Sulfur Cathodes Role in Climate Change Mitigation Strategies
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Sulfur cathode technology has emerged as a promising avenue in the field of energy storage systems, particularly in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, which have gained significant attention over the past two decades. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the 1960s when the theoretical framework for Li-S batteries was first established. However, substantial research momentum only began building in the early 2000s when the limitations of conventional lithium-ion batteries became increasingly apparent in addressing climate change challenges.
The technological trajectory of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by incremental improvements addressing key challenges such as the polysulfide shuttle effect, volume expansion issues, and low electrical conductivity. These advancements have progressively enhanced the energy density, cycle life, and overall performance of sulfur-based energy storage systems, positioning them as potential game-changers in the renewable energy landscape.
Current research trends indicate a growing focus on nanostructured carbon-sulfur composites, functional polymer binders, and advanced electrolyte formulations to overcome the inherent limitations of sulfur cathodes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches has also accelerated materials discovery and optimization processes, significantly reducing development timelines and enhancing performance metrics.
From a climate change mitigation perspective, sulfur cathode technology offers several compelling advantages. Sulfur is an abundant by-product of petroleum refining, making it environmentally advantageous to repurpose this waste material for energy storage applications. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg for LiCoO₂), potentially enabling more efficient renewable energy integration and electrification of transportation.
The primary technical objectives in this field include achieving stable long-cycle performance exceeding 1000 cycles at practical loading conditions, developing scalable manufacturing processes for commercial viability, and ensuring safety under various operational conditions. Researchers are also exploring sulfur cathodes beyond Li-S systems, including sodium-sulfur, magnesium-sulfur, and aluminum-sulfur batteries, expanding the potential application spectrum.
Industry projections suggest that successful commercialization of sulfur cathode technology could significantly accelerate the transition to renewable energy by providing cost-effective, high-capacity storage solutions for grid applications and electric vehicles. This would directly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by enabling higher renewable energy penetration and accelerating transportation electrification.
The convergence of materials science, electrochemistry, and sustainable engineering principles in sulfur cathode development represents a holistic approach to addressing climate change through advanced energy storage solutions. The technology aims not only to improve performance metrics but also to establish environmentally benign production and recycling processes, aligning with circular economy principles.
The technological trajectory of sulfur cathodes has been characterized by incremental improvements addressing key challenges such as the polysulfide shuttle effect, volume expansion issues, and low electrical conductivity. These advancements have progressively enhanced the energy density, cycle life, and overall performance of sulfur-based energy storage systems, positioning them as potential game-changers in the renewable energy landscape.
Current research trends indicate a growing focus on nanostructured carbon-sulfur composites, functional polymer binders, and advanced electrolyte formulations to overcome the inherent limitations of sulfur cathodes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches has also accelerated materials discovery and optimization processes, significantly reducing development timelines and enhancing performance metrics.
From a climate change mitigation perspective, sulfur cathode technology offers several compelling advantages. Sulfur is an abundant by-product of petroleum refining, making it environmentally advantageous to repurpose this waste material for energy storage applications. The theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries (2600 Wh/kg) far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (387 Wh/kg for LiCoO₂), potentially enabling more efficient renewable energy integration and electrification of transportation.
The primary technical objectives in this field include achieving stable long-cycle performance exceeding 1000 cycles at practical loading conditions, developing scalable manufacturing processes for commercial viability, and ensuring safety under various operational conditions. Researchers are also exploring sulfur cathodes beyond Li-S systems, including sodium-sulfur, magnesium-sulfur, and aluminum-sulfur batteries, expanding the potential application spectrum.
Industry projections suggest that successful commercialization of sulfur cathode technology could significantly accelerate the transition to renewable energy by providing cost-effective, high-capacity storage solutions for grid applications and electric vehicles. This would directly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by enabling higher renewable energy penetration and accelerating transportation electrification.
The convergence of materials science, electrochemistry, and sustainable engineering principles in sulfur cathode development represents a holistic approach to addressing climate change through advanced energy storage solutions. The technology aims not only to improve performance metrics but also to establish environmentally benign production and recycling processes, aligning with circular economy principles.
Market Analysis for Sulfur-Based Energy Storage Solutions
The global market for sulfur-based energy storage solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and cost-effective energy storage technologies. The market size for lithium-sulfur batteries alone was valued at approximately $551 million in 2022 and is projected to reach $2.1 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 18.3% during the forecast period.
The demand for sulfur-based energy storage solutions is primarily fueled by the growing adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, which require efficient energy storage systems to address intermittency issues. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards electric vehicles has created substantial demand for high-energy-density batteries, where sulfur cathodes offer promising advantages.
Regional analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates the market, accounting for over 45% of the global share, with China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe follow, with significant investments in research and development of advanced sulfur-based technologies. Emerging economies in South America and Africa represent untapped markets with considerable growth potential, particularly for off-grid and microgrid applications.
Consumer electronics represent another substantial market segment, with manufacturers seeking higher energy density solutions to extend device operation times. The telecommunications sector also shows increasing interest in sulfur-based energy storage for backup power systems, especially in remote locations where traditional grid infrastructure is unavailable or unreliable.
Market segmentation by application reveals that grid-scale energy storage currently constitutes approximately 38% of the market, followed by electric vehicles at 32%, consumer electronics at 18%, and other applications at 12%. The grid-scale segment is expected to maintain its leading position due to increasing investments in renewable energy infrastructure worldwide.
Key market drivers include declining costs of raw materials, technological advancements improving cycle life and safety, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy adoption. The abundance and low cost of sulfur, primarily available as a byproduct of petroleum refining, provide a significant economic advantage over other battery chemistries relying on scarce or expensive materials.
Market challenges include addressing technical limitations such as the "shuttle effect" in lithium-sulfur batteries, scaling up manufacturing processes, and competing with established lithium-ion technologies. However, the environmental benefits of sulfur-based solutions, including reduced carbon footprint and minimal use of critical raw materials, position them favorably in markets with strong sustainability mandates.
The demand for sulfur-based energy storage solutions is primarily fueled by the growing adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, which require efficient energy storage systems to address intermittency issues. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards electric vehicles has created substantial demand for high-energy-density batteries, where sulfur cathodes offer promising advantages.
Regional analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates the market, accounting for over 45% of the global share, with China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe follow, with significant investments in research and development of advanced sulfur-based technologies. Emerging economies in South America and Africa represent untapped markets with considerable growth potential, particularly for off-grid and microgrid applications.
Consumer electronics represent another substantial market segment, with manufacturers seeking higher energy density solutions to extend device operation times. The telecommunications sector also shows increasing interest in sulfur-based energy storage for backup power systems, especially in remote locations where traditional grid infrastructure is unavailable or unreliable.
Market segmentation by application reveals that grid-scale energy storage currently constitutes approximately 38% of the market, followed by electric vehicles at 32%, consumer electronics at 18%, and other applications at 12%. The grid-scale segment is expected to maintain its leading position due to increasing investments in renewable energy infrastructure worldwide.
Key market drivers include declining costs of raw materials, technological advancements improving cycle life and safety, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy adoption. The abundance and low cost of sulfur, primarily available as a byproduct of petroleum refining, provide a significant economic advantage over other battery chemistries relying on scarce or expensive materials.
Market challenges include addressing technical limitations such as the "shuttle effect" in lithium-sulfur batteries, scaling up manufacturing processes, and competing with established lithium-ion technologies. However, the environmental benefits of sulfur-based solutions, including reduced carbon footprint and minimal use of critical raw materials, position them favorably in markets with strong sustainability mandates.
Technical Challenges and Global Development Status
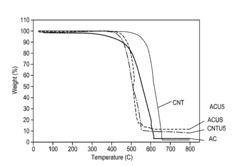
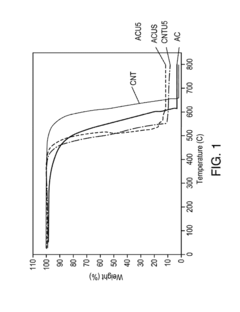
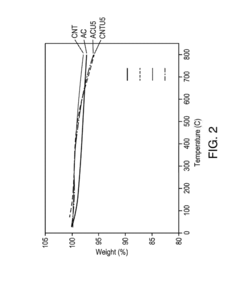
Sulfur cathodes represent a promising technology for next-generation energy storage systems, yet they face significant technical challenges that have hindered widespread commercial adoption. The primary obstacle remains the "polysulfide shuttle effect," where soluble lithium polysulfides dissolve in the electrolyte during cycling, causing capacity fading and reduced battery lifespan. Despite extensive research efforts, this phenomenon continues to limit the practical application of sulfur cathodes in commercial products.
Another critical challenge is the inherent poor electrical conductivity of sulfur, necessitating the addition of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. The volume expansion during lithiation (reaching up to 80%) creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over multiple cycles, further complicating long-term stability.
Globally, research on sulfur cathodes has accelerated significantly in the past decade, with distinct regional focuses emerging. North American institutions, particularly in the United States and Canada, have concentrated on fundamental materials science approaches, developing novel carbon hosts and functional electrolytes. The U.S. Department of Energy has established dedicated research programs through its Battery500 Consortium specifically targeting lithium-sulfur technology.
European research centers, especially in Germany, France, and the UK, have emphasized system integration and manufacturing scalability. The European Union's Horizon Europe program has allocated substantial funding for sulfur cathode development as part of its climate neutrality initiatives. Asian countries, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, lead in patent filings related to sulfur cathode technologies, with Chinese institutions demonstrating remarkable progress in practical prototype development.
Recent technological breakthroughs include the development of polar host materials that chemically bind polysulfides, advanced electrolyte formulations that suppress shuttle effects, and protective coatings that enhance cycling stability. However, the translation of these laboratory achievements to industrial-scale manufacturing remains challenging due to cost considerations and process complexity.
The current technology readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathodes varies by application, with specialized high-energy density applications reaching TRL 5-6, while mainstream applications remain at TRL 3-4. This disparity highlights the need for continued research and development to address fundamental challenges while simultaneously advancing manufacturing capabilities.
Environmental considerations present both opportunities and challenges, as sulfur itself is an abundant byproduct of petroleum refining, offering sustainability advantages. However, end-of-life recycling processes for sulfur cathodes require further development to fully realize their potential as a climate change mitigation technology.
Another critical challenge is the inherent poor electrical conductivity of sulfur, necessitating the addition of conductive additives that reduce the overall energy density of the battery system. The volume expansion during lithiation (reaching up to 80%) creates mechanical stress that degrades electrode integrity over multiple cycles, further complicating long-term stability.
Globally, research on sulfur cathodes has accelerated significantly in the past decade, with distinct regional focuses emerging. North American institutions, particularly in the United States and Canada, have concentrated on fundamental materials science approaches, developing novel carbon hosts and functional electrolytes. The U.S. Department of Energy has established dedicated research programs through its Battery500 Consortium specifically targeting lithium-sulfur technology.
European research centers, especially in Germany, France, and the UK, have emphasized system integration and manufacturing scalability. The European Union's Horizon Europe program has allocated substantial funding for sulfur cathode development as part of its climate neutrality initiatives. Asian countries, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, lead in patent filings related to sulfur cathode technologies, with Chinese institutions demonstrating remarkable progress in practical prototype development.
Recent technological breakthroughs include the development of polar host materials that chemically bind polysulfides, advanced electrolyte formulations that suppress shuttle effects, and protective coatings that enhance cycling stability. However, the translation of these laboratory achievements to industrial-scale manufacturing remains challenging due to cost considerations and process complexity.
The current technology readiness level (TRL) of sulfur cathodes varies by application, with specialized high-energy density applications reaching TRL 5-6, while mainstream applications remain at TRL 3-4. This disparity highlights the need for continued research and development to address fundamental challenges while simultaneously advancing manufacturing capabilities.
Environmental considerations present both opportunities and challenges, as sulfur itself is an abundant byproduct of petroleum refining, offering sustainability advantages. However, end-of-life recycling processes for sulfur cathodes require further development to fully realize their potential as a climate change mitigation technology.
Current Sulfur Cathode Implementation Approaches
01 Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries
Sulfur cathodes can be formulated with various compositions to enhance performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. These compositions typically include sulfur as the active material combined with conductive additives and binders. The formulations aim to address challenges such as low conductivity of sulfur and polysulfide dissolution. Advanced compositions may incorporate carbon materials, polymers, or other additives to improve conductivity, cycle life, and energy density.- Sulfur cathode compositions for lithium-sulfur batteries: Various compositions for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries have been developed to improve energy density and cycle life. These compositions typically include elemental sulfur combined with conductive materials such as carbon and polymeric binders. The cathode compositions are designed to address challenges like the polysulfide shuttle effect and volume expansion during cycling, which are common issues in sulfur-based battery systems.
- Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials: Nanostructured materials are incorporated into sulfur cathodes to enhance performance characteristics. These include carbon nanotubes, graphene, and other nanoscale carbon structures that provide improved electrical conductivity and structural stability. The nanostructured approach helps contain sulfur within the cathode structure, mitigating dissolution into the electrolyte and improving overall battery performance and longevity.
- Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes: Protective coatings and interlayers are applied to sulfur cathodes to prevent polysulfide migration and improve cycling stability. These coatings can be made from polymers, metal oxides, or composite materials that act as physical barriers while maintaining ion conductivity. The implementation of these protective layers significantly reduces capacity fading and extends the operational life of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Electrolyte systems for sulfur cathodes: Specialized electrolyte systems are developed for use with sulfur cathodes to improve performance and stability. These electrolytes often contain additives that form protective films on the cathode surface or chemically interact with polysulfides to limit their dissolution. Ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, and gel polymer electrolytes are also explored to enhance the compatibility with sulfur cathodes and improve overall battery safety.
- Manufacturing methods for sulfur cathodes: Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based processes, and advanced deposition techniques that ensure uniform sulfur distribution within the conductive matrix. The manufacturing processes focus on achieving optimal sulfur loading while maintaining good electronic conductivity and mechanical stability, which are crucial for practical lithium-sulfur battery applications.
02 Nanostructured sulfur cathode materials
Nanostructured approaches to sulfur cathode design involve creating specialized architectures at the nanoscale to improve battery performance. These include sulfur-carbon nanocomposites, core-shell structures, and hierarchical porous materials. Nanostructuring helps to physically confine sulfur, improve electronic conductivity, and mitigate polysulfide shuttling. These materials often demonstrate enhanced capacity retention and cycling stability compared to conventional sulfur cathodes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and interlayers for sulfur cathodes
Various protective coatings and interlayers can be applied to sulfur cathodes to enhance their performance and stability. These protective layers help to prevent polysulfide dissolution and migration, which are major causes of capacity fading in lithium-sulfur batteries. Materials used for these protective layers include polymers, metal oxides, and composite materials. The coatings can be applied directly to the sulfur particles or as separate layers within the battery structure.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte modifications for sulfur cathode systems
Specialized electrolyte formulations can significantly improve the performance of sulfur cathodes. These modifications may include additives that suppress polysulfide dissolution, promote the formation of stable solid-electrolyte interphases, or enhance ionic conductivity. Electrolyte engineering approaches include the use of ionic liquids, solid-state electrolytes, or gel polymer electrolytes. These modifications aim to address the polysulfide shuttle effect and improve the overall electrochemical performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes for sulfur cathodes
Various manufacturing techniques can be employed to produce high-performance sulfur cathodes. These processes include melt-diffusion methods, solution-based approaches, and advanced deposition techniques. The manufacturing process significantly impacts the distribution of sulfur within the electrode, the electrode morphology, and ultimately the battery performance. Scalable production methods that maintain uniform sulfur distribution and electrode quality are particularly important for commercial applications of lithium-sulfur batteries.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Sulfur Battery Sector
Sulfur cathodes are emerging as a critical component in climate change mitigation strategies, currently positioned in the early growth phase of industry development. The market for sulfur cathode technology is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant scale as battery technologies advance to meet decarbonization goals. Technologically, sulfur cathodes are progressing through various maturity stages, with companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology, PolyPlus Battery, and Sion Power leading commercial development. Research institutions including Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and various universities are advancing fundamental breakthroughs. Established manufacturers such as Nissan and Robert Bosch are integrating these technologies into broader energy storage solutions, while startups like Sionic Energy and Sila Nanotechnologies focus on innovative approaches to overcome existing limitations in energy density and cycle life.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL has developed advanced lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology with high energy density (over 500 Wh/kg) specifically targeting climate change mitigation applications. Their approach incorporates a novel sulfur cathode design with carbon nanotubes and graphene to create a conductive network that addresses the "shuttle effect" - a common failure mode in sulfur cathodes. CATL's solution includes a proprietary electrolyte formulation that stabilizes the lithium-sulfur interface and prevents polysulfide dissolution. The company has demonstrated scaled manufacturing capabilities for these batteries, with pilot production lines achieving consistent quality at pre-commercial volumes. Their sulfur cathode technology enables batteries with approximately 70% lower carbon footprint compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, primarily due to the abundance and low processing requirements of sulfur as a cathode material.
Strengths: Utilizes abundant, low-cost sulfur as primary material; achieves significantly higher energy density than conventional lithium-ion batteries; demonstrates lower manufacturing carbon footprint; leverages existing production infrastructure. Weaknesses: Still faces challenges with cycle life limitations compared to commercial lithium-ion; requires further optimization for fast-charging capabilities; temperature sensitivity remains a concern for certain applications.
Penn State Research Foundation
Technical Solution: Penn State Research Foundation has developed a groundbreaking approach to sulfur cathodes through their PSHC (Penn State Hierarchical Carbon) framework technology. This innovation specifically addresses climate change mitigation through more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions. Their technical approach features a multi-scale carbon architecture that hosts sulfur within precisely engineered pore structures, providing both electronic conductivity and physical confinement of active materials. The foundation's researchers have pioneered a water-based processing method that eliminates toxic solvents typically used in battery manufacturing, reducing environmental impact and production costs. Their sulfur cathodes demonstrate exceptional stability, maintaining over 85% capacity after 500 cycles at practical loading levels (>5 mg/cm²). The technology incorporates a specialized electrolyte system with functional additives that form a stable cathode-electrolyte interface, suppressing polysulfide shuttling without compromising ionic conductivity. Penn State's approach enables batteries with energy densities exceeding 400 Wh/kg while reducing manufacturing carbon footprint by approximately 35% compared to conventional lithium-ion cathode production processes.
Strengths: Environmentally friendly water-based manufacturing process; hierarchical carbon structure provides superior sulfur utilization; demonstrated long-term cycling stability; potential for cost-effective scaled production. Weaknesses: Technology still at pre-commercial scale; requires specialized electrolyte formulations; performance at extreme temperatures needs further optimization; integration with commercial cell designs still under development.
Key Patents and Innovations in Sulfur Cathode Technology
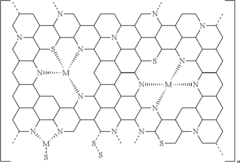
Transition metal containing nitrogen-doped carbon support structure for sulfur active material as a cathode for a lithium-sulfur battery
PatentActiveUS20180123136A1
Innovation
- Development of cathodes with a transition metal-containing nitrogen-doped carbon active material support that hosts sulfur and suppresses polysulfide diffusion through high surface area nanostructured pores, using nitrogen-containing polymers doped with transition metals like Fe, V, Mo, W, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn, which anchor soluble species and inhibit polysulfide migration.
Method for sulfur removal with a uranyl-containing carbonaceous adsorbent
PatentInactiveUS20170292078A1
Innovation
- A method using an adsorbent comprising carbonaceous materials, specifically activated carbon and carbon nanotubes doped with nanoparticles of uranyl oxide (UO3), which effectively removes sulfur compounds from hydrocarbon fluids at lower temperatures and pressures, achieving high removal efficiencies for refractory sulfur compounds like dibenzothiophene.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sulfur Cathode Technologies
The environmental impact assessment of sulfur cathode technologies reveals significant potential for climate change mitigation through multiple pathways. Sulfur cathodes represent a sustainable alternative to conventional lithium-ion battery materials, primarily due to their utilization of abundant and low-cost sulfur, which is often a waste byproduct from petroleum refining processes. This repurposing of industrial waste contributes to circular economy principles and reduces the environmental burden associated with waste management.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional cathode materials like lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) or nickel manganese cobalt (NMC). Studies demonstrate a potential reduction of 60-75% in carbon footprint during manufacturing phases, primarily due to lower energy requirements and the elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with critical minerals like cobalt and nickel.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with estimates suggesting 40-50% less water usage throughout the production chain. This reduction stems from simplified processing requirements and decreased need for water-intensive extraction activities. Additionally, the elimination of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes significantly reduces the risk of soil and water contamination during both production and end-of-life phases.
Land use impact assessments reveal further environmental advantages, as sulfur cathode supply chains require less extensive mining operations compared to conventional battery materials. This translates to reduced habitat disruption and biodiversity impacts, particularly in ecologically sensitive regions where critical mineral extraction typically occurs.
When considering end-of-life scenarios, sulfur cathodes demonstrate promising recyclability characteristics. The elemental sulfur can be recovered through established hydrometallurgical processes with recovery rates exceeding 90%, enabling closed-loop material flows that further enhance their environmental credentials. This recyclability aspect addresses growing concerns about battery waste management and resource conservation.
Energy storage applications utilizing sulfur cathode technologies can facilitate greater renewable energy integration into power grids, providing the necessary flexibility to accommodate intermittent generation sources. This grid-level application represents a significant indirect environmental benefit, potentially displacing fossil fuel-based peaking power plants and reducing associated emissions by an estimated 15-20% in optimized deployment scenarios.
Life cycle assessments indicate that sulfur cathode production generates substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional cathode materials like lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) or nickel manganese cobalt (NMC). Studies demonstrate a potential reduction of 60-75% in carbon footprint during manufacturing phases, primarily due to lower energy requirements and the elimination of energy-intensive mining operations associated with critical minerals like cobalt and nickel.
Water consumption metrics also favor sulfur cathode technologies, with estimates suggesting 40-50% less water usage throughout the production chain. This reduction stems from simplified processing requirements and decreased need for water-intensive extraction activities. Additionally, the elimination of toxic heavy metals in sulfur cathodes significantly reduces the risk of soil and water contamination during both production and end-of-life phases.
Land use impact assessments reveal further environmental advantages, as sulfur cathode supply chains require less extensive mining operations compared to conventional battery materials. This translates to reduced habitat disruption and biodiversity impacts, particularly in ecologically sensitive regions where critical mineral extraction typically occurs.
When considering end-of-life scenarios, sulfur cathodes demonstrate promising recyclability characteristics. The elemental sulfur can be recovered through established hydrometallurgical processes with recovery rates exceeding 90%, enabling closed-loop material flows that further enhance their environmental credentials. This recyclability aspect addresses growing concerns about battery waste management and resource conservation.
Energy storage applications utilizing sulfur cathode technologies can facilitate greater renewable energy integration into power grids, providing the necessary flexibility to accommodate intermittent generation sources. This grid-level application represents a significant indirect environmental benefit, potentially displacing fossil fuel-based peaking power plants and reducing associated emissions by an estimated 15-20% in optimized deployment scenarios.
Policy Frameworks Supporting Sulfur-Based Climate Solutions
The global policy landscape for sulfur-based climate solutions has evolved significantly in recent years, reflecting growing recognition of sulfur cathodes' potential in climate change mitigation. International frameworks like the Paris Agreement have created momentum for innovative energy storage technologies, with several countries implementing specific policies to accelerate adoption of sulfur-based battery technologies.
The European Union leads with its Green Deal and Circular Economy Action Plan, which explicitly supports research and development in sustainable battery technologies, including lithium-sulfur systems. Financial incentives include research grants through Horizon Europe and tax benefits for companies developing sulfur-based energy storage solutions. These policies aim to reduce dependency on critical raw materials while promoting technologies with lower carbon footprints.
In North America, the United States has incorporated sulfur-based technologies into its climate strategy through the Inflation Reduction Act and Department of Energy initiatives. These frameworks provide substantial funding for advanced battery research and manufacturing, with specific provisions for technologies utilizing abundant materials like sulfur. Tax credits for domestic production of sustainable energy storage systems further strengthen the policy support ecosystem.
Asia-Pacific nations, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have established comprehensive industrial policies promoting sulfur cathode development. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly mentions sulfur-based energy storage as a strategic technology, supported by subsidies and preferential access to resources for companies in this sector. Japan's Green Growth Strategy similarly prioritizes next-generation battery technologies with reduced environmental impact.
Developing economies are increasingly incorporating sulfur-based solutions into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement. Countries with significant mining operations are implementing policies that encourage value addition to raw sulfur through battery material production, creating economic opportunities while addressing climate goals.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address lifecycle considerations of sulfur-based technologies. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes in several jurisdictions now include provisions for battery recycling, with specific considerations for sulfur cathode materials. Standards organizations are developing certification frameworks for sustainable battery technologies that recognize the climate benefits of sulfur-based systems.
International cooperation mechanisms, including technology transfer initiatives and climate finance instruments, are increasingly supporting the deployment of sulfur-based climate solutions in developing regions. The Green Climate Fund has begun recognizing energy storage innovations, including sulfur cathodes, as eligible for climate finance support when deployed as part of renewable energy integration projects.
The European Union leads with its Green Deal and Circular Economy Action Plan, which explicitly supports research and development in sustainable battery technologies, including lithium-sulfur systems. Financial incentives include research grants through Horizon Europe and tax benefits for companies developing sulfur-based energy storage solutions. These policies aim to reduce dependency on critical raw materials while promoting technologies with lower carbon footprints.
In North America, the United States has incorporated sulfur-based technologies into its climate strategy through the Inflation Reduction Act and Department of Energy initiatives. These frameworks provide substantial funding for advanced battery research and manufacturing, with specific provisions for technologies utilizing abundant materials like sulfur. Tax credits for domestic production of sustainable energy storage systems further strengthen the policy support ecosystem.
Asia-Pacific nations, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, have established comprehensive industrial policies promoting sulfur cathode development. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly mentions sulfur-based energy storage as a strategic technology, supported by subsidies and preferential access to resources for companies in this sector. Japan's Green Growth Strategy similarly prioritizes next-generation battery technologies with reduced environmental impact.
Developing economies are increasingly incorporating sulfur-based solutions into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement. Countries with significant mining operations are implementing policies that encourage value addition to raw sulfur through battery material production, creating economic opportunities while addressing climate goals.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address lifecycle considerations of sulfur-based technologies. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes in several jurisdictions now include provisions for battery recycling, with specific considerations for sulfur cathode materials. Standards organizations are developing certification frameworks for sustainable battery technologies that recognize the climate benefits of sulfur-based systems.
International cooperation mechanisms, including technology transfer initiatives and climate finance instruments, are increasingly supporting the deployment of sulfur-based climate solutions in developing regions. The Green Climate Fund has begun recognizing energy storage innovations, including sulfur cathodes, as eligible for climate finance support when deployed as part of renewable energy integration projects.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!