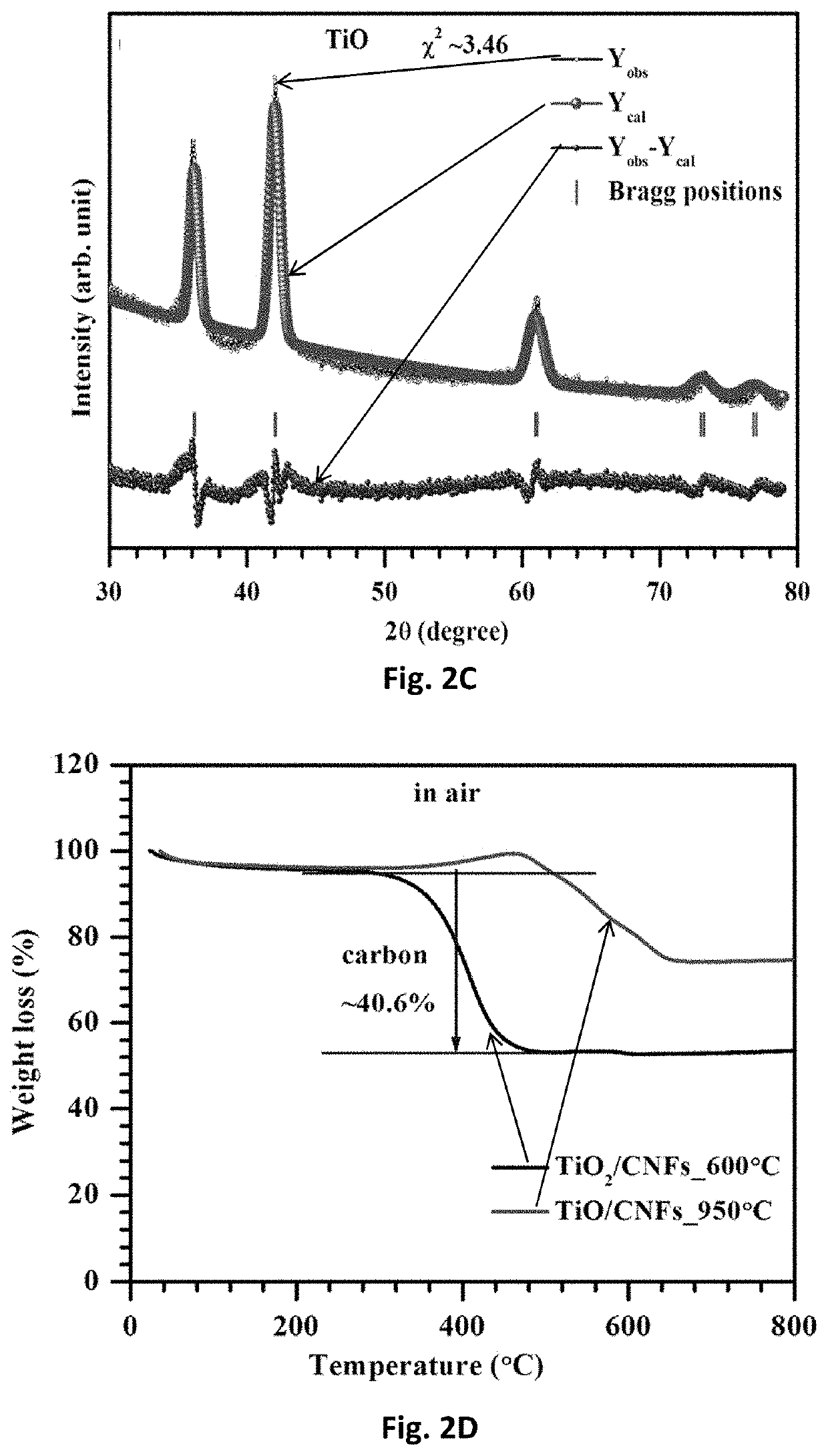
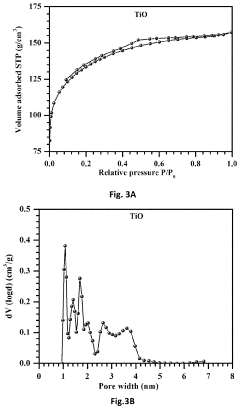
Free-standing, binder-free metal monoxide/suboxide nanofiber as cathodes or anodes for batteries
PatentActiveUS20210111390A1
Innovation
- The development of free-standing, binder-free nanofiber mats with high surface area and conductive metal oxide nanofibers, produced through electrospinning and carbothermal processes, which allow rapid sulfur diffusion and eliminate the need for harsh slurry casting, providing a robust 3D conducting network for uninterrupted electron supply and strong interactions with lithium polysulfides.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of sulfur cathode technology in high-power energy systems represents a critical consideration in the broader context of sustainable energy development. Sulfur, as an abundant non-metal element constituting approximately 0.03% of the Earth's crust, offers significant environmental advantages compared to traditional cathode materials like cobalt and nickel. The extraction processes for these conventional materials often involve intensive mining operations that result in habitat destruction, soil degradation, and water pollution.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that sulfur-based cathode production generates approximately 60-70% lower carbon emissions compared to conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. This reduction stems primarily from sulfur's status as an industrial byproduct, particularly from petroleum refining processes, where it is removed as a contaminant. Repurposing this waste stream into high-value battery components creates a circular economy opportunity that significantly enhances the sustainability profile of energy storage systems.
Water consumption metrics further highlight the environmental benefits of sulfur cathode technology. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require 40-50% less water compared to conventional cathode production. This reduced water footprint becomes increasingly important as water scarcity affects more regions globally, particularly in areas where battery manufacturing facilities are concentrated.
End-of-life considerations also favor sulfur-based systems. The recyclability of sulfur cathodes presents fewer technical challenges than conventional lithium-ion batteries, with laboratory-scale processes demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur content. This recyclability potential addresses critical concerns regarding electronic waste accumulation and resource conservation.
However, several environmental challenges remain unresolved. The formation of soluble polysulfides during battery operation can lead to capacity fading and potentially hazardous waste if not properly managed. Additionally, while sulfur itself poses minimal toxicity concerns, some conductive additives and electrolyte components used in sulfur cathode systems may present environmental risks that require further assessment and mitigation strategies.
The sustainability advantages of sulfur cathodes extend beyond direct environmental impacts to include broader socioeconomic benefits. By reducing dependence on geographically concentrated critical minerals like cobalt, sulfur-based energy storage systems can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce geopolitical vulnerabilities in the renewable energy transition. This aspect becomes particularly relevant as high-power energy applications expand across transportation, grid storage, and industrial sectors.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that sulfur-based cathode production generates approximately 60-70% lower carbon emissions compared to conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. This reduction stems primarily from sulfur's status as an industrial byproduct, particularly from petroleum refining processes, where it is removed as a contaminant. Repurposing this waste stream into high-value battery components creates a circular economy opportunity that significantly enhances the sustainability profile of energy storage systems.
Water consumption metrics further highlight the environmental benefits of sulfur cathode technology. Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes typically require 40-50% less water compared to conventional cathode production. This reduced water footprint becomes increasingly important as water scarcity affects more regions globally, particularly in areas where battery manufacturing facilities are concentrated.
End-of-life considerations also favor sulfur-based systems. The recyclability of sulfur cathodes presents fewer technical challenges than conventional lithium-ion batteries, with laboratory-scale processes demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 90% for sulfur content. This recyclability potential addresses critical concerns regarding electronic waste accumulation and resource conservation.
However, several environmental challenges remain unresolved. The formation of soluble polysulfides during battery operation can lead to capacity fading and potentially hazardous waste if not properly managed. Additionally, while sulfur itself poses minimal toxicity concerns, some conductive additives and electrolyte components used in sulfur cathode systems may present environmental risks that require further assessment and mitigation strategies.
The sustainability advantages of sulfur cathodes extend beyond direct environmental impacts to include broader socioeconomic benefits. By reducing dependence on geographically concentrated critical minerals like cobalt, sulfur-based energy storage systems can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce geopolitical vulnerabilities in the renewable energy transition. This aspect becomes particularly relevant as high-power energy applications expand across transportation, grid storage, and industrial sectors.
Cost-Performance Analysis and Commercial Viability
The economic viability of sulfur cathode technology in high-power energy systems hinges on its cost-performance ratio compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Sulfur as a cathode material offers significant cost advantages, with raw sulfur priced at approximately $0.10-0.15 per kilogram, representing less than 1% of the cost of traditional cathode materials like nickel, cobalt, and manganese compounds. This translates to a potential reduction of 30-40% in overall battery costs when accounting for manufacturing processes and auxiliary materials.
Performance metrics reveal a complex value proposition. While lithium-sulfur batteries demonstrate theoretical energy densities of 2,500-2,700 Wh/kg (compared to 250-300 Wh/kg for conventional Li-ion), practical implementations currently achieve only 400-600 Wh/kg due to technical limitations. The cost-per-kilowatt-hour metric shows promise, with projections suggesting $80-100/kWh for mature sulfur cathode systems versus $130-150/kWh for advanced Li-ion batteries.
Cycle life remains a critical challenge affecting commercial viability. Current sulfur cathode systems typically achieve 300-500 cycles before significant capacity degradation, compared to 1,000-2,000 cycles for commercial Li-ion batteries. This translates to a higher lifetime cost despite lower initial investment, particularly in high-power applications where frequent cycling is expected.
Manufacturing scalability presents both opportunities and challenges. Sulfur cathode production can leverage existing battery manufacturing infrastructure with modifications, requiring approximately 15-25% lower capital expenditure than establishing new Li-ion production lines. However, specialized equipment for handling sulfur compounds and preventing polysulfide shuttle effects adds complexity to manufacturing processes.
Market entry strategies suggest initial commercialization in niche applications where energy density outweighs cycle life concerns, such as military applications, specialized electric vehicles, and aerospace. The estimated timeline for broad commercial viability in high-power applications is 3-5 years, contingent upon resolving the polysulfide shuttle effect and improving cycle stability.
Return on investment calculations indicate that despite higher initial research and development costs, sulfur cathode technology could achieve cost parity with conventional systems within 2-3 years of mass production, with potential for 15-20% lower total cost of ownership over a 5-year period in specific high-power applications where weight and volume constraints justify premium pricing.
Performance metrics reveal a complex value proposition. While lithium-sulfur batteries demonstrate theoretical energy densities of 2,500-2,700 Wh/kg (compared to 250-300 Wh/kg for conventional Li-ion), practical implementations currently achieve only 400-600 Wh/kg due to technical limitations. The cost-per-kilowatt-hour metric shows promise, with projections suggesting $80-100/kWh for mature sulfur cathode systems versus $130-150/kWh for advanced Li-ion batteries.
Cycle life remains a critical challenge affecting commercial viability. Current sulfur cathode systems typically achieve 300-500 cycles before significant capacity degradation, compared to 1,000-2,000 cycles for commercial Li-ion batteries. This translates to a higher lifetime cost despite lower initial investment, particularly in high-power applications where frequent cycling is expected.
Manufacturing scalability presents both opportunities and challenges. Sulfur cathode production can leverage existing battery manufacturing infrastructure with modifications, requiring approximately 15-25% lower capital expenditure than establishing new Li-ion production lines. However, specialized equipment for handling sulfur compounds and preventing polysulfide shuttle effects adds complexity to manufacturing processes.
Market entry strategies suggest initial commercialization in niche applications where energy density outweighs cycle life concerns, such as military applications, specialized electric vehicles, and aerospace. The estimated timeline for broad commercial viability in high-power applications is 3-5 years, contingent upon resolving the polysulfide shuttle effect and improving cycle stability.
Return on investment calculations indicate that despite higher initial research and development costs, sulfur cathode technology could achieve cost parity with conventional systems within 2-3 years of mass production, with potential for 15-20% lower total cost of ownership over a 5-year period in specific high-power applications where weight and volume constraints justify premium pricing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!